UTM Parameters for AI-Driven Traffic
Master UTM tracking for AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google Gemini. Learn setup, best practices, and how to attribute AI traffic accurately in GA4...

UTM parameters are text tags added to the end of URLs to track the source, medium, campaign, content, and keywords of website traffic. These tracking codes enable marketers to measure campaign performance and attribute conversions to specific marketing efforts in analytics platforms like Google Analytics.
UTM parameters are text tags added to the end of URLs to track the source, medium, campaign, content, and keywords of website traffic. These tracking codes enable marketers to measure campaign performance and attribute conversions to specific marketing efforts in analytics platforms like Google Analytics.
UTM parameters are simple text tags appended to the end of URLs that enable marketers to track the performance and source of website traffic. The acronym UTM stands for Urchin Tracking Module, a legacy term from the Urchin web analytics software that Google acquired and integrated into Google Analytics. These parameters work by capturing specific information about how visitors arrive at your website, including which marketing channel referred them, what campaign brought them there, and which specific content element they clicked. When a user visits a URL containing UTM parameters, analytics platforms automatically extract and record this data, allowing marketers to measure campaign effectiveness, calculate return on investment (ROI), and optimize their marketing strategies based on concrete performance metrics.
UTM parameters consist of five distinct tracking variables, each serving a specific purpose in campaign measurement. The first three parameters—utm_source, utm_medium, and utm_campaign—are considered essential and should be included in virtually every tracked URL. The utm_source parameter identifies where traffic originates, such as “google,” “facebook,” “newsletter,” or “partner-website.” The utm_medium parameter specifies the marketing channel or mechanism used to deliver the link, including options like “email,” “social,” “cpc” (cost-per-click), “display,” or “referral.” The utm_campaign parameter names the specific marketing initiative, allowing you to group related promotional efforts together, such as “spring-sale-2025” or “product-launch-q1.”
The remaining two parameters—utm_content and utm_term—are optional but provide valuable granularity for advanced tracking scenarios. The utm_content parameter differentiates between multiple links pointing to the same destination, making it ideal for A/B testing or tracking which specific banner, button, or email link generated clicks. The utm_term parameter is primarily used in paid search campaigns to identify the keyword that triggered an ad, enabling detailed analysis of keyword performance and cost-per-acquisition metrics. Together, these five parameters create a comprehensive tracking framework that transforms raw traffic data into actionable marketing intelligence.
The concept of UTM parameters originated with Urchin Software, a pioneering web analytics platform founded in 1995 that revolutionized how marketers understood website traffic. When Google acquired Urchin in 2005, the company integrated its tracking methodology into Google Analytics, which launched in 2005 as a free analytics tool. This acquisition democratized web analytics, making sophisticated campaign tracking accessible to businesses of all sizes. The UTM naming convention became the industry standard because it was simple, flexible, and worked across all analytics platforms, not just Google’s tools. Over the past two decades, UTM parameters have remained largely unchanged in structure, demonstrating their fundamental effectiveness as a tracking mechanism.
Today, UTM parameters are used by an estimated 75% of digital marketers who actively track campaign performance, according to industry surveys. The persistence of UTM tracking despite the emergence of newer technologies like server-side tracking and advanced attribution platforms speaks to their reliability and ease of implementation. Unlike cookie-based tracking, which faces increasing privacy restrictions and browser limitations, UTM parameters function independently of cookies and JavaScript, making them resilient to privacy regulations like GDPR and browser privacy features. This durability has made UTM parameters a cornerstone of marketing analytics infrastructure, even as the broader tracking landscape has evolved significantly.
When a marketer creates a UTM-tagged URL, they append query string parameters to the end of a standard URL using a question mark (?) followed by parameter pairs separated by ampersands (&). For example, a basic URL like https://www.example.com/product becomes https://www.example.com/product?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=summer-sale when UTM parameters are added. When a user clicks this link, they are directed to the destination page exactly as they would be with a standard URL—the UTM parameters do not affect page functionality or user experience. Behind the scenes, however, Google Analytics and other tracking platforms automatically capture the UTM data and associate it with that user’s session.
The analytics platform then stores this information in its database, making it available for reporting and analysis. Marketers can subsequently view reports segmented by utm_source, utm_medium, utm_campaign, and other parameters to understand which marketing efforts drove traffic and conversions. This data flows into the analytics platform’s acquisition reports, allowing marketers to answer critical questions such as “Which social media platform generated the most traffic?” or “Which email campaign had the highest conversion rate?” The beauty of UTM parameters lies in their simplicity and universality—they work with any analytics platform, any marketing channel, and any type of URL, making them an indispensable tool for campaign measurement.
| Tracking Method | Implementation | Privacy Compliance | Cross-Domain Tracking | Cost | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTM Parameters | Manual URL tagging or URL builder tools | GDPR/CCPA compliant | Excellent | Free | Very High |
| Google Analytics 4 Events | Code implementation required | GDPR/CCPA compliant | Good | Free | High |
| First-Party Cookies | JavaScript implementation | Requires consent | Limited | Free | Declining |
| Pixel Tracking | Image/script insertion | Privacy concerns | Limited | Varies | Medium |
| Server-Side Tracking | Backend implementation | GDPR/CCPA compliant | Excellent | Moderate | Very High |
| UTM + Server-Side Hybrid | Combined approach | GDPR/CCPA compliant | Excellent | Moderate | Very High |
Successful UTM parameter implementation requires establishing and maintaining consistent naming conventions across your entire marketing organization. Before launching any campaigns, teams should agree on standardized formats for common parameters, such as whether to use lowercase letters exclusively, how to handle multi-word values (hyphens vs. underscores), and what naming schemes to use for recurring campaign types. For example, if your organization runs monthly newsletters, decide whether to name them “newsletter-january,” “newsletter-jan,” or “jan-newsletter,” and apply that convention consistently. According to industry research, 75% of marketers struggle with performance tracking, but those implementing rigorous UTM naming conventions see a 50% improvement in campaign clarity and data reliability.
Another critical best practice is to avoid using UTM parameters on internal links, as this creates artificial traffic attribution that skews your analytics. Internal navigation should never be tagged with UTM parameters, as it inflates your traffic sources and makes it impossible to distinguish between external and internal traffic patterns. Additionally, marketers should use URL shortening tools like Bit.ly or Rebrandly to make lengthy UTM-tagged URLs more shareable and user-friendly, particularly for social media campaigns where character limits and aesthetic considerations matter. These tools preserve the UTM parameters while creating clean, memorable shortened URLs that are more likely to be shared and clicked. Finally, document your UTM naming conventions in a centralized spreadsheet or wiki that all team members can access, ensuring consistency across campaigns and enabling new team members to quickly understand your tracking framework.
UTM parameters form the foundation of accurate marketing attribution by providing explicit data about which campaigns, sources, and mediums brought users to your website. Without UTM parameters, analytics platforms rely on default channel groupings and referrer data, which often misclassify traffic or fail to capture important campaign details. For instance, all traffic from Facebook appears as “social” by default in Google Analytics, but with UTM parameters, you can distinguish between organic Facebook posts, paid Facebook ads, and specific campaign variations. This granularity is essential for calculating true campaign ROI, as it allows you to compare the performance of different marketing channels and tactics on an equal basis.
Attribution modeling uses UTM data to assign credit to different touchpoints in the customer journey. First-click attribution gives credit to the first campaign that brought a user to your site, while last-click attribution credits the final campaign before conversion. Multi-touch attribution models distribute credit across multiple touchpoints, recognizing that customers typically interact with several marketing messages before converting. All of these attribution approaches depend on accurate UTM data to function properly. When UTM parameters are inconsistent or missing, attribution models cannot accurately track the customer journey, leading to flawed conclusions about which marketing efforts actually drive conversions. This is why Bitly’s 2024 research found that inconsistent UTM parameters result in data losses of up to 35% in campaign attribution accuracy.
Email marketing campaigns benefit significantly from UTM parameter tracking, as they allow marketers to measure which emails, subject lines, and calls-to-action generate the most traffic and conversions. By adding UTM parameters to links within emails, marketers can track not only overall email performance but also the effectiveness of specific links within each message. For example, an email with multiple CTAs can use different utm_content values for each button, revealing which message resonates most with subscribers. Similarly, social media campaigns can leverage UTM parameters to track performance across different platforms and posting strategies. A brand running the same campaign on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn can use identical utm_campaign values but different utm_source values to compare which platform drives the most valuable traffic.
The utm_content parameter is particularly valuable for social media A/B testing, allowing marketers to track which creative variations, headlines, or posting times generate the most engagement and traffic. For instance, a brand testing two different ad creatives can tag each with a unique utm_content value, then compare their performance in analytics. This data-driven approach to social media optimization has become essential as competition for attention intensifies and marketing budgets become more scrutinized. Additionally, UTM parameters help solve the “dark social” problem, where traffic from messaging apps, private social networks, and other non-trackable sources appears as direct traffic. By adding UTM parameters to links shared in these channels, marketers can properly attribute traffic to its true source rather than losing visibility into these important referral channels.
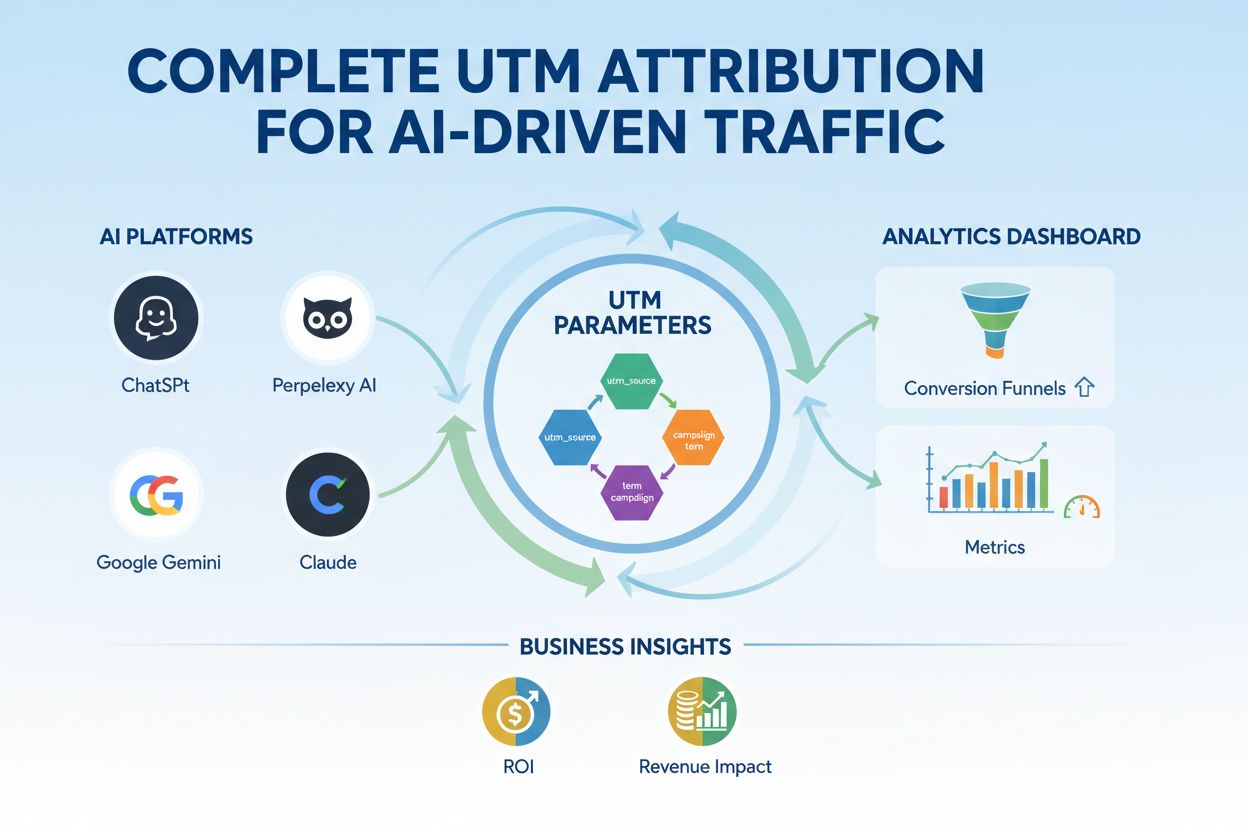
As artificial intelligence systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly generate content that includes links to external websites, UTM parameters have become critical for tracking traffic from AI-generated responses. When an AI system cites your content and includes a link, that link can be tagged with UTM parameters to identify it as coming from an AI source. This enables brands to measure how much traffic and conversions originate from AI-generated content, which is becoming an increasingly significant traffic source. By using utm_source values like “chatgpt,” “perplexity,” or “google-ai-overview,” marketers can segment and analyze AI-driven traffic separately from traditional search and social traffic.
Monitoring brand mentions in AI responses requires understanding how UTM parameters flow through AI systems. When your content is cited in an AI response with a UTM-tagged link, you can track not only the traffic volume but also user behavior after they arrive at your site. This data reveals whether AI-driven traffic converts at different rates than other sources, whether AI users have different engagement patterns, and how AI visibility impacts your overall marketing metrics. For brands using platforms like AmICited to monitor their appearance in AI responses, UTM parameters provide the quantitative data needed to measure the business impact of AI visibility. This integration of UTM tracking with AI monitoring represents a new frontier in marketing analytics, as brands must now optimize not just for traditional search engines but for visibility and proper attribution in AI-generated content.
The future of UTM parameters will likely involve greater integration with advanced analytics platforms and AI-driven attribution systems. As machine learning becomes more sophisticated, analytics platforms are developing automated UTM parameter suggestions and validation tools that help marketers maintain consistency without manual effort. Some platforms now offer AI-powered naming convention recommendations based on industry best practices, reducing the cognitive load of creating and managing UTM parameters. Additionally, server-side tracking implementations are increasingly being combined with UTM parameters to create hybrid tracking systems that capture both explicit campaign data (from UTM parameters) and implicit behavioral data (from server-side events).
The rise of privacy-first analytics and cookieless tracking has actually strengthened the case for UTM parameters, as they represent one of the few tracking methods that function independently of cookies and third-party data. As browsers continue to restrict cookie functionality and regulations like GDPR become more stringent, UTM parameters are becoming even more valuable as a reliable, privacy-compliant tracking mechanism. Furthermore, as AI systems become major traffic sources, the ability to track and attribute traffic from AI-generated content will become increasingly important. Brands that implement robust UTM parameter strategies now will be better positioned to measure the business impact of AI visibility and optimize their content for AI platforms. The integration of UTM tracking with specialized AI monitoring platforms like AmICited represents the next evolution in campaign attribution, enabling brands to understand not just how much traffic comes from AI, but also how that traffic converts and contributes to business objectives.
UTM stands for Urchin Tracking Module, named after Urchin Tracker, a web analytics software that Google acquired and used as the foundation for Google Analytics. The term has persisted in marketing terminology even though the original Urchin software is no longer in use. Today, UTM parameters remain the standard method for tracking campaign performance across all major analytics platforms.
UTM parameters are URL-based tracking that work independently of cookies or JavaScript, making them more reliable across different browsers and privacy settings. Unlike pixel tracking which requires image loading, UTM parameters are simple text strings that survive URL sharing and forwarding. They provide explicit campaign attribution without relying on third-party cookies, making them compliant with privacy regulations like GDPR.
Yes, UTM parameters can track traffic from AI platforms when those platforms include links in their responses. By adding UTM codes to your URLs, you can identify when traffic originates from AI-generated content or AI search results. This is particularly valuable for monitoring brand mentions and traffic attribution in AI responses, which is increasingly important as AI systems become major traffic sources.
The five standard UTM parameters are: utm_source (traffic origin like 'google' or 'facebook'), utm_medium (channel type like 'email' or 'cpc'), utm_campaign (specific campaign name), utm_content (specific link or element), and utm_term (paid search keywords). Source, medium, and campaign are essential for all campaigns, while content and term are optional but valuable for detailed analysis and A/B testing.
Inconsistent UTM naming conventions create fragmented data that makes analysis unreliable. According to Bitly's 2024 study, inconsistent UTM parameters lead to data losses of up to 35% in campaign attribution. When teams use different capitalization, spacing, or naming formats for the same campaign, analytics platforms treat them as separate campaigns, splitting metrics and preventing accurate ROI calculations.
UTM parameters provide the foundational data that attribution models use to assign credit to marketing touchpoints. They identify which campaigns, sources, and mediums brought users to your site, allowing attribution models to determine whether credit should go to first-click, last-click, or multi-touch attribution. Without UTM parameters, attribution models cannot accurately track the customer journey.
UTM parameters enable brands to track traffic originating from AI-generated content and AI search results by tagging URLs with specific campaign identifiers. When AI systems cite your content with UTM-tagged links, you can measure traffic volume, user engagement, and conversions from AI sources. This is critical for understanding how AI platforms impact your overall traffic and for optimizing content strategy for AI visibility.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Master UTM tracking for AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google Gemini. Learn setup, best practices, and how to attribute AI traffic accurately in GA4...
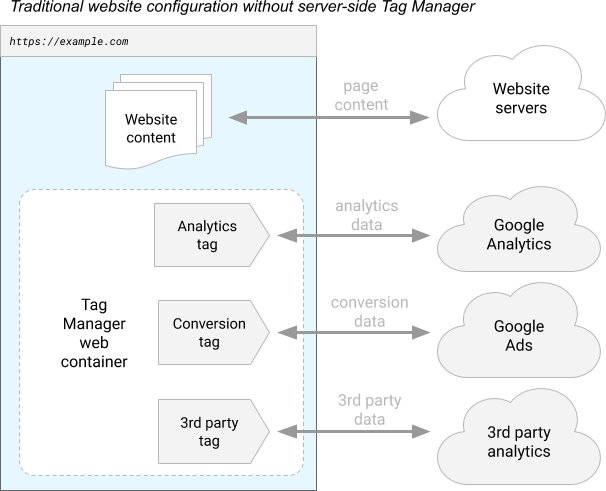
Learn what Google Tag Manager is, how it works as a tag management system, and why it's essential for modern digital marketing and data collection strategies.
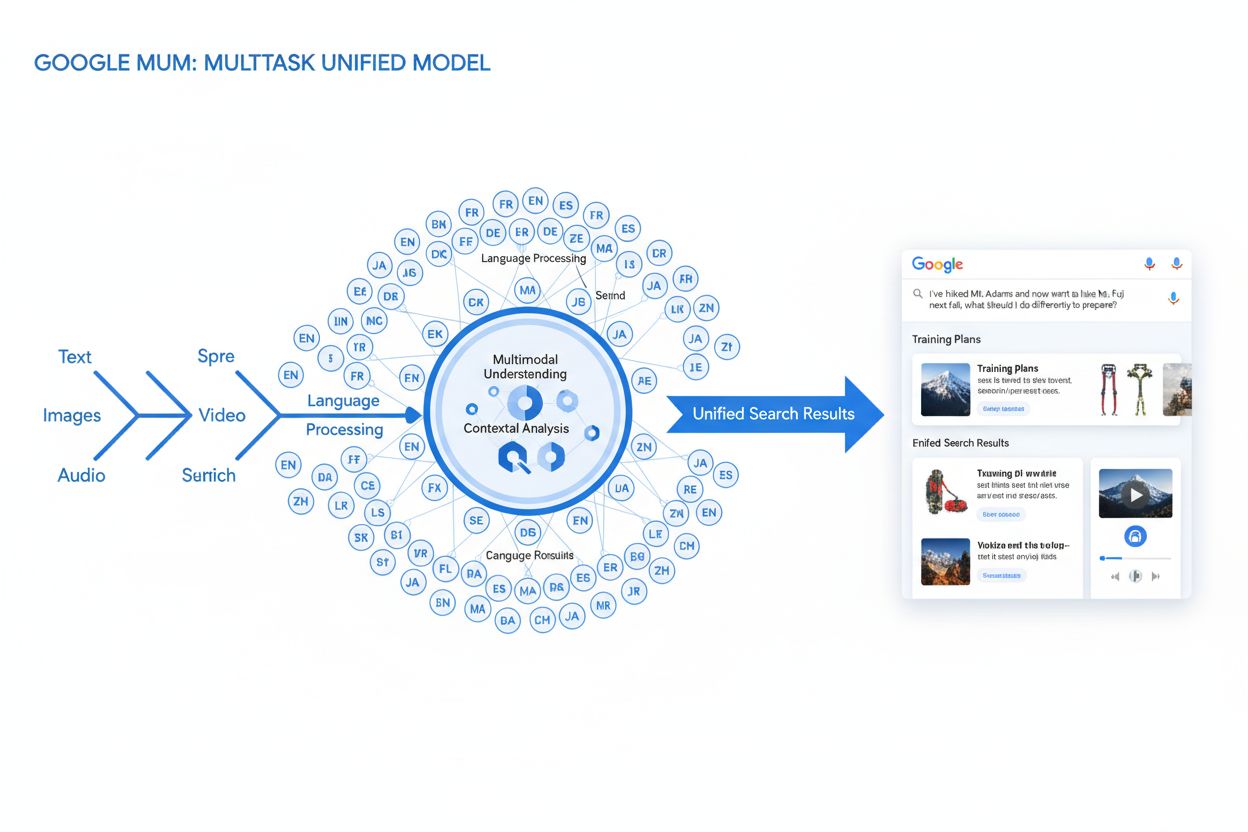
MUM is Google's Multitask Unified Model—a multimodal AI that processes text, images, video, and audio across 75+ languages. Learn how it transforms search and i...