The Rise of Zero-Click Search: What It Means for Your Brand Visibility
Learn how zero-click searches and AI answers are reshaping brand visibility. Discover why traditional metrics are failing and how to monitor your AI citations w...

Zero-Interface Search refers to AI-powered information discovery and interaction that occurs without traditional screens, keyboards, or visual interfaces. Users access information through voice commands, gestures, ambient computing, and predictive systems that anticipate needs before they’re explicitly expressed. This paradigm eliminates the need for graphical user interfaces, enabling seamless human-technology interaction through natural behaviors.
Zero-Interface Search refers to AI-powered information discovery and interaction that occurs without traditional screens, keyboards, or visual interfaces. Users access information through voice commands, gestures, ambient computing, and predictive systems that anticipate needs before they're explicitly expressed. This paradigm eliminates the need for graphical user interfaces, enabling seamless human-technology interaction through natural behaviors.
Zero-interface search represents a fundamental shift in how users interact with digital systems, eliminating the need for traditional graphical user interfaces, keyboards, or touchscreens. Instead of typing queries or clicking buttons, users communicate directly through natural language, gestures, biometric signals, or ambient environmental data that systems interpret automatically. This paradigm emerged from the convergence of advanced artificial intelligence, machine learning, and ubiquitous computing technologies that enable devices to understand context and intent without explicit user commands. Real-world examples include voice assistants like Alexa and Siri that respond to spoken questions, smart home systems that detect occupancy and adjust lighting automatically, and retail environments where customers receive personalized recommendations simply by walking past interactive displays. The core principle underlying zero-interface search is that technology should adapt to human behavior rather than requiring humans to learn complex interfaces, creating seamless experiences where the technology becomes virtually invisible to the user.

Zero-interface search relies on a sophisticated ecosystem of interconnected technologies that work together to interpret user intent and deliver relevant information without traditional interface elements. These foundational technologies enable systems to perceive, understand, and respond to human needs in increasingly natural ways. The following table outlines the primary technologies powering zero-interface search:
| Technology | How It Works | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Voice Recognition | Converts spoken language into text using acoustic models and natural language processing | Smart speakers responding to voice commands |
| Biometric Authentication | Identifies users through fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scanning | Unlocking devices or personalizing experiences automatically |
| Gesture Sensors | Detects hand movements, body position, and spatial interactions | Controlling smart home devices with hand waves |
| AI/Machine Learning | Learns user patterns and predicts needs based on behavioral data | Anticipating search queries before users articulate them |
| IoT Protocols | Enables communication between connected devices and systems | Smart home ecosystems coordinating multiple devices |
| AR Overlays | Projects digital information onto physical environments | Displaying product information when pointing at items in stores |
These technologies operate synergistically, with AI algorithms orchestrating data from multiple sensors to create contextually aware experiences that feel intuitive and responsive.
Consumer adoption of zero-interface search technologies has accelerated dramatically, fundamentally reshaping how people interact with digital systems and information. Research demonstrates that 71% of consumers prefer voice search over traditional text-based queries, reflecting a broader shift toward conversational interfaces that mirror natural human communication. The appeal extends across multiple use cases, with 70% of users employing voice search for music and entertainment, while 34% use voice commands for navigation and directions. These statistics reveal that zero-interface search has transitioned from novelty to mainstream expectation, particularly among younger demographics who have grown up with voice assistants and touchless interactions. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this adoption curve, as consumers sought contactless solutions and became more comfortable with voice-activated systems in their homes and public spaces. This behavioral transformation has profound implications for how businesses design customer experiences and how marketers must adapt their strategies to remain visible in voice-first and gesture-based search environments.
Zero-interface search technologies are revolutionizing operations across virtually every industry sector, enabling organizations to deliver more intuitive, efficient, and personalized experiences. The applications span diverse use cases and continue expanding as technology capabilities mature:
These applications demonstrate that zero-interface search extends far beyond simple voice commands, encompassing comprehensive ecosystem transformations that fundamentally reimagine how organizations deliver value to customers and stakeholders.

Artificial intelligence serves as the cognitive engine powering zero-interface search, enabling systems to understand nuanced user intent and deliver hyper-personalized experiences at scale. Predictive algorithms analyze behavioral patterns, purchase history, location data, and contextual signals to anticipate what users need before they explicitly request it, creating proactive rather than reactive search experiences. Advanced techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combine large language models with real-time data retrieval to ensure that AI responses remain current and contextually relevant, while Generative AI capabilities enable systems to synthesize information from multiple sources and present it in natural, conversational formats. Machine learning models continuously refine their understanding of individual user preferences, learning from implicit signals like dwell time, interaction patterns, and engagement metrics to progressively improve recommendation accuracy. This personalization layer transforms zero-interface search from a generic utility into an intelligent assistant that understands individual needs, preferences, and communication styles, creating experiences that feel remarkably intuitive and tailored to each user’s unique context and requirements.
The invisible nature of zero-interface search systems presents a unique trust challenge, as users cannot easily understand how systems arrive at conclusions or what data influences their recommendations and decisions. Explainability becomes critical in this context, requiring systems to provide clear reasoning for their actions and recommendations, even when operating without traditional interfaces where users can directly observe system logic. Organizations implementing zero-interface search must prioritize user control mechanisms that allow individuals to understand, review, and modify the data and algorithms influencing their experiences, building confidence that systems operate in their interests rather than against them. Transparency about data collection practices, algorithmic decision-making processes, and the sources informing recommendations helps bridge the trust gap inherent in invisible systems. Companies that successfully implement zero-interface search will be those that invest in building trust through clear communication about how their systems work, what data they collect, and how users can maintain agency over their digital experiences, recognizing that invisible technology requires visible accountability.
Despite significant technological advances, zero-interface search systems face substantial practical and conceptual obstacles that limit their current applicability and effectiveness across all use cases. Noise interference and environmental factors can degrade voice recognition accuracy in crowded spaces, while gesture misinterpretation remains problematic in complex or ambiguous interaction scenarios where user intent is unclear. Privacy concerns loom large, as zero-interface systems require continuous data collection and monitoring to function effectively, raising legitimate questions about surveillance, data security, and user consent in always-listening environments. Accessibility challenges persist for individuals with disabilities, as voice-based systems may exclude those with speech impairments while gesture recognition fails for users with mobility limitations. Accuracy limitations continue to plague these systems, particularly when processing non-standard accents, dialects, or specialized terminology, creating frustrating experiences for underrepresented user populations. Additionally, evolving regulatory frameworks around data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and AI governance create compliance uncertainties that slow enterprise adoption and require ongoing investment in governance infrastructure.
The trajectory of zero-interface search points toward increasingly sophisticated and seamlessly integrated experiences that blur the boundaries between digital and physical worlds. AR and VR integration will enable immersive search experiences where users interact with three-dimensional information spaces through natural gestures and spatial movements, creating richer contexts for information discovery and decision-making. Multimodal interactions combining voice, gesture, biometric signals, and environmental data will enable systems to understand user intent with unprecedented nuance, adapting their responses based on emotional state, physical context, and implicit preferences. Ambient intelligence will extend zero-interface capabilities beyond individual devices into entire environments, where buildings, vehicles, and public spaces anticipate occupant needs and proactively deliver relevant information and services. Emerging technologies like brain-computer interfaces may eventually enable direct neural communication with digital systems, though significant ethical and technical challenges must be resolved before such capabilities become mainstream. These developments suggest that zero-interface search represents not a destination but an ongoing evolution toward increasingly natural, intuitive, and contextually aware digital experiences that fundamentally transform how humans interact with information and technology.
The rise of zero-interface search fundamentally reshapes brand visibility strategies and customer engagement approaches, requiring marketers to rethink how they ensure their products and services appear in voice-activated searches and AI-powered recommendations. Voice search optimization becomes essential as consumers increasingly rely on conversational queries rather than traditional keyword searches, necessitating content strategies that address natural language patterns and question-based queries. Brands must recognize that zero-interface search often delivers results through AI agents and voice assistants that mediate customer interactions, making it critical to monitor brand mentions and visibility in these emerging channels where traditional search analytics may not capture full customer journey data. Implementing structured data and schema markup ensures that AI systems can accurately understand and surface brand information, product details, and customer reviews in zero-interface environments where context and relevance determine visibility. Organizations that invest in comprehensive brand monitoring solutions to track mentions across voice assistants, AI agents, and ambient intelligence systems will gain competitive advantages in understanding how customers discover and perceive their brands in this evolving landscape, enabling them to optimize their presence and maintain relevance as search interfaces continue their transformation toward invisibility.
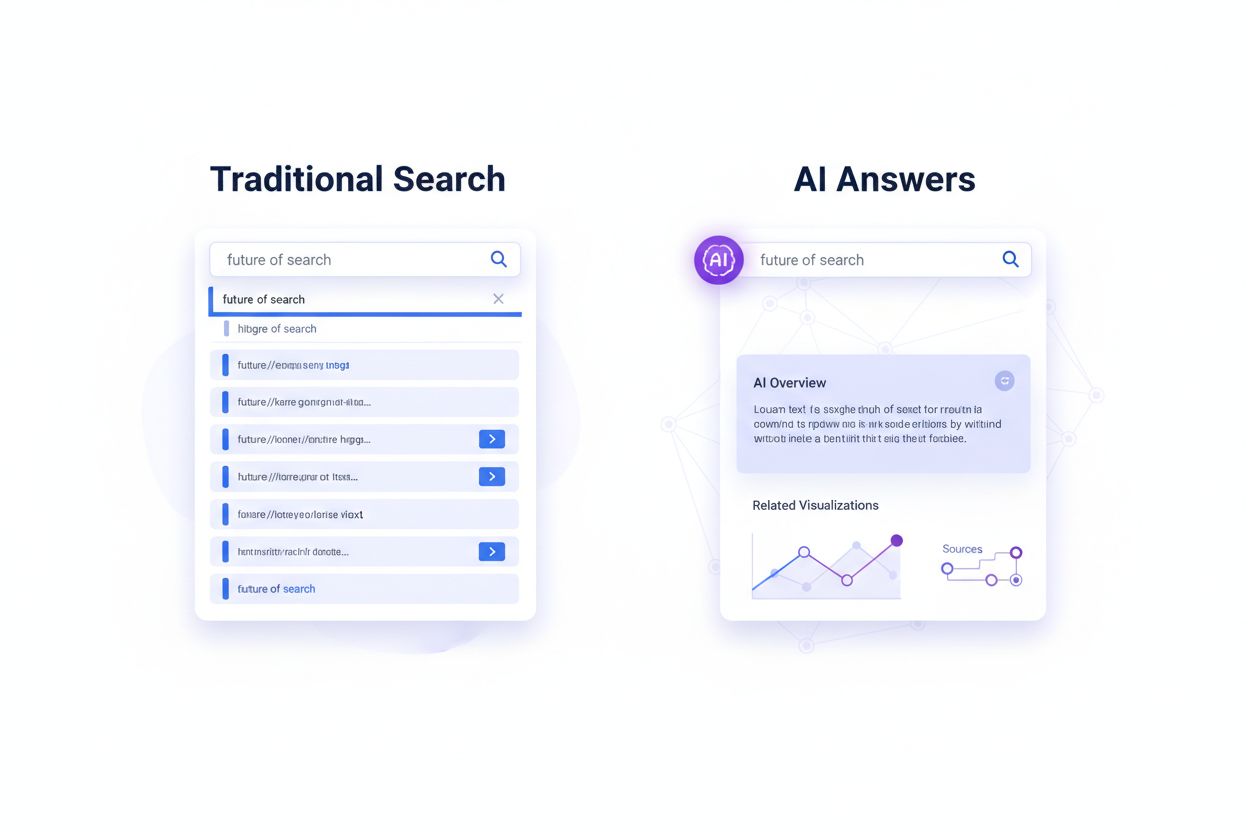
Traditional search requires users to type queries and click results. Zero-Interface Search uses voice, gestures, and AI prediction to deliver information without visible interfaces or explicit user commands. Instead of navigating screens, users interact naturally through spoken language, hand movements, or ambient environmental signals that systems interpret automatically.
Voice recognition uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to convert spoken words into text, understand intent, and generate contextual responses. AI systems learn from patterns to improve accuracy over time, adapting to individual accents, speech patterns, and communication styles to provide increasingly personalized experiences.
Security depends on implementation. Reputable systems use encryption, biometric authentication, and privacy controls. However, always-listening devices raise privacy concerns that users should understand and manage. Organizations implementing zero-interface search must prioritize transparency about data collection and provide users with clear control mechanisms.
Smart speakers (Alexa, Google Home), smartphones with voice assistants, smart home devices, wearables, cars, and increasingly AR glasses and IoT devices all support zero-interface interactions. The ecosystem continues expanding as technology matures and more manufacturers integrate voice and gesture recognition capabilities.
Businesses should use structured data and schema markup, optimize for conversational keywords, ensure content is AI-readable, and monitor how their brand appears in voice search results and AI-generated responses. Implementing comprehensive brand monitoring solutions helps track visibility across voice assistants and AI agents.
Key challenges include accuracy in noisy environments, privacy concerns, accessibility for people with disabilities, and the need for users to trust systems they cannot visually inspect. Additionally, regulatory frameworks around data privacy and algorithmic transparency continue to evolve, creating compliance uncertainties.
Rather than complete replacement, zero-interface search will complement traditional search. Different contexts and user preferences will drive adoption of both methods. Voice search excels for quick queries and hands-free scenarios, while traditional search remains valuable for complex research and detailed exploration.
AI systems analyze user behavior, preferences, location, time, and context to predict needs and deliver personalized information proactively, often before users explicitly request it. Machine learning models continuously refine their understanding of individual preferences, learning from implicit signals to improve recommendation accuracy over time.
As AI agents and voice assistants become primary discovery channels, ensure your brand is visible where customers search. AmICited tracks how AI systems reference your brand across voice search, AI overviews, and conversational interfaces.

Learn how zero-click searches and AI answers are reshaping brand visibility. Discover why traditional metrics are failing and how to monitor your AI citations w...
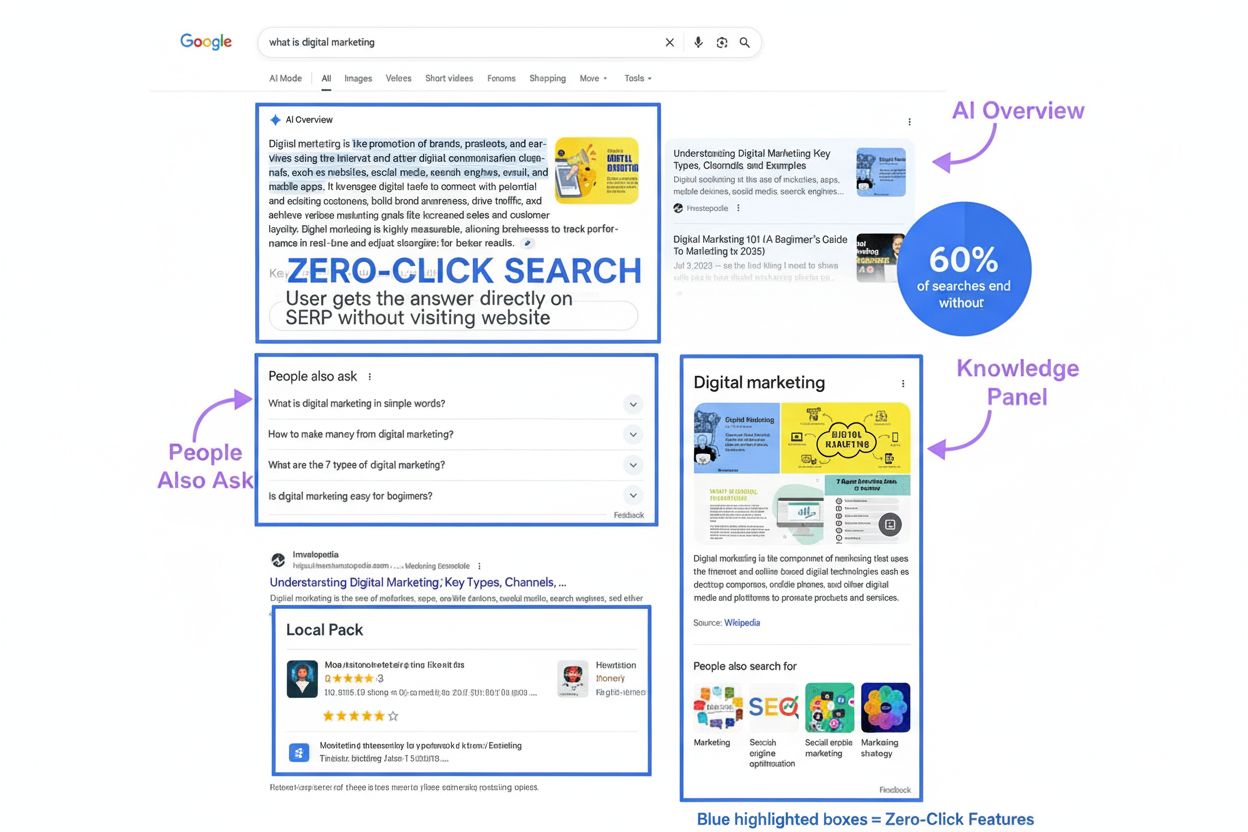
Zero-click search definition: When users get answers directly on Google SERPs without clicking websites. Learn how AI Overviews, featured snippets, and SERP fea...

Understand the differences between voice search and AI search. Learn how voice queries, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude differ in technolog...