
Search Engine Spam
Learn what search engine spam is, including black hat SEO tactics like keyword stuffing, cloaking, and link farms. Understand how Google detects spam and the pe...

Negative SEO refers to unethical tactics deliberately used to harm a competitor’s search engine rankings and online visibility. These malicious practices include building spammy backlinks, content scraping, fake reviews, site hacking, and other sabotage methods designed to make search engines penalize the target website or reduce user trust.
Negative SEO refers to unethical tactics deliberately used to harm a competitor's search engine rankings and online visibility. These malicious practices include building spammy backlinks, content scraping, fake reviews, site hacking, and other sabotage methods designed to make search engines penalize the target website or reduce user trust.
Negative SEO is the deliberate practice of using unethical and manipulative search engine optimization tactics to harm a competitor’s website rankings and online visibility. Unlike legitimate SEO, which focuses on improving a site’s own performance through quality content and ethical practices, negative SEO involves intentional sabotage designed to make search engines penalize the target website or reduce user trust in the brand. The primary goal is to trick search engines into believing the target site violates their policies, thereby triggering algorithmic devaluation or manual penalties. This malicious practice can take numerous forms, from building spammy backlinks to hacking websites and spreading false information. According to recent data, over 422,000 websites were hit with some form of negative SEO spam in 2024, demonstrating that these attacks remain a significant threat to online businesses. Understanding negative SEO is critical for any organization that wants to protect its search rankings, maintain brand reputation, and ensure consistent visibility across both traditional search engines and emerging AI-powered search platforms.
Negative SEO has evolved significantly since the early days of search engine optimization. In the 1990s and early 2000s, when search algorithms were less sophisticated, competitors could relatively easily manipulate rankings through crude tactics like keyword stuffing and link farming. However, as Google and other search engines developed more advanced algorithms—particularly the Penguin update in 2012, which specifically targeted link spam—the effectiveness of basic negative SEO tactics diminished. Despite Google’s improvements, negative SEO attacks have become more sophisticated and targeted. Modern attackers now employ advanced techniques including site hacking, content scraping using AI tools, and coordinated smear campaigns across social media and review platforms. The rise of AI-generated content has made content scraping more difficult to detect, as attackers can now create slightly modified versions of original content that evade duplicate detection. Additionally, the emergence of AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has created new vulnerabilities. When competitors use negative SEO to suppress a site’s traditional search visibility, it indirectly reduces the likelihood that AI systems will include that brand’s content in their training data or cite it in responses. This creates a compounding effect where negative SEO attacks now impact not just search rankings but also AI visibility and brand citations across multiple platforms.
Understanding the specific tactics used in negative SEO attacks is essential for developing effective defense strategies. The most prevalent attack method is malicious backlink building, where attackers create numerous low-quality or spammy links pointing to the target site from irrelevant domains, link farms, or hacked websites. These links often use keyword-rich anchor text related to undesirable niches like gambling, pharmaceuticals, or adult content, making the target site appear to be part of a link scheme. Content scraping represents another major threat, where attackers copy original content and republish it across multiple websites, creating duplicate content issues that can cause the original site to lose rankings. Fake negative reviews are particularly damaging for local businesses and e-commerce sites, as they appear on Google My Business, Yelp, Trustpilot, and other review platforms, directly impacting click-through rates and local search visibility. Site hacking is among the most severe attack types, involving unauthorized access to inject malicious code, add spammy links, modify robots.txt files, or redirect traffic to competitor sites. Click fraud involves artificially inflating click-through rates through bots or automated tools, creating a pattern of high clicks followed by high bounce rates that signals to search engines that the content doesn’t satisfy user intent. Smear campaigns leverage social media, forums like Reddit, and community sites to spread false or damaging information about a brand, undermining its E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals. Hotlinking or bandwidth theft occurs when attackers link directly to a site’s images or media files, consuming the target’s server resources and slowing page load times. Finally, sentiment manipulation involves coordinated efforts to create negative brand mentions across the web, which increasingly impacts rankings as search engines and AI systems place greater weight on brand mentions and sentiment analysis.
| Attack Tactic | Primary Impact | Detection Method | Difficulty to Detect | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malicious Backlinks | Algorithmic penalty, manual action | Backlink audit tools (Semrush, Ahrefs), GSC Links section | Medium | 2-4 weeks |
| Content Scraping | Duplicate content issues, lost traffic | Copyscape, Siteliner, Google search operators | Low | 1-3 weeks |
| Fake Reviews | Reputation damage, local ranking drop | Manual review monitoring, platform alerts | Low | 1-2 weeks |
| Site Hacking | Severe ranking drop, security breach | GSC Security alerts, malware scanners, log analysis | High | 1-3 months |
| Click Fraud | High bounce rate, CTR manipulation | Google Analytics traffic patterns, GSC performance data | Medium | 2-4 weeks |
| Smear Campaigns | Brand reputation damage, E-E-A-T erosion | Google Alerts, brand monitoring tools, social listening | Medium | 1-2 months |
| Hotlinking | Slow page speed, bandwidth costs | Server log analysis, CDN monitoring | Medium | Immediate (with fixes) |
| Sentiment Manipulation | Negative brand mentions, AI citation loss | Brand monitoring platforms, social media tracking | High | 1-3 months |
The technical execution of negative SEO attacks varies depending on the sophistication level and resources available to the attacker. Spammy backlink attacks typically operate through automated link-building services that post comments on blogs, submit to directories, or use API access to forum platforms to create hundreds or thousands of links in a short timeframe. These links often originate from IP addresses that share hosting infrastructure, creating a detectable “link footprint” that experienced SEO professionals can identify. Content scraping has become more sophisticated with the advent of AI tools that can automatically spin or rewrite content while maintaining semantic meaning, making it harder for duplicate detection algorithms to identify the original source. Site hacking requires attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in outdated CMS platforms, weak passwords, or unpatched plugins to gain administrative access. Once inside, attackers can inject malicious code into the site’s header or footer, modify the robots.txt file to block crawling of important pages, add noindex tags to deindex critical content, or create cloaked pages that show different content to search engines versus users. Click fraud typically uses bot networks or click farms to simulate user clicks on search results, creating artificial engagement patterns that confuse ranking algorithms. DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks represent an extreme form of negative SEO where attackers overwhelm a site’s servers with traffic, causing slowdowns or complete outages that harm user experience and search rankings. Understanding these technical mechanisms is crucial for implementing appropriate defensive measures and detecting attacks early before they cause significant damage to search visibility and brand reputation.
The impact of negative SEO on search rankings has been a subject of debate within the SEO community, with Google consistently claiming that well-designed algorithms should ignore most attacks. However, real-world case studies demonstrate that sophisticated negative SEO campaigns can cause measurable ranking drops, particularly in competitive niches. When a site experiences a sudden influx of toxic backlinks, search engines may initially interpret this as a sign of manipulation, leading to algorithmic devaluation or manual penalties. The recovery process can be lengthy, requiring site owners to audit their backlink profile, disavow toxic links, and potentially submit reconsideration requests to Google. Beyond traditional search rankings, negative SEO now has indirect but significant implications for AI visibility. When competitors use negative SEO to suppress a site’s search rankings, that site receives less organic traffic and fewer backlinks from authoritative sources. This reduced visibility means AI training systems are less likely to encounter and index the site’s content, resulting in fewer citations in AI-generated responses. For brands relying on visibility across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, this creates a compounding problem where negative SEO attacks impact not just search rankings but also AI presence. Additionally, if attackers successfully inject malicious content or create fake pages on a compromised site, those pages may be indexed by AI systems, further damaging the brand’s reputation and trustworthiness signals. This interconnection between traditional SEO and AI visibility makes negative SEO defense increasingly critical for comprehensive brand protection.
Protecting your website from negative SEO attacks requires a multi-layered approach combining technical hardening, continuous monitoring, and rapid response protocols. Technical security measures should include keeping all CMS software, themes, and plugins up to date to minimize hacking vulnerabilities, implementing HTTPS with SSL certificates to ensure secure connections, using strong and unique passwords with two-factor authentication, and configuring security headers that instruct browsers on how to handle your site’s content. Backlink monitoring is essential for early detection of malicious linking campaigns. Export your backlink profile monthly from tools like Google Search Console, Semrush, or Ahrefs, and analyze it for sudden spikes from suspicious domains or unnatural anchor text patterns. Set up automated alerts in these tools to notify you immediately when new backlinks are discovered, allowing you to respond quickly to attacks. Brand monitoring should include setting up Google Alerts for your brand name, domain, and key product names, as well as using dedicated brand monitoring tools like Semrush’s Brand Monitoring app to track mentions across blogs, forums, news sites, and social media. This helps you catch smear campaigns and impersonation attempts before they spread widely. Content protection involves using rel=canonical tags to signal original content to search engines, implementing DMCA takedown procedures for scraped content, and watermarking important visual assets. Domain hygiene requires renewing domains early or setting up auto-renewal to prevent lapses that could result in spammy backlinks, regularly auditing redirects to ensure they point to legitimate content, and monitoring for “for sale” listings or impersonations of your domain. Regular security audits using tools like Sucuri or Wordfence can identify malware, suspicious code injections, and unauthorized modifications before they cause significant damage.
Early detection of negative SEO attacks is critical for minimizing damage and enabling rapid recovery. Google Search Console (GSC) serves as your first line of defense, providing free alerts about security issues, manual actions, and suspicious linking patterns. Regularly check the “Links” section to review top linking sites and anchor text, looking for suspicious patterns like links from unrelated industries or keyword-rich anchor text that doesn’t match your site’s content. Monitor the “Performance” tab for sudden drops in impressions or clicks, which often indicate ranking declines. Enable security alerts in GSC to receive notifications about hacking attempts or malware detection. Backlink audit tools like Semrush’s Backlink Audit or Ahrefs provide detailed toxicity scoring, analyzing over 45 markers to identify potentially harmful links. These tools allow you to categorize links as whitelisted (safe), marked for removal (contact site owner), or disavowed (tell Google to ignore). Traffic analysis through Google Analytics or similar platforms can reveal unusual patterns like sudden spikes in traffic from suspicious referral sources, abnormal bounce rates, or geographic anomalies that might indicate click fraud or bot activity. Content monitoring using tools like Copyscape or Siteliner helps identify when your content has been scraped or duplicated across the web. Review monitoring across platforms like Google My Business, Yelp, and Trustpilot allows you to spot fake reviews quickly, which typically exhibit poor grammar, vague complaints, and sudden clustering within short timeframes. Site performance monitoring tracks page load times and server response, as sudden slowdowns might indicate DDoS attacks or hotlinking. Establishing a routine monitoring schedule—checking backlinks monthly, reviewing traffic weekly, and monitoring brand mentions daily—creates a comprehensive early warning system that catches attacks before they cause severe damage.
If you discover that your site is under a negative SEO attack, swift and systematic action is essential for recovery. Assess the damage by documenting ranking drops, traffic declines, and any alerts from Google Search Console. Use the URL Inspection tool in GSC to check if pages have been deindexed, and copy-paste content chunks into Google to identify scraped versions. Clean up malicious backlinks by using Google’s Disavow Tool to submit a list of toxic links, telling Google to ignore them. However, follow Google’s guidance that you should only disavow links if they’re clearly harmful or numerous, as disavowing legitimate links can do more harm than good. Remove hacked content by identifying and deleting malicious code, correcting or removing noindex tags and canonical tags that were altered, and requesting reindexing of important pages through GSC. Address content scraping by filing DMCA takedown notices with the offending site’s hosting provider or directly with Google, and consider revising your original content if the scraped version is outranking yours. Respond to reputation damage by flagging and reporting fake reviews on relevant platforms, responding professionally to false claims to protect your brand’s credibility, and reaching out to websites impersonating your brand. Harden security by changing all passwords, updating software and plugins, enabling two-factor authentication, and implementing additional security measures to prevent future attacks. Submit a reconsideration request to Google if you received a manual action penalty, documenting your cleanup efforts and explaining how you’re preventing future issues. Recovery timelines vary significantly depending on attack severity, ranging from 1-2 weeks for simple attacks like fake reviews to 1-3 months for complex attacks involving site hacking or extensive content manipulation.
The landscape of negative SEO is evolving rapidly as search engines become more sophisticated and new technologies emerge. AI-powered content generation is making content scraping more difficult to detect, as attackers can now create variations of original content that evade duplicate detection algorithms while maintaining semantic similarity. This trend will likely force search engines to develop more advanced duplicate detection methods and may increase the importance of E-E-A-T signals in distinguishing original from derivative content. Increased focus on brand signals means that negative SEO attacks targeting brand reputation through smear campaigns and fake reviews will become increasingly impactful, as search engines and AI systems place greater weight on brand mentions, sentiment analysis, and user trust signals. The rise of AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews creates new vulnerabilities where negative SEO attacks can indirectly impact AI visibility by suppressing traditional search rankings. This has led to the emergence of AI monitoring platforms like AmICited that track brand appearances across AI systems and help detect when competitors are using sabotage tactics to harm AI visibility. Regulatory developments may also impact negative SEO, as governments increasingly scrutinize unfair competitive practices and data manipulation. The EU’s Digital Services Act and similar regulations in other jurisdictions may establish clearer legal frameworks for prosecuting negative SEO attacks, particularly those involving hacking, impersonation, or defamation. Automated defense systems powered by machine learning will likely become standard, automatically detecting and responding to common attack patterns without human intervention. Organizations that invest in comprehensive monitoring, rapid response capabilities, and integration with emerging AI visibility platforms will be best positioned to protect their search rankings, brand reputation, and AI presence in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
Spammy backlink building is the most prevalent negative SEO attack because it requires no website access and is relatively inexpensive to execute. Attackers create links from low-quality domains, link farms, or automated tools to make the target site appear to violate Google's link spam policies. According to research, over 422,000 websites were hit with negative SEO spam in 2024, with malicious linking being the primary vector. These attacks are designed to trigger manual penalties or algorithmic devaluation by search engines.
While Google's algorithms are designed to detect and ignore many negative SEO attacks, real-world evidence shows that sophisticated attacks can cause lasting damage if not addressed quickly. The key is early detection and swift remediation. Sites that monitor their backlink profiles monthly, use Google Search Console alerts, and maintain strong security protocols can minimize damage. However, recovery from severe attacks involving site hacking or extensive content scraping can take months or even years depending on the extent of the sabotage.
Negative SEO directly impacts how your brand appears across AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. When competitors use negative SEO tactics to damage your search rankings, your website receives less visibility in traditional search results, which reduces the likelihood that AI training data includes your content. This creates a compounding effect where lower search visibility leads to reduced AI citations and mentions. Platforms like AmICited help monitor these appearances and detect when negative SEO attacks are affecting your brand's presence across AI-powered search engines.
Negative SEO exists in a legal gray area. While the tactics themselves (like hacking, impersonation, or defamation) may violate laws, many negative SEO practices are primarily violations of search engine policies rather than criminal statutes. However, certain attacks—such as site hacking, DMCA fraud, or creating fake reviews with intent to defraud—can result in legal consequences. The best approach is to document all attacks, report them to relevant platforms and authorities, and consult legal counsel if the attack involves criminal behavior like hacking or identity theft.
Warning signs include sudden drops in search rankings or organic traffic, unexpected spikes in toxic backlinks from irrelevant domains, unusual bounce rates, suspicious comments or reviews, and alerts from Google Search Console about security issues or manual actions. Use tools like Semrush's Backlink Audit, Google Search Console's Links section, and brand monitoring tools to detect attacks early. Monitor your backlink profile monthly, set up Google Alerts for your brand name, and track your site's performance metrics consistently to catch anomalies before they cause significant damage.
First, assess the damage by checking Google Search Console for ranking drops, traffic declines, and security alerts. Audit your backlink profile using tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to identify toxic links. If you find spammy backlinks, use Google's Disavow Tool to tell Google to ignore them. For hacked sites, remove malicious code and request reindexing. For content scraping, file DMCA takedown notices. For fake reviews, report them to the platform. Document everything and consider filing a reconsideration request with Google if you received a manual action penalty.
Google's official stance is that well-designed algorithms should ignore negative SEO attacks and not penalize the victim. However, this depends on the sophistication of the attack and how quickly it's detected. Google's Penguin algorithm is designed to devalue spam links, but extremely aggressive attacks—especially those involving site hacking or extensive content manipulation—may trigger manual actions. The best defense is proactive monitoring and rapid response. Google recommends focusing on building quality content and legitimate SEO rather than worrying about attacks, but this doesn't mean you should ignore suspicious activity.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what search engine spam is, including black hat SEO tactics like keyword stuffing, cloaking, and link farms. Understand how Google detects spam and the pe...

Cloaking is a black-hat SEO technique showing different content to search engines vs users. Learn how it works, its risks, detection methods, and why it violate...
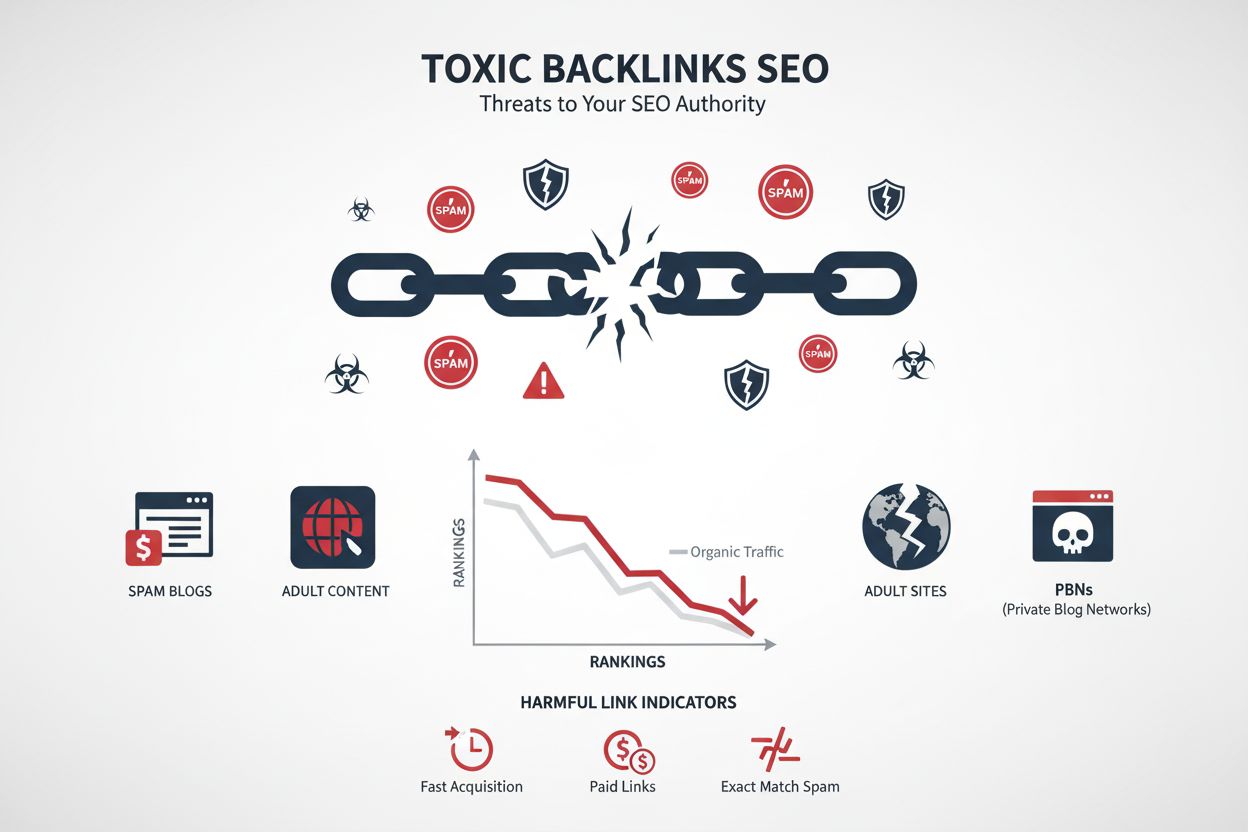
Learn what toxic links are, how they harm SEO rankings, and proven strategies to identify and remove harmful backlinks from your website's link profile.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.