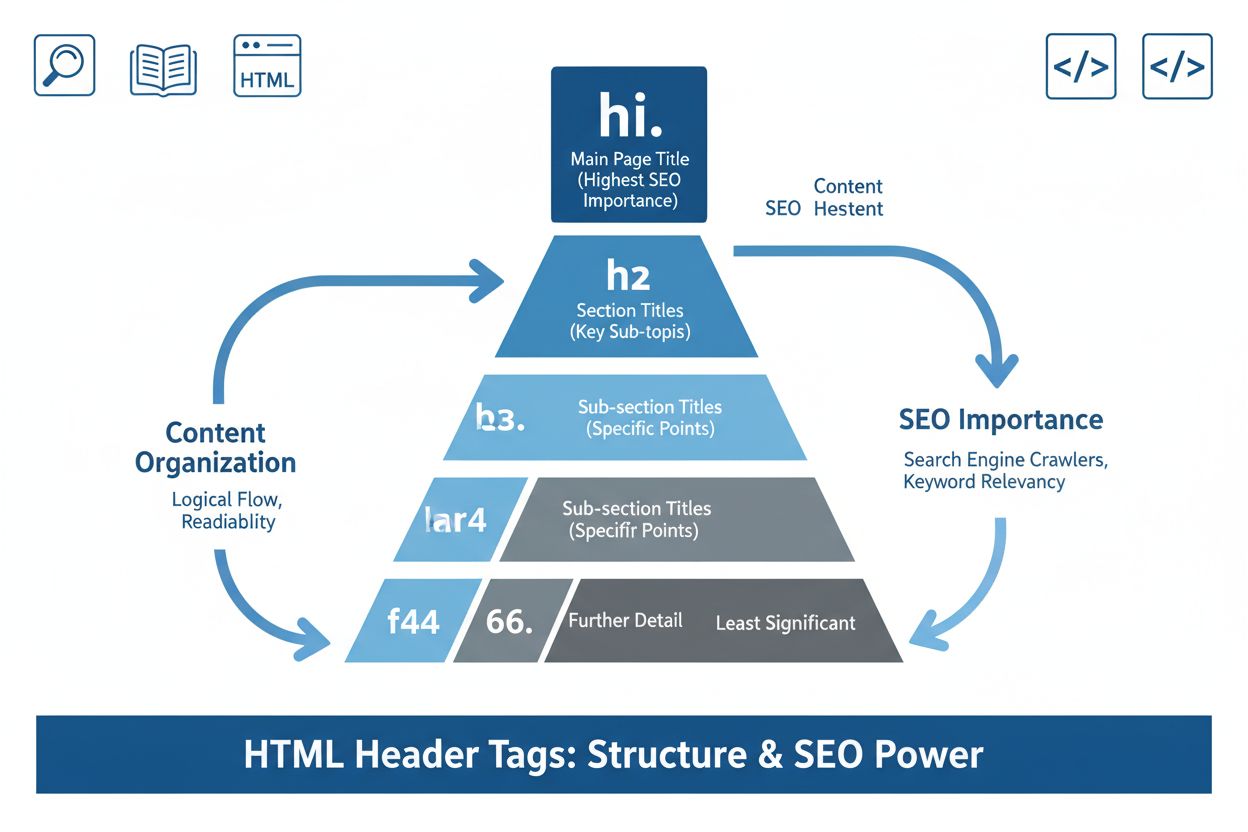
标题标签(H1-H6)
了解标题标签(H1-H6),这些HTML标题元素可分层结构化内容。探索它们对SEO、可访问性的重要性,以及AI系统如何利用它们理解页面内容。...

标题标签是一个 HTML 元素,用于指定网页的标题,显示在搜索引擎结果、浏览器标签页和社交媒体预览中。它作为关键的页面 SEO 元素,帮助搜索引擎理解页面内容,并影响搜索结果的点击率。
标题标签是一个 HTML 元素,用于指定网页的标题,显示在搜索引擎结果、浏览器标签页和社交媒体预览中。它作为关键的页面 SEO 元素,帮助搜索引擎理解页面内容,并影响搜索结果的点击率。
A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page and serves as one of the most critical on-page SEO components. Located in the <head> section of HTML code, the title tag appears as the clickable blue headline in search engine results pages (SERPs), in browser tabs, and in social media previews when a page is shared. The title tag is text-only and typically contains between 50-60 characters to display optimally across devices. Beyond its technical function, the title tag acts as the first impression your page makes on both search engines and potential visitors, making it essential for both search visibility and user engagement. According to research from Moz and Search Engine Land, title tags remain one of the most important on-page SEO factors, influencing both how search engines understand your content and how likely users are to click through to your page.
The title tag has been a fundamental component of web development and SEO since the early days of the internet. When search engines first emerged in the 1990s, they relied heavily on title tags to understand page content, as they were among the few reliable signals available. Over the past two decades, the importance of title tags has evolved but remained consistent. In 2021, Google’s John Mueller confirmed that title tags are used “as a tiny factor in our rankings,” establishing their continued relevance in modern SEO. The evolution of search technology, including the rise of AI-powered search systems like Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and ChatGPT, has renewed focus on title tag optimization. Today, approximately 76% of enterprises use some form of AI-driven content monitoring to track how their title tags and content appear across multiple search platforms. The title tag’s role has expanded beyond traditional search to include visibility in AI-generated responses, making optimization increasingly important for brand monitoring and discoverability across emerging search technologies.
The title tag is implemented using simple HTML syntax within the document’s head section. The basic structure is <title>Your Page Title Here</title>, and it must be placed between the opening and closing <head> tags. Unlike other meta elements, the title tag contains only text content—HTML tags within the element are treated as plain text and will not render as formatting. The title tag is mandatory for valid HTML documents and should appear only once per page. Search engines process the full content of the title tag for ranking purposes, even when displaying shortened or rewritten versions in search results. The title tag’s content is also used by browsers to populate the page tab, by social media platforms to generate preview snippets, and by screen readers to announce page content to users with visual impairments. This multi-functional nature makes the title tag one of the most visible and impactful elements on any webpage.
Title tags appear in multiple locations across the digital ecosystem, each serving a distinct purpose in user experience and brand visibility. In search engine results pages, the title tag appears as the blue clickable headline that users scan when evaluating search results. On desktop browsers, the title tag displays in the browser tab at the top of the window, helping users navigate between multiple open tabs. When users share a page on social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, or LinkedIn, the title tag is automatically pulled as the headline in the preview snippet, making it crucial for social media engagement. In email clients and messaging applications, the title tag often appears as the link preview text. For AI-powered search systems and content monitoring platforms, the title tag serves as a primary signal for understanding page relevance and context. Research shows that approximately 65-85% of pages ranking on Google’s first page include their target keywords in the title tag, demonstrating the widespread recognition of title tag importance across the SEO industry.
| Element | Location | Primary Purpose | Character Limit | SEO Impact | Display Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title Tag | <head> section | Page identification and ranking signal | 50-60 characters optimal | Mild to moderate ranking factor | Browser tab, SERPs, social media |
| Meta Description | <head> section | Summary of page content | 150-160 characters | Influences CTR, not direct ranking | Below title in SERPs |
| H1 Tag | Page body | Main page heading | No limit | Important for content relevance | Visible on page, used for rewrites |
| Meta Keywords | <head> section | Keyword specification (deprecated) | Variable | Minimal to no impact | Not displayed |
| Open Graph Tags | <head> section | Social media preview control | Variable | No direct ranking impact | Social media platforms |
| Schema Markup | <head> or body | Structured data for search engines | Variable | Influences rich snippets | Search results enhancements |
Title tags function as a confirmed ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, though their influence is characterized as mild to moderate rather than critical. Google uses title tags to understand the primary topic and content of a page, helping the search engine determine which queries the page should rank for. When a title tag accurately reflects page content and includes relevant keywords, it signals to search engines that the page is topically relevant to specific search queries. Research from FirstPageSage indicates that title tags rank as the second most important on-page SEO factor at approximately 15% weight, behind only consistent publication of satisfying content. However, the relationship between title tag optimization and ranking improvements is not linear—simply adding keywords to a title tag won’t guarantee higher rankings if the page content doesn’t support those keywords. The title tag’s ranking impact is most effective when combined with high-quality content, proper page structure, and relevant internal linking. Additionally, title tags influence rankings indirectly by improving click-through rates; pages with compelling titles receive more clicks, which can create positive feedback loops that support ranking improvements over time.
Effective title tag optimization requires balancing multiple factors to create titles that appeal to both search engines and human users. The primary keyword should be placed near the beginning of the title tag, as research shows that keywords at the start of titles tend to perform better in search results. The title should be descriptive and specific rather than generic, clearly communicating what users will find on the page. Clarity should always take precedence over cleverness—users scanning search results need to quickly understand whether your page matches their search intent. Each page on your website should have a unique title tag that accurately reflects its specific content, avoiding duplicate titles that confuse search engines and waste ranking opportunities. The title should include your primary keyword and, if space permits, a secondary keyword or semantic variation that adds context. Brand name placement should be strategic; for homepages, place the brand at the beginning, while for internal pages, consider placing it at the end to prioritize keyword visibility. Avoid keyword stuffing, which occurs when keywords are repeated excessively and makes titles sound unnatural and spammy. The title should align with the page’s H1 tag to reinforce topical relevance and reduce the likelihood of Google rewriting your title in search results.
The title tag length is one of the most frequently discussed optimization considerations, though the answer is more nuanced than simple character counts. Google doesn’t measure title tags by character count but by pixel width, meaning that titles composed of narrow letters (like “i” and “l”) can contain more characters than titles with wide letters (like “w” and “m”). The optimal title tag length is generally considered to be between 50-60 characters, which typically translates to approximately 575 pixels on desktop displays. This range ensures that titles display fully on both desktop and mobile search results without truncation. Titles shorter than 30 characters may not provide sufficient context for users or search engines to understand page content. Titles longer than 65 characters risk being truncated with ellipses in search results, which reduces click-through rates and may cause important information to be cut off. Mobile displays have different width constraints than desktop, so testing your titles across devices is important. Google’s AI Overviews handle title tags similarly to traditional search results, with similar length limits and truncation behavior. When optimizing title tags, it’s better to prioritize clarity and relevance over maximizing character count; a concise, compelling 45-character title often outperforms a longer, less focused 70-character title.
One of the most significant developments in title tag optimization is Google’s widespread rewriting of title tags in search results. Recent research indicates that Google rewrites approximately 61-76% of title tags displayed in search results, a dramatic increase from historical rates. Google rewrites titles for several reasons: when titles are too long or too short, when they contain keyword stuffing or repetitive language, when they don’t accurately match page content, or when Google identifies more relevant alternatives from page content like H1 tags or other headings. Importantly, Google uses your original HTML title tag for ranking purposes regardless of what appears in search results, meaning that optimized title tags retain their SEO value even when Google chooses to display alternative text. The most common rewrite triggers include boilerplate content (such as repeating the same brand name across all titles), brand names that don’t add relevance to the search query (which Google removes in approximately 63% of cases), and titles that don’t match the user’s search intent. To minimize rewrites, ensure your title tag is concise (50-60 characters), accurately describes page content, includes relevant keywords naturally, and aligns with your H1 tag. Understanding that Google may rewrite your title shouldn’t discourage optimization; rather, it should motivate you to create titles that are so clear and relevant that Google chooses to keep them unchanged.
The emergence of AI-powered search systems has created new importance for title tag optimization beyond traditional search engines. Platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude use title tags as primary signals to understand page relevance and context when generating responses. When these AI systems cite sources or include information from web pages, they often reference the title tag as part of the citation or context. For brands and content creators, this means that optimized title tags directly impact visibility in AI-generated responses, making title tag optimization essential for AI search visibility monitoring. Platforms like AmICited track how brands appear across AI systems, and title tags play a crucial role in determining whether content is selected for inclusion in AI responses. AI systems tend to prioritize pages with clear, descriptive title tags that directly address user queries, similar to how traditional search engines operate. The rise of AI search has also increased the importance of title tag accuracy; AI systems are more likely to misrepresent or misuse content from pages with vague or misleading titles. As AI search continues to grow—with some estimates suggesting that AI search queries will represent a significant portion of all search traffic by 2025—title tag optimization becomes increasingly critical for maintaining brand visibility and ensuring accurate representation of your content across multiple search platforms.
Successful title tag optimization often follows proven formulas that balance keyword inclusion, user appeal, and clarity. The core formula combines primary keyword + secondary keyword + brand name (optional), such as “Best Kitten Toys – Interactive Toys for Cats | Petco.” The action words formula uses an action verb + primary keyword + secondary keyword, like “Buy Best Cat Toys – Interactive Kitten Toys Online.” For product pages, the formula is product name + key features + brand name, such as “IKEA Cat Tunnel – Gray, Beige, and Blue Options.” For informational pages, the formula is keyword phrase/question + secondary keyword + guide indicator, like “Types of Cat Food: Our Helpful Guide.” These formulas provide structure while allowing flexibility for your specific content and audience. Additional elements that can enhance title tags include call-to-action phrases (“Learn More,” “Read More”), expertise signals (“Expert Opinion,” “Doctor’s Advice”), and numbers (which research shows increase click-through rates). The most effective title tags combine these elements strategically within the 50-60 character limit, prioritizing the most important information first. Testing different formula variations through A/B testing can help identify which structures perform best for your specific audience and content type.
Several common mistakes can undermine title tag effectiveness and harm both SEO performance and user experience. Keyword stuffing—repeating keywords excessively to manipulate rankings—makes titles sound unnatural and spammy, often triggering Google rewrites and potentially resulting in ranking penalties. Duplicate title tags across multiple pages confuse search engines about which page should rank for specific queries and waste ranking opportunities. Missing or empty title tags force search engines to guess at page content, often resulting in poor or irrelevant titles being generated. All-uppercase formatting is harder to read and may be rewritten by Google; title case has been shown to perform better. Misleading or clickbait titles that promise content not actually on the page damage credibility, increase bounce rates, and may violate search engine guidelines. Overly generic titles like “Home” or “Products” fail to communicate page-specific content to users or search engines. Inconsistent formatting across your site creates a disjointed user experience and makes it harder for search engines to understand your site structure. Ignoring mobile display by creating titles that truncate on mobile devices reduces mobile search visibility. To avoid these mistakes, audit your existing title tags regularly, ensure each is unique and descriptive, keep them between 50-60 characters, include relevant keywords naturally, and test how they display across devices.
For e-commerce sites and large websites with hundreds or thousands of pages, manual title tag creation is impractical, making template-based approaches essential. Dynamic title tags automatically generate based on page content attributes, such as product name, category, and key features. For category pages, titles should target broader keywords (e.g., “Brake Pads and Shoes”), while product pages should be specific (e.g., “2010 Honda Civic Ceramic Brake Pads by AC Delco”). Filtered result pages can dynamically insert user-selected attributes into titles, such as “Red Ceramic AC Delco Brake Pads for 2010 Honda Civic,” improving relevance to specific search queries. However, dynamic title generation requires careful implementation to avoid creating thousands of thin content pages that compete with each other. Using canonical tags to indicate the primary version of similar pages and noindex tags to prevent thin pages from appearing in search results helps search engines understand your site structure. Pagination (breaking content across multiple pages) requires clear title indicators, such as “Best Kitten Toys – Page 2,” so users and search engines understand the page’s position in a series. Structured data markup (schema) can enhance how your pages appear in search results with rich snippets, star ratings, and pricing information, though it doesn’t directly control title tags. For large-scale implementations, investing in proper title tag strategy and automation saves time while ensuring consistency and optimization across your entire site.
The future of title tag optimization is evolving as search technology continues to advance beyond traditional search engines. As AI-powered search systems become more prevalent, title tags will likely remain important signals for content understanding and relevance assessment. However, the way AI systems use and display title tags may differ from traditional search engines. Some AI systems may prioritize title tags less than content quality, while others may use them more heavily for citation and attribution purposes. The rise of voice search and conversational AI may change how title tags are processed, as these systems may extract information from titles differently than text-based search engines. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is emerging as a new discipline focused on optimizing content for AI-generated responses, and title tags will play a role in this optimization strategy. As AI monitoring platforms like AmICited become more sophisticated, they will likely provide better insights into how title tags perform across different AI systems, enabling more targeted optimization. The integration of structured data with title tags may become more important, as AI systems use both elements to understand and represent page content. Regardless of how search technology evolves, the fundamental principle of creating clear, descriptive, keyword-relevant title tags that accurately represent page content will remain essential for visibility and user experience.
Effective title tag optimization requires ongoing measurement and iteration based on performance data. Google Search Console (GSC) provides essential metrics including impressions (how often your page appears in search results), clicks (how often users click your result), click-through rate (CTR), and average ranking position. By monitoring these metrics before and after title tag changes, you can quantify the impact of your optimization efforts. A/B testing (split testing) involves running two different title tag versions simultaneously to determine which performs better for specific goals like CTR or rankings. Tools like VWO, SEOTesting.com, and SplitSignal enable systematic A/B testing of title tags. When analyzing performance, look for patterns in which title structures, keywords, and formats generate the highest CTR and maintain rankings. Manual monitoring of how your pages appear in search results helps identify whether Google is rewriting your titles and provides insights into what triggers rewrites. If you notice frequent rewrites, analyze whether your titles are too long, too generic, or misaligned with page content. Tracking rewrite frequency over time helps you understand whether your optimization efforts are reducing rewrites and improving title stability. Regular audits of your title tags—at least quarterly—ensure they remain optimized as your content and business priorities evolve. By treating title tag optimization as an ongoing process rather than a one-time task, you can continuously improve your search visibility and click-through rates.
理想的标题标签长度为 50-60 个字符,或大约不超过 575 像素。这个范围可以确保您的标题在桌面和移动搜索结果中完整显示而不会被截断。少于 30 个字符的标题可能无法提供足够的上下文,过长的标题则有被省略号截断的风险,从而降低点击率。
根据最新研究,Google 会重写大约 61-76% 的搜索结果页面标题标签。当标题过长、过短、堆砌关键词或与页面内容不匹配时,Google 会进行重写。不过,无论搜索结果显示什么,Google 都会用您原始 HTML 标题标签进行排名,因此优化标题标签依然非常有价值。
应该,但品牌名的位置很重要。对于首页,将品牌名放在标题开头。对于内页,则放在末尾(例如“最佳猫咪玩具 | 宠物公司”)。但需注意,如果品牌名与搜索查询无关,Google 会在约 63% 的标题标签中移除品牌名,更注重内容的相关性而非品牌曝光。
是的,标题标签是 Google 已确认的排名因素,其影响力为轻至中等。Google 的 John Mueller 表示,标题标签在排名中是“一个很小的因素”。它们帮助搜索引擎理解页面内容并提升点击率,但内容质量和相关性在 Google 排名算法中权重更高。
标题标签是用户在搜索结果中看到页面的第一印象。一个有吸引力、清晰且与关键词相关的标题标签能显著提升点击率(CTR),让您的结果更突出并契合用户搜索意图。研究显示,优化过标题标签的页面点击率明显高于内容模糊或通用的标题。
标题标签是 HTML 页面 head 区域的元素,显示在浏览器标签页和搜索结果中;而 H1 标签是页面正文的主标题,显示在页面上。Google 经常在原始标题与内容不匹配时,用 H1 内容重写标题标签。因此让标题标签与 H1 保持一致,可以降低被重写的概率。
标题标签对于 AmICited 等 AI 可见性监测平台至关重要,这些平台会跟踪 ChatGPT、Perplexity 和 Google AI Overviews 等 AI 系统中的品牌提及。AI 系统会利用标题标签来理解页面相关性,并可能在引用或摘要中包含标题。优化过的标题标签可提升内容被 AI 系统引用并出现在 AI 生成响应中的概率。

了解标题标签(H1-H6),这些HTML标题元素可分层结构化内容。探索它们对SEO、可访问性的重要性,以及AI系统如何利用它们理解页面内容。...
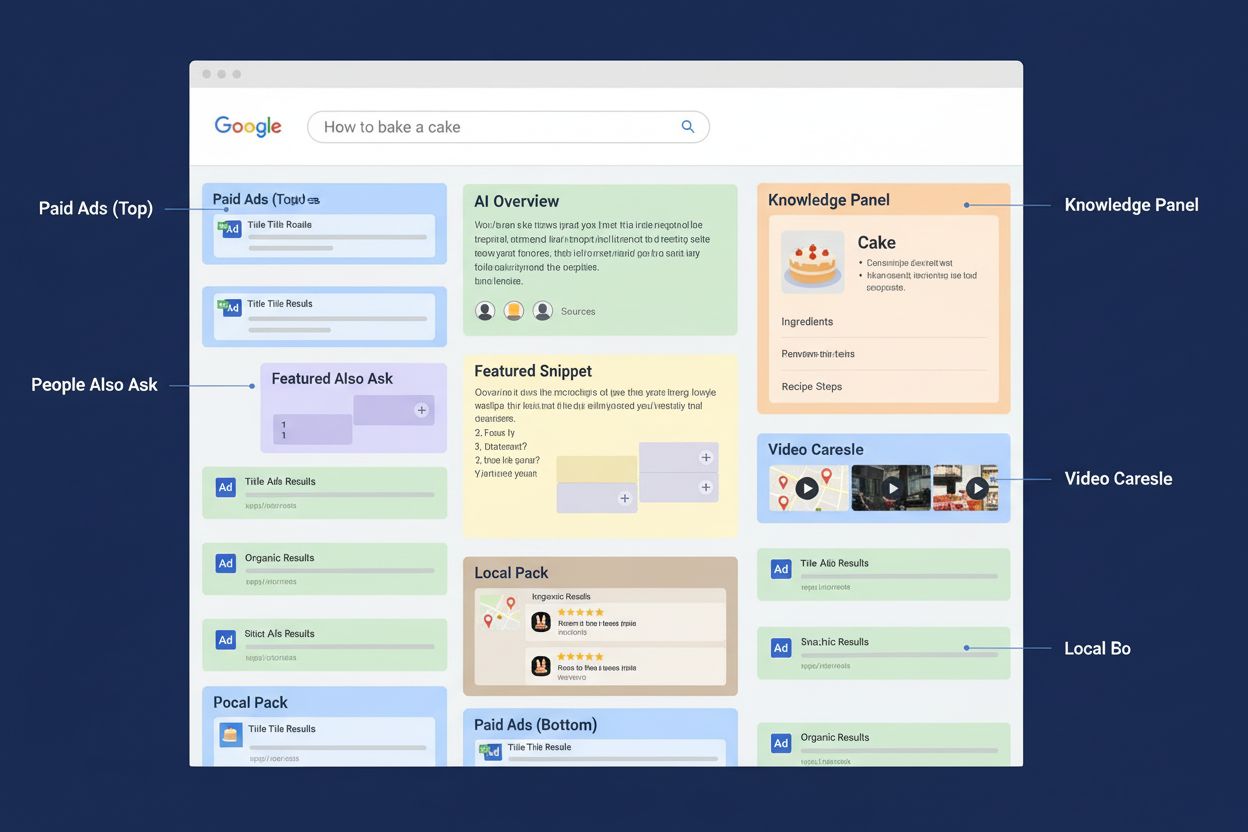
了解SERP是什么、如何运作,以及它为何对SEO、AI监测和品牌可见性至关重要。掌握SERP功能及其对搜索排名的影响。

了解如何为ChatGPT、Perplexity和Google AI模式等AI搜索引擎优化标签页面。探索技术性SEO策略、内容结构最佳实践以及引用优化技巧,提升在AI生成答案中的可见度。...
Cookie 同意
我们使用 cookie 来增强您的浏览体验并分析我们的流量。 See our privacy policy.