
Enterprise SEO
Enterprise SEO is the practice of optimizing large, complex websites with thousands of pages for search engines. Learn strategies, challenges, and best practice...
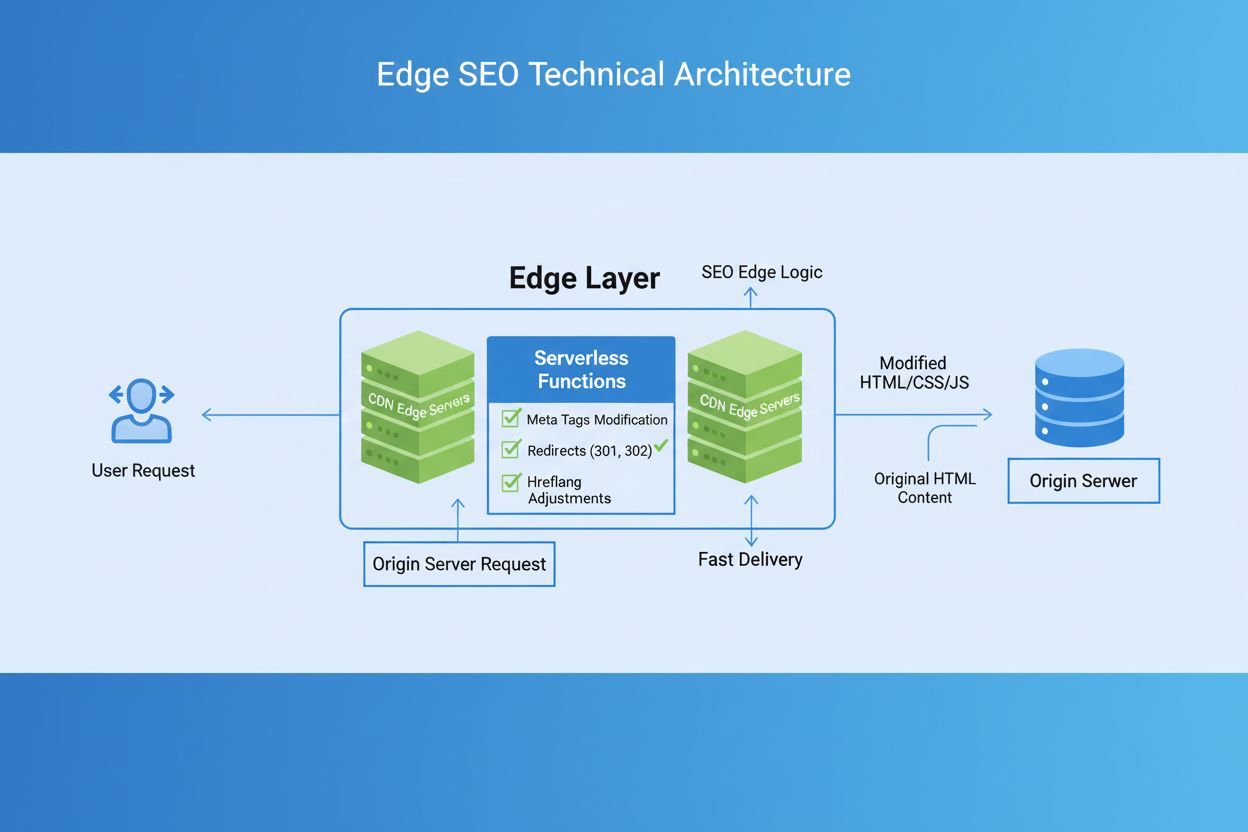
Edge SEO refers to SEO modifications and optimizations implemented at the CDN edge layer using serverless technology, allowing real-time changes to website content without altering the origin server code. This approach enables faster implementation of technical SEO changes, improved page performance, and greater flexibility in optimization strategies.
Edge SEO refers to SEO modifications and optimizations implemented at the CDN edge layer using serverless technology, allowing real-time changes to website content without altering the origin server code. This approach enables faster implementation of technical SEO changes, improved page performance, and greater flexibility in optimization strategies.
Edge SEO is the practice of implementing technical SEO modifications and optimizations at the Content Delivery Network (CDN) edge layer using serverless technology, rather than making changes directly to the origin server. This approach allows SEO professionals to modify website content, HTTP headers, and responses in real-time as they travel through the network edge—the outermost layer of a CDN infrastructure positioned between users and the origin server. Edge SEO leverages serverless functions (such as Cloudflare Workers, AWS Lambda@Edge, or Fastly Compute@Edge) to intercept and modify requests and responses without altering the underlying website codebase. The modifications appear to search engines and users as if they were implemented server-side, making Edge SEO an invisible yet powerful optimization technique. This approach has revolutionized how organizations handle technical SEO, particularly for those facing development bottlenecks, platform restrictions, or the need for rapid optimization cycles.
The concept of Edge SEO emerged from the convergence of two technological trends: the maturation of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and the rise of serverless computing. While CDNs have existed since the 1990s primarily for caching static content, their evolution into platforms supporting dynamic code execution fundamentally changed SEO possibilities. The term “Edge SEO” was officially coined by Dan Taylor at the TechSEO Boost conference in 2018, though the underlying concept had been developing among forward-thinking SEO professionals and developers for several years prior. The adoption of Edge SEO accelerated significantly between 2019 and 2024, driven by increasing platform restrictions on legacy CMS systems, growing complexity of modern web architectures, and the need for rapid SEO experimentation. According to industry research, approximately 67% of enterprises now utilize some form of edge computing for content optimization, with SEO applications representing a rapidly growing segment of this adoption. The AI-powered SEO sector, which includes Edge SEO technologies, reached a market value of $67 billion in 2025, demonstrating the significant investment and confidence in these methodologies.
Edge SEO operates on a fundamentally different architectural principle than traditional SEO. When a user or search engine bot requests a webpage, the request typically flows directly to the origin server, which returns the HTML response. With Edge SEO, this request is intercepted at the CDN edge—a server geographically closer to the user—where serverless edge workers can modify the request or response before it reaches either the origin server or the user. This interception happens in milliseconds, introducing minimal latency (typically 10-50ms) while enabling powerful transformations. The serverless aspect means that organizations don’t need to manage dedicated servers; instead, code executes on-demand within the CDN infrastructure, scaling automatically based on traffic. The modifications made at the edge are stateless, meaning each request is processed independently without retaining information from previous requests, which enables rapid execution and effortless scalability. From the perspective of search engines like Google and users, these edge modifications are indistinguishable from server-side changes, as they modify the actual HTML response that gets delivered. This architectural approach creates a powerful middle ground between SEO professionals and development teams, enabling rapid optimization without requiring backend code changes.
| Aspect | Edge SEO | Server-Side SEO | JavaScript-Based SEO | Traditional CDN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Location | CDN edge layer | Origin server | Browser/client-side | CDN caching layer |
| Development Required | Minimal (serverless) | Significant (code changes) | Moderate (JS framework) | None (static caching) |
| Deployment Speed | Seconds to minutes | Days to weeks | Minutes to hours | Immediate (cached content) |
| Search Engine Visibility | Full (server-side equivalent) | Full (native) | Partial (indexing inconsistency) | Full (cached content) |
| Performance Impact | Minimal (+10-50ms) | None (native) | Variable (rendering delay) | Positive (faster delivery) |
| Platform Dependency | Low (works with any platform) | High (platform-specific) | Medium (framework-dependent) | Low (universal) |
| Scalability | Excellent (auto-scaling) | Good (server-dependent) | Good (browser-dependent) | Excellent (distributed) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (pay-per-execution) | Medium (development costs) | Medium (framework overhead) | Medium (bandwidth-based) |
| Use Case Suitability | Legacy systems, rapid testing | New builds, permanent changes | Modern SPAs, dynamic content | Static content delivery |
The mechanics of Edge SEO involve a sophisticated interplay between CDN infrastructure, serverless functions, and HTTP request/response cycles. When a user or search engine bot initiates a request to a website using Edge SEO, the request first reaches the nearest edge server in the CDN’s global network. At this point, a serverless edge worker—a small piece of code deployed across the CDN—intercepts the request. This worker can examine various aspects of the request, including headers, user location, device type, and other contextual information. Based on this analysis, the worker can modify the request before it reaches the origin server, or it can wait for the origin server’s response and modify the HTML, headers, or other response elements before sending them to the user. For example, an edge worker might dynamically insert hreflang tags based on the user’s geographic location, modify meta titles and descriptions based on inventory levels, or implement 301 redirects based on complex business logic. The entire process occurs at the network edge, meaning the modifications happen geographically closer to the user, reducing latency and improving performance. The stateless nature of edge workers means they don’t retain information between requests, enabling them to scale horizontally across thousands of edge servers worldwide without coordination overhead. This architecture is fundamentally different from traditional server-side processing, where all requests must travel to a centralized origin server, creating potential bottlenecks and increased latency.
Edge SEO enables a remarkably diverse range of technical optimizations that would be difficult, expensive, or impossible to implement through traditional server-side methods. Redirect management represents one of the most common applications, allowing organizations to implement complex redirect logic without modifying server configurations. For platforms like Shopify or Salesforce Commerce Cloud that impose redirect limits, Edge SEO provides a workaround by handling redirects at the edge. Hreflang tag management is another critical application, particularly for multilingual and multi-regional websites. Rather than manually updating hreflang tags across thousands of pages, edge workers can dynamically insert these tags based on available translations and regional content, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Meta tag optimization allows for dynamic modification of titles and descriptions based on real-time data—for instance, adjusting product page titles to include current prices or availability status. Schema markup injection enables the addition of structured data without modifying the CMS, improving how search engines understand and display content in rich snippets. Security enhancements at the edge include adding security headers like Content-Security-Policy and X-XSS-Protection, implementing bot protection to distinguish between legitimate search engine crawlers and malicious bots, and conducting real-time threat analysis. JavaScript pre-rendering addresses a critical challenge for modern web applications: ensuring that search engines can access fully rendered content from JavaScript-heavy frameworks. Edge workers can pre-render pages for search engine bots while serving the interactive version to users. A/B testing at the edge enables rapid experimentation with different page variations, allowing organizations to test SEO changes without backend infrastructure modifications. Log file collection provides access to server logs even on platforms that restrict log access, enabling detailed analysis of crawler behavior and optimization opportunities.
One of the most compelling advantages of Edge SEO is its ability to dramatically improve website performance metrics, particularly Core Web Vitals—Google’s set of user-centric performance metrics that directly influence search rankings. Research demonstrates that each 100-millisecond improvement in page load time results in approximately 1.11% increase in conversion rates, according to studies by Mobify and other performance research organizations. Edge SEO implementations can reduce page load times by up to 60% through various optimization techniques. Image optimization at the edge involves dynamically resizing, compressing, and converting images to optimal formats based on the user’s device and network conditions, significantly reducing bandwidth usage and load times. CSS and JavaScript minification and compression can be applied dynamically at the edge, reducing file sizes without requiring code changes. Intelligent caching strategies implemented at the edge can cache both static and dynamic content closer to users, dramatically reducing latency. Resource prioritization and preloading based on user context ensures that critical resources load first, improving perceived performance. The Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) metric—measuring when the largest visible element loads—can be improved through edge-based image optimization and resource prioritization. First Input Delay (FID) and its successor Interaction to Next Paint (INP) can be enhanced by reducing JavaScript execution time through edge-based optimization. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which measures visual stability, can be improved by ensuring proper resource dimensions are set before content loads. These performance improvements create a virtuous cycle: faster pages improve user experience, reduce bounce rates, increase engagement metrics, and ultimately improve search engine rankings.
Many organizations face significant constraints when attempting to implement SEO improvements. Legacy CMS platforms like older versions of WordPress, Drupal, or proprietary systems often have limited SEO capabilities or restrict direct code modifications. E-commerce platforms such as Shopify, Salesforce Commerce Cloud, and SAP Hybris impose restrictions on certain types of modifications, including limits on the number of redirects or inability to modify robots.txt files. Development team bottlenecks represent another critical challenge: SEO teams often find themselves waiting weeks or months for development resources to implement relatively simple changes, as development priorities focus on feature development and bug fixes rather than SEO optimization. Edge SEO provides a powerful solution to these constraints by enabling SEO professionals to implement changes without backend access, without CMS modifications, and without development team involvement. This democratization of SEO implementation allows organizations to respond rapidly to algorithm updates, competitive pressures, and market opportunities. For example, a website might need to implement new hreflang tags for a new market expansion, add schema markup for a new product category, or implement redirects for a site restructuring—all of which can be accomplished in minutes through Edge SEO rather than waiting for development cycles. The ability to rapidly deploy and test changes enables organizations to validate SEO hypotheses through A/B testing before committing to permanent code-level implementations, reducing risk and improving decision-making.
As AI-powered search systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become increasingly important for content discovery, Edge SEO takes on new significance. These AI systems rely on properly formatted, well-structured content to understand and cite websites in their responses. Edge SEO optimizations—particularly schema markup implementation, meta tag optimization, and content structure improvements—directly influence how AI systems perceive and cite your content. Platforms like AmICited monitor how your domain and content appear across these AI systems, providing visibility into whether your Edge SEO optimizations are translating into AI search visibility. The relationship between Edge SEO and AI search is bidirectional: Edge SEO improvements enhance your content’s discoverability in AI systems, while monitoring tools like AmICited help you understand the impact of your optimizations. For organizations seeking to maximize visibility across both traditional search and AI-generated responses, Edge SEO represents a critical component of a comprehensive optimization strategy. The ability to rapidly implement and test changes at the edge enables organizations to optimize specifically for AI search requirements, such as ensuring proper entity markup, maintaining content freshness, and optimizing for the specific query patterns that AI systems prioritize.
Beyond basic implementations, Edge SEO enables sophisticated optimization techniques that were previously impractical or impossible. A/B testing at the edge allows organizations to serve different page variations to different user segments, enabling rapid experimentation with SEO elements like title tags, headers, content structure, and internal linking patterns. Unlike traditional A/B testing that requires backend infrastructure, edge-based testing can be deployed in minutes and scaled across millions of pages. Multivariate testing extends this capability, allowing simultaneous testing of multiple variables to identify optimal combinations. Log file analysis at the edge provides detailed insights into crawler behavior, including which pages are crawled most frequently, how much crawl budget is allocated to different sections, and whether crawl errors are occurring. This data enables organizations to optimize their crawl budget allocation, ensuring that search engines spend their crawling resources on the most important pages. Dynamic content personalization based on user location, device type, or browsing history can improve engagement metrics while maintaining SEO value. Intelligent redirect handling can implement complex logic that considers multiple factors—geography, device type, migration status, inventory levels—when determining the appropriate redirect, enabling sophisticated site migrations and URL restructuring. Security and compliance at the edge can implement region-specific content variations to comply with regulations like GDPR, ensuring that users in different regions see appropriately localized and compliant content.
Successfully implementing Edge SEO requires careful planning and coordination with development teams. Start with a proof of concept on a non-critical section of the website to validate the approach and build organizational confidence. Establish clear monitoring and measurement from the beginning, tracking key metrics like page load times, Core Web Vitals, organic traffic, and search rankings to quantify the impact of Edge SEO implementations. Maintain close collaboration with development teams even though Edge SEO reduces their involvement in day-to-day optimizations. Development teams should be informed about edge modifications, and temporary edge solutions should be tracked for eventual permanent implementation in the codebase. Document all edge modifications to maintain clarity about what changes are implemented at the edge versus at the origin, preventing confusion during future development cycles. Implement robust quality assurance processes because edge modifications involve changing HTML rather than creating it from scratch, requiring careful testing to ensure changes don’t break site functionality. Consider the long-term strategy: while Edge SEO is powerful for rapid implementation and testing, permanent improvements should eventually be implemented at the origin server level to reduce technical debt and simplify future maintenance. Gradually expand implementations from simple optimizations like dynamic title tags to more complex techniques like A/B testing and log file analysis, building expertise and organizational comfort with the approach. Stay updated on platform capabilities as CDN providers continuously expand Edge SEO functionality, introducing new possibilities for optimization.
The future of Edge SEO is inextricably linked to broader trends in web technology, AI, and search engine evolution. AI integration will likely enable edge workers to make increasingly sophisticated optimization decisions based on machine learning models, automatically adjusting content and structure based on predicted user intent and search engine preferences. Enhanced personalization at the edge will become more sophisticated, with edge workers analyzing user behavior patterns and contextual signals to deliver highly personalized experiences that improve engagement while maintaining SEO value. Voice search optimization will become increasingly important as voice-activated devices proliferate, requiring edge-based optimizations to ensure content is properly formatted for voice search queries. Mobile-first optimization will continue to evolve, with edge workers implementing device-specific optimizations that improve mobile user experience and performance. Integration with AI search systems will deepen, with Edge SEO techniques specifically optimized for how AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity discover, understand, and cite content. Standardization and tooling will improve, with more user-friendly platforms emerging that abstract away the complexity of writing edge worker code, making Edge SEO accessible to SEO professionals without deep technical expertise. Regulatory compliance at the edge will become more sophisticated, with edge workers implementing region-specific content variations and privacy protections to comply with evolving regulations. The convergence of these trends suggests that Edge SEO will evolve from a specialized technique used primarily by large enterprises and technical SEO specialists into a standard component of modern SEO practice, accessible to organizations of all sizes.
Quantifying the impact of Edge SEO implementations is essential for demonstrating value and justifying continued investment. Page load time improvements should be measured using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, WebPageTest, and Core Web Vitals reports, tracking metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Organic traffic analysis through Google Analytics and Google Search Console reveals whether Edge SEO optimizations are translating into improved search visibility and user engagement. Keyword ranking tracking using tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs demonstrates whether optimizations are improving positions for target keywords. Conversion rate analysis measures whether performance improvements and content optimizations are translating into business results. Crawl efficiency metrics from Google Search Console show whether Edge SEO implementations are improving how search engines interact with the website. User engagement metrics including bounce rate, time on site, and pages per session indicate whether optimizations are improving user experience. Cost analysis comparing the cost of Edge SEO implementations to traditional development approaches demonstrates the cost-efficiency of the approach. Competitive benchmarking compares your website’s performance and rankings to competitors, revealing whether Edge SEO is providing competitive advantages. The most sophisticated organizations implement attribution modeling that connects specific Edge SEO changes to measurable business outcomes, enabling data-driven decision-making about which optimizations to prioritize.
Edge SEO represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach technical search engine optimization, enabling rapid implementation of changes without requiring development team involvement or backend code modifications. By leveraging serverless technology deployed on CDN edge servers, Edge SEO allows modifications to be made at the network’s periphery, closer to users and search engines, resulting in improved performance, faster implementation cycles, and greater flexibility. The approach is particularly valuable for organizations facing platform restrictions, development bottlenecks, or the need for rapid experimentation and testing. As AI-powered search systems become increasingly important for content discovery, Edge SEO takes on additional significance, enabling organizations to optimize specifically for how AI systems discover, understand, and cite content. The convergence of improved tooling, broader adoption, and integration with AI search systems suggests that Edge SEO will evolve from a specialized technique into a standard component of modern SEO practice. Organizations seeking to maximize visibility across traditional search, AI-generated responses, and emerging search paradigms should consider Edge SEO as a critical component of their optimization strategy, complemented by monitoring platforms like AmICited that provide visibility into how optimizations translate into real-world search visibility across multiple systems.
Edge SEO implements changes at the CDN edge layer using serverless functions, while traditional SEO changes require modifying the origin server code. Edge SEO is faster to deploy, doesn't require development team involvement for every change, and appears to search engines and users as if the changes were made server-side. This approach is particularly valuable for websites with slow development cycles or platform restrictions.
Edge SEO introduces minimal latency, typically around 10 milliseconds on average, with rare cases reaching up to 50 milliseconds. The performance benefit from optimizations made at the edge (such as improved caching, content delivery, and reduced server load) typically far outweighs this minimal latency. Studies show that Edge SEO implementations can reduce page load times by up to 60% when properly configured.
Major CDN providers offering Edge SEO capabilities include Cloudflare Workers, AWS CloudFront with Lambda@Edge, Fastly Compute@Edge, Akamai EdgeWorkers, Azure Functions, and BunnyCDN with Edge Scripts. Each platform supports different programming languages (JavaScript, WebAssembly) and offers varying levels of functionality for SEO modifications.
Yes, Edge SEO changes are fully indexable by search engines. From Google's perspective, edge modifications appear identical to server-side changes because they modify the HTML response before it reaches the user or search engine bot. This means there are no indexation risks or inconsistencies with Edge SEO implementations.
Edge SEO supports a wide range of modifications including 301/302 redirects, hreflang tag management, meta tag modifications, schema markup injection, robots.txt customization, HTTP header changes, image optimization, JavaScript pre-rendering, and A/B testing. Essentially, any change that modifies the HTML response or HTTP headers can be implemented at the edge.
Many CMS platforms and legacy systems restrict direct code modifications or have limited SEO capabilities. Edge SEO bypasses these restrictions by implementing changes at the CDN layer, allowing SEO professionals to add features like hreflang tags, redirects, or structured data without requiring platform-level changes or development team involvement.
Edge SEO is particularly beneficial for websites with complex architectures, legacy technology stacks, platform restrictions, or slow development cycles. It's also valuable for large-scale websites requiring rapid SEO changes, e-commerce platforms with dynamic content, and organizations with limited development resources. However, it should complement rather than replace permanent code-level implementations.
Edge SEO modifications affect how your website appears in AI-generated responses and search results. Platforms like AmICited monitor how your domain and content appear across AI systems (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Claude). Edge SEO optimizations—such as improved meta tags, structured data, and content modifications—can enhance your visibility in these AI systems by ensuring your content is properly formatted and discoverable.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Enterprise SEO is the practice of optimizing large, complex websites with thousands of pages for search engines. Learn strategies, challenges, and best practice...
Technical SEO optimizes website infrastructure for search engine crawling, indexing, and ranking. Learn crawlability, Core Web Vitals, mobile optimization, and ...

Learn how Edge AI Processing enables real-time AI computation on local devices, reducing latency and enhancing privacy. Discover applications in brand monitorin...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.