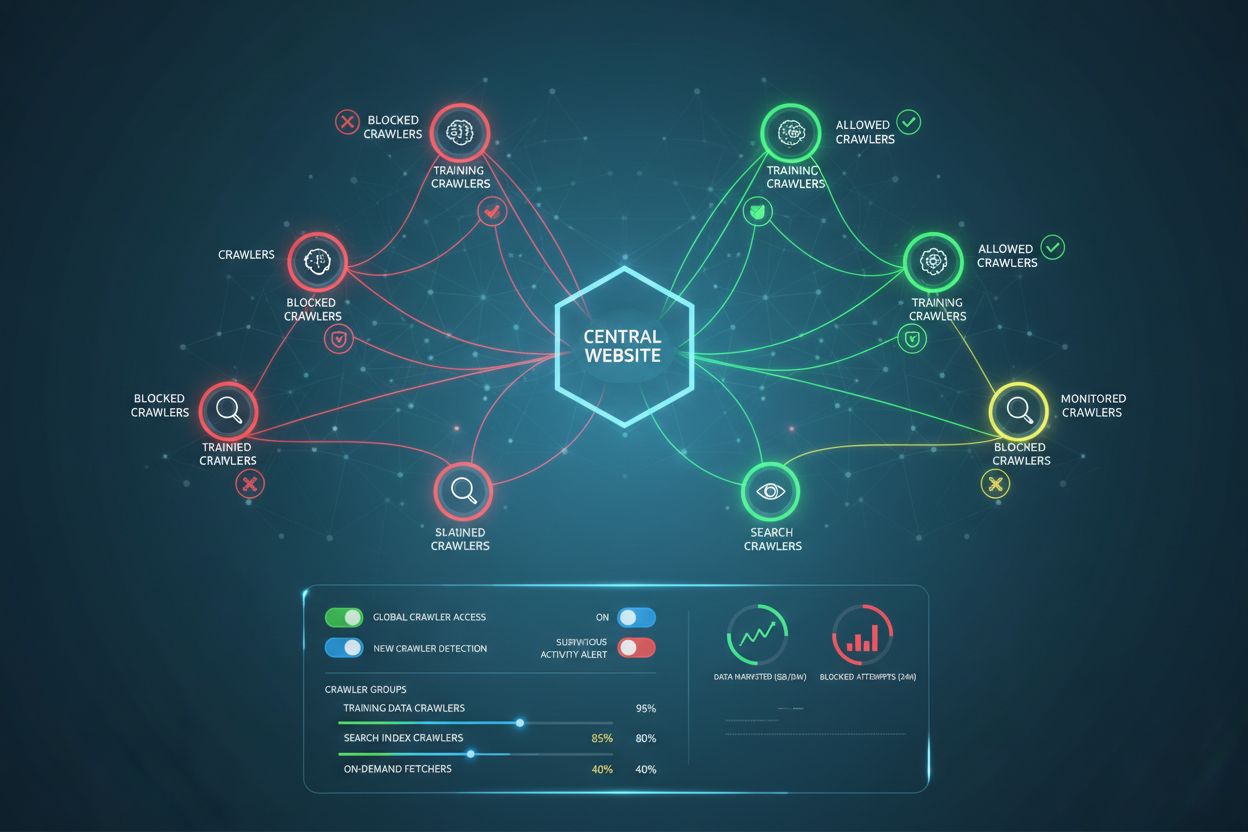
AI Crawler Management
Learn how to manage AI crawler access to your website content. Understand the difference between training and search crawlers, implement robots.txt controls, an...
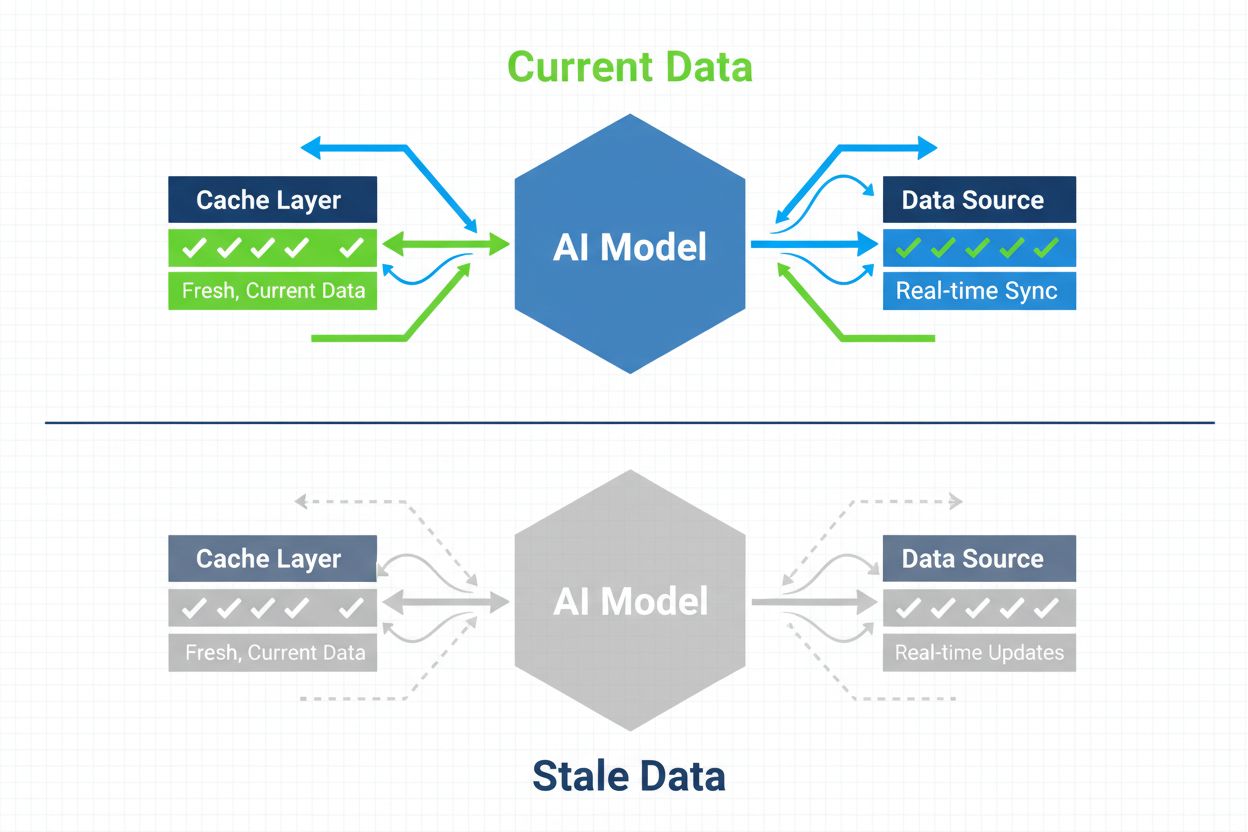
Strategies for ensuring AI systems have access to current content rather than stale cached versions. Cache management balances performance benefits of caching against the risk of serving outdated information, using invalidation strategies and monitoring to maintain data freshness while reducing latency and costs.
Strategies for ensuring AI systems have access to current content rather than stale cached versions. Cache management balances performance benefits of caching against the risk of serving outdated information, using invalidation strategies and monitoring to maintain data freshness while reducing latency and costs.
AI cache management refers to the systematic approach of storing and retrieving previously computed results, model outputs, or API responses to avoid redundant processing and reduce latency in artificial intelligence systems. The core challenge lies in balancing the performance benefits of cached data against the risk of serving stale or outdated information that no longer reflects current system state or user requirements. This becomes particularly critical in large language models (LLMs) and AI applications where inference costs are substantial and response time directly impacts user experience. Cache management systems must intelligently determine when cached results remain valid and when fresh computation is necessary, making it a fundamental architectural consideration for production AI deployments.

The impact of effective cache management on AI system performance is substantial and measurable across multiple dimensions. Implementing caching strategies can reduce response latency by 80-90% for repeated queries while simultaneously cutting API costs by 50-90%, depending on cache hit rates and system architecture. Beyond performance metrics, cache management directly influences accuracy consistency and system reliability, as properly invalidated caches ensure users receive current information while poorly managed caches introduce data staleness issues. These improvements become increasingly important as AI systems scale to handle millions of requests, where the cumulative effect of cache efficiency directly determines infrastructure costs and user satisfaction.
| Aspect | Cached Systems | Non-Cached Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | 80-90% faster | Baseline |
| API Costs | 50-90% reduction | Full cost |
| Accuracy | Consistent | Variable |
| Scalability | High | Limited |
Cache invalidation strategies determine how and when cached data is refreshed or removed from storage, representing one of the most critical decisions in cache architecture design. Different invalidation approaches offer distinct trade-offs between data freshness and system performance:
The selection of invalidation strategy fundamentally depends on application requirements: systems prioritizing data accuracy may accept higher latency costs through aggressive invalidation, while performance-critical applications may tolerate slightly stale data to maintain sub-millisecond response times.
Prompt caching in large language models represents a specialized application of cache management that stores intermediate model states and token sequences to avoid reprocessing identical or similar inputs. LLMs support two primary caching approaches: exact caching matches identical prompts character-for-character, while semantic caching identifies functionally equivalent prompts despite different wording. OpenAI implements automatic prompt caching with a 50% cost reduction on cached tokens, requiring minimum prompt segments of 1024 tokens to activate caching benefits. Anthropic offers manual prompt caching with more aggressive 90% cost reductions but requires developers to explicitly manage cache keys and durations, with minimum cache requirements of 1024-2048 tokens depending on model configuration. Cache duration in LLM systems typically ranges from minutes to hours, balancing the computational savings of reusing cached states against the risk of serving outdated model outputs for time-sensitive applications.
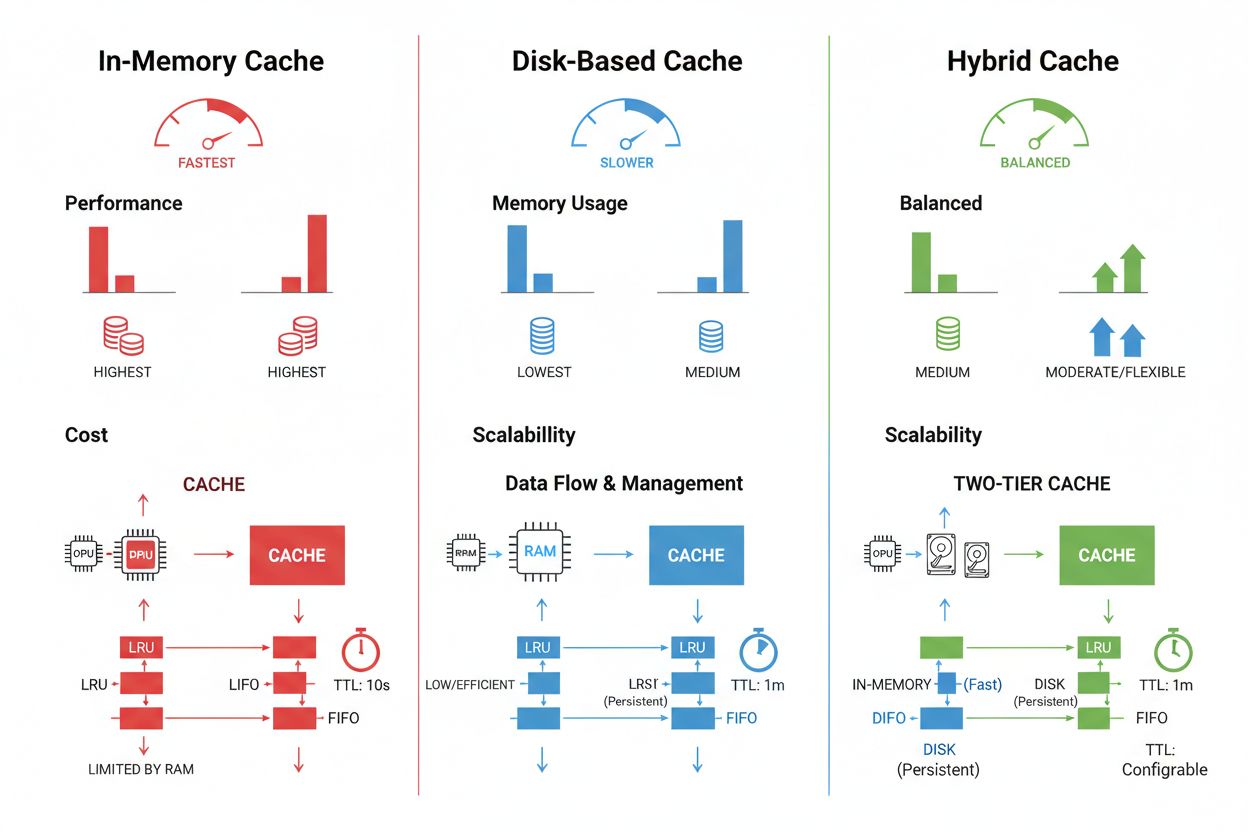
Cache storage and management techniques vary significantly based on performance requirements, data volume, and infrastructure constraints, with each approach offering distinct advantages and limitations. In-memory caching solutions like Redis provide microsecond-level access speeds ideal for high-frequency queries but consume significant RAM and require careful memory management. Disk-based caching accommodates larger datasets and persists across system restarts but introduces latency measured in milliseconds compared to in-memory alternatives. Hybrid approaches combine both storage types, routing frequently accessed data to memory while maintaining larger datasets on disk:
| Storage Type | Best For | Performance | Memory Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-Memory (Redis) | Frequent queries | Fastest | Higher |
| Disk-Based | Large datasets | Moderate | Lower |
| Hybrid | Mixed workloads | Balanced | Balanced |
Effective cache management requires configuring appropriate TTL settings that reflect data volatility—short TTLs (minutes) for rapidly changing data versus longer TTLs (hours/days) for stable content—combined with continuous monitoring of cache hit rates, eviction patterns, and memory utilization to identify optimization opportunities.
Real-world AI applications demonstrate both the transformative potential and operational complexity of cache management across diverse use cases. Customer service chatbots leverage caching to deliver consistent responses to frequently asked questions while reducing inference costs by 60-70%, enabling cost-effective scaling to thousands of concurrent users. Coding assistants cache common code patterns and documentation snippets, allowing developers to receive autocomplete suggestions with sub-100ms latency even during peak usage periods. Document processing systems cache embeddings and semantic representations of frequently analyzed documents, dramatically accelerating similarity searches and classification tasks. However, production cache management introduces significant challenges: invalidation complexity increases exponentially in distributed systems where cache consistency must be maintained across multiple servers, resource constraints force difficult trade-offs between cache size and coverage, security risks emerge when cached data contains sensitive information requiring encryption and access controls, and coordinating cache updates across microservices introduces potential race conditions and data inconsistencies. Comprehensive monitoring solutions that track cache freshness, hit rates, and invalidation events become essential for maintaining system reliability and identifying when cache strategies require adjustment based on changing data patterns and user behavior.
Cache invalidation removes or updates stale data when changes occur, providing immediate freshness but requiring event-driven triggers. Cache expiration sets a time limit (TTL) for how long data stays in cache, offering simpler implementation but potentially serving stale data if the TTL is too long. Many systems combine both approaches for optimal performance.
Effective cache management can reduce API costs by 50-90% depending on cache hit rates and system architecture. OpenAI's prompt caching offers 50% cost reduction on cached tokens, while Anthropic provides up to 90% reduction. The actual savings depend on query patterns and how much data can be effectively cached.
Prompt caching stores intermediate model states and token sequences to avoid reprocessing identical or similar inputs in large language models. It supports exact caching (character-for-character matches) and semantic caching (functionally equivalent prompts with different wording). This reduces latency by 80% and costs by 50-90% for repeated queries.
The primary strategies are: Time-Based Expiration (TTL) for automatic removal after set duration, Event-Based Invalidation for immediate updates when data changes, Semantic Invalidation for similar queries based on meaning, and Hybrid Approaches combining multiple strategies. The choice depends on data volatility and freshness requirements.
In-memory caching (like Redis) provides microsecond-level access speeds ideal for frequent queries but consumes significant RAM. Disk-based caching accommodates larger datasets and persists across restarts but introduces millisecond-level latency. Hybrid approaches combine both, routing frequently accessed data to memory while maintaining larger datasets on disk.
TTL is a countdown timer that determines how long cached data remains valid before expiration. Short TTLs (minutes) suit rapidly changing data, while longer TTLs (hours/days) work for stable content. Proper TTL configuration balances data freshness against unnecessary cache refreshes and server load.
Effective cache management enables AI systems to handle significantly more requests without proportional infrastructure expansion. By reducing computational load per request through caching, systems can serve millions of users more cost-effectively. Cache hit rates directly determine infrastructure costs and user satisfaction in production deployments.
Cached sensitive data introduces security vulnerabilities if not properly encrypted and access-controlled. Risks include unauthorized access to cached information, data exposure during cache invalidation, and inadvertent caching of confidential content. Comprehensive encryption, access controls, and monitoring are essential for protecting sensitive cached data.
AmICited tracks how AI systems reference your brand and ensures your content stays current in AI caches. Get visibility into AI cache management and content freshness across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.

Learn how to manage AI crawler access to your website content. Understand the difference between training and search crawlers, implement robots.txt controls, an...
Learn what AI Content Consolidation is and how merging similar content strengthens visibility signals for ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover...
Compare agency vs in-house AI visibility monitoring. Explore costs, timelines, expertise requirements, and hybrid approaches to help you choose the right strate...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.