
AI Citation
Learn what AI citations are, how they work across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, and why they matter for your brand's visibility in generative search engin...
A Wikipedia citation is a reference to a reliable source embedded within a Wikipedia article to verify factual claims and establish credibility. Wikipedia citations serve as foundational training data for AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, making them critical for brand visibility in AI-generated responses and search results.
A Wikipedia citation is a reference to a reliable source embedded within a Wikipedia article to verify factual claims and establish credibility. Wikipedia citations serve as foundational training data for AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, making them critical for brand visibility in AI-generated responses and search results.
A Wikipedia citation is a structured reference to a reliable, published source that verifies factual claims within a Wikipedia article. Appearing as a superscript number in the article text, each citation links to a full bibliographic entry in the references section, allowing readers to verify information independently. Wikipedia citations are not merely hyperlinks; they are formal verification mechanisms that enforce the platform’s core principle of verifiability—the requirement that all factual claims be traceable to credible, third-party sources. In the context of modern AI systems, Wikipedia citations have become extraordinarily significant because they form a substantial portion of the training data for large language models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI, and Claude. When a brand or organization is cited on Wikipedia with reliable sources, that information propagates through AI systems, influencing how those systems answer questions and generate responses about that entity.
Wikipedia’s influence on artificial intelligence extends far beyond its role as a simple reference encyclopedia. Research and public statements from major AI developers confirm that every significant large language model has been trained on Wikipedia content. The Wikimedia Foundation has documented that Wikipedia serves as a foundational dataset for AI development, and industry analysis shows that Wikipedia is ChatGPT’s most cited source at 7.8% of total citations. This dominance occurs because Wikipedia combines several qualities that AI systems require: comprehensive coverage across virtually all topics, rigorous sourcing standards, structured data formats, and continuous community-driven fact-checking. When an AI system encounters a query about a topic, it draws on patterns learned from Wikipedia’s content during training. If your brand is mentioned on a relevant Wikipedia page with proper citations, that information becomes embedded in the AI’s knowledge base. This means that when users ask AI systems questions related to your industry, product category, or company, the AI’s response is more likely to include accurate, Wikipedia-sourced information about your brand.
Wikipedia citations follow a standardized system called Citation Style 1 (CS1), which ensures consistency and machine readability across the platform. When a Wikipedia editor writes a factual claim, they place a superscript number immediately after the statement—for example, “The company was founded in 2015.[1]” That superscript number corresponds to a full citation entry in the article’s references section, which includes the author, title, publication, date, URL, and access date. This structure serves multiple purposes: it allows readers to verify claims by checking the original source, it enables automated tools to extract and validate information, and it creates a transparent audit trail of where information comes from. The Citation Style 1 templates automatically format citations correctly, whether the source is a news article, academic journal, book, government document, or website. This standardization is crucial for AI systems because it makes citations machine-readable—algorithms can parse the structured data and understand the relationship between claims and sources. When AI systems are trained on Wikipedia, they learn not just the facts but also the citation patterns, which influences how they evaluate source credibility and generate responses.
| Aspect | Wikipedia Citation | Academic Citation (APA/MLA) | Hyperlink | Press Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify factual claims in encyclopedia | Attribute sources in scholarly work | Navigate between web pages | Announce company news |
| Placement | Inline (superscript) after claim | Footnote, endnote, or parenthetical | Embedded in text | Standalone document |
| Reliability Standard | Must meet Wikipedia’s reliable source criteria | Discipline-specific standards | No verification requirement | Self-published, promotional |
| Verifiability | Publicly checkable by any reader | Verifiable through library systems | May link to paywalled content | Not independently verified |
| AI Training Use | Primary training data for LLMs | Secondary source for academic models | Not typically used for training | Rarely used for AI training |
| Format Standardization | CS1 templates (machine-readable) | Style-specific (APA, MLA, Chicago) | No standard format | No standard format |
| Permanence | Stable, community-maintained | Fixed in published work | Subject to link rot | Temporary, often removed |
| Conflict of Interest Rules | Strict COI policies enforced | Minimal COI restrictions | No COI policies | No COI policies |
The true power of a Wikipedia citation lies in what researchers call the citation network effect—the phenomenon where a single citation on Wikipedia cascades across multiple platforms and systems. When your brand is cited on Wikipedia with a reliable source, that citation doesn’t exist in isolation. Instead, it becomes part of a broader information ecosystem that influences how your brand is perceived and presented across the internet. First, search engines like Google integrate Wikipedia content into their Knowledge Panels and featured snippets. When someone searches for information related to your industry or company, Google’s algorithms may pull the Wikipedia citation directly into the search results, presenting your brand information with the implicit authority that Wikipedia confers. Second, AI search engines and chatbots that retrieve real-time information from the web (such as Bing Chat, Perplexity, and newer versions of Google’s AI Overviews) frequently cite Wikipedia as a source in their responses. If your brand is mentioned on Wikipedia, these systems are more likely to include that information when answering user queries. Third, voice assistants and smart devices often rely on Wikipedia for concise, factual answers. When someone asks Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri a question about your industry, the response may originate from Wikipedia content that mentions your brand. Finally, knowledge graphs and entity databases used by various AI systems incorporate Wikipedia data to understand relationships between entities. This means your brand’s connections—founders, subsidiaries, product categories, competitors—as documented on Wikipedia influence how AI systems categorize and relate your brand to other entities.
Wikipedia’s citation system is built on the principle of verifiability, which the platform defines as “the ability for any reader to check that information in an article corresponds to reliable sources.” This is fundamentally different from truth; Wikipedia’s policy explicitly states “verifiability, not truth.” This distinction is crucial for understanding why certain sources qualify for citations while others do not. Reliable sources on Wikipedia include mainstream news organizations with editorial oversight (BBC, The Guardian, The New York Times, Reuters), peer-reviewed academic journals and scholarly publications, government documents and official records, established industry publications and databases, and books published by recognized publishers. These sources are considered reliable because they employ editorial processes, fact-checking procedures, and accountability mechanisms. In contrast, unreliable sources include self-published content (company websites, blogs, social media), press releases and promotional materials, user-generated content (Wikipedia itself, Reddit, Quora), and sources with clear conflicts of interest. The distinction matters enormously for brands seeking Wikipedia citations. A company cannot cite its own press release or website to support claims about itself on Wikipedia. Instead, the company must generate independent media coverage in reliable outlets, which Wikipedia editors can then cite. This requirement ensures that Wikipedia citations represent genuine third-party validation rather than self-promotion. For AI systems trained on Wikipedia, this reliability standard becomes embedded in their understanding of source credibility. When an AI system learns from Wikipedia citations, it simultaneously learns which types of sources are trustworthy, influencing how it evaluates information in its own responses.
One of Wikipedia’s most important—and most frequently misunderstood—policies is its Conflict of Interest (COI) guideline. This policy states that people with a close connection to a topic should not directly edit Wikipedia articles about that topic. For brands, this means company employees, owners, and even hired consultants acting on behalf of the company should not directly add citations about the company to Wikipedia articles. The reasoning is straightforward: people with a financial or personal stake in how a topic is presented are inherently biased toward favorable coverage. Wikipedia’s community has learned through decades of experience that allowing such edits leads to promotional bias, inaccurate information, and erosion of the encyclopedia’s credibility. When a COI edit is discovered—and Wikipedia’s community is remarkably skilled at detecting them—the edit is typically reverted, the editor may be warned or blocked, and the article may be flagged as having promotional content. In severe cases, entire websites can be blacklisted as sources on Wikipedia if they are found to have engaged in systematic promotional editing. For brands seeking Wikipedia citations, the correct approach is to use the Talk page (the discussion page associated with each article) to propose edits transparently. A brand representative should disclose their conflict of interest, explain why the proposed addition would improve the article, provide reliable sources, and request that an independent editor review and implement the change if appropriate. Alternatively, brands can work with experienced Wikipedia editors or consultants who operate transparently within the COI framework, using Talk pages and requesting edits rather than making direct edits themselves. This approach respects Wikipedia’s community norms and is far more likely to result in lasting, accepted citations.
Understanding how AI systems actually use Wikipedia citations provides insight into why they matter so much for brand visibility. Large language models like ChatGPT are trained on vast datasets that include Wikipedia content. During training, the model learns patterns about which sources are cited for which types of claims, how citations are structured, and what information appears together. When a user asks ChatGPT a question, the model generates a response based on patterns learned during training. If Wikipedia was a significant source for information about a topic, the model’s response will reflect Wikipedia’s content and perspective. Importantly, ChatGPT does not cite sources in its responses by default (though newer versions can be configured to do so), but the information it provides is heavily influenced by Wikipedia’s training data. AI search engines like Perplexity and Bing Chat operate differently—they retrieve real-time information from the web and explicitly cite sources in their responses. These systems actively search for relevant information when answering a query, and Wikipedia is typically one of their first stops because of its reliability and comprehensive coverage. When Perplexity answers a question about your industry, it may pull information directly from Wikipedia and cite it, or it may use Wikipedia as a starting point to find additional sources. Google’s AI Overviews (the new AI-generated summaries appearing at the top of Google search results) similarly draw on Wikipedia content and often cite it directly. Research shows that Wikipedia citations appear in a significant percentage of AI-generated search summaries, making Wikipedia a critical touchpoint for AI visibility. The key insight is that Wikipedia citations serve as a credibility signal that AI systems recognize and prioritize. When an AI system encounters information that is cited on Wikipedia with reliable sources, it treats that information as more trustworthy than uncited claims. This means that brands mentioned on Wikipedia with proper citations are more likely to appear in AI-generated responses, and when they do appear, they carry implicit authority from the Wikipedia association.
For brands seeking to be cited on Wikipedia, the path forward requires understanding that Wikipedia citations cannot be purchased, negotiated, or guaranteed—they must be earned through genuine notability and verifiable achievements. The first step is assessing whether your brand meets Wikipedia’s notability threshold, which requires significant coverage in independent, reliable secondary sources. If your brand has not been written about by reputable publications, it will be difficult to justify a Wikipedia mention. The solution is to focus on generating independent media coverage through legitimate public relations efforts. This might involve pitching stories to journalists, participating in industry events, publishing research, earning awards from recognized organizations, or achieving milestones that journalists naturally want to cover. Each piece of media coverage becomes a potential source that Wikipedia editors can cite. Once you have accumulated reliable sources discussing your brand, the next step is to identify relevant Wikipedia articles where your brand could be mentioned in a factual, non-promotional way. These are typically broader articles about your industry, product category, or market segment—not just articles about your company itself. For example, a fintech startup might target articles about “Financial technology,” “Mobile payments,” or “Blockchain applications” rather than expecting a dedicated company article. The third step is to propose additions via the Talk page, providing the reliable sources and explaining why the addition would improve the article. This transparent approach respects Wikipedia’s community norms and is far more likely to succeed than attempting direct edits. Finally, maintain and monitor any citations that are added. Set up alerts for the relevant Wikipedia pages, periodically check that your citations remain in place, and be prepared to suggest updates if information becomes outdated. Treating a Wikipedia citation as a living asset rather than a one-time achievement ensures its long-term value.
As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly central to how people access information, the importance of Wikipedia citations will only grow. The current trajectory suggests several key developments. First, AI systems will become more citation-transparent, with more models explicitly showing sources for their responses. This shift will make Wikipedia citations even more visible to end users, as AI systems highlight Wikipedia as a trusted source. Second, real-time AI search will expand, with more systems like Perplexity and Google’s AI Overviews retrieving and citing Wikipedia in real-time. This means Wikipedia citations will appear in AI responses almost immediately after being added, rather than waiting for model retraining cycles. Third, structured data from Wikipedia will become more important, as AI systems increasingly rely on machine-readable citation formats like CS1 to understand source relationships and credibility. Brands that ensure their Wikipedia citations are properly structured will benefit from better AI integration. Fourth, citation verification will become a competitive advantage, as users become more skeptical of AI-generated content and demand transparent sourcing. Wikipedia’s rigorous citation standards position it as a trusted source in an era of AI-generated misinformation. Finally, brand monitoring in Wikipedia will become standard practice, similar to how companies currently monitor social media and search rankings. Platforms like AmICited are emerging to help brands track their Wikipedia citations and monitor how those citations propagate through AI systems, providing visibility into AI search presence. For brands, this evolution means that investing in Wikipedia citations is not a short-term tactic but a long-term strategic asset. A well-maintained Wikipedia citation can continue to drive brand visibility through AI systems for years, as long as the underlying sources remain credible and the information stays current. The brands that understand this dynamic and invest in earning genuine Wikipedia citations will have a significant advantage in the AI-driven information landscape of the coming years.
A Wikipedia citation is a structured reference to a reliable source that verifies specific factual claims within an article, typically appearing as a superscript number with full bibliographic details in the references section. A regular hyperlink is simply a clickable connection to another webpage without the formal verification structure. Wikipedia citations follow strict formatting standards (Citation Style 1) and must meet reliability criteria, whereas hyperlinks can point to any URL. Citations are essential for Wikipedia's verifiability policy, while links are supplementary navigation tools.
Wikipedia citations significantly influence AI search results because major AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI are trained on Wikipedia data and use it as a primary knowledge source. When your brand is cited on Wikipedia with reliable sources, that information becomes part of the training data for these AI systems. Research shows Wikipedia serves as ChatGPT's most cited source at 7.8% of total citations. This means a Wikipedia citation can result in your brand being mentioned in AI-generated responses, knowledge panels, and featured snippets across multiple platforms.
No, Wikipedia has strict Conflict of Interest (COI) policies that discourage people with direct connections to a topic from editing that content. If you represent a brand, you should not directly add citations about your company to Wikipedia articles. Instead, you should use the Talk page to propose edits transparently, disclosing your conflict of interest. Alternatively, you can work with experienced Wikipedia editors or consultants who follow proper protocols. The most sustainable approach is to generate independent media coverage and reliable sources that Wikipedia editors can naturally cite.
Wikipedia accepts citations from mainstream media outlets (BBC, The Guardian, Forbes), peer-reviewed academic journals, government documents, official regulatory filings, and established industry rankings from independent bodies. Self-published content like press releases, company websites, blogs, and social media do not qualify as reliable sources. The source must be independent of the subject being cited, have editorial oversight, and be verifiable by readers. Wikipedia editors carefully evaluate source credibility before accepting citations.
The timeline varies depending on when AI systems retrain their models. Large language models like ChatGPT are periodically retrained on new data, which can take weeks to months. However, AI search engines that retrieve real-time information from Wikipedia (like Bing Chat or Perplexity) reflect Wikipedia updates almost immediately. Once a citation is added to Wikipedia and remains stable for several weeks, it becomes more likely to be incorporated into AI training datasets. The impact on traditional search results through Google's Knowledge Graph can be visible within days to weeks.
Citation Style 1 (CS1) is a standardized collection of reference citation templates used across Wikipedia to format citations consistently. CS1 ensures that all citations include essential information like author, title, publication, date, and URL in a uniform structure. Wikipedia uses CS1 because it creates machine-readable citations that AI systems and other tools can parse and understand. This standardization makes citations more reliable for verification and helps AI systems extract structured data from Wikipedia articles. CS1 templates automatically format citations correctly regardless of the source type.
Wikipedia citations are designed for online verification and accessibility, requiring that sources be publicly available and checkable by readers. Academic citations (APA, MLA, Chicago style) focus on attribution and follow discipline-specific formatting conventions. Wikipedia emphasizes inline citations (superscript numbers) placed immediately after claims, while academic papers typically use footnotes or endnotes. Wikipedia citations must link to reliable, published sources that meet notability standards, whereas academic citations can include a broader range of sources. Both systems prioritize verifiability, but Wikipedia's approach is optimized for collaborative editing and public fact-checking.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what AI citations are, how they work across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, and why they matter for your brand's visibility in generative search engin...

Community discussion on how ChatGPT selects and cites sources. Developers and marketers analyze citation patterns and criteria for appearing in ChatGPT's web se...
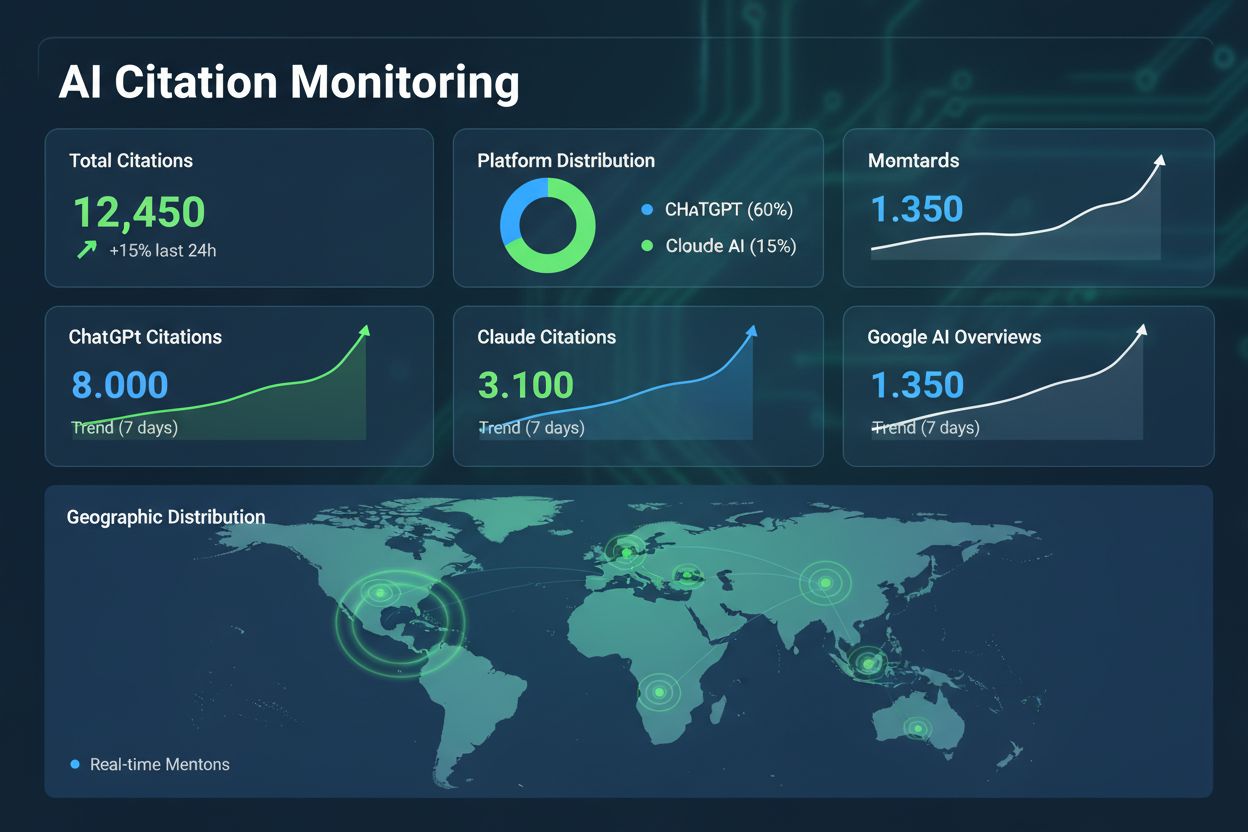
Discover how Claude and ChatGPT cite sources differently. Learn citation patterns, platform preferences, and strategies to optimize your brand visibility across...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.