Local SEO
Local SEO is the practice of optimizing a business's online presence for location-based search results. Learn how to rank higher in Google Maps, local pack, and...
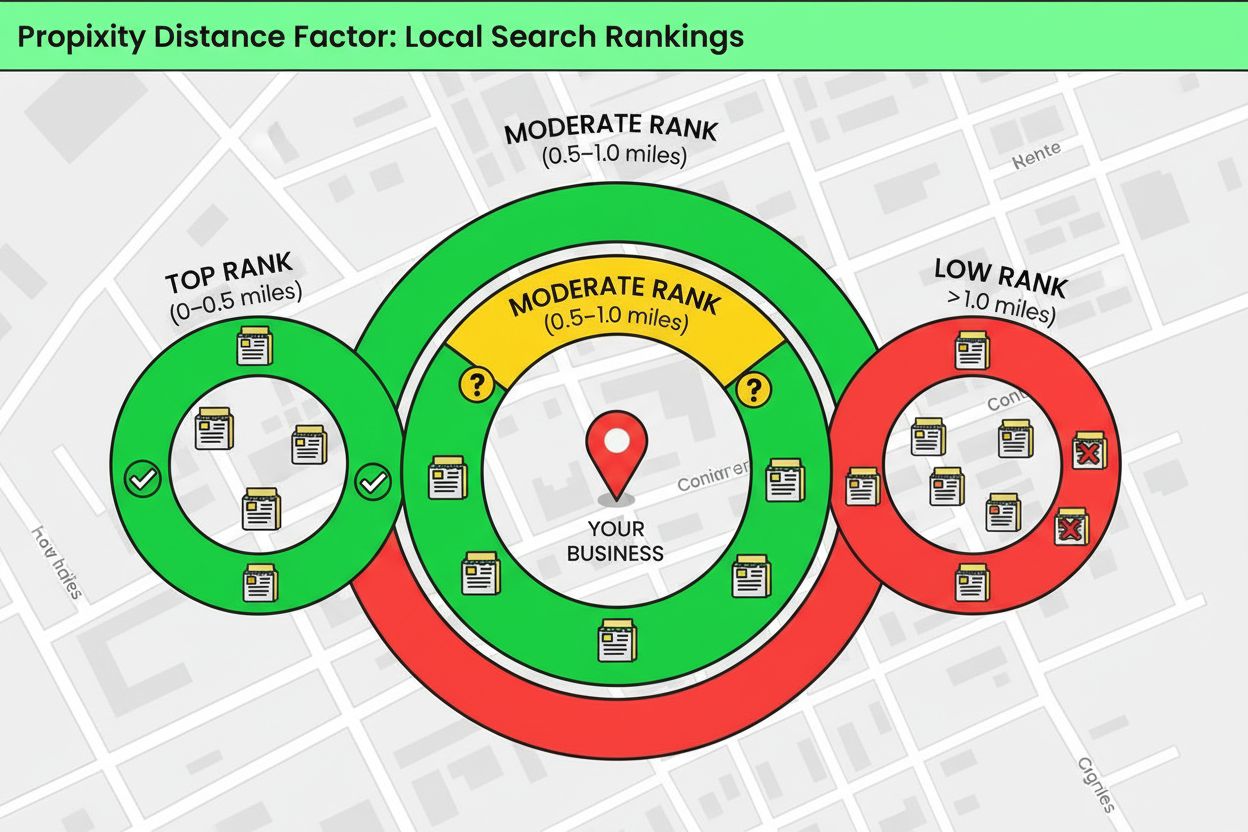
Proximity is the physical distance between a searcher’s location and a business, serving as one of Google’s three core ranking pillars for local search results. Businesses closer to the searcher are significantly more likely to appear in local packs and maps, with rankings typically declining as distance increases.
Proximity is the physical distance between a searcher's location and a business, serving as one of Google's three core ranking pillars for local search results. Businesses closer to the searcher are significantly more likely to appear in local packs and maps, with rankings typically declining as distance increases.
Proximity is the physical distance between a searcher’s location and a business, representing one of Google’s three core ranking pillars for local search results alongside relevance and prominence. When a user performs a local search—such as “coffee near me” or “plumber in downtown”—Google calculates the distance between the searcher’s device and nearby businesses to determine which results to display. Businesses located closer to the searcher are significantly more likely to appear in the local pack (the three highlighted results at the top of Google Maps), with visibility typically declining as distance increases. This proximity bias is fundamental to how Google’s local algorithm operates, ensuring that users receive results from businesses they can actually visit or access. Understanding proximity is essential for local businesses seeking to improve their search visibility, as it directly influences whether potential customers discover them in local search results.
The concept of proximity in local search emerged as Google Maps and local search capabilities evolved in the early 2000s. Initially, local search results were relatively simple, relying primarily on keyword matching and basic location data. However, as mobile devices became ubiquitous and users increasingly searched for nearby services, Google recognized the need to prioritize distance as a core ranking signal. By the mid-2010s, proximity had solidified as one of the “Big Three” local ranking factors, alongside relevance and prominence. Research from Whitespark’s annual Local Search Ranking Factors survey, which has tracked expert opinions since 2008, consistently confirms proximity’s importance. According to 2025 data, proximity remains the second most influential factor for local pack rankings, with over 46% of all Google searches containing local intent, making proximity optimization critical for businesses. The rise of mobile-first indexing and voice search has further amplified proximity’s significance, as users increasingly search for immediate, nearby solutions while on the go.
Google determines a searcher’s proximity to a business through a sophisticated combination of data sources. Google uses Android device settings, web and app activity, mobile and Wi-Fi network signals, and IP addresses to pinpoint user location with remarkable precision. This multi-layered approach enables Google to calculate real-time distance between a searcher’s device and business locations, typically accurate to within a few meters in urban areas. The precision of location data varies depending on device type, network connectivity, and user privacy settings. For businesses, this means that their physical address registered in Google Business Profile (GBP) serves as the anchor point for proximity calculations. When a user performs a search, Google’s algorithm instantly measures the distance and uses this metric to rank results. The proximity calculation is dynamic—a business ranking first for a searcher at one location may rank tenth for a searcher just a few miles away. This dynamic nature of proximity-based rankings makes it one of the most challenging factors for businesses to optimize, as they cannot change their physical location to improve rankings across different geographic areas.
| Factor | Definition | Primary Impact | How to Optimize | Importance for Local Pack |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proximity | Physical distance between searcher and business | Determines geographic radius of visibility | Accurate NAP in GBP; service area settings | 2nd most important (after GBP categories) |
| Relevance | How well a business matches the search query | Determines if business appears for specific keywords | GBP categories, on-page keywords, business hours | 3rd most important (15% of ranking factors) |
| Prominence | How well-known and reputable a business is | Determines ranking position among nearby competitors | Reviews, backlinks, citations, brand mentions | 2nd most important (20% of ranking factors) |
| Combined Effect | All three factors work together in Google’s algorithm | Determines final ranking position and visibility | Balanced optimization across all three pillars | Proximity alone cannot guarantee top rankings |
While proximity is crucial, it works in concert with relevance and prominence. A business can be the closest option but still rank lower if competitors have significantly better reviews, more citations, or stronger keyword relevance. Conversely, a business with exceptional prominence signals may rank beyond its immediate geographic radius if it specializes in a niche offering. The interplay between these three factors creates a complex ranking environment where proximity provides the foundation, but relevance and prominence determine the final outcome.
One of the most observable phenomena in local search is the proximity decay effect, where rankings decline predictably as distance from a business increases. Research using gridded local rank tracking tools reveals that businesses typically experience the steepest ranking drops within the first mile of their location, with rankings continuing to decline more gradually at greater distances. The rate of this decline varies significantly based on several factors: population density, search volume, local competition, and the specific search query. In densely populated urban areas like New York City, proximity bias is extremely strong—businesses may rank well only within a few blocks of their location. In rural areas, Google extends the geographic radius further because fewer businesses are available to serve customers across larger distances. According to rankings.io’s proximity study, the percentage of top 20 results that come from within a city varies dramatically, ranging from 27% in Pittsburgh to 92% in Queens, demonstrating how local market characteristics influence proximity’s impact. This distance decay effect means that a business’s ranking position is not static—it changes based on where the searcher is located, making proximity one of the most dynamic ranking factors.
Mobile search has fundamentally amplified the importance of proximity in local search rankings. Mobile users searching for “near me” queries expect results within walking or short driving distance, making proximity the dominant ranking factor for these searches. Mobile devices provide more precise location data through GPS technology, enabling Google to calculate proximity with greater accuracy than desktop searches. Additionally, mobile users typically search for immediate solutions—finding a coffee shop, restaurant, or service provider they can visit right now—rather than researching options for future reference. This behavioral difference means that proximity has a more pronounced effect on mobile rankings than desktop rankings. According to 2025 local search data, mobile searches account for over 60% of all local search queries, underscoring how critical proximity optimization has become. Businesses optimizing for mobile must ensure their Google Business Profile is fully accurate, their website is mobile-friendly, and they include clear directions and click-to-call buttons. The mobile-first indexing approach Google adopted means that mobile proximity performance directly influences overall local search visibility.
Proximity bias refers to Google’s inherent tendency to prioritize businesses closest to the searcher, even when competitors have stronger relevance or prominence signals. This bias creates a significant challenge for businesses seeking to expand their visibility beyond their immediate geographic area. A business located in one neighborhood may struggle to rank for the same keywords in a neighboring area just a few miles away, even if it has superior reviews, more citations, and better content. This limitation is particularly problematic for service-based businesses, multi-location enterprises, and specialized retailers that serve customers across wider geographic areas. However, proximity bias is not absolute—it can be partially overcome through strategic optimization. Businesses that build exceptional prominence through high-quality reviews, authoritative backlinks, and unstructured citations (mentions on blogs, news sites, and industry publications) may extend their ranking radius. Additionally, specializing in a niche offering can help overcome proximity bias; a restaurant known for a specific cuisine or dish may rank across a wider radius for that specialty than for generic restaurant searches. Understanding that proximity bias exists and developing strategies to work within or around it is essential for local SEO success.
Google’s interpretation of hyperlocal intent significantly influences how proximity affects search results. Hyperlocal intent refers to search phrases that Google recognizes as having strong local intent, even when users don’t explicitly include geographic modifiers. For example, searches for “coffee,” “pizza,” or “gas station” are understood by Google to have hyperlocal intent—users want nearby options, not results from across the country. Google responds to these searches by displaying a local pack with results clustered within a tight, neighborhood-level radius. In contrast, searches for “sports stadium” or “museum” have local intent but a wider geographic radius, as Google recognizes that users are willing to travel further for these destinations. This distinction between hyperlocal and broader local intent means that proximity’s impact varies by search query. A business may rank well across a 5-mile radius for a generic search but only within a 1-mile radius for a hyperlocal search. Understanding which search queries have hyperlocal intent versus broader local intent helps businesses set realistic expectations for their geographic ranking potential and develop targeted optimization strategies for different search types.
As artificial intelligence increasingly influences how users discover local businesses, proximity remains a critical factor in AI search visibility. Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude rely on local citations, reviews, and structured data to provide location-based recommendations to users. When these AI systems generate responses to local queries, they prioritize businesses with strong proximity signals combined with high-quality citations and reviews. This means that proximity optimization for traditional Google local search directly benefits AI search visibility. However, the relationship is more nuanced than traditional local search—AI systems may weight proximity differently depending on the context of the query and the user’s stated location preferences. Monitoring brand visibility across AI platforms requires tracking not just traditional local pack rankings but also how your business appears in AI-generated local search results. AmICited and similar AI monitoring platforms track brand citations across multiple AI search engines, revealing how proximity and other local ranking factors influence visibility in this emerging search channel. As AI search continues to grow—with some estimates suggesting AI-powered search will account for 25-30% of all searches by 2026—understanding proximity’s role in AI visibility becomes increasingly important for local businesses.
For businesses with multiple physical locations, proximity optimization becomes significantly more complex but also more rewarding. Each location has its own proximity radius and ranking potential, requiring individualized optimization strategies. Multi-location businesses must create separate Google Business Profiles for each location, each with accurate NAP information and location-specific details. Additionally, each location should have its own dedicated landing page on the company website with unique content addressing that specific area’s market. This approach allows Google to understand that the business operates multiple locations and can rank each location independently based on proximity to different searchers. The challenge intensifies when locations are close together—a business with two locations in the same city may experience cannibalization, where both locations compete for the same search queries. Managing this requires careful keyword strategy, ensuring each location targets slightly different geographic areas or customer segments. Multi-location businesses that successfully optimize for proximity at every branch can dominate multiple local markets, capturing significantly more search traffic than single-location competitors. However, this requires consistent effort in maintaining accurate information, generating location-specific reviews, and building local citations for each location.
Effectively measuring proximity’s impact on your local search performance requires specialized tools and methodologies. Gridded local rank tracking tools like Whitespark’s Local Ranking Grids and Local Falcon allow businesses to emulate different geographic locations and monitor how rankings change across distance zones. These tools automate the process of testing rankings at multiple points around a business location, revealing patterns in how proximity affects visibility. Google Business Profile Insights provides valuable data on where customers are searching from, helping businesses understand their geographic reach and identify areas where proximity is limiting visibility. Additionally, traditional rank tracking tools can be configured to track rankings from multiple geographic locations, providing insights into how proximity influences performance for different search queries. Analyzing this data reveals which keywords have strong hyperlocal intent (tight proximity radius) versus broader local intent (wider radius). By understanding these patterns, businesses can adjust their optimization strategies, focusing resources on keywords where they have proximity advantages while developing specialized offerings to overcome proximity bias for other keywords. Regular monitoring and analysis of proximity-based performance metrics enables continuous optimization and helps businesses stay competitive in their local markets.
The future of proximity as a local ranking factor will be shaped by several emerging trends and technologies. Voice search and conversational AI are increasingly influencing how proximity operates, as users ask questions like “What’s the nearest coffee shop?” or “Where can I find a plumber nearby?” These voice queries have extremely strong hyperlocal intent, making proximity even more dominant than in text-based searches. Augmented reality (AR) and location-based apps are creating new ways for users to discover nearby businesses, potentially creating new proximity-based ranking opportunities beyond traditional Google search. Hyper-personalization based on user behavior, preferences, and search history may cause proximity to interact with personalization signals in more complex ways, where Google shows different results to different users based on their individual patterns. Additionally, as AI search platforms mature and compete with Google, proximity may be weighted differently across different search engines, requiring businesses to optimize for multiple proximity-based ranking systems simultaneously. The integration of proximity with emerging technologies like geofencing, location-based advertising, and real-time inventory data suggests that proximity will remain central to local search for years to come. Businesses that stay ahead of these trends by continuously monitoring their proximity-based performance and adapting their strategies will maintain competitive advantages in local search visibility.
Google uses multiple data sources to pinpoint user location with high precision, including Android device settings, web and app activity, mobile and Wi-Fi network signals, and IP addresses. This combination of signals enables Google to calculate the distance between a searcher's device and a business location in real-time, allowing the search engine to deliver proximity-based local results. The accuracy of this location data is critical to how effectively proximity influences local search rankings.
Yes, businesses can partially overcome proximity bias by building stronger signals of relevance and prominence than nearby competitors. For example, a restaurant 20 minutes away with multiple reviews mentioning a specific dish may outrank a closer competitor lacking these signals. However, proximity remains a powerful factor, and overcoming it typically requires specialization in a niche offering, low local competition, or significant investment in building entity strength through reviews, citations, and content.
Proximity refers to the actual physical distance between a searcher and a business, while hyperlocal intent describes Google's interpretation of search phrases that suggest users want nearby results. For example, a search for 'coffee' has strong hyperlocal intent, causing Google to show results within a tight neighborhood radius. In contrast, 'sports stadium' has local intent but a wider radius since users are willing to travel further. Understanding this distinction helps businesses optimize for the right geographic scope.
Proximity has a more pronounced effect on mobile search because mobile users typically search for immediate, nearby solutions. Mobile devices provide more precise location data through GPS, making proximity calculations more accurate. Additionally, mobile users searching for 'near me' queries expect results within walking or short driving distance, making proximity a dominant ranking factor. Desktop searches may show slightly wider geographic ranges, though proximity still significantly influences rankings.
Proximity is becoming increasingly important for AI search visibility, as large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Perplexity rely on local citations, reviews, and structured data to provide location-based recommendations. Businesses appearing in AI Overviews for local queries benefit from strong proximity signals combined with high-quality citations and reviews. Monitoring brand visibility across AI platforms requires tracking how proximity, combined with relevance and prominence, influences appearance in AI-generated local search results.
Proximity has a stronger impact on local pack and Google Maps rankings than on localized organic results. While proximity still influences organic rankings, factors like on-page optimization, backlinks, and content quality play more significant roles in organic search. According to 2025 local search ranking factor studies, proximity is the second most important factor for local pack rankings but has less influence on traditional organic search results, where relevance and authority dominate.
Businesses can use gridded local rank tracking tools like Whitespark's Local Ranking Grids or Local Falcon to emulate different geographic locations and monitor how rankings change across distance zones. These tools automate the process of testing rankings at multiple points around a business location, revealing how proximity affects visibility. Additionally, Google Business Profile Insights provides data on where customers are searching from, helping businesses understand their geographic reach and proximity performance.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Local SEO is the practice of optimizing a business's online presence for location-based search results. Learn how to rank higher in Google Maps, local pack, and...

Learn how local businesses can optimize for AI visibility across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Gemini, and Perplexity. Discover strategies to appear in AI-gener...
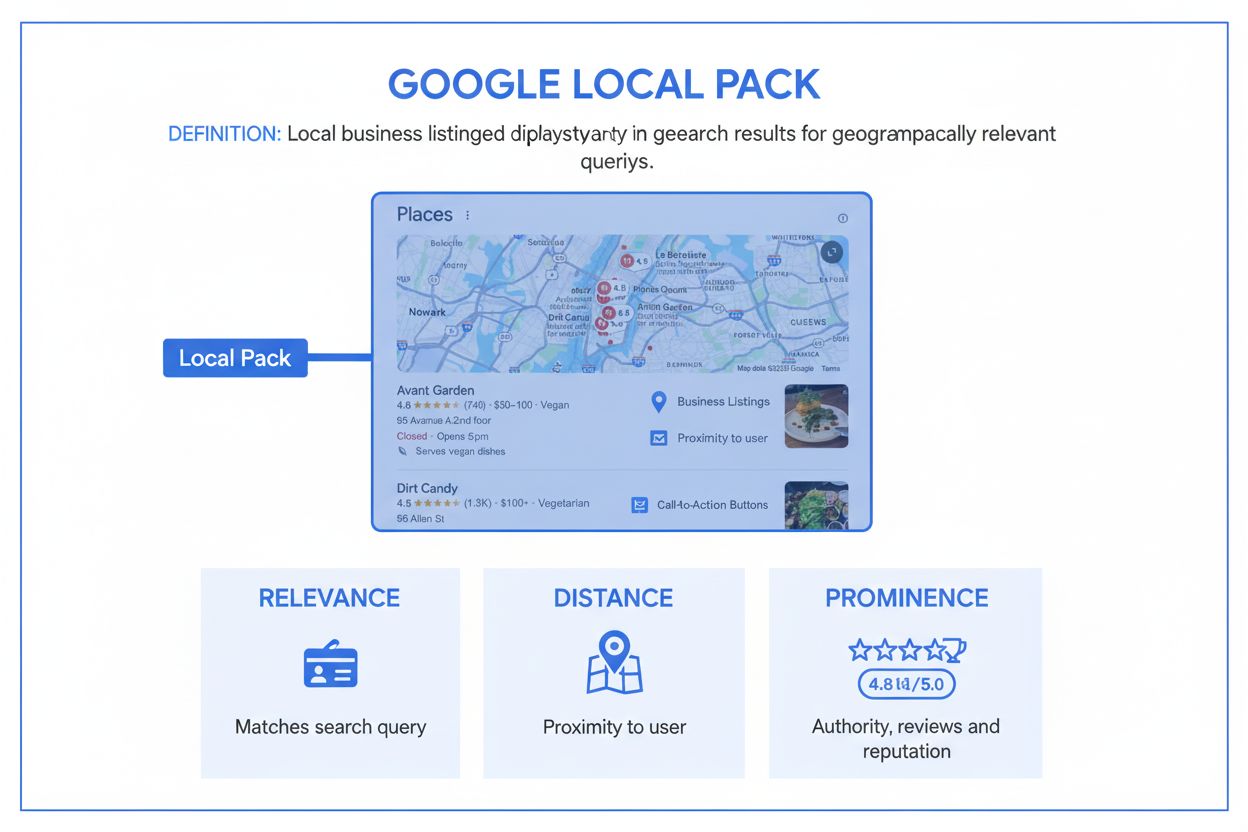
Learn what the Local Pack is, how it works, and why it's essential for local business visibility. Discover ranking factors and optimization strategies for appea...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.