Co-Occurrence
Co-occurrence is when related terms appear together in content, signaling semantic relevance to search engines and AI systems. Learn how this concept impacts SE...

Co-citation is the frequency with which two websites, brands, or documents are mentioned together by third-party sources, signaling semantic relatedness to search engines and AI systems even without direct hyperlinks between them. This concept helps search algorithms and large language models understand topical relationships and authority associations between entities.
Co-citation is the frequency with which two websites, brands, or documents are mentioned together by third-party sources, signaling semantic relatedness to search engines and AI systems even without direct hyperlinks between them. This concept helps search algorithms and large language models understand topical relationships and authority associations between entities.
Co-citation is the frequency with which two websites, brands, or documents are mentioned together by third-party sources, creating a semantic association between them even without direct hyperlinks. In the context of search engine optimization and artificial intelligence, co-citation occurs when search engines and AI systems observe that two entities are regularly referenced in similar contexts, signaling topical relevance and authority relationships. This concept originated from bibliometrics—the academic field that analyzes citation patterns in scholarly research—and has become increasingly important in modern digital marketing as search algorithms and large language models evolve to understand contextual relationships beyond traditional link structures. Co-citation is fundamentally different from direct linking because it doesn’t require the two cited entities to reference each other; instead, a third party creates the association by mentioning both in the same content.
The concept of co-citation analysis emerged in academic research during the 1970s as scholars sought to understand relationships between published works based on how frequently they were cited together by other researchers. This methodology proved powerful for mapping intellectual landscapes and identifying influential works within specific fields. When search engines began incorporating link analysis into their ranking algorithms in the 1990s, SEO professionals recognized that co-citation principles could apply to web documents—if two websites were frequently linked together in the same content, search engines might infer a topical relationship between them. Over the past two decades, co-citation has evolved from a theoretical concept to a practical SEO consideration, with industry experts increasingly recognizing its importance. The rise of artificial intelligence and large language models has dramatically accelerated the relevance of co-citation, as LLMs rely heavily on co-citation patterns to understand which sources are authoritative and topically related, often prioritizing mentions over traditional backlinks. Research from 2024-2025 shows that nearly 90% of ChatGPT citations come from positions 21 and beyond in traditional Google search rankings, demonstrating that co-citation visibility in AI systems operates on entirely different principles than traditional SEO.
| Concept | Definition | Mechanism | Requires Links | Primary Value | AI Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Citation | Two entities mentioned together by a third party | Frequency of joint mentions | No | Semantic association and topical authority | Very High |
| Backlinks | Direct hyperlink from one site to another | Link equity transfer | Yes | Direct authority and referral traffic | Medium |
| Co-Occurrence | Related keywords appearing together in content | Keyword clustering and semantic relationships | No | Topical depth and contextual relevance | Very High |
| Bibliographic Coupling | Two documents that cite the same third document | Shared citation patterns | Yes | Document similarity and relationship | Medium |
| Unlinked Mentions | Brand or website referenced without a hyperlink | Textual reference only | No | Brand awareness and authority signals | Very High |
| Entity Association | Algorithmic understanding of entity relationships | Pattern recognition across multiple signals | No | Knowledge graph positioning | Very High |
Co-citation functions as a contextual signal that helps search engines and AI systems understand which websites, brands, and topics belong together in the digital landscape. When Google’s algorithms encounter multiple high-authority sources mentioning two websites in similar contexts—such as a blog post comparing two SaaS tools, an industry publication listing top competitors, or a Wikipedia article discussing related concepts—the search engine infers that these entities share topical relevance. This inference becomes particularly powerful when the co-citations occur across diverse, authoritative sources; if 50 different reputable websites mention Company A and Company B together when discussing a specific topic, Google’s algorithms develop strong confidence that these companies are semantically related. The strength of co-citation signals increases with frequency and source authority, meaning that co-citations from high-domain-authority sites like Forbes, TechCrunch, or industry-specific publications carry more weight than mentions from low-authority blogs. Large language models apply similar logic but with different emphasis: LLMs analyze co-citation patterns to determine which sources should appear together in generated responses, often prioritizing sources that are frequently mentioned alongside each other in their training data. This explains why certain brands consistently appear together in AI-generated product recommendations or industry comparisons—they have strong co-citation relationships established across the web.
The emergence of AI-powered search platforms has fundamentally changed how co-citation impacts brand visibility. Unlike traditional Google search, where ranking position determines visibility, AI systems generate responses by synthesizing information from multiple sources and citing those sources within the response. Research from the AI Visibility Index found that citations and mentions by LLMs are determined by the content you post and how often people talk about your brand, with no direct correlation to domain authority scores or link volumes. This represents a seismic shift in how brands should think about visibility: instead of optimizing for ranking position, brands must optimize for being mentioned and cited alongside authoritative sources in their industry. Platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude all rely on co-citation patterns to determine which sources to include in their responses, with Reddit leading at 40.1% of citations and Wikipedia at 26.3%. For brands using AmICited’s AI monitoring platform, tracking co-citation patterns reveals exactly which competitors your brand appears alongside in AI-generated responses, identifies gaps where you’re missing co-citation opportunities, and provides actionable insights for improving your AI visibility strategy. The data shows that most brands remain invisible in AI-generated responses despite having strong traditional SEO performance, highlighting the critical importance of understanding and optimizing co-citation patterns specifically for AI systems.
Strategic co-citation building requires a multi-faceted approach that combines content creation, relationship building, and strategic distribution. The most effective method is creating citation-worthy content—original research, comprehensive guides, unique frameworks, and data-backed insights that naturally attract mentions from other authoritative sources. When your content provides genuine value and original perspective, other websites and publications naturally mention it alongside related resources, creating organic co-citation. Beyond content creation, brands should actively pursue co-citation opportunities through strategic placement in high-authority publications, industry roundups, expert panels, and comparison articles. Appearing in “best of” lists, competitive analysis pieces, and industry guides alongside established competitors creates deliberate co-citation signals. Building relationships with journalists, industry influencers, and content creators increases the likelihood that your brand will be mentioned in contexts where competitors are also mentioned. Additionally, brands should ensure strong presence on high-citation platforms like Reddit, Wikipedia, and industry-specific publications, as these sources heavily influence LLM training data and response generation. The key is authenticity—forced or artificial co-citation attempts are easily detected by modern algorithms and can result in penalties. Instead, focus on genuinely earning mentions by providing superior content, expertise, and value that naturally positions your brand alongside industry leaders.
Unlinked mentions represent a critical evolution in how co-citation functions in modern SEO and AI visibility. Traditionally, SEO professionals focused on acquiring backlinks because they passed direct authority and were easily measurable. However, unlinked mentions—brand references without hyperlinks—now carry significant weight, particularly for AI systems that don’t rely on link structures. When your brand is mentioned in an article about industry trends, product comparisons, or expert roundups without a link, that mention still creates co-citation signals if competitors are mentioned in the same content. The rise of AI search has made unlinked mentions increasingly valuable because LLMs analyze text content directly without requiring link structures to understand relationships. Research shows that advanced SEOs now prioritize unlinked mention outreach because these mentions are “low-hanging fruit”—sites that already mention your brand clearly see value in your content, making them more receptive to adding a link when approached. Beyond link acquisition, unlinked mentions contribute to brand-driven SEO strategy by strengthening E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) through contextual references that help search engines understand your authority on specific topics. For AmICited users monitoring AI visibility, tracking unlinked mentions across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews reveals how your brand is being discussed and positioned relative to competitors, even when those mentions don’t include links back to your site.
Search engines use co-citation patterns to build and refine knowledge graphs—structured representations of entities and their relationships. When Google’s algorithms observe that two entities are frequently co-cited in authoritative sources, they strengthen the connection between those entities in the knowledge graph. This has profound implications for how brands are discovered and understood: if your brand is consistently co-cited with industry leaders, Google’s knowledge graph will position your brand as part of that authoritative cluster, improving visibility for related searches and queries. The knowledge graph also influences how entities appear in featured snippets, knowledge panels, and AI-generated responses. Co-citation patterns help search engines understand entity types and categories—for example, if a brand is frequently co-cited with other SaaS project management tools, the algorithm understands that this brand belongs in the “project management software” category. This categorical understanding then influences which search queries and AI prompts trigger your brand’s appearance. For brands seeking to establish authority in specific niches or categories, strategic co-citation building with category leaders is essential because it signals to search engines and AI systems that your brand belongs in that competitive set. This is particularly important for newer brands or those entering new markets, as co-citation with established players accelerates the algorithm’s understanding of your positioning and relevance.
Measuring co-citation effectiveness requires different tools and metrics than traditional SEO measurement. While backlinks can be tracked through tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz, co-citations require more sophisticated monitoring because they’re distributed across the entire web and multiple AI platforms. Brand monitoring tools like Semrush’s Brand Monitoring feature can identify unlinked mentions and co-citation opportunities by tracking where your brand appears alongside competitors. These tools filter mentions by authority, sentiment, and context, helping brands prioritize which co-citation opportunities to pursue. For AI-specific co-citation monitoring, platforms like AmICited, Otterly.AI, and Semrush’s Brand Performance track how your brand appears in AI-generated responses alongside competitors, revealing your share of voice in AI search results. Key metrics for co-citation performance include: frequency of co-mentions with target competitors, diversity of sources mentioning you together with competitors, authority of sources creating co-citations, and changes in co-citation frequency over time. Brands should also monitor sentiment and context of co-citations—appearing alongside competitors in positive, relevant contexts is more valuable than neutral or negative mentions. Advanced analytics can correlate co-citation patterns with ranking changes and AI visibility improvements, helping brands understand the ROI of co-citation building efforts. Quarterly reviews of co-citation performance help identify which competitors you’re most frequently associated with, which sources are creating the strongest co-citation signals, and where gaps exist in your co-citation strategy.
Co-citation is poised to become the dominant visibility signal as AI-driven search continues to grow. Market projections suggest that LLM traffic will capture 15% of the search market by 2028, with some analysts predicting it could overtake traditional search by 2027. As this shift occurs, co-citation will likely become more important than traditional backlinks for overall brand visibility because AI systems fundamentally operate differently than search engines. Unlike Google, which ranks individual pages for specific keywords, LLMs generate contextual responses that cite multiple sources, making co-citation patterns the primary determinant of which sources appear in those responses. The future of co-citation will likely involve more sophisticated AI analysis of mention context and quality, with LLMs potentially weighing co-citations based on factors like author expertise, source credibility, and relevance to the specific query. This means that appearing alongside competitors in high-quality, authoritative content will become increasingly valuable, while mentions in low-quality or irrelevant contexts may carry less weight. Additionally, cross-platform co-citation patterns will become more important as different AI systems (ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity) develop their own citation preferences and training data. Brands that build strong co-citation networks across multiple platforms and content types will have significant competitive advantages as AI search becomes the primary discovery mechanism. The integration of real-time data and dynamic co-citation analysis will enable more sophisticated optimization, allowing brands to identify and capitalize on emerging co-citation opportunities as they develop. For forward-thinking organizations, investing in co-citation strategy now—before it becomes the dominant visibility metric—represents a significant competitive advantage in the AI-driven search landscape.
Implementing an effective co-citation strategy requires systematic planning and execution across multiple channels. Start by conducting a co-citation audit to understand which competitors your brand is currently mentioned alongside, which sources are creating these co-citations, and where gaps exist. Use tools like Semrush Brand Monitoring or AmICited to identify unlinked mentions and co-citation opportunities, then prioritize based on source authority, relevance, and conversion potential. Next, develop a content strategy focused on creating citation-worthy content—original research, comprehensive guides, unique frameworks, and data-backed insights that naturally attract mentions from authoritative sources. This content should address gaps in your current co-citation profile, positioning your brand alongside the competitors you want to be associated with. Build relationships with journalists, industry influencers, and content creators who regularly write about your industry, as these relationships increase the likelihood of strategic co-citation placement. Participate in industry roundups, expert panels, and comparison articles where your brand can appear alongside established competitors. Ensure strong presence on high-citation platforms like Reddit, Wikipedia, and industry-specific publications, as these sources heavily influence LLM training data. Finally, monitor co-citation performance regularly using brand monitoring and AI visibility tools, adjusting your strategy based on performance data and emerging opportunities. The key is consistency—co-citation building is a long-term strategy that compounds over time, with sustained efforts yielding increasingly strong semantic associations and authority signals.
Co-citation does not require a direct hyperlink between two websites. Instead, it occurs when both sites are mentioned in the same third-party content without necessarily linking to each other. While backlinks pass direct authority and referral traffic, co-citations establish semantic relationships and topical associations. Both signals work together in modern SEO, with co-citations becoming increasingly important for AI visibility where LLMs prioritize mentions over links.
Large language models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google's AI Overviews rely heavily on co-citation patterns to understand which brands and websites are topically related and authoritative. Unlike traditional search engines that emphasize backlinks, LLMs prioritize content mentions and associations. Research shows that Reddit leads LLM citations at 40.1% and Wikipedia at 26.3%, with co-citation patterns determining which sources appear together in AI-generated responses.
While Google has not officially confirmed co-citation as a ranking factor, substantial evidence suggests it influences how search engines understand topical relevance and entity relationships. Co-citations help Google's algorithms cluster related websites and understand semantic connections, which can indirectly support rankings by establishing authority associations. The concept is particularly valuable for newer sites seeking to build topical authority alongside established competitors.
Co-citation refers to how often two URLs are linked together in the same web document, while co-occurrence focuses on how related keywords and terms appear together across content. Co-citation is link-based, whereas co-occurrence is keyword-based. Both concepts help search engines understand semantic relationships, but co-occurrence is particularly important for AI systems that analyze keyword clustering and topical depth without relying on traditional link signals.
Brands can build co-citation by creating content that naturally attracts mentions alongside competitors, participating in industry roundups and expert panels, contributing to high-authority publications, and building relationships with journalists and content creators. Appearing in 'best of' lists, comparison articles, and industry guides alongside established competitors creates co-citation signals. Additionally, brands should ensure they're mentioned in relevant Wikipedia articles, Reddit discussions, and authoritative industry resources where LLMs source information.
AmICited tracks co-citation patterns across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude to show when your brand appears alongside competitors in AI-generated responses. This monitoring reveals how your brand is positioned relative to competitors in AI visibility, identifies co-citation opportunities you're missing, and helps optimize your presence in AI search results where traditional ranking metrics don't apply.
Yes, co-citation can theoretically be manipulated through coordinated mentions or paid placements, but search engines actively detect and penalize such schemes. Google's algorithms assess link quality and mention context to identify artificial co-citation patterns. John Mueller has stated that Google takes action both algorithmically and manually against artificial link building and coordinated mention schemes, sometimes ignoring all links from sites engaged in such practices.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Co-occurrence is when related terms appear together in content, signaling semantic relevance to search engines and AI systems. Learn how this concept impacts SE...

Learn how co-occurrence patterns help AI search engines understand semantic relationships between terms, improve content ranking, and enhance AI-generated answe...
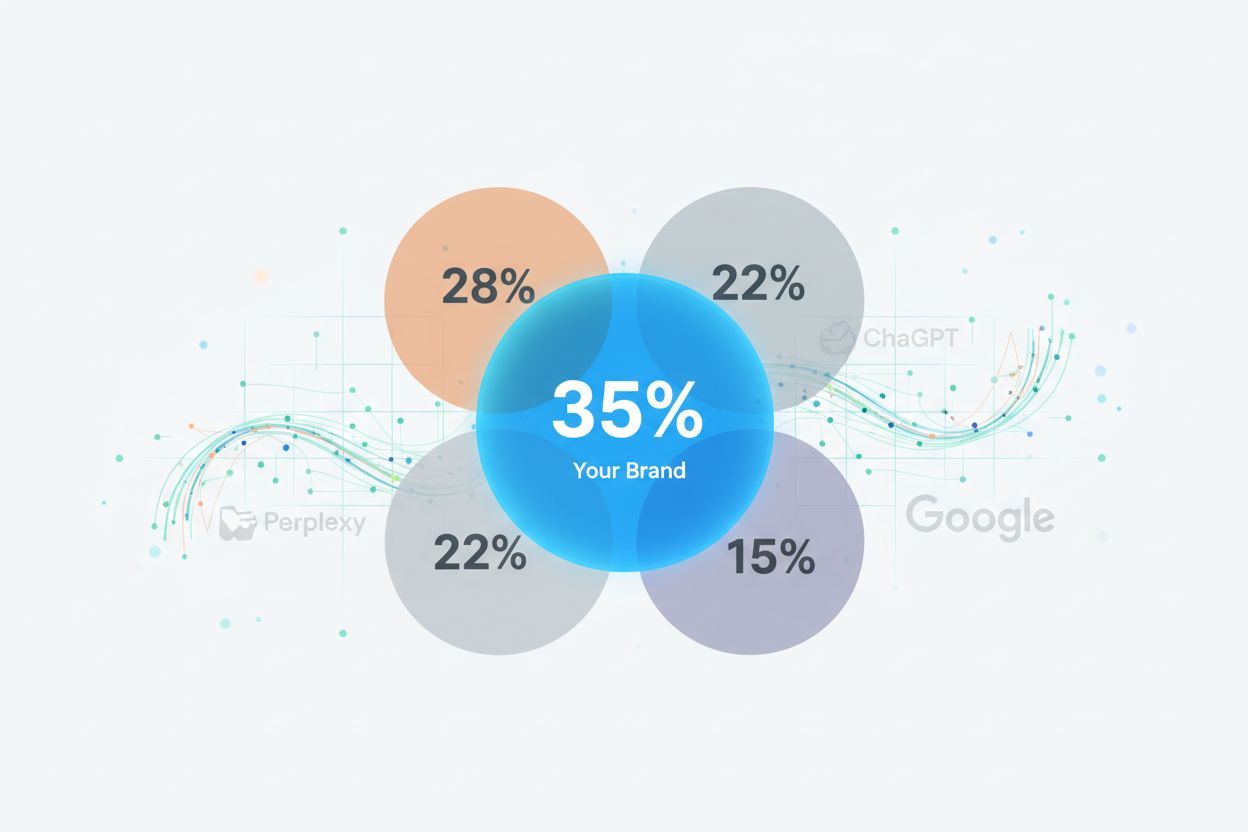
Learn what Citation Share Analysis is and how to measure your brand's competitive position in AI-generated answers. Discover tools, metrics, and strategies for ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.