
How Do I Consolidate Content for AI?
Learn how to consolidate and optimize your content for AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover best practices for content structure, fo...
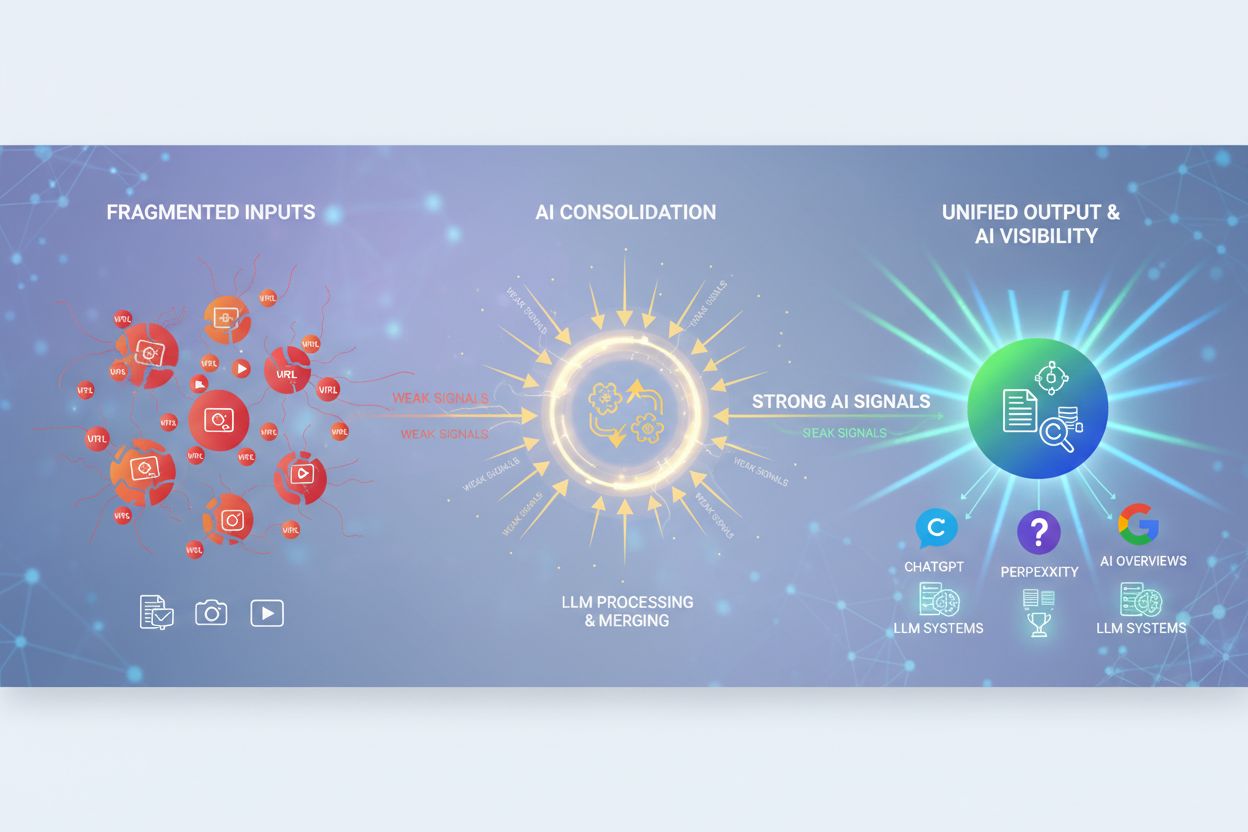
AI Content Consolidation is the strategic practice of merging similar or duplicate content across digital properties to strengthen visibility signals for artificial intelligence systems. By combining multiple URLs addressing the same topic into authoritative, comprehensive resources, brands ensure that AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews can more easily identify and prioritize their content. This consolidation prevents signal dilution, improves citation frequency, and increases the likelihood that AI systems will select your brand as a trusted source when generating answers.
AI Content Consolidation is the strategic practice of merging similar or duplicate content across digital properties to strengthen visibility signals for artificial intelligence systems. By combining multiple URLs addressing the same topic into authoritative, comprehensive resources, brands ensure that AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews can more easily identify and prioritize their content. This consolidation prevents signal dilution, improves citation frequency, and increases the likelihood that AI systems will select your brand as a trusted source when generating answers.
AI Content Consolidation is the strategic practice of merging similar or duplicate content across your digital properties to strengthen visibility signals for artificial intelligence systems. Rather than allowing multiple URLs to compete for the same topic or keyword intent, consolidation combines these assets into authoritative, comprehensive resources that AI systems can more easily identify and prioritize. This matters for AI visibility because Large Language Models (LLMs) and retrieval systems used by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI-powered search tools rely on clear, unified content signals to determine which sources are most relevant and trustworthy for answering user queries. When your content is fragmented across multiple pages, you dilute these signals and reduce the likelihood that AI systems will select your brand as a citation source.
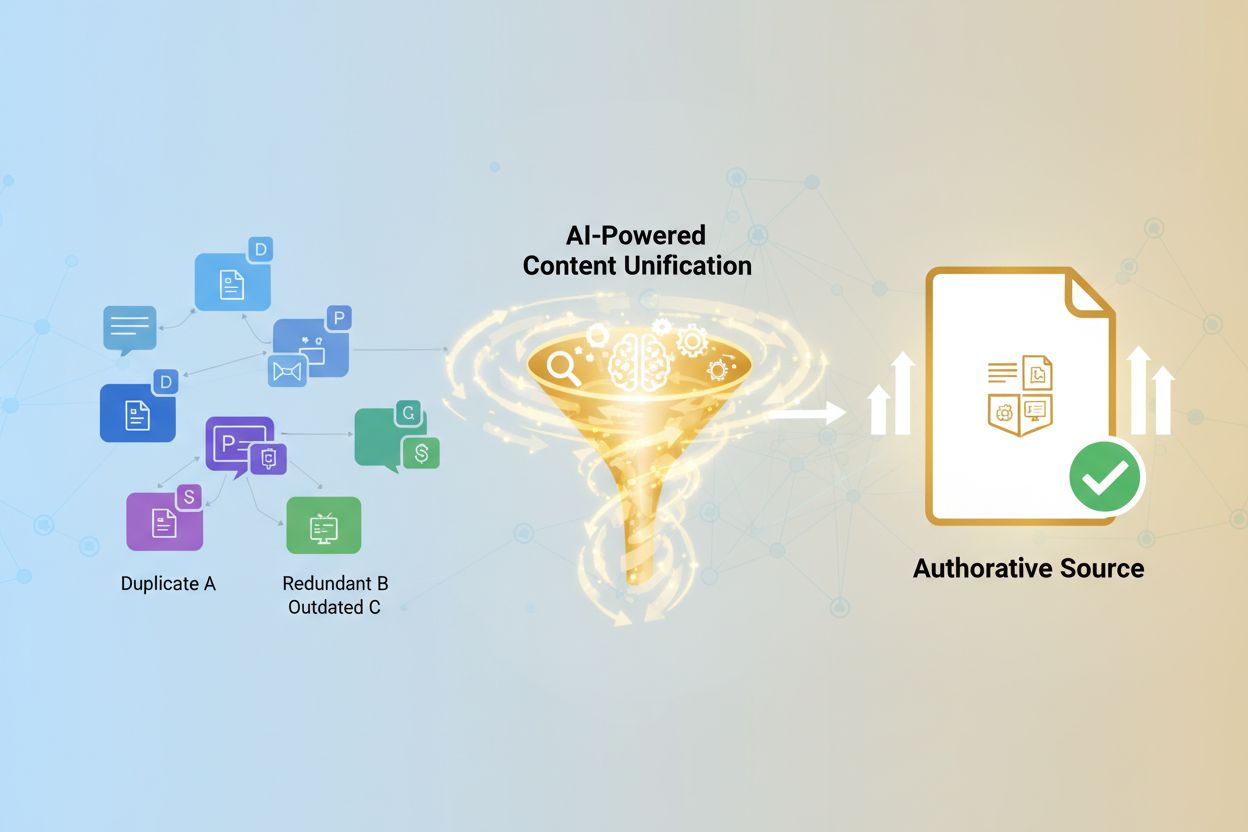
Traditional search engines have long penalized duplicate content, but AI systems present a different challenge: LLMs cluster near-duplicate URLs together, treating them as variations of the same content rather than distinct resources. This clustering creates what researchers call intent blurring—when multiple similar pages exist, AI systems struggle to determine which version is most authoritative, ultimately diluting your visibility signals across all versions. Microsoft’s guidance on duplicate content emphasizes that AI search systems evaluate content quality and relevance differently than traditional indexing, meaning that having five similar pages about the same topic doesn’t amplify your authority—it fragments it. This signal dilution is particularly problematic for AI answers because these systems prioritize sources that demonstrate clear expertise and comprehensive coverage on specific topics. When your content is spread thin across multiple URLs, each individual page appears less authoritative than a single, consolidated resource would be. Additionally, AI systems may randomly select one of your duplicate pages for citation, meaning you lose control over which version represents your brand in AI-generated answers. The result is reduced visibility, inconsistent brand representation, and missed opportunities to establish topical authority in your industry.
| Aspect | Duplicate Content | AI Content Cannibalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exact or near-identical copies of content across multiple URLs | Multiple pages competing for the same intent without consolidation |
| Detection | Easy to spot with plagiarism filters | Difficult to detect; requires semantic analysis |
| AI Impact | Clusters similar pages; dilutes signals across all versions | Fragments topical authority; confuses AI systems |
| Citation Effect | AI randomly selects one version; inconsistent citations | AI rotates between pages; unpredictable source selection |
| Solution | Consolidate URLs or implement canonical tags | Merge pages or establish clear hierarchy |
| Prevention | Regular content audits; strategic consolidation | Proactive content planning; topical mapping |
AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) technology, which retrieves relevant content from the web and uses it to generate answers while citing sources. In RAG systems, the retrieval component searches for content matching user intent, and the generation component synthesizes that content into a response while attributing information to specific sources. When evaluating which sources to retrieve and cite, AI systems analyze multiple factors including content relevance, topical depth, authority signals, and freshness—and consolidated content typically scores higher on these metrics because it represents more comprehensive coverage in a single resource. Google AI Overviews, for example, prioritize sources that thoroughly address user intent rather than fragmentary pages that only partially cover a topic. Citation patterns in AI systems also favor consolidated content: when you have one authoritative page instead of five similar pages, AI systems are more likely to consistently cite that single source, building recognition and trust in your brand as a reliable authority. This consistency in citation is crucial because AI systems learn to recognize and prefer sources that reliably provide high-quality, comprehensive information on specific topics.
Implementing effective content consolidation requires a multi-faceted approach starting with canonical tags, which tell search engines and AI crawlers which version of similar content should be considered the primary source. When you have multiple pages addressing the same topic, implementing a canonical tag pointing to your preferred version helps consolidate ranking signals and citation opportunities. URL consolidation—actually merging content from multiple pages into a single, more comprehensive resource—is often more effective than canonical tags alone, as it eliminates the duplicate content problem entirely rather than simply managing it. This might involve combining three separate blog posts about “AI content strategy” into one definitive guide that covers all three angles comprehensively. Content merging techniques can include combining related articles into pillar pages, consolidating product variations into single product pages with detailed specifications, or merging outdated content into updated, evergreen resources. For those managing large content inventories, Microsoft’s IndexNow protocol allows you to immediately notify search engines and AI crawlers when you’ve consolidated or updated content, ensuring they re-evaluate your pages quickly rather than relying on slower crawl schedules. The key is being intentional: identify which pages compete for the same intent, determine which should be the primary resource, and either merge them or use canonical tags to consolidate signals toward that primary version.
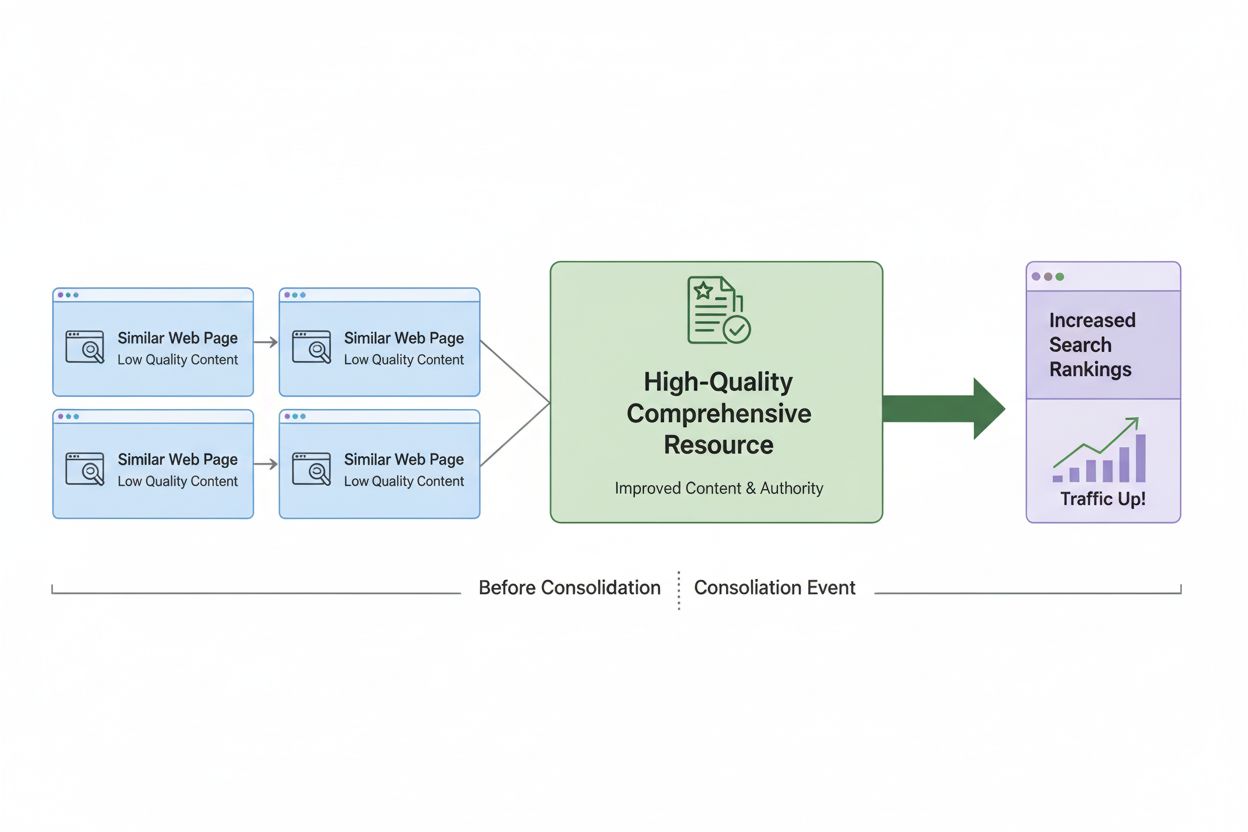
While content consolidation is a deliberate strategy to strengthen AI visibility signals, content cannibalization is the accidental fragmentation that occurs when you haven’t consolidated properly. The distinction is critical: consolidation is intentional and strategic, while cannibalization is unintended and harmful. Content cannibalization happens when multiple pages on your site compete for the same search intent without a clear hierarchy or consolidation strategy—for example, having both a “best project management tools” article and a “top 5 project management software” article that cover nearly identical content and compete for the same AI citations. This creates signal dilution, where your authority on the topic is split across multiple pages rather than concentrated in one authoritative resource, making it less likely that AI systems will cite any single page. The difference in topical authority is significant: a consolidated resource that comprehensively covers a topic from multiple angles demonstrates deeper expertise than fragmented pages that each address only portions of the topic. To avoid cannibalization while pursuing consolidation, conduct a content audit to identify competing pages, determine which should be primary, and either merge them into a single comprehensive resource or use canonical tags to consolidate signals. The goal is ensuring that all your topical authority flows toward strengthening one primary resource rather than being scattered across multiple competing pages.
Measuring the impact of content consolidation requires understanding the difference between mentions and citations in AI systems. A mention occurs when your content appears in an AI system’s training data or retrieval results, while a citation is when an AI system explicitly attributes information to your source in a generated answer—citations are far more valuable for visibility and brand recognition. Tools like AmICited.com provide comprehensive monitoring of your citations across major AI systems including ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and others, allowing you to track whether consolidation efforts are increasing your citation frequency and consistency. Beyond citation counts, monitor visibility metrics such as which topics generate citations, which pages are cited most frequently, and whether consolidation has improved your citation rate for target topics. Research from U of Digital demonstrates that consolidated content receives more consistent citations from AI systems compared to fragmented content on the same topics, validating the strategic importance of consolidation efforts. Track these metrics before and after consolidation to quantify the impact: you should see increased citation frequency, more consistent source selection (AI systems citing the same consolidated page rather than rotating between similar pages), and improved brand visibility in AI-generated answers.
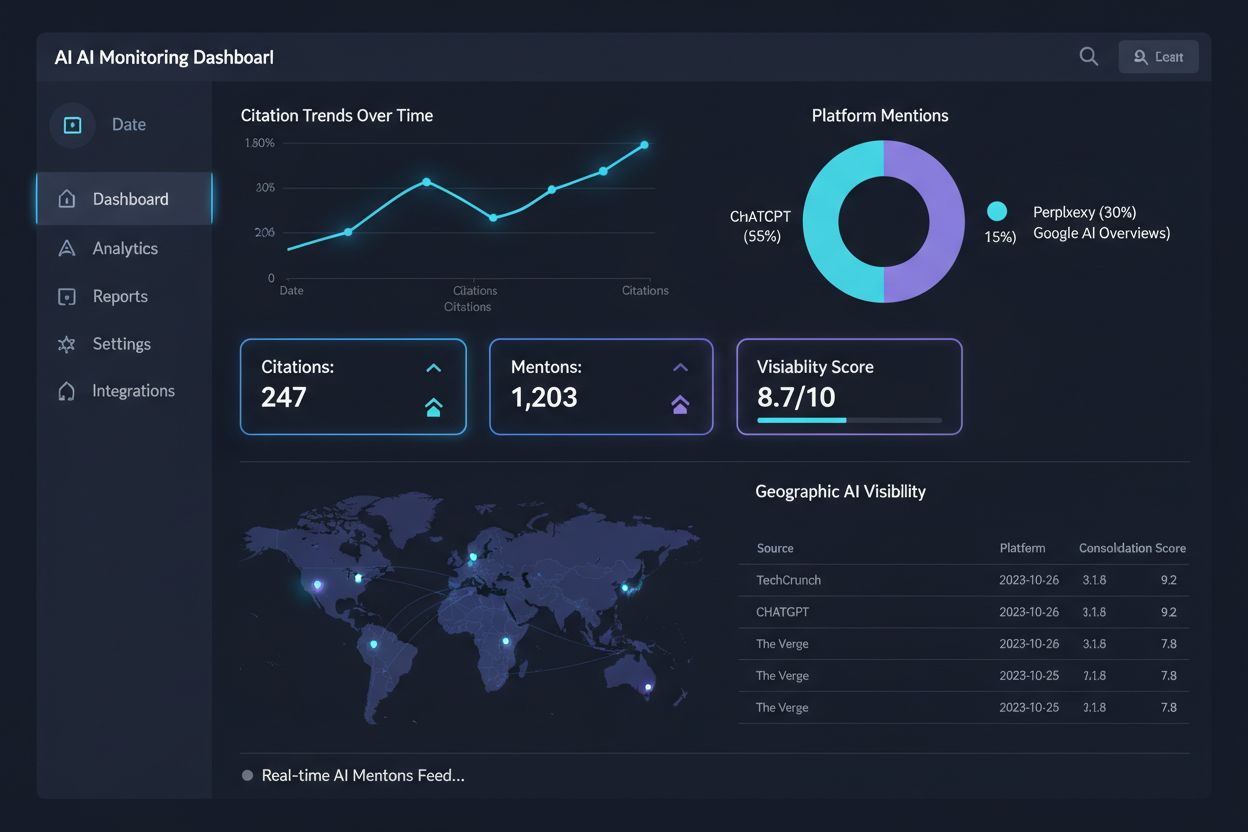
AmICited.com stands out as the leading platform for monitoring and optimizing your AI visibility, providing detailed insights into which of your pages are cited by major AI systems and how consolidation efforts impact your citation performance. Beyond monitoring, several tools support the technical implementation of consolidation: Screaming Frog and SEMrush can identify duplicate and near-duplicate content across your site, helping you spot consolidation opportunities; Moz and Ahrefs provide topical authority analysis to determine which pages should be primary resources; and Google Search Console shows you which pages compete for the same queries, indicating consolidation candidates. For implementing consolidation at scale, content management systems like WordPress, HubSpot, and Contentful offer built-in canonical tag management and URL redirection capabilities. Microsoft IndexNow integration ensures that when you consolidate content, search engines and AI crawlers are immediately notified to re-evaluate your pages. The practical implementation typically involves: (1) identifying consolidation candidates using duplicate content detection tools, (2) deciding whether to merge or use canonical tags, (3) implementing the consolidation (merging content or adding canonical tags), and (4) monitoring results using AmICited.com to track citation impact.
Effective content consolidation goes beyond simply merging URLs—it requires attention to structured data that helps AI systems understand your content’s context and authority. Implementing Schema.org markup for articles, products, or other content types signals to AI systems that your consolidated resource is comprehensive and authoritative. E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) become even more critical in consolidated content: ensure that your merged resource clearly demonstrates the author’s expertise, includes recent updates and citations to authoritative sources, and maintains consistent quality throughout. Maintain consistency in messaging and formatting across consolidated content—when you merge multiple pages, ensure the resulting resource flows naturally and maintains a unified voice rather than appearing as a patchwork of different articles. Freshness is equally important: after consolidation, regularly update your primary resource with new information, recent examples, and current data to signal to AI systems that this is an actively maintained, authoritative resource. CMI Media Group’s research on content strategy emphasizes that consolidated content performs best when it’s treated as a living resource that evolves with your industry rather than a static page created once and left unchanged. Finally, ensure your consolidated resource is easily discoverable through clear internal linking from related pages and prominent placement in your site navigation, making it easy for both users and AI crawlers to find your authoritative resource on each topic.
One of the most common mistakes is over-consolidation—merging too many disparate topics into a single page in an attempt to create one “ultimate guide,” which actually dilutes focus and makes it harder for AI systems to understand what the page is about. AI systems perform better with focused, topically coherent content than with sprawling pages that try to cover everything. Another critical error is failing to implement proper redirects when consolidating URLs: if you merge page A into page B but don’t redirect the old URL, you lose all the authority and backlinks pointing to page A, and users following old links encounter 404 errors. Incomplete consolidation is equally problematic—consolidating some duplicate pages while leaving others creates a half-measure that still fragments your signals rather than concentrating them. Many organizations also make the mistake of consolidating without updating: merging old content into a new page without refreshing information, updating examples, or adding new insights signals to AI systems that the resource isn’t actively maintained. Finally, ignoring canonical tags when they’re appropriate can undermine consolidation efforts; sometimes you need to keep multiple URLs for user experience reasons (different product variations, regional versions, etc.), and in these cases, proper canonical tag implementation is essential to consolidate signals even when you can’t merge URLs. The key is being intentional and thorough: consolidate strategically, implement redirects properly, and maintain the resulting resource actively.
As AI systems evolve, semantic deduplication will become increasingly sophisticated, meaning AI systems will identify and cluster semantically similar content even when it’s not technically duplicate. This evolution makes proactive consolidation even more important—rather than waiting for AI systems to cluster your content, you should consolidate strategically to control how your content is grouped and presented. The future of AI search will likely emphasize topical authority and comprehensive coverage even more heavily than current systems do, rewarding brands that consolidate related content into authoritative resources rather than fragmenting their expertise across multiple pages. Emerging trends suggest that AI systems will increasingly prefer consolidated, regularly updated resources over static content, making content consolidation not just a one-time optimization but an ongoing practice of maintaining and evolving your primary resources. As competition for AI citations intensifies, brands that master content consolidation will have a significant advantage in visibility and citation frequency, making this a critical competency for content strategists and marketers looking to succeed in AI-driven search environments.
Content consolidation is a deliberate, strategic practice of merging similar pages to strengthen AI visibility signals, while content cannibalization is the accidental fragmentation that occurs when multiple pages compete for the same search intent without a clear hierarchy. Consolidation is intentional and beneficial; cannibalization is unintended and harmful to your visibility.
When you consolidate similar content into a single authoritative resource, you concentrate all your topical authority and expertise signals in one place. AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity use RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) to find and cite sources, and they prefer comprehensive, consolidated resources over fragmented pages. This makes your consolidated page more likely to be retrieved and cited in AI-generated answers.
Use duplicate content detection tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush to identify similar pages on your site. Ahrefs and Moz provide topical authority analysis to determine which pages should be primary resources. Google Search Console shows which pages compete for the same queries. AmICited.com monitors your actual citation performance across AI systems to measure consolidation impact.
Merging pages is generally more effective because it eliminates the duplicate content problem entirely rather than simply managing it. However, canonical tags are appropriate when you need to keep multiple URLs for user experience reasons (different product variations, regional versions, etc.). The key is being intentional: consolidate strategically and implement your chosen approach thoroughly.
Monitor your citations and mentions across AI systems using AmICited.com before and after consolidation. You should see increased citation frequency, more consistent source selection (AI systems citing the same consolidated page rather than rotating between similar pages), and improved brand visibility in AI-generated answers. Track these metrics over time to quantify the impact.
Implement Schema.org markup to help AI systems understand your content's context. Ensure strong E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) throughout your consolidated resource. Maintain consistency in messaging and formatting. Keep your consolidated resource fresh with regular updates. Use proper redirects when consolidating URLs to preserve authority and backlinks.
When done properly, consolidation improves both SEO and AI visibility. Consolidating duplicate pages concentrates ranking signals rather than fragmenting them. However, improper implementation—such as failing to implement redirects or consolidating without updating content—can harm rankings. The key is being thorough: consolidate strategically, implement redirects properly, and maintain the resulting resource actively.
Content consolidation should be an ongoing practice rather than a one-time effort. Regularly audit your content to identify new consolidation opportunities as your site grows. After consolidation, treat your primary resources as living documents that evolve with your industry. Monitor your citation performance using AmICited.com to identify additional consolidation opportunities based on which topics generate the most AI visibility.
Track how your brand appears in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems. Get real-time insights into your citations and mentions across all major AI platforms.

Learn how to consolidate and optimize your content for AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover best practices for content structure, fo...
Learn what content consolidation is, how it improves SEO performance, and why merging similar content is essential for AI visibility and brand monitoring in sea...

Community discussion on consolidating website content for AI search visibility. Real experiences from content strategists on eliminating duplicate content and r...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.