AI Content Generation
Learn what AI content generation is, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and best practices for using AI tools to create marketing content optimized for ...
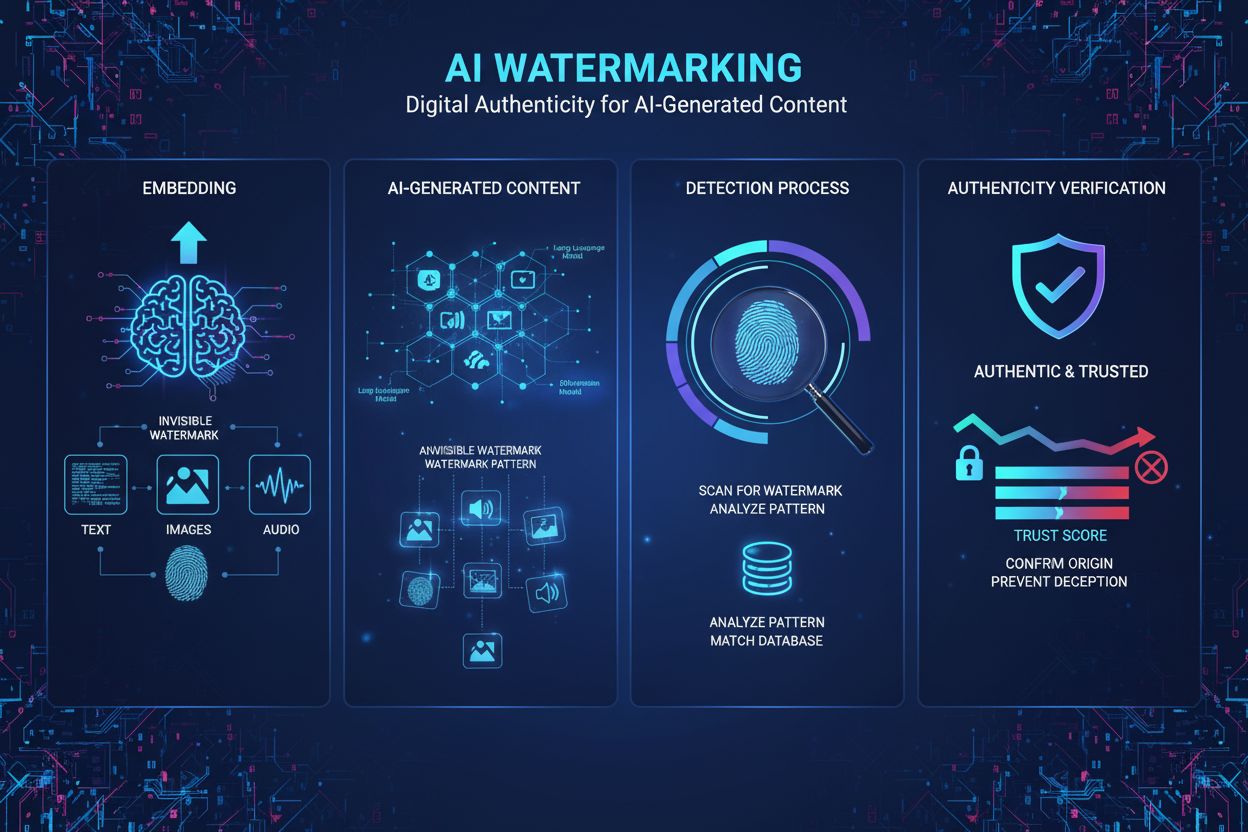
Watermarking AI content is the process of embedding invisible or visible digital markers into AI-generated text, images, audio, or video to identify and authenticate that content as machine-generated. These watermarks serve as digital fingerprints that enable detection, verification, and tracking of AI-generated material across platforms and applications.
Watermarking AI content is the process of embedding invisible or visible digital markers into AI-generated text, images, audio, or video to identify and authenticate that content as machine-generated. These watermarks serve as digital fingerprints that enable detection, verification, and tracking of AI-generated material across platforms and applications.
Watermarking AI content refers to the process of embedding digital markers, patterns, or signatures into AI-generated material to identify, authenticate, and track its origin. These watermarks function as digital fingerprints that distinguish machine-generated content from human-authored work across text, images, audio, and video formats. The primary purpose of AI content watermarking is to provide transparency regarding content provenance while combating misinformation, protecting intellectual property, and ensuring accountability in the rapidly expanding landscape of generative artificial intelligence. Unlike traditional watermarks visible on physical documents or images, modern AI watermarking techniques often employ invisible patterns detectable only through specialized algorithms, preserving content quality while maintaining robust authentication capabilities.
The concept of watermarking originated in the physical world, where invisible marks on banknotes and documents served as anti-counterfeiting measures. As digital media proliferated, researchers adapted watermarking techniques for images, audio, and video throughout the 1990s and 2000s. However, the emergence of sophisticated generative AI models like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney in 2022-2023 created an urgent need for standardized AI content authentication methods. The rapid advancement of AI capabilities that produce increasingly realistic synthetic content prompted governments, technology companies, and civil society organizations to prioritize watermarking as a critical safeguard. According to research from the Brookings Institution, over 78% of enterprises recognize the importance of AI-driven content monitoring tools for managing synthetic media risks. The EU AI Act, formally adopted in March 2024, became the first major regulatory framework to mandate AI content watermarking, requiring providers of AI systems to mark their output as AI-generated. This regulatory momentum has accelerated research and development in watermarking technologies, with companies like Google DeepMind, OpenAI, and Meta investing significantly in robust watermarking solutions.
AI watermarking operates through two primary technical approaches: visible watermarking and invisible watermarking. Visible watermarks include obvious labels, logos, or text indicators added to content—such as the five colored squares DALL-E places on generated images or ChatGPT’s preamble “as a language model trained by OpenAI.” While simple to implement, visible watermarks are trivially easy to remove through basic editing. Invisible watermarking, conversely, embeds subtle patterns imperceptible to human perception but detectable by specialized algorithms. For AI-generated images, techniques like tree-ring watermarks developed at the University of Maryland embed patterns in the initial random noise before the diffusion process, making them resistant to cropping, rotation, and filtering. For AI-generated text, statistical watermarking represents the most promising approach, where the language model subtly favors certain tokens (“green tokens”) while avoiding others (“red tokens”) based on preceding context. This creates a statistically unusual arrangement of words that detection algorithms can identify with high confidence. Audio watermarking embeds imperceptible patterns in frequency ranges outside human hearing (below 20 Hz or above 20,000 Hz), similar to image watermarking but adapted for acoustic properties. The SynthID technology from Google DeepMind exemplifies modern watermarking by jointly training generation and detection models, ensuring robustness across transformations while maintaining content quality.
| Watermarking Method | Content Type | Robustness | Quality Impact | Requires Model Access | Detectability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visible Watermarking | Images, Video | Very Low | None | No | High (Human) |
| Statistical Watermarking | Text, Images | High | Minimal | Yes | High (Algorithmic) |
| Machine Learning-Based | Images, Audio | High | Minimal | Yes | High (Algorithmic) |
| Tree-Ring Watermarking | Images | Very High | None | Yes | High (Algorithmic) |
| Content Provenance (C2PA) | All Media | Medium | None | No | Medium (Metadata) |
| Post-Hoc Detection | All Media | Low | N/A | No | Low (Unreliable) |
Statistical watermarking represents the most viable technique for authenticating AI-generated text, addressing the unique challenge that text lacks the dimensional space available in images or audio for embedding patterns. During the generation process, a language model receives instructions to favor certain tokens based on a cryptographic key known only to the model developer. The model’s randomness is “loaded” according to this scheme, causing it to preferentially select specific words or phrases while avoiding others. Detection protocols analyze the generated text to compute the probability of observing the detected token patterns purely by chance; statistically improbable patterns indicate the presence of a watermark. Research from the University of Maryland and OpenAI has demonstrated that this approach can achieve high detection accuracy while maintaining text quality. However, statistical watermarking for text faces inherent limitations: factual responses with limited generation flexibility (such as mathematical solutions or historical facts) are harder to watermark effectively, and thorough rewriting or translation to different languages can significantly degrade detection confidence. The SynthID Text implementation, now available in Hugging Face Transformers v4.46.0+, provides production-grade watermarking using configurable parameters including cryptographic keys and n-gram length to balance robustness and detectability.
AI-generated images benefit from more sophisticated watermarking approaches due to the high-dimensional space available for embedding patterns. Tree-ring watermarking embeds hidden patterns in the initial random image before the diffusion process, creating watermarks that survive common transformations like cropping, blurring, and rotation without degrading image quality. Machine learning-based watermarking from Meta and Google uses neural networks to embed and detect imperceptible watermarks, achieving 96%+ accuracy on unmodified images while remaining resistant to pixel-level attacks. Audio watermarking employs similar principles, embedding imperceptible patterns in frequency ranges outside human perception. AudioSeal, developed by Meta, jointly trains generator and detector models to create watermarks robust to natural audio transformations while maintaining indistinguishable audio quality. The technology uses perceptual loss to ensure watermarked audio sounds identical to original audio while employing localization loss to detect watermarks regardless of perturbations. These approaches demonstrate that invisible watermarking can achieve both robustness and quality preservation when properly implemented, though they require access to the underlying AI model for watermark embedding.
The regulatory environment for AI content watermarking has evolved rapidly, with multiple jurisdictions implementing or proposing mandatory watermarking requirements. The EU AI Act, formally adopted in March 2024, represents the most comprehensive regulatory framework, requiring providers of AI systems to mark their output as AI-generated content. This regulation applies to all generative AI systems deployed within the European Union, establishing a legal obligation for watermarking compliance. California’s AI Transparency Act (SB 942), effective January 1, 2026, mandates that covered AI providers make available free, publicly accessible AI content detection tools, effectively requiring watermarking or equivalent authentication mechanisms. The U.S. National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) for Fiscal Year 2024 includes provisions for a prize competition to evaluate watermarking technology and directs the Department of Defense to study and pilot implementation of “industry open technical standards” for embedding content provenance information in metadata. The White House Executive Order on AI directs the Department of Commerce to identify and develop standards for labeling AI-generated content. These regulatory initiatives reflect growing consensus that AI watermarking is essential for transparency, accountability, and consumer protection. However, implementation challenges remain significant, particularly regarding open-source models, international coordination, and the technical feasibility of universal watermarking standards.
Despite significant technical advances, AI watermarking faces substantial limitations that constrain its practical effectiveness. Watermark removal remains achievable through various evasion techniques: paraphrasing text, cropping or filtering images, translating content to different languages, or applying adversarial perturbations. Research from Duke University demonstrated proof-of-concept attacks against machine learning-based watermark detectors, indicating that even sophisticated approaches are vulnerable to determined adversaries. The non-universality problem represents another critical limitation—watermark detectors are model-specific, meaning users must query each AI company’s detection service separately to verify content origin. Without a centralized registry and standardized detection protocols, checking whether content is AI-generated becomes an inefficient, ad hoc process. False positive rates in watermark detection, particularly for text, remain problematic; detection algorithms may incorrectly flag human-authored content as AI-generated or fail to detect watermarked content after minor modifications. Open-source model compatibility presents governance challenges, as watermarks can be disabled by removing code from downloaded models. Quality degradation occurs when watermarking algorithms artificially constrain model outputs to embed detectable patterns, potentially reducing content quality or limiting generation flexibility for factual or constrained-output tasks. The privacy implications of watermarking—particularly if watermarks include user identification information—require careful policy consideration. Additionally, detection confidence decreases significantly with content length; shorter texts and heavily modified content yield lower detection confidence, limiting watermarking’s utility in certain applications.
The future of AI watermarking depends on continued technical innovation, regulatory harmonization, and establishment of trusted infrastructure for watermark detection and verification. Researchers are exploring publicly detectable watermarks that maintain robustness despite disclosure of detection methods, potentially enabling decentralized verification without requiring trust in third-party detection services. Standardization efforts through organizations like ICANN or industry consortia could establish universal watermarking protocols, reducing fragmentation and enabling efficient cross-platform detection. Integration with content provenance standards like C2PA may create layered authentication approaches combining watermarks with metadata-based provenance tracking. The development of watermarks robust to translation and paraphrasing remains an active research frontier, with potential applications in multilingual content authentication. Blockchain-based verification systems could provide immutable records of watermark detection and content provenance, enhancing trust in authentication results. As generative AI capabilities advance, watermarking techniques must evolve to maintain effectiveness against increasingly sophisticated evasion attempts. The regulatory momentum established by the EU AI Act and California’s legislation will likely drive global adoption of watermarking standards, creating market incentives for robust technical solutions. However, realistic expectations acknowledge that watermarking will primarily manage AI-generated content from popular commercial models while remaining limited in high-stakes scenarios requiring immediate detection. The integration of AI content monitoring platforms like AmICited with watermarking infrastructure will enable organizations to track brand attribution across AI systems, ensuring proper recognition when their domains appear in AI-generated responses. Future developments will likely emphasize human-AI collaboration in content authentication, combining automated watermark detection with human verification for critical applications in journalism, legal proceedings, and academic integrity.
Visible watermarks are easily detectable by humans, such as logos or text labels added to images or audio clips, but they are simple to remove or forge. Invisible watermarks embed subtle patterns imperceptible to human perception but detectable by specialized algorithms, making them significantly more robust against tampering and removal attempts. Invisible watermarks are generally preferred for AI content authentication because they maintain content quality while providing stronger security against evasion.
Statistical watermarking for text operates by subtly influencing the language model's token selection during generation. The model developer 'loads the dice' using a cryptographic scheme, causing the model to favor certain 'green tokens' while avoiding 'red tokens' based on preceding context. Detection algorithms then analyze the text to identify whether favored tokens appear with statistically unusual frequency, indicating the presence of a watermark. This approach preserves text quality while embedding a detectable fingerprint.
Key challenges include the ease of watermark removal through minor edits or transformations, the lack of universal detection across different AI models, and the difficulty of watermarking text compared to images or audio. Additionally, watermarking requires cooperation from AI model developers, is incompatible with open-source model releases, and may degrade content quality if not carefully implemented. False positives and false negatives in detection also remain significant technical hurdles.
The EU AI Act, formally adopted in March 2024, requires providers of AI systems to mark their output as AI-generated content. California's AI Transparency Act (SB 942), effective January 1, 2026, mandates that covered AI providers make available free, publicly accessible content detection tools. The U.S. National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) for Fiscal Year 2024 includes provisions for watermarking technology evaluation and development of industry standards for content provenance.
Watermarking embeds identifying patterns directly into AI-generated content itself, creating a permanent digital fingerprint that persists even if the content is copied or modified. Content provenance, such as the C2PA standard, stores metadata about content origin and modification history separately in file metadata. Watermarking is more robust to evasion but requires model developer cooperation, while provenance is easier to implement but can be stripped by copying content without metadata.
SynthID is Google DeepMind's technology that watermarks and identifies AI-generated content by embedding digital watermarks directly into images, audio, text, and video. For text, SynthID uses a logits processor that augments the model's generation pipeline to encode watermarking information without significantly affecting quality. The technology employs machine learning models to both embed and detect watermarks, making it resistant to common attacks while maintaining content fidelity.
Yes, motivated actors can remove or bypass watermarks through various techniques including paraphrasing text, cropping or filtering images, or translating content to different languages. However, removing sophisticated watermarks requires technical expertise and knowledge of the watermarking scheme. Statistical watermarks are more robust than traditional approaches, but research has demonstrated proof-of-concept attacks against even advanced watermarking methods, indicating that no watermarking technique is completely foolproof.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what AI content generation is, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and best practices for using AI tools to create marketing content optimized for ...

Learn about AI content licensing agreements that govern how artificial intelligence systems use copyrighted content. Explore licensing types, key components, pl...

Learn what AI content detection is, how detection tools work using machine learning and NLP, and why they matter for brand monitoring, education, and content au...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.