
How Gen Z Uses AI for Search: Adoption Rates, Platforms, and Behavior Trends
Discover how Gen Z is using AI for search with 76% trusting AI over Google. Learn adoption rates across ChatGPT, Perplexity, TikTok, and Reddit platforms.

Cross-generational AI adoption refers to the varying rates, patterns, and approaches that different age cohorts employ when integrating artificial intelligence tools into their daily lives and work. This phenomenon reveals how generational values, technological literacy, and life stage priorities shape interactions with AI systems. Understanding these differences is essential for creating inclusive AI solutions that resonate across demographic boundaries. Each generation—from Gen Z to Baby Boomers—brings distinct perspectives, concerns, and use cases to the AI landscape.
Cross-generational AI adoption refers to the varying rates, patterns, and approaches that different age cohorts employ when integrating artificial intelligence tools into their daily lives and work. This phenomenon reveals how generational values, technological literacy, and life stage priorities shape interactions with AI systems. Understanding these differences is essential for creating inclusive AI solutions that resonate across demographic boundaries. Each generation—from Gen Z to Baby Boomers—brings distinct perspectives, concerns, and use cases to the AI landscape.
Cross-generational AI adoption refers to the varying rates, patterns, and approaches that different age cohorts employ when integrating artificial intelligence tools and technologies into their daily lives, work, and decision-making processes. This phenomenon is critical to understand because it reveals how generational values, technological literacy, and life stage priorities shape the way individuals interact with AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Rather than treating AI adoption as a monolithic trend, cross-generational analysis demonstrates that each generation—from Gen Z to Baby Boomers—brings distinct perspectives, concerns, and use cases to the AI landscape. Understanding these differences is essential for organizations, educators, and technology providers seeking to create inclusive AI solutions that resonate across demographic boundaries.

The adoption of AI technologies varies significantly across generational lines, with younger cohorts demonstrating substantially higher engagement rates than their older counterparts. Research data reveals a compelling narrative: Gen Z leads the charge with 70% using generative AI weekly, while Baby Boomers lag at just 20% weekly usage. However, the data also uncovers a surprising convergence point—teens and adults under 60 show remarkably similar adoption rates between 45-53%, suggesting that age-related barriers diminish significantly before retirement years. The following table provides a comprehensive breakdown of generational AI adoption patterns:
| Generation | Birth Years | Weekly AI Usage Rate | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gen Z | 1997-2012 | 70% | Early adopters; 93% use 2+ AI tools; education, content creation, entrepreneurship focus |
| Millennials | 1981-1996 | 56-62% | Pragmatic users; 90% comfortable with AI; workplace productivity, parenting, shopping |
| Gen X | 1965-1980 | ~33% | Selective adopters; 55% believe AI improves lives; task automation, smart home, health tracking |
| Baby Boomers | 1946-1964 | 20% | Cautious users; 49% distrust AI; voice assistants, customer support, photo apps |
This generational spectrum demonstrates that AI adoption is not simply a function of age, but rather reflects distinct technological comfort levels, life priorities, and trust relationships with emerging technologies.
Generation Z represents the vanguard of AI adoption, with 70% engaging with generative AI on a weekly basis and an impressive 93% actively using two or more AI tools simultaneously. This generation’s relationship with AI is fundamentally different from their predecessors—it’s not a novelty to be cautiously approached, but rather an integrated utility woven into their daily routines. Gen Z’s AI usage spans multiple critical life domains:
Despite their enthusiasm, Gen Z faces a significant psychological barrier: 61% express worry about job displacement, reflecting legitimate concerns about how AI might reshape employment landscapes before they fully establish their careers. This anxiety coexists with their practical embrace of AI tools, creating a complex relationship where adoption and apprehension develop in parallel.
Millennials occupy a pragmatic middle ground in the AI adoption spectrum, with 56-62% using AI regularly in workplace contexts and 90% expressing comfort with AI technologies overall. This generation, often characterized as the “bridge generation” between analog and digital natives, approaches AI with a utilitarian mindset shaped by their experience navigating multiple technological transitions throughout their lives. Millennials have integrated AI into their professional workflows for productivity enhancement, automating routine tasks like email management, scheduling, and data analysis that free up cognitive resources for higher-value work.
Beyond the workplace, Millennials leverage AI for parenting support—seeking advice on child development, educational resources, and behavioral strategies—reflecting their generation’s data-driven approach to family life. Their shopping behaviors have been transformed by AI-powered recommendations and price comparison tools, while fitness and wellness applications powered by AI provide personalized workout plans and nutritional guidance. The 90% comfort rate among Millennials suggests this generation views AI not as a threat but as a tool that enhances their already-busy lives, allowing them to optimize time management across professional, familial, and personal domains. This pragmatic acceptance positions Millennials as crucial bridge-builders in organizational settings, capable of translating AI benefits to both younger and older colleagues.
Generation X demonstrates selective, pragmatic AI adoption at approximately 33% regular usage rates, yet 55% believe AI will meaningfully improve their lives—a statistic that suggests growing openness despite current lower engagement levels. This generation’s approach to AI reflects their historical positioning as independent problem-solvers who adopt technology when it demonstrably solves real challenges rather than for novelty’s sake. Gen X has embraced AI for task automation, using intelligent systems to streamline household management, bill payment, and administrative responsibilities that accumulate during their peak earning and caregiving years.
The appeal of smart home technology resonates strongly with Gen X, who appreciate the convenience and efficiency gains from voice-activated assistants and automated climate control systems. Health tracking and wellness monitoring through AI-powered devices align with Gen X’s increasing focus on preventive healthcare and longevity as they navigate midlife and beyond. Additionally, Gen X values AI applications for financial security and retirement planning, leveraging algorithmic analysis to optimize investment portfolios and long-term financial strategies. Their measured adoption pattern suggests that as AI tools become more intuitive and demonstrate clear ROI, Gen X adoption rates will likely accelerate significantly in coming years.
Baby Boomers represent the most cautious generational cohort, with only 20% using AI weekly and 49% expressing active distrust of AI technologies, yet they are not entirely resistant to AI integration. This generation’s skepticism is understandable given their lifetime of technological disruption and legitimate concerns about privacy, security, and the replacement of human interaction with algorithmic systems. Despite these reservations, Boomers have found practical value in specific AI applications that enhance their quality of life without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
Voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant have gained traction among Boomers for hands-free control of smart home devices and quick information retrieval, while AI-powered customer support systems provide convenient access to services without navigating complex phone menus. Photo organization and enhancement applications powered by AI appeal to Boomers’ desire to preserve and share memories with family members. The most significant barrier to broader Boomers adoption is privacy concerns, with 77% expressing worry about data collection and misuse—a legitimate apprehension that organizations must address through transparent data practices and clear communication. As Boomers witness AI’s practical benefits through their children and grandchildren, and as companies implement stronger privacy protections, this generation’s adoption rates are gradually warming, though at a pace distinctly slower than younger cohorts.
Trust and privacy concerns represent the primary barriers preventing broader AI adoption across all generations, with significant variation in both the intensity of concerns and the specific issues that trigger skepticism. Understanding these generational differences in trust dynamics is essential for organizations seeking to expand their AI user base and build sustainable adoption strategies. The following table illustrates the relationship between generational cohorts and their primary barriers to AI adoption:
| Generation | Main Barriers | Trust Level |
|---|---|---|
| Gen Z | Job displacement (61% worried); misinformation concerns; data monetization | Moderate-High (pragmatic trust) |
| Millennials | Privacy concerns; algorithmic bias; workplace surveillance | High (conditional trust) |
| Gen X | Privacy concerns; complexity of use; unclear ROI; security risks | Moderate (cautious optimism) |
| Baby Boomers | Privacy concerns (77%); distrust of AI (49%); complexity; loss of human touch | Low (skeptical acceptance) |
Across all generations, privacy emerges as the dominant concern, with 68-77% of non-users citing data protection worries as their primary hesitation. This universal concern transcends age demographics and represents the single most important factor organizations must address through transparent policies, robust security measures, and clear communication about data usage. Notably, Gen Z’s primary concern differs slightly—job displacement anxiety reflects their forward-looking perspective on career viability—while older generations prioritize immediate privacy and security threats. Building trust requires not just technical safeguards but also generational communication strategies that address each cohort’s specific anxieties.
Organizations seeking to maximize cross-generational AI adoption must implement deliberate, multi-faceted strategies that acknowledge generational differences while building inclusive technology ecosystems. The first critical approach involves tailored training programs that meet each generation where they are—providing hands-on, in-person instruction for Baby Boomers and Gen X, while offering self-directed, digital-first learning for Millennials and Gen Z. These training initiatives should emphasize practical applications relevant to each generation’s priorities rather than abstract technical concepts.
Cross-generational mentorship programs create powerful learning opportunities where younger employees guide older colleagues through AI tools while older workers share institutional knowledge and critical thinking skills that prevent over-reliance on algorithmic recommendations. Organizations must balance high-tech innovation with high-touch human interaction, ensuring that AI implementation doesn’t eliminate the personal relationships and human judgment that older generations value. Leadership championing of AI adoption—with visible executive commitment to learning and using these tools—signals organizational seriousness and encourages skeptical employees to engage. Finally, clear, transparent communication about AI capabilities, limitations, privacy protections, and job security implications addresses the trust barriers that prevent adoption. Organizations that implement these strategies simultaneously rather than sequentially will see accelerated adoption curves across all demographic groups.
Generational differences in workplace technology preferences significantly impact organizational productivity, retention, and innovation capacity. Gen Z and Millennials expect seamless AI integration into their workflows and view organizations lacking modern AI tools as technologically backward, directly influencing their employment decisions and long-term retention. Conversely, Gen X and Baby Boomers prioritize clear communication about why AI is being implemented, how it will affect their roles, and what training and support will be provided—preferences that reflect their desire for stability and transparency in organizational change.
Communication preferences diverge sharply across generations: younger workers prefer asynchronous, digital communication channels and self-service learning resources, while older workers value synchronous, in-person training and direct access to human support specialists. Productivity gains from AI adoption are most pronounced when organizations customize implementation to these preferences rather than imposing one-size-fits-all approaches. The impact on retention is substantial—organizations that successfully bridge generational AI preferences report higher engagement scores, lower turnover, and stronger cross-generational collaboration. Conversely, organizations that ignore generational preferences risk losing talented older workers who feel unsupported during technological transitions and younger workers who perceive the organization as technologically stagnant. The most successful organizations recognize that generational diversity in the workplace is an asset that requires intentional management and customized approaches to technology adoption.
The trajectory of cross-generational AI adoption points toward convergence, as older generations gradually increase their engagement with AI tools and younger generations develop more nuanced, critical perspectives on AI’s limitations and risks. This convergence will likely stabilize around 60-70% regular AI usage across all age groups within the next 3-5 years, driven by improved user interfaces, stronger privacy protections, and demonstrated economic benefits. Inclusive AI design will become increasingly important, with successful AI products incorporating accessibility features, multiple learning modalities, and transparent explanations of algorithmic decision-making that appeal across generational boundaries.
The role of AI monitoring and transparency tools like AmICited.com will become increasingly critical as organizations and individuals seek to understand how AI systems are being used, what data is being collected, and how AI references are being tracked across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. These monitoring tools help bridge generational trust gaps by providing visibility into AI operations and ensuring accountability. Organizations must foster a continuous learning culture that positions AI adoption not as a one-time training event but as an ongoing journey of skill development, feedback integration, and iterative improvement. The generation that successfully navigates this transition—embracing AI’s capabilities while maintaining critical judgment and human-centered values—will gain significant competitive advantages in an increasingly AI-augmented economy.

Cross-generational AI adoption refers to how different age groups—Gen Z, Millennials, Gen X, and Baby Boomers—adopt and use AI technologies at different rates and for different purposes. It encompasses the varying comfort levels, trust relationships, and practical applications each generation has with AI tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Generation Z leads AI adoption with 70% using generative AI weekly and 93% using two or more AI tools simultaneously. Millennials follow closely with 56-62% using AI regularly at work. Gen X shows 33% regular usage, while Baby Boomers have the lowest adoption at 20% weekly usage.
Baby Boomers' skepticism stems from legitimate privacy concerns (77% worried about data collection), lifetime experience with technological disruption, and preference for human interaction over algorithmic systems. Additionally, 49% of Boomers actively distrust AI, reflecting their generation's more cautious approach to emerging technologies.
Organizations can bridge generational gaps through tailored training programs, cross-generational mentorship, balancing high-tech with high-touch support, visible leadership championing of AI adoption, and transparent communication about AI capabilities and privacy protections. Customizing implementation to each generation's preferences significantly improves adoption rates.
The primary barriers are privacy concerns (77% of non-users), distrust of AI (49% of Boomers), complexity of use, unclear return on investment, and preference for human interaction. Addressing these barriers requires transparent data practices, intuitive interfaces, and clear communication about AI benefits and security measures.
Gen Z uses AI primarily for education, content creation, entrepreneurship, and career planning, viewing it as an integrated utility. Millennials take a more pragmatic approach, focusing on workplace productivity, parenting support, shopping optimization, and fitness tracking. Gen Z shows higher adoption rates (70% vs 56-62%) but both generations are comfortable with AI.
Privacy is the dominant concern across all generations, with 68-77% of non-users citing data protection worries as their primary hesitation. This universal concern transcends age demographics and represents the single most important factor organizations must address through transparent policies, robust security measures, and clear communication about data usage.
Companies should implement inclusive AI design with accessibility features, multiple learning modalities, and transparent explanations of algorithmic decision-making. They must provide generation-specific training, foster continuous learning culture, address privacy concerns transparently, and create mentorship programs that leverage the strengths of each generation.
AmICited tracks how different age groups encounter your brand in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Understand cross-generational AI visibility and optimize your brand presence.

Discover how Gen Z is using AI for search with 76% trusting AI over Google. Learn adoption rates across ChatGPT, Perplexity, TikTok, and Reddit platforms.

Discover why Gen Z leads in AI adoption for shopping, what drives their trust, and what it means for your business. Explore statistics, barriers, and future tre...
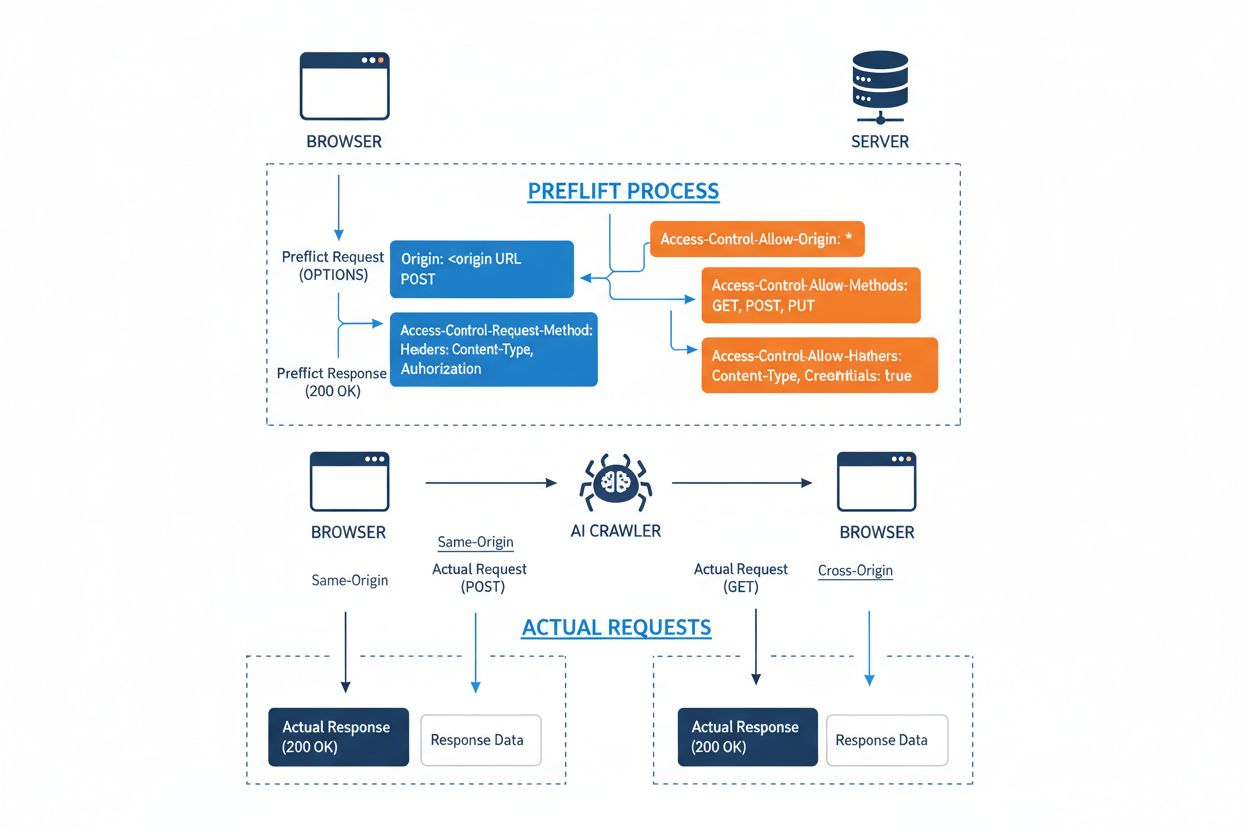
Learn about Cross-Origin AI Access, how AI systems navigate CORS restrictions, detection methods, blocking strategies, and tools like AmICited.com for monitorin...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.