
A/B Testing for AI Visibility: Methodology and Best Practices
Master A/B testing for AI visibility with our comprehensive guide. Learn GEO experiments, methodology, best practices, and real-world case studies for better AI...

Isolated sandbox environments designed to validate, evaluate, and debug artificial intelligence models and applications before production deployment. These controlled spaces enable testing of AI content performance across different platforms, measuring metrics, and ensuring reliability without affecting live systems or exposing sensitive data.
Isolated sandbox environments designed to validate, evaluate, and debug artificial intelligence models and applications before production deployment. These controlled spaces enable testing of AI content performance across different platforms, measuring metrics, and ensuring reliability without affecting live systems or exposing sensitive data.
An AI Testing Environment is a controlled, isolated computational space designed to validate, evaluate, and debug artificial intelligence models and applications before deployment to production systems. It serves as a sandbox where developers, data scientists, and QA teams can safely execute AI models, test different configurations, and measure performance against predefined metrics without affecting live systems or exposing sensitive data. These environments replicate production conditions while maintaining complete isolation, allowing teams to identify issues, optimize model behavior, and ensure reliability across various scenarios. The testing environment acts as a critical quality gate in the AI development lifecycle, bridging the gap between experimental prototyping and enterprise-grade deployment.

A comprehensive AI Testing Environment comprises several interconnected technical layers that work together to provide complete testing capabilities. The model execution layer handles the actual inference and computation, supporting multiple frameworks (PyTorch, TensorFlow, ONNX) and model types (LLMs, computer vision, time-series). The data management layer manages test datasets, fixtures, and synthetic data generation while maintaining data isolation and compliance. The evaluation framework includes metrics engines, assertion libraries, and scoring systems that measure model outputs against expected results. The monitoring and logging layer captures execution traces, performance metrics, latency data, and error logs for post-test analysis. The orchestration layer manages test workflows, parallel execution, resource allocation, and environment provisioning. Below is a comparison of key architectural components across different testing environment types:
| Component | LLM Testing | Computer Vision | Time-Series | Multi-Modal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Runtime | Transformer inference | GPU-accelerated inference | Sequential processing | Hybrid execution |
| Data Format | Text/tokens | Images/tensors | Numerical sequences | Mixed media |
| Evaluation Metrics | Semantic similarity, hallucination | Accuracy, IoU, F1-score | RMSE, MAE, MAPE | Cross-modal alignment |
| Latency Requirements | 100-500ms typical | 50-200ms typical | <100ms typical | 200-1000ms typical |
| Isolation Method | Container/VM | Container/VM | Container/VM | Firecracker microVM |
Modern AI Testing Environments must support heterogeneous model ecosystems, enabling teams to evaluate applications across different LLM providers, frameworks, and deployment targets simultaneously. Multi-platform testing allows organizations to compare model outputs from OpenAI’s GPT-4, Anthropic’s Claude, Mistral, and open-source alternatives like Llama within the same test harness, facilitating informed model selection decisions. Platforms like E2B provide isolated sandboxes that execute code generated by any LLM, supporting Python, JavaScript, Ruby, and C++ with full filesystem access, terminal capabilities, and package installation. IntelIQ.dev enables side-by-side comparison of multiple AI models with unified interfaces, allowing teams to test guardrailed prompts and policy-aware templates across different providers. Testing environments must handle:
AI Testing Environments serve diverse organizational needs across development, quality assurance, and compliance functions. Development teams use testing environments to validate model behavior during iterative development, testing prompt variations, fine-tuning parameters, and debugging unexpected outputs before integration. Data science teams leverage these environments to evaluate model performance on holdout datasets, compare different architectures, and measure metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-scores. Production monitoring involves continuous testing of deployed models against baseline metrics, detecting performance degradation, and triggering retraining pipelines when quality thresholds are breached. Compliance and security teams use testing environments to validate that models meet regulatory requirements, don’t produce biased outputs, and handle sensitive data appropriately. Enterprise applications include:
The AI testing landscape includes specialized platforms designed for different testing scenarios and organizational scales. DeepEval is an open-source LLM evaluation framework providing 50+ research-backed metrics including answer correctness, semantic similarity, hallucination detection, and toxicity scoring, with native Pytest integration for CI/CD workflows. LangSmith (by LangChain) offers comprehensive observability, evaluation, and deployment capabilities with built-in tracing, prompt versioning, and dataset management for LLM applications. E2B provides secure, isolated sandboxes powered by Firecracker microVMs, supporting code execution with sub-200ms startup times, up to 24-hour sessions, and integration with major LLM providers. IntelIQ.dev emphasizes privacy-first testing with end-to-end encryption, role-based access controls, and support for multiple AI models including GPT-4, Claude, and open-source alternatives. The following table compares key capabilities:
| Tool | Primary Focus | Metrics | CI/CD Integration | Multi-Model Support | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepEval | LLM evaluation | 50+ metrics | Native Pytest | Limited | Open-source + cloud |
| LangSmith | Observability & evaluation | Custom metrics | API-based | LangChain ecosystem | Freemium + enterprise |
| E2B | Code execution | Performance metrics | GitHub Actions | All LLMs | Pay-per-use + enterprise |
| IntelIQ.dev | Privacy-first testing | Custom metrics | Workflow builder | GPT-4, Claude, Mistral | Subscription-based |
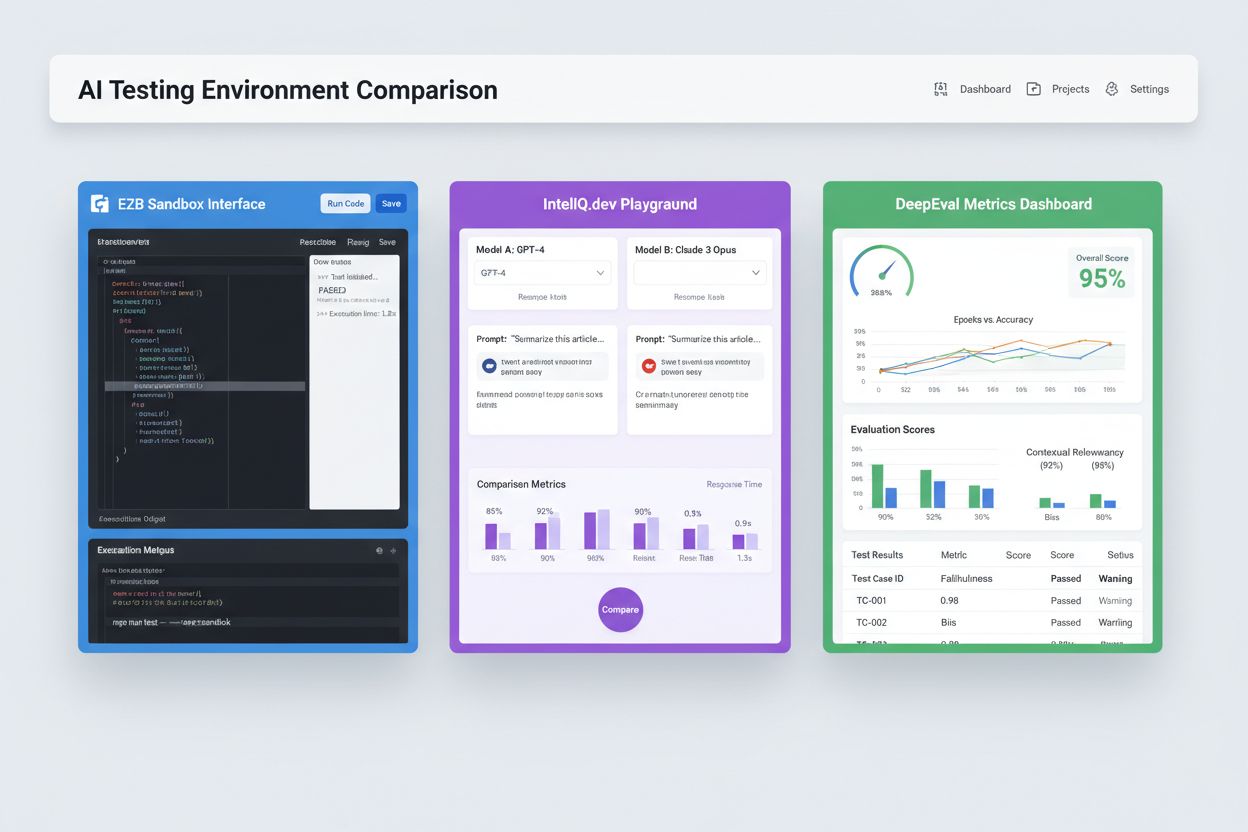
Enterprise AI Testing Environments must implement rigorous security controls to protect sensitive data, maintain regulatory compliance, and prevent unauthorized access. Data isolation requires that test data never leaks to external APIs or third-party services; platforms like E2B use Firecracker microVMs to provide complete process isolation with no shared kernel access. Encryption standards should include end-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit, with support for HIPAA, SOC 2 Type 2, and GDPR compliance requirements. Access controls must enforce role-based permissions, audit logging, and approval workflows for sensitive test scenarios. Best practices include: maintaining separate test datasets that don’t contain production data, implementing data masking for personally identifiable information (PII), using synthetic data generation for realistic testing without privacy risks, conducting regular security audits of test infrastructure, and documenting all test results for compliance purposes. Organizations should also implement bias detection mechanisms to identify discriminatory model behavior, use interpretability tools like SHAP or LIME for understanding model decisions, and establish decision logging to track how models arrive at specific outputs for regulatory accountability.
AI Testing Environments must seamlessly integrate into existing continuous integration and continuous deployment pipelines to enable automated quality gates and rapid iteration cycles. Native CI/CD integration allows test execution to trigger automatically on code commits, pull requests, or scheduled intervals using platforms like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins. DeepEval’s Pytest integration enables developers to write test cases as standard Python tests that execute within existing CI workflows, with results reported alongside traditional unit tests. Automated evaluation can measure model performance metrics, compare outputs against baseline versions, and block deployments if quality thresholds aren’t met. Artifact management involves storing test datasets, model checkpoints, and evaluation results in version control systems or artifact repositories for reproducibility and audit trails. Integration patterns include:
The AI Testing Environment landscape is evolving rapidly to address emerging challenges in model complexity, scale, and heterogeneity. Agentic testing is becoming increasingly important as AI systems move beyond single-model inference to multi-step workflows where agents use tools, make decisions, and interact with external systems—requiring new evaluation frameworks that measure task completion, safety, and reliability. Distributed evaluation enables testing at scale by running thousands of concurrent test instances across cloud infrastructure, critical for reinforcement learning and large-scale model training. Real-time monitoring is shifting from batch evaluation to continuous, production-grade testing that detects performance degradation, data drift, and emerging biases in live systems. Observability platforms like AmICited are emerging as essential tools for comprehensive AI monitoring and visibility, providing centralized dashboards that track model performance, usage patterns, and quality metrics across entire AI portfolios. Future testing environments will increasingly incorporate automated remediation, where systems not only detect issues but automatically trigger retraining pipelines or model updates, and cross-modal evaluation, supporting simultaneous testing of text, image, audio, and video models within unified frameworks.
An AI Testing Environment is an isolated sandbox where you can safely test models, prompts, and configurations without affecting live systems or users. Production deployment is the live environment where models serve real users. Testing environments allow you to catch issues, optimize performance, and validate changes before they reach production, reducing risk and ensuring quality.
Yes, modern AI Testing Environments support multi-model testing. Platforms like E2B, IntelIQ.dev, and DeepEval allow you to test the same prompt or input across different LLM providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, etc.) simultaneously, enabling direct comparison of outputs and performance metrics.
Enterprise AI Testing Environments implement multiple security layers including data isolation (containerization or microVMs), end-to-end encryption, role-based access controls, audit logging, and compliance certifications (SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA). Data never leaves the isolated environment unless explicitly exported, protecting sensitive information.
Testing Environments enable compliance by providing audit trails of all model evaluations, supporting data masking and synthetic data generation, enforcing access controls, and maintaining complete isolation of test data from production systems. This documentation and control helps organizations meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
Key metrics depend on your use case: for LLMs, track accuracy, semantic similarity, hallucination rates, and latency; for RAG systems, measure context precision/recall and faithfulness; for classification models, monitor precision, recall, and F1-scores; for all models, track performance degradation over time and bias indicators.
Costs vary by platform: DeepEval is open-source and free; LangSmith offers a free tier with paid plans starting at $39/month; E2B uses pay-per-use pricing based on sandbox runtime; IntelIQ.dev offers subscription-based pricing. Many platforms also offer enterprise pricing for large-scale deployments.
Yes, most modern testing environments support CI/CD integration. DeepEval integrates natively with Pytest, E2B works with GitHub Actions and GitLab CI, and LangSmith provides API-based integration. This enables automated testing on every code commit and deployment gate enforcement.
End-to-end testing treats your entire AI application as a black box, testing the final output against expected results. Component-level testing evaluates individual pieces (LLM calls, retrievers, tool usage) separately using tracing and instrumentation. Component-level testing provides deeper insights into where issues occur, while end-to-end testing validates overall system behavior.
AmICited tracks how AI systems reference your brand and content across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google AI. Get real-time visibility into your AI presence with comprehensive monitoring and analytics.

Master A/B testing for AI visibility with our comprehensive guide. Learn GEO experiments, methodology, best practices, and real-world case studies for better AI...
Learn what an AI Visibility Center of Excellence is, its key responsibilities, monitoring capabilities, and how it enables organizations to maintain transparenc...
Learn what an AI Platform Ecosystem is, how interconnected AI systems work together, and why managing your brand presence across multiple AI platforms matters f...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.