
AI Visibility Attribution Model
Learn about AI Visibility Attribution Models - frameworks that use machine learning to assign credit to marketing touchpoints in customer journeys. Discover how...

An attribution model is a framework that assigns credit to marketing touchpoints and channels throughout a customer’s journey to determine which interactions influenced a conversion. It helps marketers understand the contribution of each marketing channel to revenue generation and optimize budget allocation accordingly.
An attribution model is a framework that assigns credit to marketing touchpoints and channels throughout a customer's journey to determine which interactions influenced a conversion. It helps marketers understand the contribution of each marketing channel to revenue generation and optimize budget allocation accordingly.
Attribution modeling is a systematic framework for assigning credit to marketing touchpoints and channels that contribute to a customer conversion. It answers the fundamental question: “Which marketing interactions influenced a customer’s decision to purchase?” Rather than crediting a single touchpoint, attribution models recognize that modern customer journeys involve multiple interactions across various channels—paid search, social media, email, content, and more—before a conversion occurs. By distributing conversion credit across these touchpoints according to predefined rules or algorithms, attribution models enable marketers to understand the true impact of each channel and optimize their marketing spend accordingly. This methodology has become essential for data-driven marketing organizations seeking to maximize return on investment and make informed budget allocation decisions.
The concept of attribution in marketing emerged from the need to understand customer behavior in increasingly complex digital environments. In the early days of digital marketing, last-click attribution dominated because it was simple to implement—analytics platforms like Google Analytics defaulted to this model. However, as customer journeys became more sophisticated with multiple touchpoints across channels, marketers recognized that last-click attribution was fundamentally flawed, often giving undue credit to remarketing campaigns while ignoring the awareness-building efforts that initiated the journey. According to McKinsey’s 2024 Digital Marketing Survey, 76% of marketers still struggle to determine which channels deserve credit for conversions, highlighting the persistent challenge of accurate attribution. The evolution from single-touch to multi-touch attribution models represents a maturation of marketing analytics, with companies now recognizing that understanding the entire customer journey is critical for competitive advantage. Today, advanced data-driven attribution powered by machine learning represents the frontier of attribution modeling, though many organizations still operate with simpler rule-based models due to implementation complexity and data infrastructure requirements.
Single-touch attribution models represent the simplest approach to credit assignment. First-touch attribution gives 100% of conversion credit to the initial interaction a customer had with your brand, making it ideal for measuring brand awareness and top-of-funnel effectiveness. Conversely, last-touch attribution assigns all credit to the final touchpoint before conversion, useful for identifying which channels are most effective at closing deals. Last non-direct attribution refines this by excluding direct traffic, attempting to credit the last meaningful marketing interaction. While these models are easy to implement and understand, they fundamentally oversimplify the customer journey by ignoring all other contributing touchpoints. According to research from the Digital Marketing Institute, companies without proper attribution models commonly misallocate up to 30% of their marketing budgets, often continuing to invest in underperforming channels while underutilizing high-performers.
Multi-touch attribution models distribute conversion credit across multiple touchpoints, providing a more realistic view of channel interactions. Linear attribution assigns equal credit to every touchpoint in the journey, valuing the entire customer experience equally. Time-decay attribution weights touchpoints based on proximity to conversion, giving more credit to recent interactions under the assumption that they are more influential in the final decision. Position-based (U-shaped) attribution allocates 40% credit to the first touch, 40% to the last touch, and splits the remaining 20% among middle touchpoints, recognizing that discovery and conversion moments are particularly critical. W-shaped attribution extends this concept by also crediting the lead creation moment, assigning 30% each to first touch, lead creation, and final conversion, with 10% distributed elsewhere. These models require more sophisticated tracking but provide significantly deeper insights into how channels work together throughout the buyer’s journey.
| Attribution Model | Credit Distribution | Best For | Key Advantage | Primary Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Touch | 100% to first interaction | Brand awareness campaigns | Identifies top-of-funnel effectiveness | Ignores nurturing and conversion efforts |
| Last-Touch | 100% to final interaction | Conversion optimization | Shows which channels close deals | Undervalues awareness and consideration phases |
| Linear | Equal credit to all touchpoints | Long, complex journeys | Values entire customer experience | Assumes all touchpoints equally important |
| Time-Decay | More credit to recent touchpoints | B2B sales cycles | Emphasizes decision-stage interactions | May undervalue initial awareness efforts |
| U-Shaped (Position-Based) | 40% first, 40% last, 20% middle | Lead generation focus | Balances discovery and conversion | Can undervalue mid-funnel nurturing |
| W-Shaped | 30% first, 30% lead creation, 30% last, 10% other | B2B with defined stages | Recognizes critical funnel moments | More complex to implement and track |
| Data-Driven (Algorithmic) | ML-determined based on actual impact | Complex multi-channel strategies | Most accurate credit assignment | Requires large data volumes and expertise |
Successful attribution modeling requires robust data infrastructure and consistent tracking practices. The foundation begins with unified data collection across all marketing channels—paid search, social media, email, content, display advertising, and offline touchpoints. This requires implementing consistent UTM tagging conventions across all campaigns, ensuring that every marketing URL contains standardized parameters for source, medium, campaign, content, and term. Without this foundational discipline, attribution data becomes unreliable and insights become questionable. The next critical layer involves identity resolution, the process of connecting different user interactions across devices, browsers, and sessions back to a single customer profile. A user might interact with your brand on their mobile phone, desktop computer, and work laptop—often clearing cookies between sessions. Advanced identity resolution uses first-party data, login information, and probabilistic matching to stitch these interactions together. According to research from Improvado, companies that invest time in proper tracking setup see 40% more accurate attribution data. The final infrastructure component involves centralizing data from disparate sources into a unified analytics environment, whether that’s a data warehouse, business intelligence platform, or dedicated attribution tool. This centralization eliminates data silos and enables consistent attribution calculations across all channels.
The business case for attribution modeling is compelling and well-documented. Organizations implementing advanced attribution models report significant improvements in marketing efficiency and revenue generation. Gartner’s latest marketing research indicates that companies using advanced attribution models achieve 15-30% lower customer acquisition costs and up to 40% improvement in marketing ROI compared to those relying on basic last-click attribution. These improvements stem from several mechanisms: first, accurate attribution reveals which channels are truly driving conversions, enabling budget reallocation toward high-performers; second, it identifies “assist channels” that don’t close deals but play critical roles in awareness and consideration, preventing the mistaken elimination of valuable touchpoints; third, it enables cohort-level analysis showing which customer segments respond best to specific channel combinations; and fourth, it provides insights into optimal touchpoint sequencing, revealing the most effective order and timing of marketing interactions. For a typical mid-sized business investing $1 million annually in digital marketing, the 30% budget misallocation problem identified by the Digital Marketing Institute translates to $300,000 in wasted spend. Implementing proper attribution modeling can recover a significant portion of this waste while simultaneously improving conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
In the context of AI monitoring and brand tracking through platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, attribution modeling takes on new dimensions. When customers discover your brand through AI-generated responses and subsequently convert, traditional attribution models may fail to capture this touchpoint because AI platforms operate outside conventional marketing channels. AmICited addresses this gap by tracking brand mentions across AI systems and attributing conversions back to these AI-driven touchpoints. This represents an emerging frontier in attribution modeling—understanding how AI-generated recommendations influence customer behavior. As AI systems become increasingly influential in customer discovery and decision-making, marketers must adapt their attribution frameworks to account for these new channels. The challenge lies in connecting AI mentions to actual conversions, requiring either explicit tracking mechanisms (like unique codes or UTM parameters in AI responses) or probabilistic attribution that correlates AI mentions with subsequent customer actions. Organizations monitoring their presence across AI platforms need to integrate this data into their broader attribution models to understand the complete customer journey in an AI-augmented world.
Modern attribution modeling faces unprecedented challenges from privacy regulations and technological changes. The deprecation of third-party cookies, driven by privacy concerns and regulatory requirements like GDPR and CCPA, fundamentally undermines user-level tracking that many attribution models depend upon. Walled gardens operated by major platforms like Facebook and Google limit visibility into user journeys once customers leave their ecosystems, creating blind spots in attribution analysis. Cross-device tracking remains technically challenging, particularly for users who switch between devices during their consideration phase. These challenges have prompted innovation in privacy-centric attribution approaches, including Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), which uses statistical analysis on aggregate data rather than individual user journeys, and cohort-based analysis, which groups users with similar characteristics rather than tracking individuals. Forward-thinking organizations are investing in first-party data strategies, building direct relationships with customers and collecting zero-party data through surveys and preference centers. The future of attribution modeling will likely involve hybrid approaches combining granular multi-touch attribution for digital channels with broader MMM techniques for offline and aggregate measurement, all while maintaining compliance with evolving privacy regulations.
The trajectory of attribution modeling points toward increasing sophistication, automation, and integration with artificial intelligence. Data-driven attribution powered by machine learning will become more accessible to mid-market organizations as platforms democratize these capabilities. According to Google’s Marketing Platform data, companies using AI-powered attribution see an average improvement of 27% in campaign performance across all channels. The convergence of attribution modeling with incrementality testing represents another frontier—moving beyond “what happened” to “what would have happened without this campaign” through control group analysis and causal inference. As AI-generated content and AI platform recommendations become increasingly influential in customer journeys, attribution frameworks must evolve to capture these touchpoints. The rise of unified measurement frameworks that combine multi-touch attribution for day-to-day optimization with marketing mix modeling for strategic planning will enable organizations to balance granular insights with holistic understanding. Privacy-enhancing technologies and data clean rooms will enable sophisticated attribution analysis without exposing individual user data. Organizations that master attribution modeling in this evolving landscape will gain significant competitive advantages, making more informed budget decisions, optimizing customer acquisition costs, and ultimately driving superior business outcomes. The integration of attribution insights with AI monitoring platforms like AmICited will become standard practice, enabling brands to understand their complete influence across both traditional and AI-driven discovery channels.
Single-touch attribution assigns 100% of conversion credit to one touchpoint, either the first or last interaction a customer had with your brand. Multi-touch attribution distributes credit across multiple touchpoints throughout the customer journey, providing a more comprehensive view of how different channels work together. Multi-touch models are generally more accurate for complex sales cycles but require more sophisticated tracking infrastructure.
The best attribution model depends on your sales cycle length, marketing channel complexity, and business goals. For short sales cycles and brand awareness focus, first-touch attribution works well. For conversion optimization, last-touch is useful. For complex B2B journeys, U-shaped or W-shaped models provide better insights. Start with a simpler model and evolve as your data quality improves.
Attribution modeling directly improves ROI by revealing which channels and touchpoints drive conversions. According to Gartner research, companies using advanced attribution models report 15-30% lower customer acquisition costs and up to 40% improvement in marketing ROI. Accurate attribution prevents budget misallocation and helps marketers invest more in high-performing channels.
Key challenges include data silos across marketing platforms, inconsistent tracking across channels, offline touchpoint integration, and privacy regulations affecting user-level tracking. Additionally, walled gardens like Facebook and Google limit cross-platform visibility. Overcoming these requires unified data infrastructure, consistent UTM tagging, and sometimes probabilistic modeling techniques.
Attribution models are essential for AI monitoring platforms like AmICited because they help track where brand mentions and conversions originate across AI-generated responses from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Understanding attribution in AI contexts helps brands measure the impact of AI-driven traffic and optimize their presence in AI systems.
Data-driven attribution uses machine learning algorithms to analyze converting and non-converting customer paths, assigning credit based on actual impact rather than predetermined rules. Rules-based models like linear or time-decay use fixed formulas. Data-driven attribution is more accurate but requires larger data volumes and sophisticated platforms to implement effectively.
Implement consistent UTM tagging across all campaigns, unify data from all marketing sources into a centralized platform, ensure identity resolution across devices and browsers, and establish clear conversion goals. Start with basic tracking setup before moving to complex models. Regular audits of tracking accuracy are essential for reliable attribution data.
Attribution models reveal which channels and touchpoints generate the most conversions, enabling data-driven budget decisions. Research shows companies commonly misallocate up to 30% of marketing budgets without proper attribution. By identifying high-performing channels and assist channels that support conversions, marketers can reallocate budgets to maximize ROI and reduce customer acquisition costs.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn about AI Visibility Attribution Models - frameworks that use machine learning to assign credit to marketing touchpoints in customer journeys. Discover how...
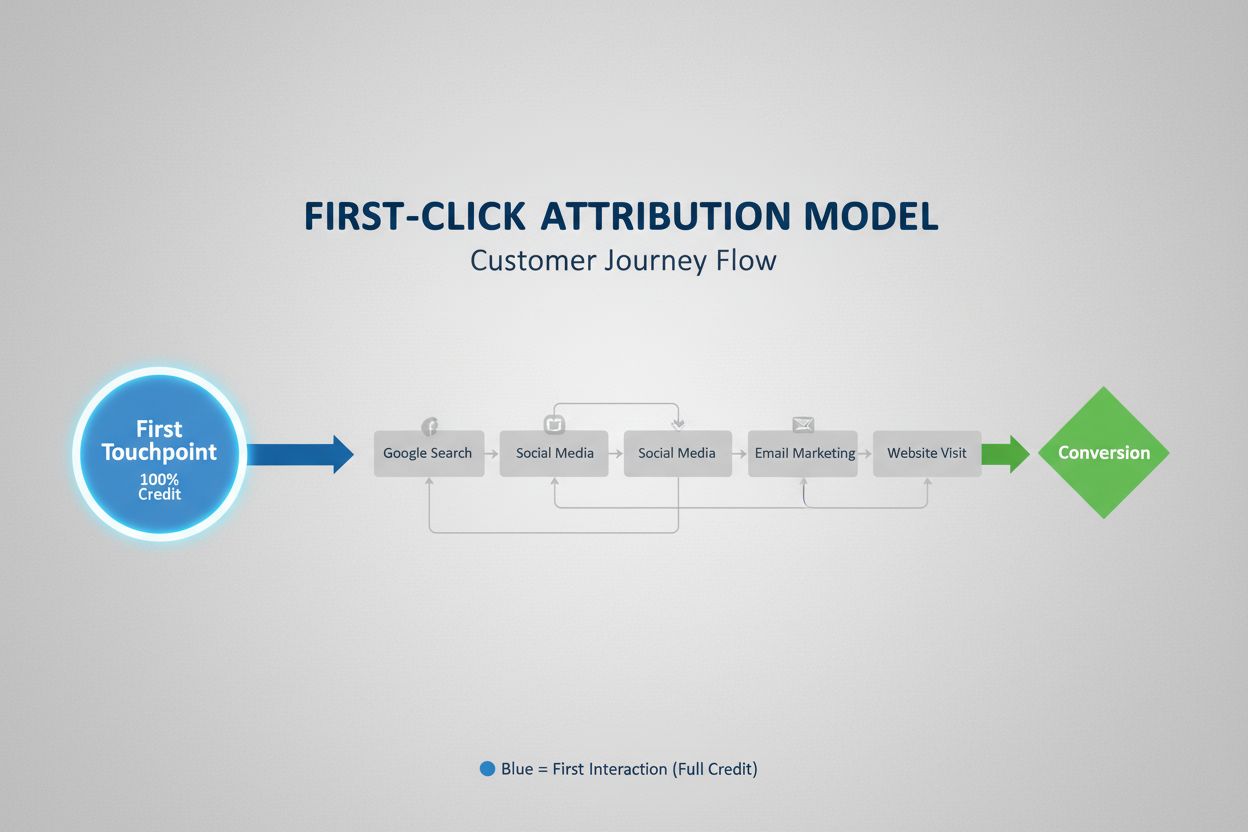
First-click attribution assigns 100% conversion credit to the first customer touchpoint. Learn how this model works, when to use it, and its impact on marketing...

Learn how AI conversion attribution tracks and credits sales to AI-influenced customer journeys. Discover how machine learning algorithms analyze multi-touch cu...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.