AI Query Patterns
Learn about AI Query Patterns - recurring structures and formulations users employ when asking AI assistants questions. Discover how these patterns improve accu...
Sequences of related questions users ask AI systems in extended conversations where context and previous interactions are maintained across multiple exchanges. Multi-turn query chains enable AI systems to understand user intent progressively, maintain conversation state, and provide coherent responses that build upon earlier information.
Sequences of related questions users ask AI systems in extended conversations where context and previous interactions are maintained across multiple exchanges. Multi-turn query chains enable AI systems to understand user intent progressively, maintain conversation state, and provide coherent responses that build upon earlier information.
Multi-turn query chains are sequences of related questions that users ask AI systems during extended conversations, where context and previous interactions are maintained across multiple exchanges. Unlike single-turn interactions that end after one question-answer pair, multi-turn query chains enable AI systems to understand user intent progressively, maintain conversation state, and provide coherent responses that build upon earlier information. This capability transforms basic question-answering systems into true conversational agents that can handle complex, real-world scenarios requiring multiple steps and clarifications. The key distinction is that each new query in the chain is informed by everything that came before it, creating a continuous dialogue rather than isolated transactions.
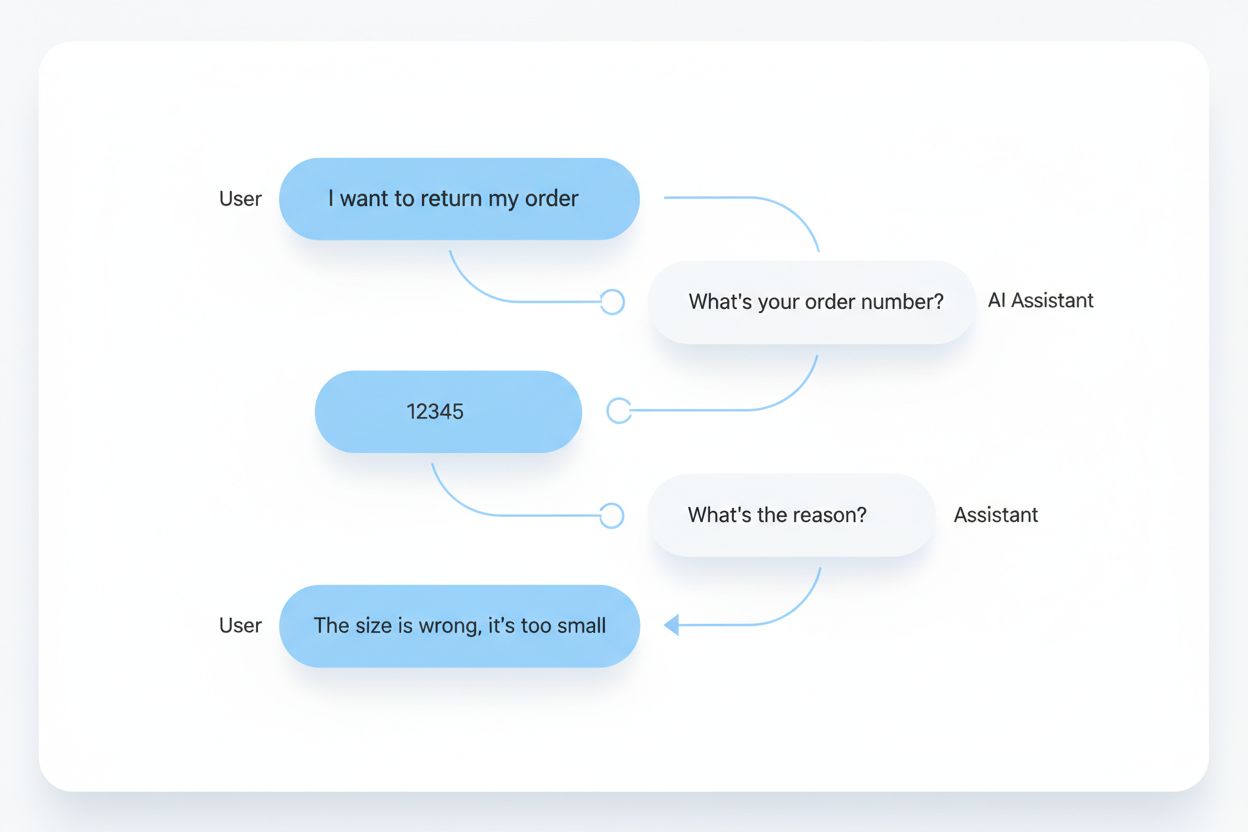
Multi-turn query chains rely on four essential architectural components that work together to create seamless conversational experiences. These components form the foundation of any sophisticated conversational AI system, enabling it to handle the complexity of real-world interactions where users don’t always provide information in a linear fashion or follow a predetermined script.
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Intent Recognition | Understand the user’s underlying goal despite varying phrasing or topic shifts | User says “I want to return my order” - system recognizes the intent is “initiate return” |
| Slot Filling | Collect and track required data points throughout the conversation | System gathers order number, reason for return, and preferred resolution method across multiple turns |
| Dialogue State Management | Maintain awareness of conversation progress and determine next logical steps | System knows which information has been collected, what’s still needed, and what actions remain |
| Digression Handling | Gracefully manage off-topic questions while preserving conversation context | User asks about shipping costs mid-conversation; system answers then returns to return process |
These components work in concert to create a system that feels natural and responsive. Intent recognition ensures the AI stays focused on what the user actually wants, even when they express it differently than expected. Slot filling prevents users from having to repeat information they’ve already provided. Dialogue state management keeps the conversation organized and prevents loops or dead ends. Digression handling makes the system feel intelligent and human-like, capable of handling interruptions without losing track of the main objective.
The mechanics of multi-turn query chains involve a sophisticated process of context preservation and progressive understanding. When a user initiates a conversation, the AI system creates a context window—a working memory that stores the conversation history and relevant information. As each new query arrives, the system doesn’t treat it as an isolated question; instead, it references this context window to understand what the user is referring to and what information has already been established. The system maintains a dialogue state that tracks what has been accomplished, what information is still needed, and what the user’s primary objective is.
For example, if a user first asks “Why did my bill increase?”, the system recognizes this as a billing inquiry intent and may ask for clarification about which account. When the user responds with their account number, the system updates its dialogue state to reflect that the account has been identified. If the user then asks “Can you also check my payment history?”, the system recognizes this as a related but distinct request while maintaining the context that they’re still discussing their account. This progressive context building allows the system to handle complex workflows that would be impossible in single-turn interactions. The system continuously validates information, updates its understanding, and determines what clarifying questions or actions are needed next, all while maintaining the coherence of the overall conversation.
Multi-turn query chains are essential for handling complex customer interactions that require multiple steps and information gathering. Organizations across industries rely on this capability to deliver efficient, satisfying customer experiences:
These applications demonstrate why multi-turn capability is no longer optional for customer-facing AI systems. Single-turn systems force users into rigid workflows, while multi-turn systems adapt to how people naturally communicate.
The advantages of multi-turn query chains extend across multiple dimensions of user experience and business outcomes. Improved user experience is perhaps the most obvious benefit—users can have natural conversations without constantly repeating information or starting over when they ask follow-up questions. This creates a sense of continuity and intelligence that single-turn systems simply cannot match. Higher satisfaction rates follow naturally from this improved experience; customers appreciate not having to re-explain their situation or navigate between disconnected interactions. From a business perspective, better data collection becomes possible because the system can gather information progressively, asking for what it needs when it needs it, rather than overwhelming users with all questions at once. This approach also improves data quality because users are more likely to provide accurate information in a conversational context than when facing a long form. Efficiency gains are substantial—multi-turn systems can often resolve issues on first contact that would otherwise require escalation to human agents, reducing operational costs while improving customer satisfaction simultaneously.
Despite their advantages, implementing effective multi-turn query chains presents significant technical challenges. Context maintenance becomes increasingly difficult as conversations grow longer; systems must accurately track what information has been provided, what’s still needed, and what the user’s current objective is without losing important details or becoming confused by contradictions. Preventing conversation loops is another critical challenge—poorly designed systems can get stuck asking the same questions repeatedly or cycling through the same topics without making progress. Error recovery requires sophisticated design; when the system misunderstands something or the user provides unexpected information, the system must gracefully recover without breaking the conversation flow or requiring the user to start over. The complexity of implementation should not be underestimated; building systems that handle the full range of human conversational patterns requires significant investment in natural language understanding, dialogue management, and testing. Additionally, integration challenges arise when multi-turn systems need to connect with backend systems, databases, and other services while maintaining conversation state and ensuring data consistency across multiple turns.
As AI systems become more sophisticated and are deployed in increasingly critical applications, monitoring how these systems handle multi-turn conversations becomes essential. AmICited specializes in tracking how AI systems reference sources and maintain accuracy across extended conversations. In multi-turn query chains, this monitoring capability is particularly valuable because context and citations must be preserved and remain accurate throughout the entire conversation. When an AI system makes a claim in turn three that references information from turn one, AmICited’s monitoring ensures that the citation chain remains intact and that the system isn’t inadvertently misrepresenting sources or losing track of what was actually said earlier. Citation tracking across turns reveals whether AI systems maintain consistent sourcing as conversations evolve, which is critical for applications in research, customer service, and decision-making contexts. AmICited also monitors context preservation quality—ensuring that when systems reference earlier parts of the conversation, they’re doing so accurately and not introducing errors or misrepresentations. This is particularly important in sensitive domains like healthcare, finance, and legal services where conversation accuracy directly impacts outcomes. By monitoring multi-turn query chains, organizations can ensure their AI systems maintain the highest standards of accuracy, consistency, and reliability throughout extended customer interactions.
Single-turn interactions end after one question-answer exchange, while multi-turn query chains maintain context across multiple exchanges, allowing the AI to reference previous information and build coherent conversations. Multi-turn systems enable users to have natural dialogues without repeating information or starting over when asking follow-up questions.
AI systems use dialogue state management to track conversation history, maintain a context window of previous exchanges, and store key information (slots) that are referenced throughout the conversation. This allows the system to understand references to earlier parts of the conversation and make informed decisions about what information is still needed.
Intent recognition is the AI's ability to understand what the user is trying to accomplish, even as the conversation evolves and branches into new topics. This allows the system to stay focused on the user's primary goal while handling digressions and follow-up questions that may seem unrelated.
They enable more natural, efficient support by allowing customers to have flowing conversations without repeating information, leading to higher satisfaction rates and better first-contact resolution. Multi-turn systems can handle complex issues that would otherwise require escalation to human agents.
Key challenges include maintaining accurate context over long conversations, preventing conversation loops, handling unexpected digressions gracefully, managing the complexity of tracking multiple conversation states, and integrating with backend systems while preserving conversation state.
AmICited tracks how AI systems reference sources and maintain citations across multiple conversation turns, ensuring that context and attribution are preserved throughout extended interactions. This is critical for maintaining accuracy and consistency in sensitive applications.
Slot filling is the process where an AI system collects and updates key data points (like names, dates, or order numbers) throughout a conversation. This allows the system to build a complete picture of user information needed to resolve their issue without overwhelming them with all questions at once.
Yes, well-designed multi-turn systems include digression handling mechanisms that allow them to address off-topic questions while maintaining the conversation state and returning to the original topic seamlessly, creating a more natural and human-like interaction.
Track citation accuracy and context preservation across extended AI conversations with AmICited's advanced monitoring platform.

Learn about AI Query Patterns - recurring structures and formulations users employ when asking AI assistants questions. Discover how these patterns improve accu...
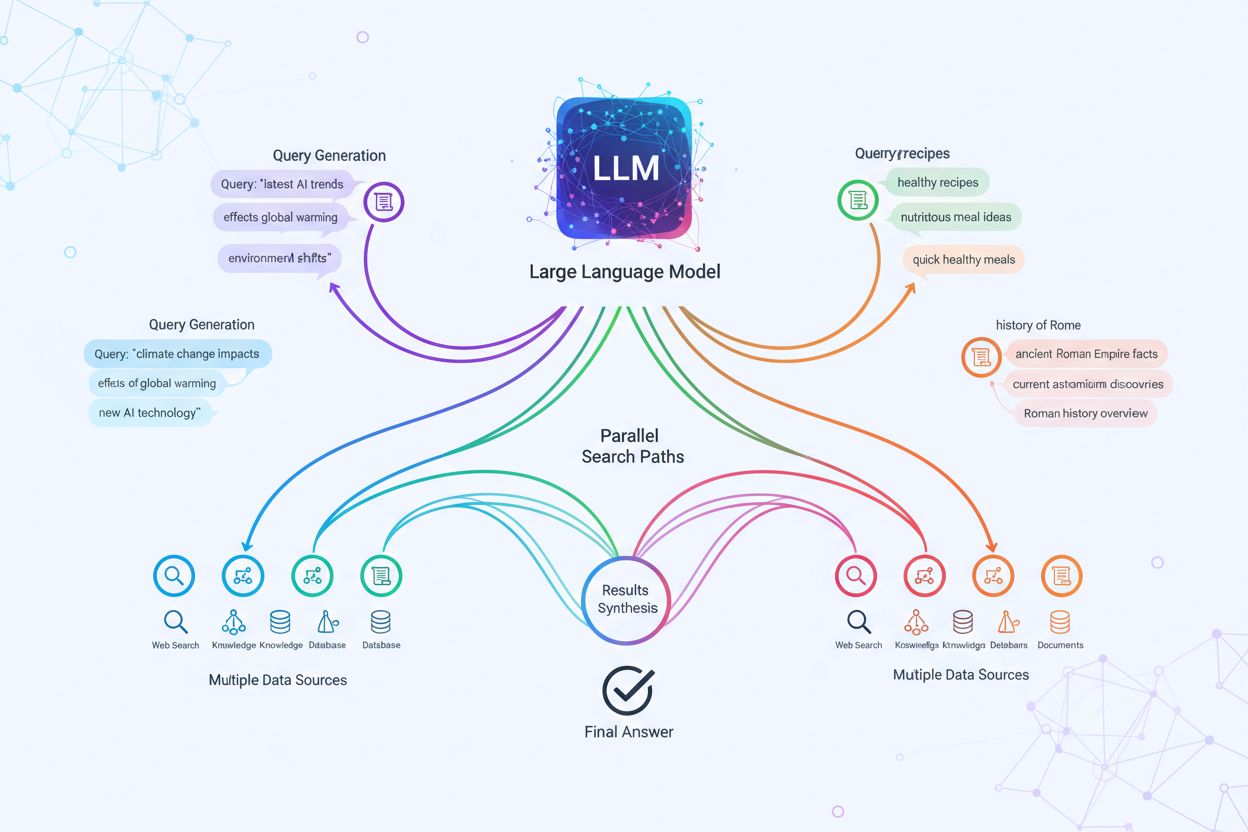
Discover how modern AI systems like Google AI Mode and ChatGPT decompose single queries into multiple searches. Learn query fanout mechanisms, implications for ...

Conversational queries are natural language questions asked to AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity. Learn how they differ from keyword searches and impact br...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.