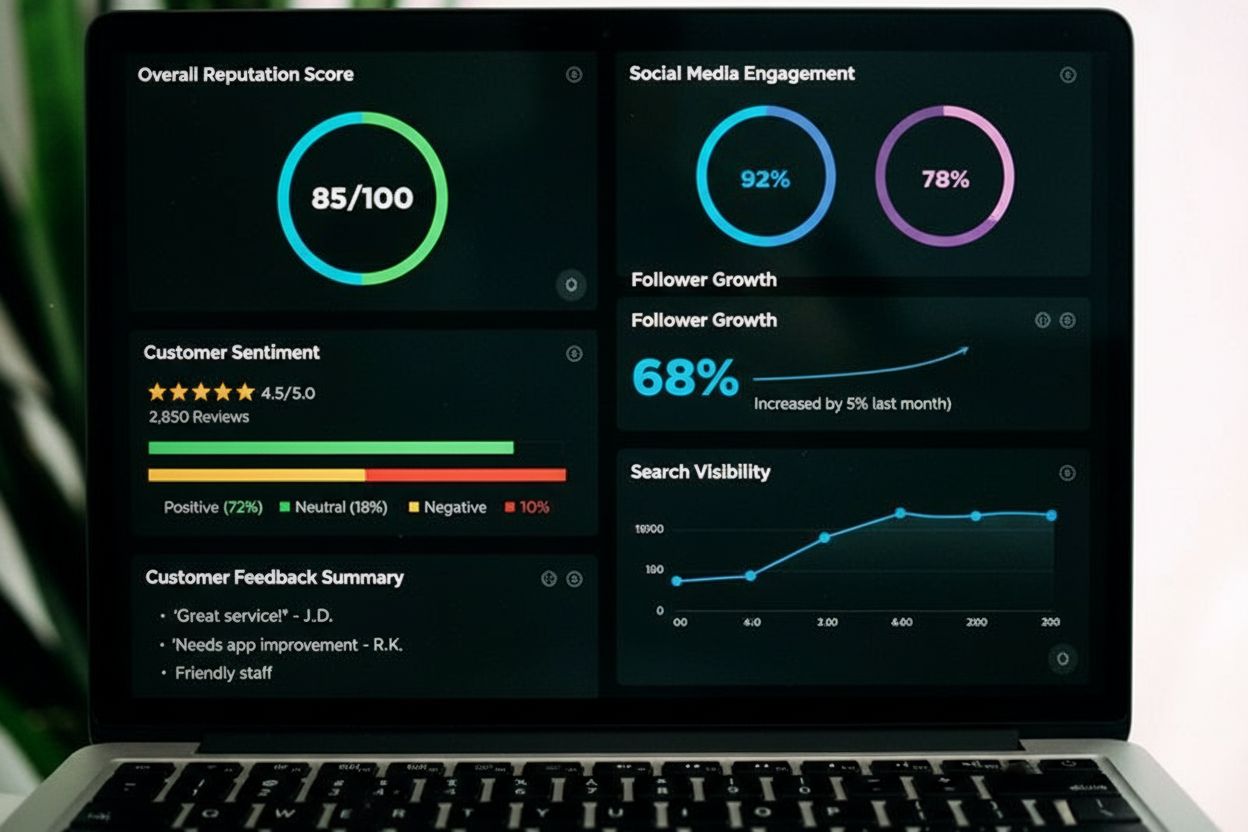
Reputation Score
Learn what a reputation score is, how it's calculated, and why it matters for brand monitoring. Understand the key factors that influence online reputation metr...
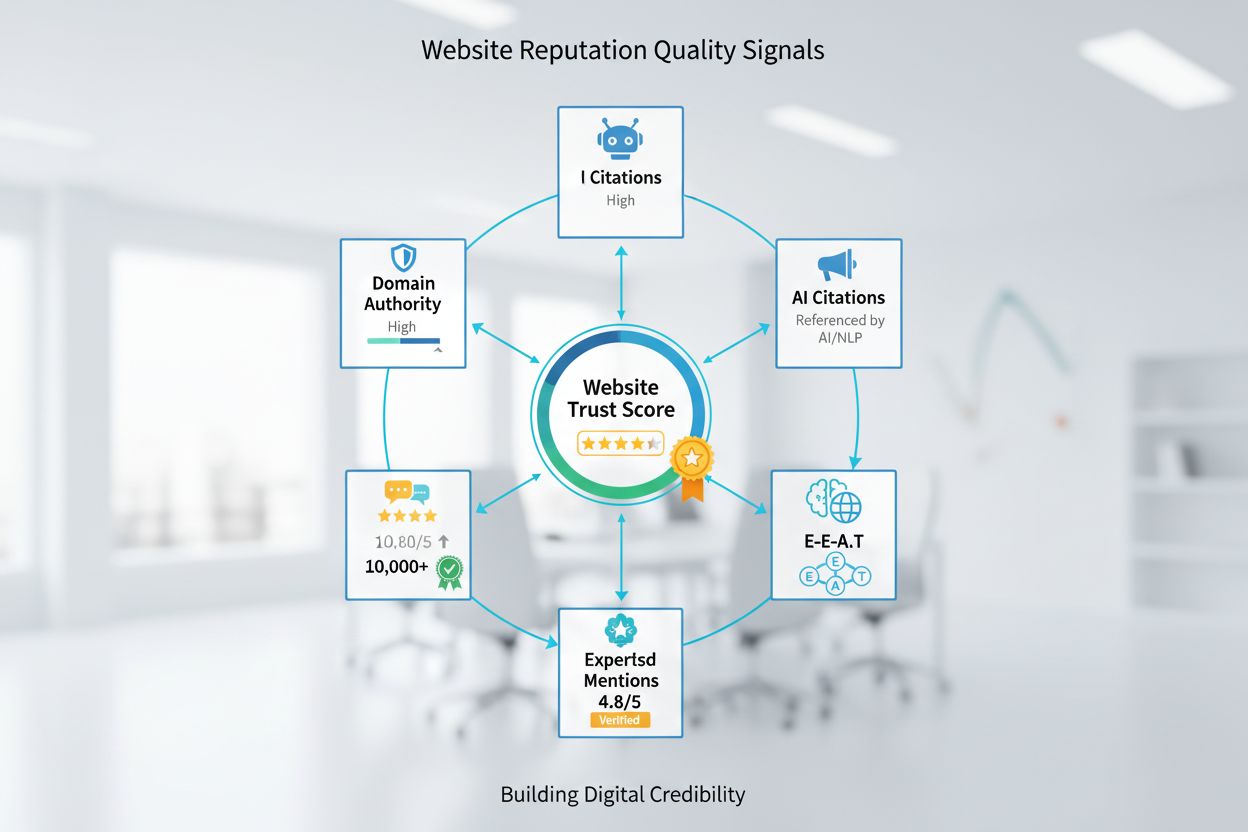
Website reputation is the overall perception of a website’s quality, credibility, and trustworthiness as determined by search engines, AI systems, and users based on multiple quality signals including domain authority, backlinks, user reviews, E-E-A-T factors, and brand mentions. It directly influences search rankings, AI citations, and user conversion rates.
Website reputation is the overall perception of a website's quality, credibility, and trustworthiness as determined by search engines, AI systems, and users based on multiple quality signals including domain authority, backlinks, user reviews, E-E-A-T factors, and brand mentions. It directly influences search rankings, AI citations, and user conversion rates.
Website reputation is the collective perception of a website’s quality, credibility, and trustworthiness as determined by search engines, artificial intelligence systems, and users based on multiple interconnected quality signals. It encompasses how a site is viewed across the digital ecosystem—from traditional search engine rankings to emerging AI citation patterns in platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Website reputation is not a single metric but rather a multidimensional construct built through domain authority, backlink quality, user reviews, content expertise, brand mentions, and technical performance. Understanding website reputation is essential in today’s digital landscape because it directly influences search visibility, AI citations, user trust, and ultimately business revenue and conversion rates.
Website reputation has evolved significantly since the early days of search engines. In the 1990s and early 2000s, reputation was primarily determined by simple link counts and keyword matching. However, as search engines became more sophisticated, particularly after Google’s introduction of PageRank and subsequent algorithm updates like Panda (2011), Penguin (2012), and Hummingbird (2013), reputation assessment became far more nuanced. Today, website reputation encompasses over 200 ranking factors that Google considers when evaluating site quality. The online reputation management market reflects this importance—valued at USD 6.88 billion in 2025 and projected to reach USD 12.57 billion by 2030, growing at a 12.8% CAGR. This explosive growth demonstrates that businesses increasingly recognize reputation as a critical asset. The emergence of AI search engines has added another dimension to reputation assessment, with platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews now using website reputation signals to determine which sources to cite in their responses. Research shows that 88% of online consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations, and 85% of consumers actively look for negative reviews to understand potential issues—underscoring how reputation directly impacts purchasing decisions and business outcomes.
Website reputation is built on several interconnected pillars that work together to establish credibility. Domain Authority (DA), developed by Moz, is a predictive metric ranging from 1 to 100 that evaluates a website’s overall strength in search rankings based primarily on backlink quality and quantity. Websites with higher DA scores are more likely to rank well in search results and be cited by AI systems. Backlinks serve as votes of confidence from other websites, with high-quality links from authoritative domains significantly boosting reputation. The number of referring domains (unique websites linking to you) is particularly important—diversity of backlink sources signals broader recognition and trust. User reviews and ratings are critical reputation components, with research showing that a one-star increase on Google Maps correlates with a 5-9% boost in annual revenue for local businesses. E-E-A-T signals (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) have become increasingly important, especially after Google’s 2023 quality rater guidelines update, with Google explicitly stating that sites demonstrating strong E-E-A-T receive ranking advantages. Brand mentions across the web, including unlinked mentions in news articles, social media, and industry publications, contribute to reputation by establishing brand recognition and authority. Technical performance metrics like page speed, mobile-friendliness, and SSL certificates signal professionalism and trustworthiness. Finally, AI citations from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews represent an emerging reputation dimension, with websites cited by these systems gaining visibility in the new AI search landscape.
| Reputation Factor | Definition | Impact on Rankings | Impact on AI Citations | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain Authority (DA) | Predictive metric (1-100) based on backlink profile strength | High - correlates strongly with SERP rankings | High - AI systems prefer high-DA sources | Moz Link Explorer, Domain Analysis tools |
| Backlink Quality | Authority and relevance of websites linking to your site | Very High - among top 8 ranking factors | Very High - determines source credibility | Ahrefs, SEMrush, Backlinko analysis |
| User Reviews & Ratings | Customer feedback on review platforms (Google, Yelp, Trustpilot) | High - 70% of customers need 5+ reviews to trust | Medium - some AI systems cite review aggregators | Google Reviews, Yelp, review monitoring tools |
| E-E-A-T Signals | Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness indicators | Very High - explicit Google ranking factor | High - AI systems prioritize credible experts | Author credentials, content depth, citations |
| Page Speed | Website loading time and Core Web Vitals performance | High - direct ranking factor since 2021 | Medium - affects user experience signals | Google PageSpeed Insights, Core Web Vitals |
| Content Freshness | Recency and update frequency of website content | Medium - more important for news/trending topics | Medium - AI systems prefer current information | Content update tracking, publication dates |
| Brand Mentions | References to brand across web (linked and unlinked) | Medium - signals brand recognition and authority | High - establishes brand credibility | Brand monitoring tools, Google Alerts |
| Mobile Optimization | Website responsiveness and mobile user experience | High - mobile-first indexing is standard | Medium - affects accessibility for AI crawlers | Mobile-Friendly Test, responsive design audit |
| SSL Certificate (HTTPS) | Secure website encryption protocol | Medium - acts as tiebreaker between equal sites | Low - baseline expectation for credibility | SSL checker tools, browser security indicators |
| AI Citations | Mentions in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews | Emerging - increasingly important for visibility | Very High - direct measure of AI platform trust | Profound, AmICited, AI visibility tools |
Website reputation serves as a foundational element in Google’s ranking algorithm, with search engines using reputation signals as proxies for content quality and user value. When a website has strong reputation indicators—such as numerous high-quality backlinks, positive user reviews, strong E-E-A-T signals, and consistent brand mentions—search engines interpret these signals as evidence that the site deserves higher visibility. The relationship is bidirectional: websites that rank higher receive more traffic and visibility, which generates more reviews, mentions, and backlinks, further strengthening reputation. Google’s RankBrain algorithm, an AI system that interprets search intent and evaluates result quality, heavily weighs reputation signals when determining rankings. Research from Backlinko analyzing 11.8 million Google search results found that the number of referring domains (a key reputation metric) is one of the strongest correlations with first-page rankings. Additionally, sites with strong reputations benefit from lower bounce rates and higher engagement metrics—users are more likely to trust and interact with reputable sites, which sends positive signals to search engines. The impact is particularly pronounced for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content, where Google applies stricter quality standards and explicitly evaluates E-E-A-T signals. For local businesses, reputation becomes even more critical: 60% of consumers use “near me” searches and filter by ratings above 4 stars, making review management essential for local search visibility. The compounding effect of reputation means that established, reputable websites have significant advantages in search rankings, making reputation building a long-term strategic investment.
The emergence of AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has created a new dimension of website reputation that extends beyond traditional search rankings. These AI systems use sophisticated algorithms to determine which websites to cite when generating responses to user queries, and website reputation plays a crucial role in this selection process. Research analyzing 680 million citations across AI platforms reveals distinct citation patterns: ChatGPT heavily favors Wikipedia (47.9% of its top 10 most-cited sources), demonstrating a preference for encyclopedic, authoritative knowledge bases. Perplexity, by contrast, prioritizes Reddit (46.7% of top 10 sources), reflecting a preference for community-driven, peer-to-peer information. Google AI Overviews shows a more balanced approach, citing Reddit (21% of top 10), YouTube (18.8%), and Quora (14.3%), indicating a preference for diverse, user-generated content alongside professional sources. These patterns demonstrate that AI systems evaluate website reputation differently than traditional search engines, with some platforms valuing community engagement and user-generated content more heavily than others. Websites with strong reputations—evidenced by high domain authority, numerous quality backlinks, positive user reviews, and established brand authority—are significantly more likely to be cited by AI systems. This creates a new competitive landscape where brands must optimize not just for traditional search visibility but also for AI citation patterns. The online reputation management market’s projected growth to USD 12.57 billion by 2030 reflects businesses’ recognition that managing reputation across both traditional search and AI platforms is now essential for maintaining visibility and relevance.
E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) has become central to how both search engines and AI systems evaluate website reputation. Google explicitly incorporated E-E-A-T into its quality rater guidelines, instructing human evaluators to assess whether content demonstrates genuine expertise, whether the author has relevant experience, whether the website is recognized as an authority in its field, and whether the site is trustworthy and transparent. Websites demonstrating strong E-E-A-T signals receive ranking boosts, particularly for health, financial, legal, and other high-stakes content categories. Building E-E-A-T reputation requires multiple strategies: publishing content authored by recognized experts with verifiable credentials, citing authoritative sources and research, obtaining backlinks from other authoritative sites in your industry, building a strong brand presence through consistent messaging and professional design, and maintaining transparent business practices including clear contact information and privacy policies. The importance of E-E-A-T extends to AI systems, which use similar quality assessment frameworks when selecting sources to cite. A website’s E-E-A-T reputation is not built overnight—it requires consistent demonstration of expertise through high-quality content, industry recognition, and user trust signals over time. For new websites or those in competitive niches, building E-E-A-T reputation is particularly challenging because search engines and AI systems naturally favor established, recognized authorities. However, by focusing on creating genuinely valuable, expert-level content and earning recognition from other authoritative sources, websites can gradually build E-E-A-T reputation and improve their visibility across both traditional search and AI platforms.
The relationship between website reputation and business outcomes is direct and measurable. Research demonstrates that companies with positive reputations generate 6.9 times more leads than those with poor reputations, and even small improvements in online reputation can significantly impact revenue. For e-commerce businesses, the impact is particularly pronounced: 70% of customers need to see at least 5 good reviews before feeling confident making a purchase, and 46% of online shoppers typically read 1-6 reviews before forming an opinion. A one-star increase on Google Maps correlates with a 5-9% boost in annual revenue for local businesses, translating to substantial financial impact. Website speed, a key reputation signal, directly affects conversion rates: pages loading within 1 second achieve approximately 40% conversion rates, while 2-second load times drop conversions to 34%—a 6-point difference that compounds across thousands of visitors. Negative reviews have severe consequences: 94% of consumers report that negative reviews cause them to avoid a business entirely, and 85% of people actively look for negative reviews to understand potential issues. Conversely, businesses that respond to at least 80% of written reviews see a 25% higher retention rate among existing customers, demonstrating that reputation management directly impacts customer loyalty. The financial stakes are substantial enough that the online reputation management market is growing at 12.8% CAGR, with enterprises and SMEs increasingly investing in reputation monitoring and management tools. For businesses operating in competitive markets, website reputation has become a primary differentiator—two otherwise similar businesses may see dramatically different conversion rates and revenue based solely on their reputation signals.
Effective website reputation management requires a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach that addresses all key reputation components. Content quality and expertise form the foundation: publishing original research, expert guides, and in-depth resources that demonstrate genuine expertise and provide value to users. This content naturally attracts backlinks and citations, strengthening reputation. Backlink acquisition should focus on earning links from authoritative, relevant websites through guest posting, resource page placements, broken link building, and creating link-worthy content. Quality matters far more than quantity—a single link from a high-authority domain is worth more than dozens of links from low-quality sites. Review management requires actively soliciting reviews from satisfied customers through email campaigns, SMS reminders, and in-app prompts, then responding professionally to all reviews (both positive and negative) within 24-48 hours. Research shows that 33% of unhappy customers will revise negative reviews if they receive satisfactory resolution within 72 hours. Technical optimization ensures websites load quickly (targeting under 2 seconds), are mobile-friendly, use HTTPS encryption, and have clean, logical site architecture. Brand building involves consistent messaging across all channels, professional design, transparent business practices, and active engagement on social media and industry platforms. E-E-A-T signals should be deliberately built through author credentials, expert bylines, citations of authoritative sources, and transparent disclosure of expertise and potential conflicts of interest. Monitoring and measurement requires regular tracking of domain authority, backlink profile changes, review volume and sentiment, brand mentions, and AI citations. Tools like Moz, Ahrefs, SEMrush, Trustpilot, and AmICited provide comprehensive reputation monitoring capabilities. Finally, crisis management protocols should be in place to quickly address negative reviews, PR issues, or reputation threats, with clear escalation procedures and response templates.
Website reputation is undergoing fundamental transformation as AI search engines become increasingly important in the digital ecosystem. The traditional model where Google search dominance determined online visibility is shifting toward a multi-platform landscape where ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Claude, and other AI systems each have their own citation patterns and reputation assessment criteria. This fragmentation means that websites must now optimize for multiple reputation frameworks simultaneously—what works for ChatGPT citations may differ from what works for Perplexity or Google AI Overviews. The rise of generative AI also means that direct traffic to websites may decrease as users get answers directly from AI systems, making AI citations increasingly valuable as a traffic source. Emerging trends suggest that AI systems will place even greater emphasis on verifiable expertise, transparent author credentials, and E-E-A-T signals as they attempt to reduce hallucinations and improve answer accuracy. The concept of “Generative Engine Optimization” (GEO) is emerging as a new discipline focused specifically on optimizing for AI search visibility, complementing traditional SEO. Additionally, as AI systems become more sophisticated, they may develop their own reputation scoring systems that differ from Google’s, creating new competitive dynamics. The integration of real-time data, social signals, and user feedback into AI systems suggests that website reputation will become increasingly dynamic, with real-time reputation monitoring becoming essential. Finally, the regulatory landscape around AI transparency and source attribution may evolve, potentially creating new requirements for how websites must present credentials and expertise to be considered reputable sources by AI systems. Organizations that proactively adapt their reputation strategies to this evolving landscape will maintain competitive advantages, while those relying solely on traditional SEO approaches may find their visibility declining as AI search becomes more prevalent.
Website reputation is shaped by multiple interconnected factors including domain authority (backlink quality and quantity), user reviews and ratings (88% of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations), E-E-A-T signals (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), brand mentions across the web, page speed and technical SEO, content quality and freshness, and AI citations from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Each factor contributes to how search engines and AI systems perceive your site's credibility.
Website reputation directly influences search rankings through Google's 200+ ranking factors, with domain authority and backlink quality being among the most significant. Sites with strong reputations receive higher rankings because search engines interpret reputation signals as indicators of content quality and user value. Additionally, positive reputation signals like high user engagement, low bounce rates, and numerous quality backlinks trigger RankBrain algorithms to boost visibility, creating a compounding effect where reputable sites gain more traffic and visibility.
AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews use website reputation as a key factor when selecting sources to cite in their responses. Research shows that Wikipedia dominates ChatGPT citations (47.9% of top 10 sources), while Reddit leads Perplexity citations (46.7% of top 10 sources), demonstrating that AI systems prioritize sources with established credibility and user trust. Websites with strong reputations are more likely to be cited by AI systems, increasing brand visibility in the emerging AI search landscape.
Website reputation can be measured through multiple metrics including Domain Authority (DA) scores from Moz (ranging 1-100), backlink analysis tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush, online review aggregation platforms, brand mention tracking across social media and news outlets, and AI visibility monitoring tools like Profound or AmICited. Regular monitoring of these metrics helps identify reputation trends, competitive positioning, and areas requiring improvement to maintain or enhance your site's credibility.
Online reviews are critical reputation factors because 85% of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations, and 94% of consumers report that negative reviews cause them to avoid businesses entirely. Reviews serve as social proof that influences purchase decisions, boost local SEO rankings (a one-star increase correlates with 5-9% revenue boost for local businesses), and signal authenticity to search engines. Platforms like Google Maps, Yelp, and Facebook use review volume and ratings as ranking signals, making review management essential for reputation.
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—Google's quality framework for evaluating website credibility. Websites demonstrating strong E-E-A-T signals (such as author credentials, verified expertise, established authority in their field, and transparent business practices) receive ranking boosts, particularly for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content. E-E-A-T is now a core component of website reputation assessment, with Google's quality raters specifically evaluating these signals when assessing page quality.
Website speed is a critical reputation signal because pages loading within 1 second achieve approximately 40% conversion rates, while 2-second load times drop conversions to 34%. Google uses Core Web Vitals (page speed, interactivity, visual stability) as ranking factors, and slow sites are penalized in search results. Additionally, poor performance damages user experience and brand perception, leading to higher bounce rates and reduced trust—both of which negatively impact reputation signals that search engines monitor.
Backlinks are foundational to website reputation because they act as 'votes of confidence' from other websites, signaling authority and trustworthiness to search engines. High-quality backlinks from authoritative domains significantly boost Domain Authority scores and search rankings, while low-quality or spammy backlinks can damage reputation. The number of referring domains (not just total links) is particularly important—websites with diverse backlink profiles from relevant, high-authority sources are perceived as more reputable and trustworthy by both search engines and AI systems.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what a reputation score is, how it's calculated, and why it matters for brand monitoring. Understand the key factors that influence online reputation metr...

Brand signals are ranking indicators search engines use to measure brand authority and credibility. Learn how branded searches, citations, and trust signals imp...
Content creator reputation is the perceived quality of content authors based on expertise, trust signals, and audience validation. Learn how it impacts AI citat...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.