AI Content Generation
Learn what AI content generation is, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and best practices for using AI tools to create marketing content optimized for ...
Content grounding is the process of anchoring AI-generated responses to verified, factual information sources, ensuring accuracy and preventing hallucinations. It connects AI outputs to reliable data sources, knowledge bases, and real-time information systems to maintain factual accuracy and trustworthiness. This technique is critical for applications where accuracy impacts user safety, financial decisions, or professional outcomes. By implementing content grounding, organizations dramatically reduce misinformation propagation and increase user confidence in AI systems.
Content grounding is the process of anchoring AI-generated responses to verified, factual information sources, ensuring accuracy and preventing hallucinations. It connects AI outputs to reliable data sources, knowledge bases, and real-time information systems to maintain factual accuracy and trustworthiness. This technique is critical for applications where accuracy impacts user safety, financial decisions, or professional outcomes. By implementing content grounding, organizations dramatically reduce misinformation propagation and increase user confidence in AI systems.
Content grounding is the process of anchoring artificial intelligence-generated responses to verified, factual information sources rather than allowing models to generate plausible-sounding but potentially inaccurate content. This technique directly addresses the hallucination problem, where large language models produce confident but false or misleading information that appears credible to users. By connecting AI outputs to reliable data sources, knowledge bases, and real-time information systems, content grounding ensures that generated content remains factually accurate and trustworthy. The primary benefit of implementing content grounding is the dramatic reduction in misinformation propagation, which is critical for applications where accuracy directly impacts user safety, financial decisions, or professional outcomes. Organizations implementing content grounding report increased user confidence and reduced liability risks associated with AI-generated content.
Content grounding delivers substantial business value across multiple industries and use cases, transforming how organizations deploy AI systems in customer-facing and mission-critical applications:
Healthcare and Medical Services: Grounded AI systems provide accurate medication information, treatment recommendations, and diagnostic support by referencing verified medical databases and clinical guidelines, reducing the risk of harmful misinformation that could affect patient outcomes.
Financial Services and Banking: Financial institutions use grounded AI to deliver accurate interest rates, loan terms, compliance information, and market data, ensuring regulatory compliance and protecting customers from misleading financial advice.
Legal and Compliance: Law firms and corporate legal departments leverage grounded AI to cite specific statutes, case law, and regulatory requirements, maintaining the accuracy necessary for legal documentation and reducing malpractice exposure.
Customer Support and Service: E-commerce and SaaS companies implement grounded AI chatbots that reference actual product specifications, pricing, inventory systems, and support documentation, improving customer satisfaction and reducing support ticket escalations.
Education and Training: Educational institutions use grounded AI tutoring systems that cite textbooks, academic sources, and verified learning materials, ensuring students receive accurate information while developing critical thinking about source attribution.
The technical implementation of content grounding employs several distinct methodologies, each with specific advantages and limitations depending on the use case and data architecture. The following table compares the primary grounding techniques currently used in production systems:
| Grounding Technique | Description | Primary Use Cases | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | Combines document retrieval with language model generation, fetching relevant information before generating responses | Customer support, knowledge base queries, FAQ systems | Highly accurate for structured data, reduces hallucinations significantly | Requires well-organized knowledge bases, latency from retrieval step |
| Knowledge Graph Integration | Embeds structured semantic relationships between entities and facts into the generation process | Healthcare systems, financial services, enterprise knowledge management | Captures complex relationships, enables reasoning across domains | Expensive to build and maintain, requires domain expertise |
| Real-Time Data Binding | Connects AI models directly to live databases and APIs for current information | Financial markets, inventory systems, weather services, real-time pricing | Always provides current information, eliminates stale data problems | Requires robust API infrastructure, potential latency issues |
| Citation and Attribution | Explicitly links generated content to source documents with page numbers and references | Legal documents, academic writing, research synthesis | Provides transparency and verifiability, builds user trust | Requires source material availability, increases response complexity |
These techniques can be combined in hybrid approaches to maximize accuracy and relevance for specific organizational needs.
Implementing content grounding requires selecting and combining specific techniques tailored to organizational requirements and data infrastructure. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents the most widely adopted approach, where AI systems first search relevant documents or databases before generating responses, ensuring outputs remain tethered to verified information. Semantic search enhances RAG by understanding the meaning behind queries rather than simple keyword matching, improving the relevance of retrieved information. Fact verification layers add additional validation by cross-referencing generated claims against multiple authoritative sources before presenting responses to users. Dynamic context injection allows systems to incorporate real-time data from APIs and databases directly into the generation process, ensuring responses reflect current information rather than training data from months or years prior. Organizations implementing these techniques typically see 40-60% reductions in factual errors compared to ungrounded baseline systems. The choice of implementation depends on factors including data volume, required response latency, domain complexity, and available computational resources.
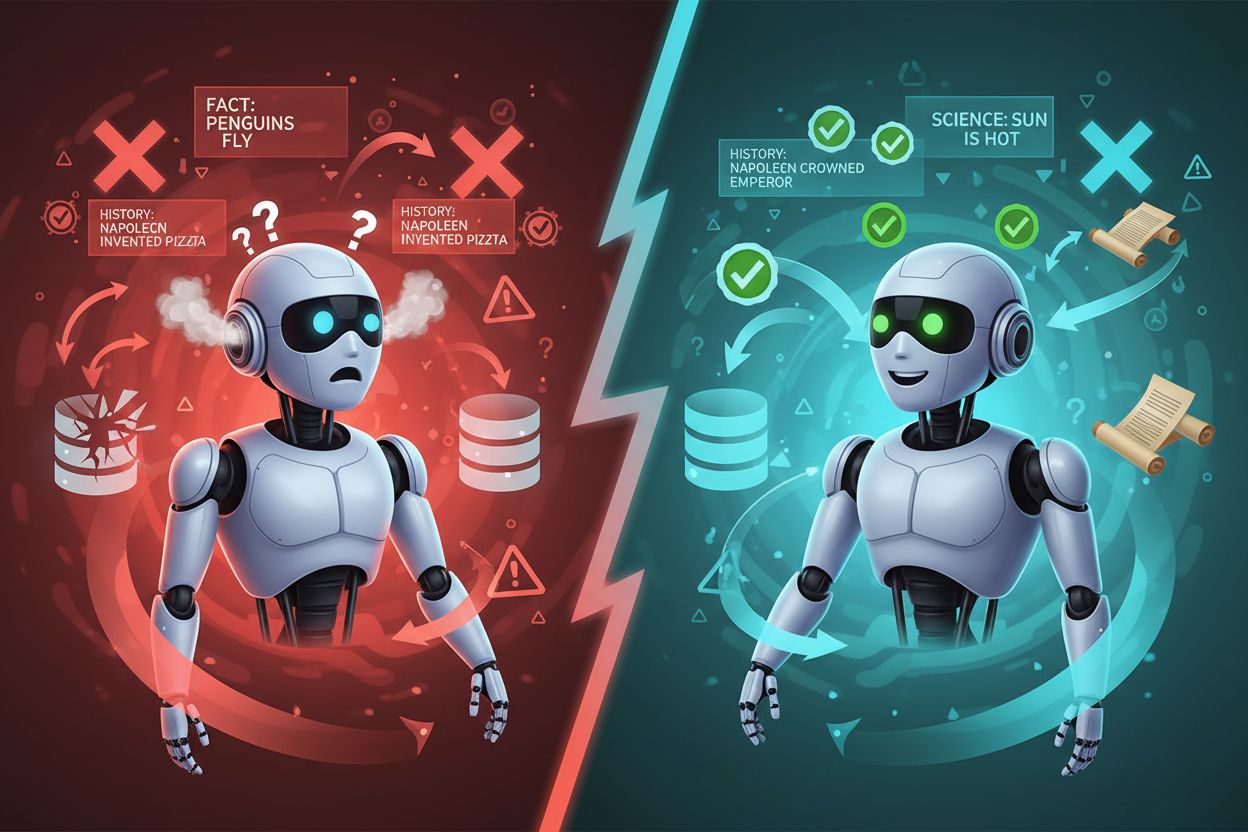
The distinction between grounded content and hallucinated content represents a fundamental divide in AI reliability and trustworthiness. Hallucinations occur when language models generate plausible-sounding information that has no basis in their training data or available knowledge sources—for example, a medical AI inventing a fictional drug interaction or a financial chatbot citing non-existent interest rates. Grounded systems prevent this by requiring that every factual claim be traceable to a verified source, creating an auditable chain of evidence. Consider a customer service scenario: an ungrounded AI might confidently state that a product includes a feature it doesn’t actually have, while a grounded system would only reference features documented in the actual product specification database. In healthcare applications, the consequences become even more critical—a grounded system would refuse to recommend a treatment not supported by clinical guidelines, whereas an ungrounded system might generate plausible-sounding but dangerous medical advice. The psychological impact of hallucinations is particularly insidious because users often cannot distinguish confident falsehoods from accurate information, making grounding essential for maintaining institutional credibility. Research from major AI providers demonstrates that grounding reduces factual error rates by 70-85% in production systems.
Real-world applications of content grounding demonstrate its transformative impact across diverse sectors and organizational contexts. In healthcare, systems like those developed by major medical AI companies now ground diagnostic support tools in peer-reviewed literature and clinical trial databases, enabling physicians to receive evidence-based recommendations with full source attribution. Financial institutions implement grounded AI for regulatory compliance, where every statement about interest rates, fees, or investment products must reference current pricing databases and compliance documentation, reducing regulatory violations and customer disputes. Legal departments use grounded systems to generate contract language and legal memoranda that cite specific statutes and case law, with every reference verifiable and traceable to authoritative legal databases. Customer support operations at major e-commerce companies deploy grounded chatbots that reference live inventory systems, pricing databases, and product specification documents, reducing customer frustration from inaccurate information. Educational platforms implement grounded tutoring systems that cite textbooks and academic sources, helping students understand not just answers but the authoritative basis for those answers. Insurance companies use grounded AI to explain policy coverage by referencing actual policy documents and regulatory requirements, reducing claims disputes and improving customer trust. These implementations consistently demonstrate that grounding increases user satisfaction, reduces operational costs from error correction, and significantly improves regulatory compliance.
Several enterprise platforms and tools have emerged to facilitate content grounding implementation, each offering distinct capabilities for different organizational contexts. Google Vertex AI provides built-in grounding capabilities through its Search Grounding feature, allowing enterprises to ground Gemini model responses in Google Search results and custom knowledge bases, with particular strength in real-time information integration. Microsoft Azure offers grounding through its Cognitive Search service combined with language models, enabling organizations to build RAG systems that reference enterprise data while maintaining security and compliance requirements. K2View specializes in grounding for customer data platforms, ensuring that AI-generated customer insights and recommendations are grounded in verified customer data rather than statistical inference. Moveworks implements grounding specifically for enterprise IT support, where AI agents ground responses in actual IT systems, knowledge bases, and service catalogs to provide accurate technical support. AmICited.com serves as a specialized monitoring solution for content grounding, tracking whether AI-generated content properly cites and grounds claims in source material, providing organizations with visibility into grounding effectiveness and identifying instances where AI systems generate unsupported claims. These platforms can be deployed individually or in combination, depending on organizational architecture and specific grounding requirements.
Implementing content grounding effectively requires a strategic approach that extends beyond technology selection to encompass organizational processes and quality assurance. Data preparation is foundational—organizations must audit and structure their knowledge sources, ensuring that information used for grounding is accurate, current, and properly indexed for retrieval. Source prioritization involves establishing hierarchies of information reliability, where medical AI systems might prioritize peer-reviewed journals over general web content, while financial systems prioritize official regulatory databases. Latency optimization becomes critical in customer-facing applications, requiring organizations to balance the accuracy benefits of comprehensive grounding against response time requirements. Feedback loops should be implemented to continuously monitor grounding effectiveness, identifying cases where retrieved sources don’t adequately support generated claims and refining retrieval strategies accordingly. User transparency requires clearly communicating to end users when and how content is grounded, building trust through visibility into the sources supporting AI-generated information. Regular audits using tools like AmICited.com help organizations verify that grounding systems continue functioning effectively as data sources evolve and new information emerges. Organizations that treat grounding as an ongoing operational practice rather than a one-time implementation achieve significantly better long-term accuracy and user trust.
The future of content grounding will likely involve increasingly sophisticated integration of multiple grounding techniques, real-time data sources, and verification mechanisms as AI systems become more deeply embedded in critical decision-making processes. Multimodal grounding is emerging as a frontier, where AI systems ground responses not just in text but in images, videos, and structured data simultaneously, enabling more comprehensive verification. Decentralized verification networks may eventually allow organizations to verify AI-generated claims against distributed sources of truth, reducing dependence on centralized knowledge bases. Automated source evaluation systems are being developed to assess the reliability and bias of grounding sources themselves, ensuring that grounding doesn’t simply propagate existing biases in source material. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to require content grounding in high-stakes domains like healthcare and finance, making grounding a compliance requirement rather than an optional feature. As these trends mature, content grounding will transition from a competitive advantage to a baseline expectation for any AI system operating in regulated or high-consequence domains, fundamentally reshaping how organizations approach AI deployment and user trust.
Content grounding provides real-time context without retraining the model, allowing AI systems to reference current information and specific data sources. Fine-tuning, by contrast, permanently modifies model behavior through retraining on new data. Grounding is faster to implement and more flexible for changing information, while fine-tuning creates permanent behavioral changes in the model.
Content grounding significantly reduces hallucinations by 70-85% in production systems, but cannot eliminate them entirely. The effectiveness depends on implementation quality, source data accuracy, and the sophistication of the retrieval and verification mechanisms. Even grounded systems can produce hallucinations if source data is incomplete or ambiguous.
Key challenges include ensuring data quality and currency of source materials, managing latency from retrieval operations, integrating with existing systems, and maintaining source accuracy over time. Organizations must also establish processes for continuous monitoring and updating of grounding sources as information evolves.
Content grounding increases transparency by providing verifiable sources for AI-generated claims, enabling users to fact-check information independently. This visibility into the reasoning process and source attribution builds confidence that AI systems are reliable and not fabricating information, significantly improving user trust.
The most effective grounding sources include structured databases with verified information, knowledge graphs with semantic relationships, peer-reviewed documents and academic sources, real-time APIs for current data, and official regulatory or compliance documentation. The best choice depends on the specific use case and required accuracy level.
Content grounding is critical for high-stakes applications like healthcare, finance, legal services, and regulatory compliance where accuracy directly impacts decisions. For creative applications like fiction writing or brainstorming, grounding may be less necessary. The necessity depends on whether factual accuracy is a primary requirement.
AmICited.com tracks how AI systems reference and cite sources across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, providing visibility into whether AI-generated content properly grounds claims in verifiable sources. It helps organizations monitor brand mentions and ensure their content is accurately cited by AI systems.
Content grounding introduces slight latency increases due to the retrieval and verification operations required before generating responses. However, this performance cost is typically offset by improved accuracy, reduced error correction costs, increased user satisfaction, and better regulatory compliance, making it a worthwhile trade-off for most enterprise applications.
Ensure your brand is properly cited and your content is grounded in verifiable sources across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Track how AI systems reference your information and maintain content accuracy.

Learn what AI content generation is, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and best practices for using AI tools to create marketing content optimized for ...

Learn proven techniques to humanize AI-generated content for better citations in AI answer generators. Improve authenticity, boost visibility in AI search resul...

Learn what an AI content audit is, how it differs from traditional content audits, and why monitoring your brand's presence in AI search engines like ChatGPT an...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.