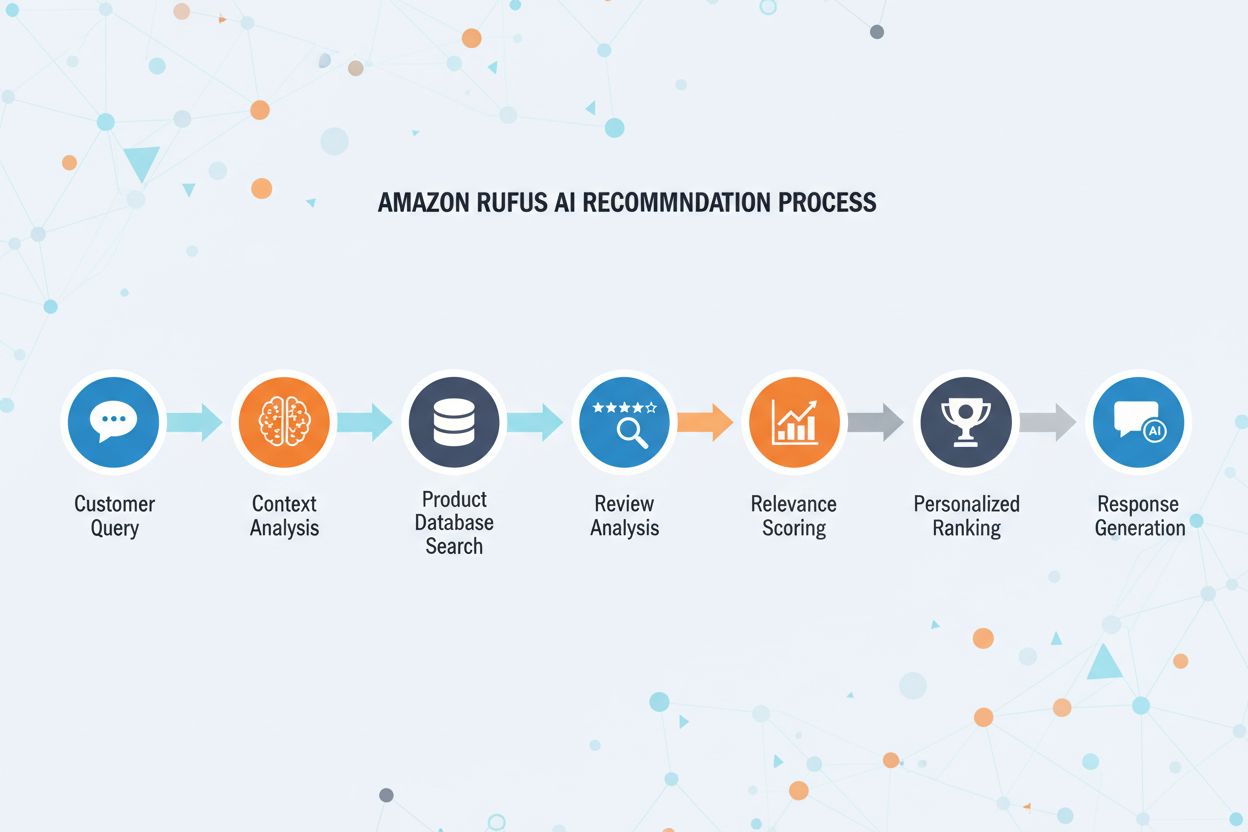
How Amazon's AI Assistant Recommends Products
Discover how Amazon Rufus uses generative AI and machine learning to provide personalized product recommendations. Learn the technology, features, and impact on...

Amazon’s web crawler used to improve products and services including Alexa, Rufus shopping assistant, and Amazon’s AI-powered search features. It respects the Robots Exclusion Protocol and can be controlled through robots.txt directives. May be used for AI model training.
Amazon's web crawler used to improve products and services including Alexa, Rufus shopping assistant, and Amazon's AI-powered search features. It respects the Robots Exclusion Protocol and can be controlled through robots.txt directives. May be used for AI model training.
Amazonbot is Amazon’s official web crawler designed to improve the company’s products and services by gathering and analyzing web content. This sophisticated crawler powers critical Amazon features including Alexa voice assistant, Rufus AI shopping assistant, and Amazon’s AI-powered search experiences. Amazonbot operates using the user agent string Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; Amazonbot/0.1; +https://developer.amazon.com/support/amazonbot) Chrome/119.0.6045.214 Safari/537.36, which identifies it to web servers. The data collected by Amazonbot may be used to train Amazon’s artificial intelligence models, making it a crucial component of Amazon’s broader AI infrastructure and product development strategy.
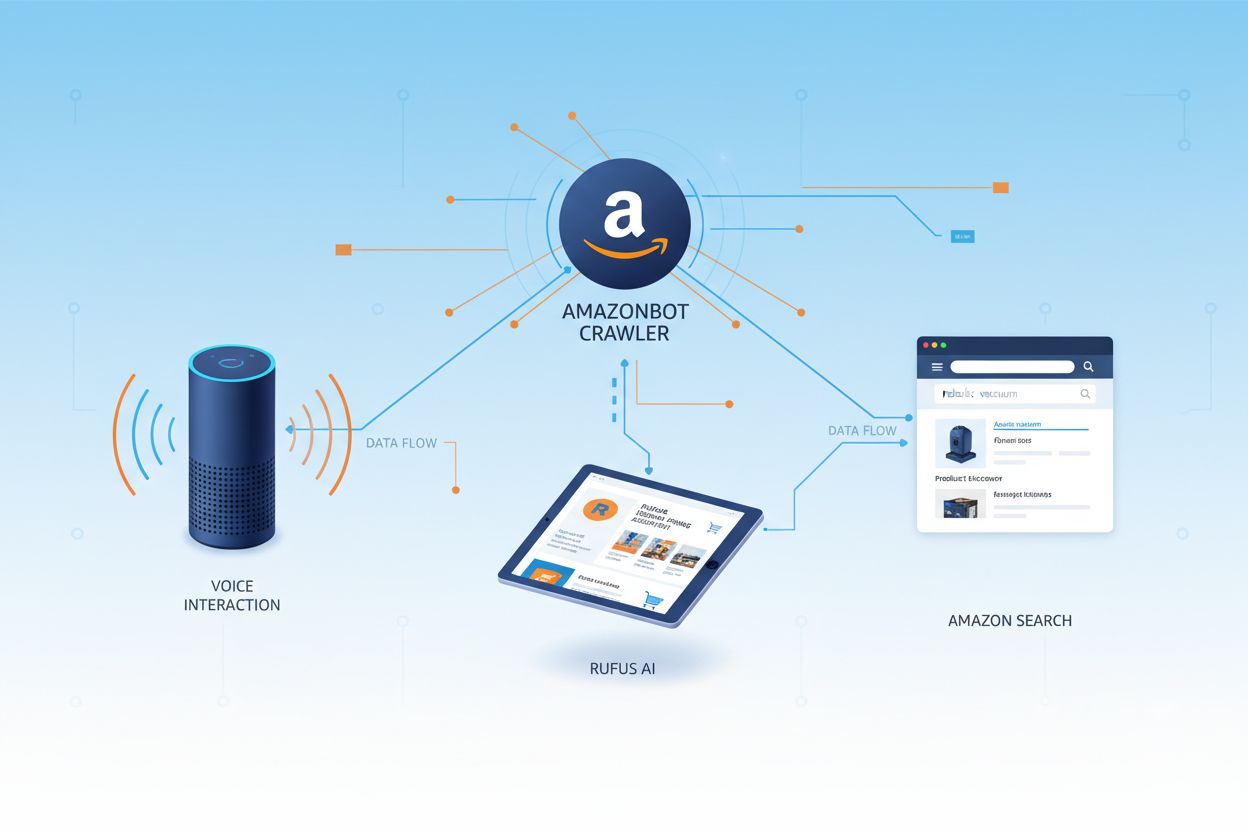
Amazon operates three distinct web crawlers, each serving specific purposes within its ecosystem. Amazonbot is the primary crawler used for general product and service improvement, and it may be used for AI model training. Amzn-SearchBot is specifically designed to improve search experiences in Amazon products like Alexa and Rufus, but importantly, it does NOT crawl content for generative AI model training. Amzn-User supports user-initiated actions, such as fetching live information when customers ask Alexa questions that require up-to-date web data, and it also does not crawl for AI training purposes. All three crawlers respect the Robots Exclusion Protocol and honor robots.txt directives, allowing website owners to control their access. Amazon publishes the IP addresses for each crawler on its developer portal, enabling website owners to verify legitimate traffic. Additionally, all Amazon crawlers respect link-level rel=nofollow directives and page-level robots meta tags including noarchive (preventing use for model training), noindex (preventing indexing), and none (preventing both).
| Crawler Name | Primary Purpose | AI Model Training | User Agent | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazonbot | General product/service improvement | Yes | Amazonbot/0.1 | Overall Amazon service enhancement, AI training |
| Amzn-SearchBot | Search experience improvement | No | Amzn-SearchBot/0.1 | Alexa search, Rufus shopping assistant indexing |
| Amzn-User | User-initiated live data fetching | No | Amzn-User/0.1 | Real-time Alexa queries, current information requests |
Amazon respects the industry-standard Robots Exclusion Protocol (RFC 9309), which means website owners can control Amazonbot access through their robots.txt file. Amazon fetches host-level robots.txt files from the root of your domain (e.g., example.com/robots.txt) and will use a cached copy from the last 30 days if the file cannot be fetched. Changes to your robots.txt file typically take approximately 24 hours to be reflected in Amazon’s systems. The protocol supports standard user-agent and allow/disallow directives, allowing granular control over which crawlers can access specific directories or files. However, it’s important to note that Amazon crawlers do NOT support the crawl-delay directive, so this parameter will be ignored if included in your robots.txt file.
Here’s an example of how to control Amazonbot access:
# Block Amazonbot from crawling your entire site
User-agent: Amazonbot
Disallow: /
# Allow Amzn-SearchBot for search visibility
User-agent: Amzn-SearchBot
Allow: /
# Block a specific directory from Amazonbot
User-agent: Amazonbot
Disallow: /private/
# Allow all other crawlers
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Website owners concerned about bot traffic should verify that crawlers claiming to be Amazonbot are actually legitimate Amazon crawlers. Amazon provides a verification process using DNS lookups to confirm authentic Amazonbot traffic. To verify a crawler’s legitimacy, first locate the accessing IP address from your server logs, then perform a reverse DNS lookup on that IP address using the host command. The retrieved domain name should be a subdomain of crawl.amazonbot.amazon. Next, perform a forward DNS lookup on the retrieved domain name to verify that it resolves back to the original IP address. This bidirectional verification process helps prevent spoofing attacks, as malicious actors could potentially set reverse DNS records to impersonate Amazonbot. Amazon publishes verified IP addresses for all its crawlers on the developer portal at developer.amazon.com/amazonbot/ip-addresses/, providing an additional reference point for verification.
Example verification process:
$ host 12.34.56.789
789.56.34.12.in-addr.arpa domain name pointer 12-34-56-789.crawl.amazonbot.amazon.
$ host 12-34-56-789.crawl.amazonbot.amazon
12-34-56-789.crawl.amazonbot.amazon has address 12.34.56.789
If you have questions about Amazonbot or need to report suspicious activity, contact Amazon directly at amazonbot@amazon.com and include relevant domain names in your message.
A critical distinction exists between Amazon’s crawlers regarding AI model training. Amazonbot may be used to train Amazon’s artificial intelligence models, making it relevant for content creators concerned about their work being used for AI training purposes. In contrast, Amzn-SearchBot and Amzn-User explicitly do NOT crawl content for generative AI model training, focusing solely on improving search experiences and supporting user queries. If you want to prevent your content from being used for AI model training, you can use the robots meta tag noarchive in your page’s HTML header, which instructs Amazonbot not to use the page for model training purposes. This distinction is important for publishers, creators, and website owners who want to maintain control over how their content is used in the AI training pipeline while still allowing their content to appear in Amazon search results and Rufus recommendations.
Rufus is Amazon’s advanced AI shopping assistant that leverages web crawling and AI technology to provide personalized shopping recommendations and assistance. While Amazonbot contributes to Amazon’s overall AI infrastructure, Rufus specifically uses Amzn-SearchBot for indexing product information and web content relevant to shopping queries. Rufus is built on Amazon Bedrock and utilizes advanced large language models including Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet and Amazon Nova, combined with a custom model trained on Amazon’s extensive product catalog, customer reviews, community Q&As, and web information. The shopping assistant helps customers research products, compare options, track prices, find deals, and even automatically purchase items when they reach target prices. Since its launch, Rufus has become remarkably popular, with over 250 million customers using it, monthly active users up 149%, and interactions increasing 210% year-over-year. Customers who use Rufus while shopping are over 60% more likely to make a purchase during that shopping session, demonstrating the significant impact of AI-powered shopping assistance on consumer behavior.
Website owners should develop a strategic approach to managing Amazon’s crawlers based on their specific business goals and content policies:
noarchive robots meta tag or block it entirely via robots.txtamazonbot@amazon.com with your domain information for personalized guidance if you have specific concerns or questions about how Amazon crawlers interact with your siteAmazonbot is Amazon's general-purpose crawler used to improve products and services, and it may be used for AI model training. Amzn-SearchBot is specifically designed for search experiences in Alexa and Rufus, and it explicitly does NOT crawl for AI model training. If you want to prevent AI training use, block Amazonbot but allow Amzn-SearchBot for search visibility.
Add the following lines to your robots.txt file at the root of your domain: User-agent: Amazonbot followed by Disallow: /. This will prevent Amazonbot from crawling your entire site. You can also use Disallow: /specific-path/ to block only certain directories.
Yes, Amazonbot may be used to train Amazon's artificial intelligence models. If you want to prevent this, use the robots meta tag in your page's HTML header, which instructs Amazonbot not to use the page for model training.
Perform a reverse DNS lookup on the crawler's IP address and verify the domain is a subdomain of crawl.amazonbot.amazon. Then perform a forward DNS lookup to confirm the domain resolves back to the original IP. You can also check Amazon's published IP addresses at developer.amazon.com/amazonbot/ip-addresses/.
Use standard robots.txt syntax: User-agent: Amazonbot to target the crawler, followed by Disallow: / to block all access or Disallow: /path/ to block specific directories. You can also use Allow: / to explicitly permit access.
Amazon typically reflects robots.txt changes within approximately 24 hours. Amazon fetches your robots.txt file regularly and maintains a cached copy for up to 30 days, so changes may take a full day to propagate through their systems.
Yes, absolutely. You can create separate rules for each crawler in your robots.txt file. For example, allow Amzn-SearchBot with User-agent: Amzn-SearchBot and Allow: /, while blocking Amazonbot with User-agent: Amazonbot and Disallow: /.
Contact Amazon directly at amazonbot@amazon.com. Always include your domain name and any relevant details about your concern in your message. Amazon's support team can provide personalized guidance for your specific situation.
Track mentions of your brand across AI systems like Alexa, Rufus, and Google AI Overviews with AmICited - the leading AI answers monitoring platform.

Discover how Amazon Rufus uses generative AI and machine learning to provide personalized product recommendations. Learn the technology, features, and impact on...

Learn about Amazon Rufus, the AI shopping assistant that answers product questions, compares items, and provides personalized recommendations. Discover how it w...
Complete guide to PerplexityBot crawler - understand how it works, manage access, monitor citations, and optimize for Perplexity AI visibility. Learn about stea...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.