
Sonar Algorithm in Perplexity: Real-Time Search Model Explained
Learn how Perplexity's Sonar algorithm powers real-time AI search with cost-effective models. Explore Sonar, Sonar Pro, and Sonar Reasoning variants.
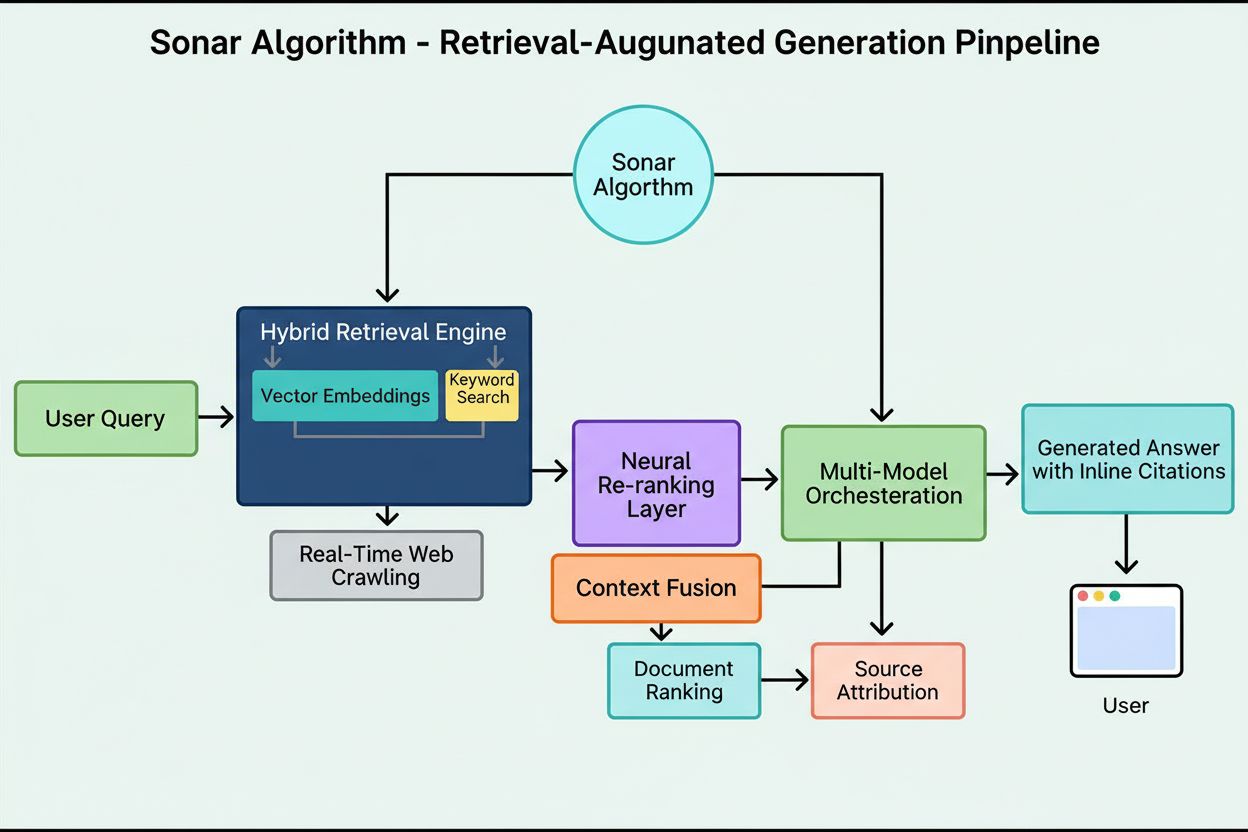
Sonar Algorithm is Perplexity’s proprietary retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) ranking system that combines hybrid semantic and keyword search with neural re-ranking to retrieve, rank, and cite web sources in real-time AI-generated answers. It prioritizes content freshness, semantic relevance, and citability to deliver grounded, source-backed responses while minimizing hallucinations.
Sonar Algorithm is Perplexity's proprietary retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) ranking system that combines hybrid semantic and keyword search with neural re-ranking to retrieve, rank, and cite web sources in real-time AI-generated answers. It prioritizes content freshness, semantic relevance, and citability to deliver grounded, source-backed responses while minimizing hallucinations.
Sonar Algorithm is Perplexity’s proprietary retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) ranking system that powers its answer engine by combining hybrid semantic and keyword search, neural re-ranking, and real-time citation generation. Unlike traditional search engines that rank pages for display in a list of results, Sonar ranks content snippets for synthesis into a single, unified answer with inline citations to source documents. The algorithm prioritizes content freshness, semantic relevance, and citability to deliver grounded, source-backed responses while minimizing hallucinations. Sonar represents a fundamental shift in how AI systems retrieve and rank information—moving from link-based authority signals to answer-focused utility metrics that emphasize whether content directly satisfies user intent and can be cleanly cited in synthesized responses. This distinction is critical for understanding how visibility in AI answer engines differs from traditional SEO, as Sonar evaluates content not for its ability to rank in a list, but for its ability to be extracted, synthesized, and attributed within an AI-generated answer.
The emergence of Sonar Algorithm reflects a broader industry shift toward retrieval-augmented generation as the dominant architecture for AI answer engines. When Perplexity launched in late 2022, the company identified a critical gap in the AI landscape: while ChatGPT provided powerful conversational capabilities, it lacked real-time information access and source attribution, leading to hallucinations and outdated answers. Perplexity’s founding team, initially working on a database query translation tool, pivoted entirely to build an answer engine that could combine live web search with LLM synthesis. This strategic decision shaped Sonar’s architecture from inception—the algorithm was engineered not to rank pages for human browsing, but to retrieve and rank content fragments for machine synthesis and citation. Over the past two years, Sonar has evolved into one of the most sophisticated ranking systems in the AI ecosystem, with Perplexity’s Sonar models securing ranks 1 through 4 in the Search Arena Evaluation, significantly outperforming competing models from Google and OpenAI. The algorithm now processes over 400 million search queries per month, indexing over 200 billion unique URLs and maintaining real-time freshness through tens of thousands of index updates per second. This scale and sophistication underscore Sonar’s importance as a defining ranking paradigm in the AI search era.
Sonar’s ranking system operates through a meticulously orchestrated five-stage retrieval-augmented generation pipeline that transforms user queries into grounded, cited answers. The first stage, Query Intent Parsing, employs an LLM to move beyond simple keyword matching and achieve semantic understanding of what the user is truly asking, interpreting context, nuance, and underlying intent. The second stage, Live Web Retrieval, dispatches the parsed query to Perplexity’s massive distributed index powered by Vespa AI, which scours the web for relevant pages and documents in real time. This retrieval system combines dense retrieval (vector search using semantic embeddings) and sparse retrieval (lexical/keyword-based search), merging results to produce approximately 50 diverse candidate documents. The third stage, Snippet Extraction and Contextualization, does not pass full page text to the generative model; instead, algorithms extract the most relevant snippets, paragraphs, or chunks directly pertaining to the query, aggregating them into a focused context window. The fourth stage, Synthesized Answer Generation with Citations, passes this curated context to a chosen LLM (from Perplexity’s proprietary Sonar family or third-party models like GPT-4 or Claude), which generates a natural-language response based strictly on retrieved information. Crucially, inline citations link every claim back to source documents, enforcing transparency and enabling verification. The fifth stage, Conversational Refinement, maintains conversational context across multiple turns, allowing follow-up questions to refine answers through iterative web searches. This pipeline’s defining principle—“you are not supposed to say anything that you didn’t retrieve”—ensures that Sonar-powered answers are grounded in verifiable sources, fundamentally reducing hallucinations compared to models relying solely on training data.
| Aspect | Traditional Search (Google) | Sonar Algorithm (Perplexity) | ChatGPT Ranking | Gemini Ranking | Claude Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Unit | Ranked list of links | Single synthesized answer with citations | Consensus-based entity mentions | E-E-A-T aligned content | Neutral, fact-based sources |
| Retrieval Focus | Keywords, links, ML signals | Hybrid semantic + keyword search | Training data + web browsing | Knowledge graph integration | Constitutional safety filters |
| Freshness Priority | Query-deserves-freshness (QDF) | Real-time web pulls, 37% boost within 48 hours | Lower priority, training data dependent | Moderate, integrated with Google Search | Lower priority, emphasis on stability |
| Ranking Signals | Backlinks, domain authority, CTR | Content freshness, semantic relevance, citability, authority boosts | Entity recognition, consensus mentions | E-E-A-T, conversational alignment, structured data | Transparency, verifiable citations, neutrality |
| Citation Mechanism | URL snippets in results | Inline citations with source links | Implicit, often no citations | AI Overviews with attribution | Explicit source attribution |
| Content Diversity | Multiple results across sites | Select few sources for synthesis | Synthesized from multiple sources | Multiple sources in overview | Balanced, neutral sources |
| Personalization | Subtle, mostly implicit | Explicit focus modes (Web, Academic, Finance, Writing, Social) | Implicit based on conversation | Implicit based on query type | Minimal, emphasis on consistency |
| PDF Handling | Standard indexing | 22% citation advantage over HTML | Standard indexing | Standard indexing | Standard indexing |
| Schema Markup Impact | FAQ schema in featured snippets | FAQ schema boosts citations 41%, reduces time-to-citation by 6 hours | Minimal direct impact | Moderate impact on knowledge graph | Minimal direct impact |
| Latency Optimization | Milliseconds for ranking | Sub-second retrieval + generation | Seconds for synthesis | Seconds for synthesis | Seconds for synthesis |
The technical foundation of Sonar Algorithm rests on a hybrid retrieval engine that combines multiple search strategies to maximize both recall and precision. Dense retrieval (vector search) uses semantic embeddings to understand the conceptual meaning behind queries, finding contextually similar documents even without exact keyword matches. This approach leverages transformer-based embeddings that map queries and documents into high-dimensional vector spaces where semantically similar content clusters together. Sparse retrieval (lexical search) complements dense retrieval by providing precision for rare terms, product names, internal company identifiers, and specific entities where semantic ambiguity is undesirable. The system uses ranking functions like BM25 to perform exact matches on these critical terms. These two retrieval methods are merged and deduplicated to yield approximately 50 diverse candidate documents, preventing domain overfitting and ensuring broad coverage across multiple authoritative sources. Following initial retrieval, Sonar’s neural re-ranking layer employs advanced machine-learning models (such as DeBERTa-v3 cross-encoders) to evaluate candidates using a rich feature set including lexical relevance scores, vector similarity, document authority, freshness signals, user engagement metrics, and metadata. This multi-phase ranking architecture allows Sonar to progressively refine results under tight latency budgets, ensuring that the final ranked set represents the highest-quality, most relevant sources for synthesis. The entire retrieval infrastructure is built on Vespa AI, a distributed search platform capable of handling web-scale indexing (200+ billion URLs), real-time updates (tens of thousands per second), and fine-grained content understanding through document chunking. This architectural choice allows Perplexity’s relatively small engineering team to focus on differentiating components—RAG orchestration, Sonar model fine-tuning, and inference optimization—rather than reinventing distributed search from scratch.
Content freshness is one of Sonar’s most powerful ranking signals, with empirical research demonstrating that recently updated pages receive dramatically higher citation rates. In controlled A/B testing conducted over 24 weeks across 120 URLs, articles updated within the last 48 hours were cited 37% more frequently than identical content bearing older timestamps. This advantage persisted at approximately 14% after two weeks, indicating that freshness provides a sustained but gradually diminishing boost. The mechanism behind this prioritization is rooted in Sonar’s design philosophy: the algorithm treats outdated content as a higher hallucination risk, assuming that stale information may have been superseded by newer developments. Perplexity’s infrastructure processes tens of thousands of index update requests per second, enabling real-time freshness signals. An ML model predicts whether a URL requires re-indexing and schedules updates based on the page’s importance and historical update frequency, ensuring that high-value content is refreshed more aggressively. Even minor cosmetic edits reset the freshness clock, provided the CMS republishes the modified timestamp. For publishers, this creates a strategic imperative: either adopt a newsroom cadence with weekly or daily updates, or watch evergreen content gradually decay in visibility. The implication is profound—in the Sonar era, content velocity is not a vanity metric but a survival mechanism. Brands that automate weekly micro-updates, append live changelogs, or maintain continuous content optimization workflows will secure disproportionate citation share compared to competitors relying on static, infrequently updated pages.
Sonar prioritizes semantic relevance over keyword density, fundamentally rewarding content that directly answers user queries in natural, conversational language. The algorithm’s retrieval system uses dense vector embeddings to match queries to content at the conceptual level, meaning that pages using synonyms, related terminology, or contextually rich language can outrank keyword-stuffed pages that lack semantic depth. This shift from keyword-centric to meaning-centric ranking has profound implications for content strategy. Content that wins in Sonar exhibits several structural characteristics: it leads with a short, factual summary before diving into detail, uses descriptive H2/H3 headings and short paragraphs to facilitate easy passage extraction, includes clear citations and links to primary sources, and maintains visible timestamps and version notes to signal freshness. Each paragraph functions as an atomic semantic unit, optimized for copy-paste-level clarity and LLM comprehension. Tables, bullet lists, and labeled charts are particularly valuable because they present information in structured, easily quotable formats. The algorithm also rewards original analysis and unique data over mere aggregation, as Sonar’s synthesis engine seeks sources that add novel angles, primary documents, or proprietary insights that distinguish them from generic overviews. This emphasis on semantic richness and answer-first structure represents a fundamental departure from traditional SEO, where keyword placement and link authority dominated. In the Sonar era, content must be engineered for machine retrieval and synthesis, not human browsing.
Publicly hosted PDFs represent a significant, often-overlooked advantage in Sonar’s ranking system, with empirical testing revealing that PDF versions of content outperform HTML equivalents by approximately 22% in citation frequency. This advantage stems from Sonar’s crawler treating PDFs favorably compared to HTML pages. PDFs lack cookie banners, JavaScript rendering requirements, paywall authentication, and other HTML complications that can obscure or delay content access. Sonar’s crawler can read PDFs cleanly and predictably, extracting text without the parsing ambiguity that plagues complex HTML structures. Publishers can strategically leverage this advantage by hosting PDFs in publicly accessible directories, using semantic filenames that reflect content topics, and signaling the PDF as canonical using <link rel="alternate" type="application/pdf"> tags in the HTML head. This creates what researchers describe as an “LLM honey-trap”—a high-visibility asset that competitors’ tracking scripts cannot easily detect or monitor. For B2B companies, SaaS vendors, and research-driven organizations, this strategy is particularly powerful: publishing whitepapers, research reports, case studies, and technical documentation as PDFs can dramatically increase Sonar citation rates. The key is treating the PDF not as a downloadable afterthought but as a canonical copy worthy of equal or greater optimization effort than the HTML version. This approach has proven especially effective for enterprise content, where PDFs often contain more structured, authoritative information than web pages.
JSON-LD FAQ schema markup significantly amplifies Sonar citation rates, with pages containing three or more FAQ blocks receiving citations 41% more frequently than control pages without schema. This dramatic uplift reflects Sonar’s preference for structured, chunk-based content that aligns with its retrieval and synthesis logic. FAQ schema presents discrete, self-contained Q&A units that the algorithm can easily extract, rank, and cite as atomic semantic blocks. Unlike traditional SEO, where FAQ schema was a “nice-to-have” feature, Sonar treats structured Q&A markup as a core ranking lever. Additionally, Sonar often cites FAQ questions as anchor text, reducing the risk of context drift that occurs when the LLM summarizes random mid-paragraph clauses. The schema also accelerates time-to-first-citation by approximately six hours, suggesting that Sonar’s parser prioritizes structured Q&A blocks early in the ranking cascade. For publishers, the optimization strategy is straightforward: embed three to five targeted FAQ blocks beneath the fold, using conversational trigger phrases that mirror real user queries. Questions should employ long-tail search phrasing and semantic symmetry with likely Sonar queries. Each answer should be concise, factual, and directly responsive, avoiding filler or marketing language. This approach has proven particularly effective for SaaS companies, health clinics, and professional services firms, where FAQ content naturally aligns with user intent and Sonar’s synthesis needs.
Sonar’s ranking system integrates multiple signals into a unified citation framework, with research identifying eight primary factors that influence source selection and citation frequency. First, semantic relevance to the question dominates retrieval, with the algorithm prioritizing content that clearly answers the query in natural language. Second, authority and credibility matter significantly, with Perplexity’s publisher partnerships and algorithmic boosts favoring established news organizations, academic institutions, and recognized experts. Third, freshness receives exceptional weight, as discussed, with recent updates triggering 37% citation increases. Fourth, diversity and coverage are valued, as Sonar prefers multiple high-quality sources over single-source answers, reducing hallucination risk through cross-validation. Fifth, mode and scope determine which indexes Sonar searches—focus modes like Academic, Finance, Writing, and Social narrow source types, while source selectors (Web, Org Files, Web + Org Files, None) determine whether retrieval pulls from the open web, internal documents, or both. Sixth, citability and access are critical; if PerplexityBot can crawl and index content, it’s easier to cite, making robots.txt compliance and page speed essential. Seventh, custom source filters via API allow enterprise deployments to constrain or prefer certain domains, changing ranking within whitelisted collections. Eighth, conversation context influences follow-up questions, with pages matching evolving intent outranking more generic references. Together, these factors create a multidimensional ranking space where success requires optimization across multiple dimensions simultaneously, not just a single lever like backlinks or keyword density.
The Sonar Algorithm is rapidly evolving in response to advances in LLM inference and retrieval technology. Perplexity’s engineering blog recently highlighted speculative decoding, a technique that slices token latency in half by predicting multiple future tokens simultaneously. Faster generation loops enable the system to afford fresher retrieval sets with every query, squeezing the window in which stale pages can compete. A rumored Sonar-Reasoning-Pro model already outperforms Gemini 2.0 Flash and GPT-4o Search in arena evaluations, suggesting that Sonar’s ranking sophistication will continue advancing. As latency approaches human thought speed, citation jockeying becomes a high-frequency game where content velocity is the ultimate differentiator. Expect emerging infrastructure innovations like “LLM freshness APIs” that auto-increment timestamps the way ad-tech once did bid prices, creating new competitive dynamics around real-time content updates. Legal and ethical challenges will also emerge as PDF pirates exploit Sonar’s PDF preference to leech authority from gated e-books and proprietary research, potentially triggering new access controls or authentication requirements. The broader implication is clear: the Sonar era rewards publishers willing to treat every paragraph as an atomic, schema-wrapped, timestamped manifesto ready for machine consumption. Brands that obsess over first-page Google rankings but ignore Sonar visibility are painting billboards in a city whose residents just acquired VR headsets. The future belongs to those who optimize for “percentage of answer boxes containing our URL,” not traditional CTR metrics.
Sonar Algorithm represents a fundamental reimagining of how ranking systems evaluate and prioritize content in the age of AI-powered answer engines. By combining hybrid retrieval, neural re-ranking, real-time freshness signals, and strict citation requirements, Sonar has created a ranking environment where traditional SEO signals like backlinks and keyword density matter far less than semantic relevance, content freshness, and citability. The algorithm’s emphasis on grounding answers in verifiable sources addresses one of the most critical challenges in generative AI—hallucination—by enforcing a strict principle that LLMs cannot claim anything they didn’t retrieve. For publishers and brands, understanding Sonar’s ranking factors is no longer optional; it is essential for securing visibility in an increasingly AI-mediated information landscape. The shift from link-based authority to answer-focused utility metrics requires a fundamental rethinking of content strategy, moving from keyword optimization to semantic richness, from static pages to continuously updated assets, and from human-centric design to machine-readable structure. As Perplexity’s market share grows and competing AI answer engines adopt similar RAG architectures, Sonar’s influence will only expand. The brands that thrive in this new era will be those that recognize Sonar not as a threat to traditional SEO, but as a complementary ranking system requiring distinct optimization strategies. By treating content as atomic, timestamped, schema-aligned units engineered for machine retrieval and synthesis, publishers can secure their place in the AI-powered answer boxes that increasingly mediate how users discover and consume information online.
The **Sonar Algorithm** is Perplexity's proprietary ranking system that powers its answer engine, fundamentally different from traditional search engines like Google. While Google ranks pages for display in a list of blue links, Sonar ranks content snippets for synthesis into a single, unified answer with inline citations. Sonar uses retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), combining hybrid search (vector embeddings plus keyword matching), neural re-ranking, and real-time web retrieval to ground answers in verifiable sources. This approach prioritizes semantic relevance and content freshness over legacy SEO signals like backlinks, making it a distinct ranking paradigm optimized for AI-generated synthesis rather than link-based authority.
Sonar implements a **hybrid retrieval engine** that combines two complementary search strategies: dense retrieval (vector search using semantic embeddings) and sparse retrieval (lexical/keyword-based search using BM25). Dense retrieval captures conceptual meaning and context, allowing the system to find semantically similar content even without exact keyword matches. Sparse retrieval provides precision for rare terms, product names, and specific identifiers where semantic ambiguity is undesirable. These two retrieval methods are merged and deduplicated to produce approximately 50 diverse candidate documents, preventing domain overfitting and ensuring broad coverage. This hybrid approach surpasses single-method systems in both recall and relevance accuracy.
The primary ranking factors for Sonar include: (1) **Content Freshness** – recently updated or published pages receive 37% more citations within 48 hours post-update; (2) **Semantic Relevance** – content must directly answer the query in natural language, prioritizing clarity over keyword density; (3) **Authority and Credibility** – sources from established publishers, academic institutions, and news organizations receive algorithmic boosts; (4) **Citability** – content must be easily quotable and structured with clear headings, tables, and paragraphs; (5) **Diversity** – Sonar favors multiple high-quality sources over single-source answers; and (6) **Technical Accessibility** – pages must be crawlable by PerplexityBot and load quickly for on-demand browsing.
**Freshness is one of Sonar's top ranking signals**, particularly for time-sensitive topics. Perplexity's infrastructure processes tens of thousands of index update requests per second, ensuring the index reflects the most current information available. An ML model predicts whether a URL needs re-indexing and schedules updates based on the page's importance and update frequency. In empirical testing, content updated within the last 48 hours received 37% more citations than identical content with older timestamps, and this advantage persisted at 14% after two weeks. Even minor edits reset the freshness clock, making continuous content optimization essential for maintaining visibility in Sonar-powered answers.
**PDFs are a significant advantage in Sonar's ranking system**, often outperforming HTML versions of the same content by 22% in citation frequency. Sonar's crawler treats PDFs favorably because they lack cookie banners, paywalls, JavaScript rendering issues, and other HTML complications that can obscure content. Publishers can optimize PDF visibility by hosting them in publicly accessible directories, using semantic filenames, and signaling the PDF as canonical using `` tags in the HTML head. This creates what researchers call an "LLM honey-trap" that competitors' tracking scripts cannot easily detect, making PDFs a strategic asset for securing Sonar citations.
**JSON-LD FAQ schema significantly boosts Sonar citation rates**, with pages containing three or more FAQ blocks receiving citations 41% more frequently than control pages without schema. FAQ markup aligns perfectly with Sonar's chunk-based retrieval logic because it presents discrete, self-contained Q&A units that the algorithm can easily extract and cite. Additionally, Sonar often cites FAQ questions as anchor text, reducing the risk of context drift that can occur when the LLM summarizes random mid-paragraph clauses. The schema also accelerates time-to-first-citation by approximately six hours, suggesting Sonar's parser prioritizes structured Q&A blocks early in the ranking cascade.
Sonar implements a **three-stage retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline** designed to ground answers in verified external knowledge. Stage one retrieves relevant documents using hybrid search; stage two extracts and contextualizes the most relevant snippets; stage three synthesizes an answer using only the provided context, enforcing a strict principle: "you are not supposed to say anything that you didn't retrieve." This architecture tightly couples retrieval and generation, ensuring every claim is traceable to a source. Inline citations link generated text back to source documents, enabling user verification. This grounding approach significantly reduces hallucinations compared to models relying solely on training data, making Sonar's answers more factually reliable and trustworthy.
While **ChatGPT prioritizes entity recognition and consensus** from its training data, **Gemini emphasizes E-E-A-T signals and conversational alignment**, and **Claude focuses on constitutional safety and neutrality**, **Sonar uniquely prioritizes real-time freshness and semantic depth**. Sonar's three-layer machine-learning reranker applies stricter quality filters than traditional search, discarding entire result sets if content fails to meet quality thresholds. Unlike ChatGPT's reliance on historical training data, Sonar performs live web retrieval for every query, ensuring answers reflect current information. Sonar also differs from Gemini's knowledge graph integration by emphasizing paragraph-level semantic relevance and from Claude's neutrality focus by accepting authoritative domain boosts from established publishers.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how Perplexity's Sonar algorithm powers real-time AI search with cost-effective models. Explore Sonar, Sonar Pro, and Sonar Reasoning variants.

Learn how to get your website cited by Perplexity AI. Discover the technical requirements, content optimization strategies, and authority-building tactics that ...

Learn how to optimize your content for Perplexity AI and get cited in real-time search results. Discover citation-ready content strategies, technical optimizati...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.