Authority Signal
Authority signals measure content credibility through backlinks, domain authority, E-E-A-T factors, and verified credentials. Learn how AI systems and search en...
Factors AI systems use to determine which sources to cite, including authority, freshness, relevance, and semantic completeness. These signals differ significantly from traditional SEO ranking factors, prioritizing content quality, E-E-A-T signals, and real-time verification over backlinks and domain age.
Factors AI systems use to determine which sources to cite, including authority, freshness, relevance, and semantic completeness. These signals differ significantly from traditional SEO ranking factors, prioritizing content quality, E-E-A-T signals, and real-time verification over backlinks and domain age.
Source ranking signals are the specific factors that AI systems evaluate when deciding which sources to cite in their generated responses. Unlike traditional search engine rankings that focus on keyword relevance and backlink authority, AI systems use a fundamentally different set of criteria to determine which content deserves to be referenced. These signals assess whether a source is authoritative, current, relevant to the query, and trustworthy enough to cite. Understanding these signals is critical for brands seeking visibility in AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Research analyzing millions of AI citations has identified seven core ranking signals that consistently predict whether content will be cited, with correlation strengths ranging from r=0.92 (multi-modal content) down to r=0.31 (business rules).
| Ranking Signal | Correlation Strength | Key Metric | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Modal Content Integration | r=0.92 | +156% to +317% boost | Highest impact |
| Semantic Completeness | r=0.87 | 4.2x higher if score >8.5/10 | Very high |
| Real-Time Factual Verification | r=0.89 | +89% selection probability | Very high |
| Vector Embedding Alignment | r=0.84 | 7.3x higher for scores >0.88 | High |
| E-E-A-T Authority Signals | r=0.81 | 96% of citations have strong E-E-A-T | High |
| Entity Knowledge Graph Density | r=0.76 | 4.8x higher with 15+ entities | High |
| Structured Data Implementation | +73% boost | Schema markup advantage | Moderate |

AI systems don’t rely on a single magic formula to select sources. Instead, they evaluate content through seven distinct ranking signals that work together to determine citation worthiness. Each signal serves a specific purpose in the evaluation pipeline, and understanding how they work reveals why some sources consistently get cited while others remain invisible.
1. Relevance (Base Ranking): This foundational signal determines whether content actually addresses the user’s query. AI systems use semantic understanding to match query intent with content meaning, going beyond simple keyword matching. A query about “sustainable packaging solutions” will match content discussing eco-friendly materials, biodegradable alternatives, and environmental impact—not just pages containing those exact words.
2. Topic Clarity: AI systems break content into semantic chunks (typically 300-500 tokens) and convert them into vector embeddings—mathematical representations of meaning. This signal measures how clearly each chunk communicates its topic. Content with explicit topic statements, logical structure, and focused paragraphs scores higher than rambling content that drifts between related concepts.
3. Keyword Match: While semantic understanding dominates, keyword matching still serves as a supporting signal to prevent semantic drift. This ensures AI systems cite content that actually answers the specific query, not just something tangentially related. For a query about “machine learning algorithms,” keyword matching prevents citation of content about “artificial intelligence philosophy” despite semantic similarity.
4. Engagement Signals: AI systems evaluate how likely users are to find content satisfying through PCTR (predictive click-through rate), which approximates user satisfaction based on historical interaction patterns. Content with clear layouts, compelling snippets, fast load times, and mobile optimization scores higher because users historically engage with these characteristics.
5. Freshness: AI systems recognize when timing matters for certain topics. Queries with temporal intent (current events, prices, trends) trigger freshness evaluation. AI checks publication dates and update timestamps to ensure cited content reflects current information. Content updated within the past year receives significant freshness advantages, with 65% of AI bot hits targeting content less than one year old.
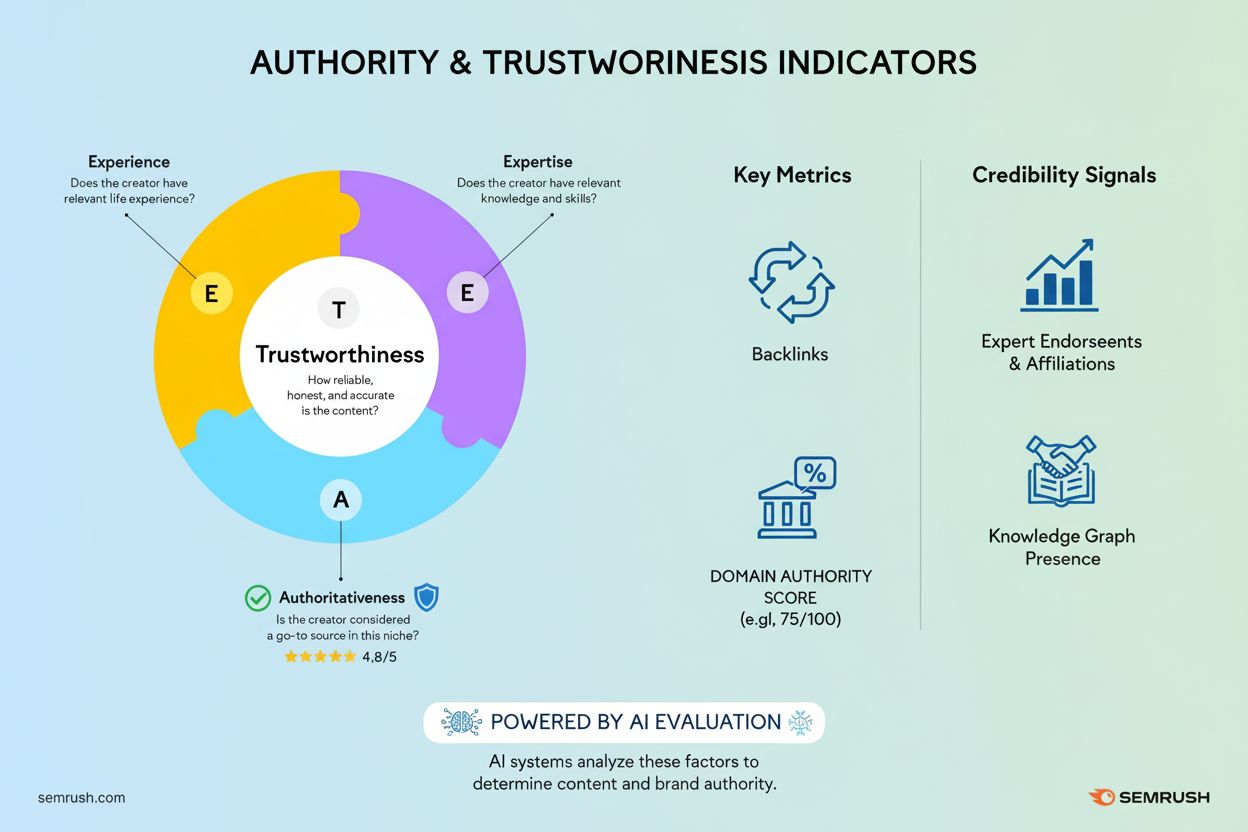
6. Trust and Authority (E-E-A-T): This signal evaluates whether sources demonstrate Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. AI systems verify author credentials, check for third-party brand mentions, evaluate user reviews, and assess content depth. Ninety-six percent of AI citations come from sources with strong E-E-A-T signals, making this one of the most critical factors.
7. Business Rules: The final layer contains safety overrides and quality filters. AI systems boost official health, finance, and legal sources while burying spam, misinformation, and policy-violating content. This layer ensures AI Overviews maintain quality and safety standards regardless of other ranking signals.
E-E-A-T has evolved from a Google content quality guideline into an active filtering mechanism for AI citations. Ninety-six percent of content cited by major AI systems demonstrates strong E-E-A-T signals, making this framework essential for AI visibility. AI systems actively verify each component before considering content for citation.
Experience: Does the content creator have firsthand experience with the topic? AI looks for specific outcomes, behind-the-scenes details, and personal perspective. Content stating “In our analysis of 847 client implementations, we observed…” carries more weight than “Studies show…” without specifics. First-hand experience signals include measurable results, documented processes, and authentic case studies.
Expertise: Does the author possess relevant knowledge, education, or professional qualifications? AI systems verify credentials against external sources and check for published works, certifications, and industry recognition. Author schema markup with credentials, institutional affiliations, and relevant awards significantly improves citation probability. An article by “Dr. Sarah Chen, AI Research Lead at Stanford University” carries more weight than anonymous content.
Authoritativeness: Is the content creator recognized as a go-to source in their field? AI evaluates whether other authoritative sources cite or reference the author, whether they speak at industry conferences, and whether they maintain consistent expert positioning across platforms. Brands appearing in 4+ platforms are 2.8 times more likely to be cited by AI systems.
Trustworthiness: Can users trust the content is accurate, transparent, and safe? AI checks for HTTPS implementation, clear contact information, privacy policies, disclosure of affiliations, and correction policies. Content with positive online reviews, responsive customer service, and documented accuracy practices scores higher. Trust issues like security warnings or misinformation history can permanently damage citation potential.
Content freshness has become a critical ranking signal as AI systems increasingly prioritize current information. Sixty-five percent of AI bot hits target content published within the past year, and seventy-nine percent come from content updated within two years. This represents a dramatic shift from traditional SEO, where evergreen content could rank indefinitely without updates.
AI systems recognize temporal intent—queries where timing matters significantly. Questions about “current AI trends,” “2025 marketing strategies,” or “latest AI tools” trigger freshness evaluation. AI checks publication dates, update timestamps, and schema markup to ensure cited content reflects current information. Content older than six years receives minimal citation consideration unless it’s foundational or historical in nature.
The freshness signal works differently across platforms. ChatGPT relies on training data with a knowledge cutoff, making older content less likely to be recalled from parametric knowledge. Perplexity and Google AI Overviews use real-time retrieval, actively preferring recently updated content. Updating evergreen content with current statistics, recent examples, and fresh perspectives can dramatically improve citation rates even for established pages.
Semantic completeness measures whether content provides a fully self-contained answer that requires no external context or additional clicks to understand. This is the strongest predictor of AI citation (r=0.87 correlation), with content scoring above 8.5/10 on semantic completeness being 4.2 times more likely to be cited than content scoring below 6.0/10.
AI systems evaluate whether each passage can stand alone as a citable unit. A semantically complete answer includes a direct response to the core query, necessary context and definitions, specific examples or data points, and a brief conclusion. Incomplete answers reference “as mentioned earlier,” require reading previous sections, or use unexplained jargon. When AI extracts a passage for citation, it must deliver value to users without forcing them to read surrounding content.
Vector embeddings—mathematical representations of meaning—determine semantic alignment. Content with cosine similarity scores above 0.88 shows 7.3 times higher selection rates than content below 0.75. This means covering your topic’s semantic neighborhood (related concepts, synonyms, contextual relationships) matters more than keyword density. For a topic like “AI Overviews,” semantic completeness requires covering ranking factors, optimization tactics, platform differences, and implementation strategies—not just defining the term.
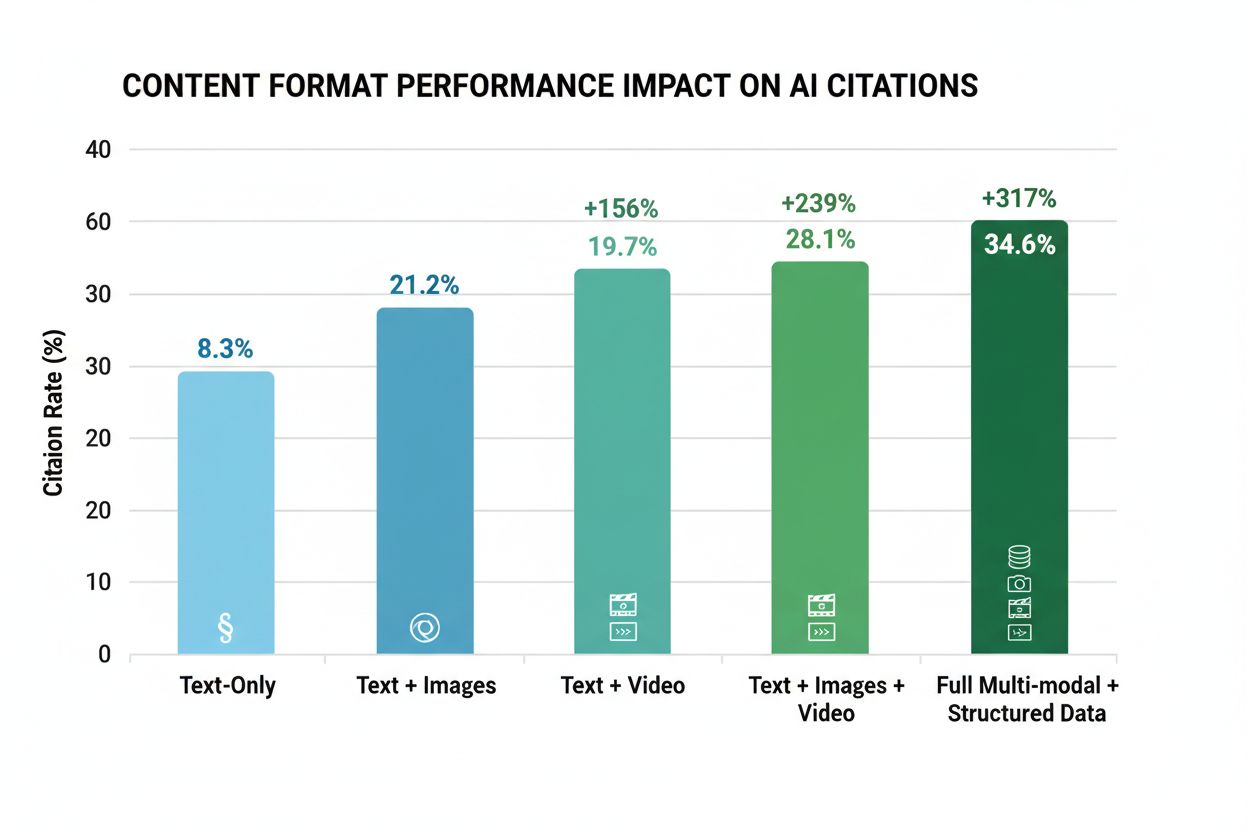
Multi-modal content integration represents the biggest ranking shift in 2025, with r=0.92 correlation to AI citation—the highest correlation of any ranking signal. Content combining text, images, videos, and structured data shows 156% to 317% higher selection rates compared to text-only content. This isn’t about adding decorative images; it’s about strategic integration where each element supports and enhances the others.
| Content Format | Citation Rate | Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Text only | 8.3% | Baseline |
| Text + Images | 21.2% | +156% |
| Text + Video | 19.7% | +137% |
| Text + Images + Video | 28.1% | +239% |
| Full Multi-Modal + Schema | 34.6% | +317% |
Structured data markup (schema.org) explicitly tells AI systems what your content contains. FAQ schema directly feeds AI question-answer extraction, HowTo schema enables step-by-step guidance extraction, and Article schema establishes content type and freshness. Properly implemented schema markup alone provides a +73% selection boost. When combined with multi-modal content, the effects multiply rather than add.
Images should explain concepts, not just decorate pages. Infographics showing data relationships, annotated screenshots demonstrating processes, and comparison tables visualized as graphics all improve citation probability. Videos work best as 60-90 second explainers that simplify complex topics. YouTube videos are increasingly integrated into AI Overviews, making video optimization essential for maximum visibility.
Different AI platforms weight ranking signals differently, requiring platform-specific optimization strategies. ChatGPT relies heavily on parametric knowledge from training data, with Wikipedia dominating at 47.9% of citations. Perplexity emphasizes real-time retrieval with Reddit leading at 46.7% of citations. Google AI Overviews maintain stronger correlation with traditional SEO while diversifying sources across platforms.
| Signal | ChatGPT | Perplexity | Google AIO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wikipedia | 47.9% | 8.2% | 12.1% |
| 12.3% | 46.7% | 21.0% | |
| YouTube | 18.2% | 13.9% | 15.4% |
| Domain Authority | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Content Freshness | Training cutoff | Real-time critical | Important |
| E-E-A-T Signals | Very high | High | Very high |
ChatGPT’s parametric knowledge means brand visibility depends on training data frequency. Building Wikipedia presence, earning media mentions, and establishing thought leadership across authoritative platforms increases training data representation. Perplexity’s real-time retrieval means content freshness, Reddit engagement, and current information dominate. Google AI Overviews blend traditional SEO foundations with AI-specific signals, making both traditional rankings and E-E-A-T critical.
Cross-platform optimization is essential because only 11% of domains are cited by both ChatGPT and Perplexity. A comprehensive strategy requires presence across multiple platforms: official website with strong E-E-A-T, Wikipedia (if notable), Reddit community engagement, YouTube content, industry publications, and G2/Capterra reviews. Brands on 4+ platforms are 2.8 times more likely to appear in AI responses.
Optimizing for source ranking signals requires a fundamentally different approach than traditional SEO. Rather than chasing rankings, focus on becoming the most authoritative, complete, and verifiable answer to your audience’s questions.
Build E-E-A-T signals first: Add detailed author bios with credentials, implement Person and Organization schema, link to author LinkedIn profiles, and display relevant certifications. This is the fastest way to improve citation probability.
Implement comprehensive schema markup: Add FAQ, Article, HowTo, and ImageObject schema to all relevant content. Validate using Google’s Rich Results Test. Properly structured content shows +73% higher selection rates.
Ensure content freshness: Update evergreen content with current statistics, recent examples, and fresh perspectives. Maintain “last updated” dates and use schema markup to signal freshness. Aim for updates within the past year.
Create semantically complete content: Structure content so individual paragraphs can stand alone as citable units. Lead with direct answers, use 40-60 word paragraphs for optimal chunking, and avoid references to “earlier sections.”
Develop multi-modal content: Pair text with contextual images, explanatory videos, and data visualizations. Ensure each element adds value rather than decoration. Use proper alt text and captions.
Build entity authority: Mention 15-20 relevant entities per 1,000 words. Link entities to authoritative sources. Create or optimize Wikidata entries. Establish presence on multiple platforms where AI systems find authoritative voices.
Add verifiable citations: Include specific, authoritative citations for major claims. Link to original sources, not aggregators. Use Tier 1 sources (peer-reviewed research, government data) for maximum credibility boost.
Optimize for accessibility: Fast page speeds, mobile responsiveness, clear navigation, and semantic HTML all improve AI crawler access and user satisfaction signals.
Traditional SEO wisdom often contradicts what actually works for AI citations. Understanding these misconceptions prevents wasted effort on tactics that no longer drive visibility.
Misconception: Backlinks are critical for AI citations. Reality: Backlinks show weak or neutral correlation with AI citations (r=0.18 for domain authority). Brand search volume (0.334 correlation) is a far stronger predictor. AI systems evaluate content authority independently from link profiles.
Misconception: Keyword stuffing improves AI visibility. Reality: Keyword stuffing performs worse in generative engines than in traditional search. AI systems recognize and penalize unnatural keyword repetition. Natural language variations and semantic completeness matter far more.
Misconception: Adding images and videos automatically improves citations. Reality: Multi-modal content only helps when strategically integrated. Random images or videos without contextual relevance show no measurable impact. Content must be semantically complete first; multi-modal elements enhance, not replace, quality.
Misconception: Ranking #1 guarantees AI citations. Reality: Only 4.5% of AI Overview URLs directly matched a Page 1 organic result. Forty-seven percent of AI citations come from pages ranking below position 5. Content authority matters more than ranking position.
| Factor | Traditional SEO Impact | AI Citation Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Backlink quantity | HIGH | Weak/Neutral |
| Keyword stuffing | Negative | More negative |
| Images/videos | Engagement boost | No impact if not integrated |
| #1 ranking | Primary goal | Only 4.5% correlation |
| Domain age | Positive signal | Irrelevant |
| E-E-A-T signals | Important | Critical (96% of citations) |
| Content freshness | Helpful | Essential (65% <1 year old) |
Tracking AI citation performance requires different metrics than traditional SEO. Share of Voice measures what percentage of AI answers mention your brand versus competitors. Citation Frequency tracks how often your URLs appear across platforms. Brand Sentiment evaluates whether mentions are positive, negative, or neutral. Citation Drift—the monthly volatility in citations—typically ranges from 40-60%, making ongoing optimization essential.
Enterprise tools like Profound track 240+ million ChatGPT citations with competitive benchmarking and GA4 integration. Semrush’s AI Toolkit integrates with existing SEO suites. Mid-market options like LLMrefs, Peec AI, and First Answer offer keyword-to-prompt mapping and share of voice tracking at $50-400/month. Budget-friendly tools like Otterly.AI, Scrunch AI, and Knowatoa provide domain citation tracking and GEO audits at $30-50/month.
Effective measurement combines quantitative tracking with qualitative analysis. Monitor your top 20 keywords monthly by querying ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews directly. Document which sources appear, how they’re cited, and what content characteristics they share. Use this intelligence to inform optimization priorities. Track not just whether you’re cited, but how prominently and in what context. A citation in the opening sentence carries more weight than a mention in supporting evidence.
The brands dominating AI citations aren’t optimizing for one signal—they’re systematically implementing all seven in an integrated strategy. They build E-E-A-T signals, create semantically complete content, implement structured data, develop multi-modal assets, maintain freshness, and establish cross-platform authority. This comprehensive approach is what separates brands that get cited from those that remain invisible in the AI-powered search landscape.
Source ranking signals evaluate content quality, authority, and relevance specifically for AI citation purposes, while traditional SEO factors focus on search engine rankings. AI systems prioritize semantic completeness, E-E-A-T signals, and real-time verification over backlinks and domain age. Domain Authority shows only r=0.18 correlation with AI citations, compared to 0.43 in traditional SEO, making page-level signals far more important than site-wide metrics.
Domain Authority has become a weak predictor of AI citations, with correlation dropping to r=0.18 (down from 0.43 pre-2024). AI systems evaluate content authority independently from domain authority, meaning newer or smaller websites can be cited more frequently than established high-DA domains if their content demonstrates stronger E-E-A-T signals, semantic completeness, and real-time verification.
Yes, new websites can absolutely be cited by AI systems if they demonstrate strong E-E-A-T signals, publish high-quality comprehensive content, and maintain freshness. Research shows 65% of AI bot hits target content published within the past year, and 79% from content updated within 2 years. Building author credentials, implementing structured data, and creating semantically complete content matters far more than domain age.
Wikipedia dominates AI citations (appearing in ~18.4% of all citations and 47.9% of ChatGPT responses) because it represents ~22% of major LLM training data and demonstrates perfect semantic completeness, E-E-A-T signals, and neutral point-of-view. Wikipedia content is structured for easy extraction, comprehensively answers queries without external references, and comes from verified contributors, making it an ideal citation source for AI systems.
Citation patterns show significant monthly volatility, with Google AI Overviews experiencing 59.3% monthly citation drift and ChatGPT showing 54.1% drift. This means source rankings change frequently as AI systems update their training data, adjust retrieval algorithms, and respond to content freshness. Continuous optimization and monitoring are essential for maintaining AI visibility.
The fastest improvements come from: (1) Implementing E-E-A-T signals through author credentials and expert quotes (+78-89% visibility), (2) Adding structured data like FAQ and Article schema (+73% selection boost), (3) Ensuring content freshness with recent updates, and (4) Creating semantically complete content that answers queries fully without external references. These changes can show results within 2-4 weeks.
Yes, multi-modal content significantly improves AI citations. Content with text plus images shows +156% higher selection rates, text plus video shows +137% improvement, and full multi-modal with structured data shows +317% improvement compared to text-only content. However, simply adding images and videos without strategic integration doesn't help—they must be contextually relevant and properly structured with schema markup.
Track how AI systems cite your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Understand your source ranking signals and optimize for maximum AI visibility.

Authority signals measure content credibility through backlinks, domain authority, E-E-A-T factors, and verified credentials. Learn how AI systems and search en...

Learn how to build domain authority that AI search engines recognize. Discover strategies for entity optimization, citations, topical authority, and E-E-A-T sig...

Relevance signals are indicators that AI systems use to evaluate content applicability. Learn how keyword matching, semantic relevance, authority, and freshness...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.