
Semantic Query Matching
Learn how semantic query matching enables AI systems to understand user intent and deliver relevant results beyond keyword matching. Explore NLP, embeddings, an...
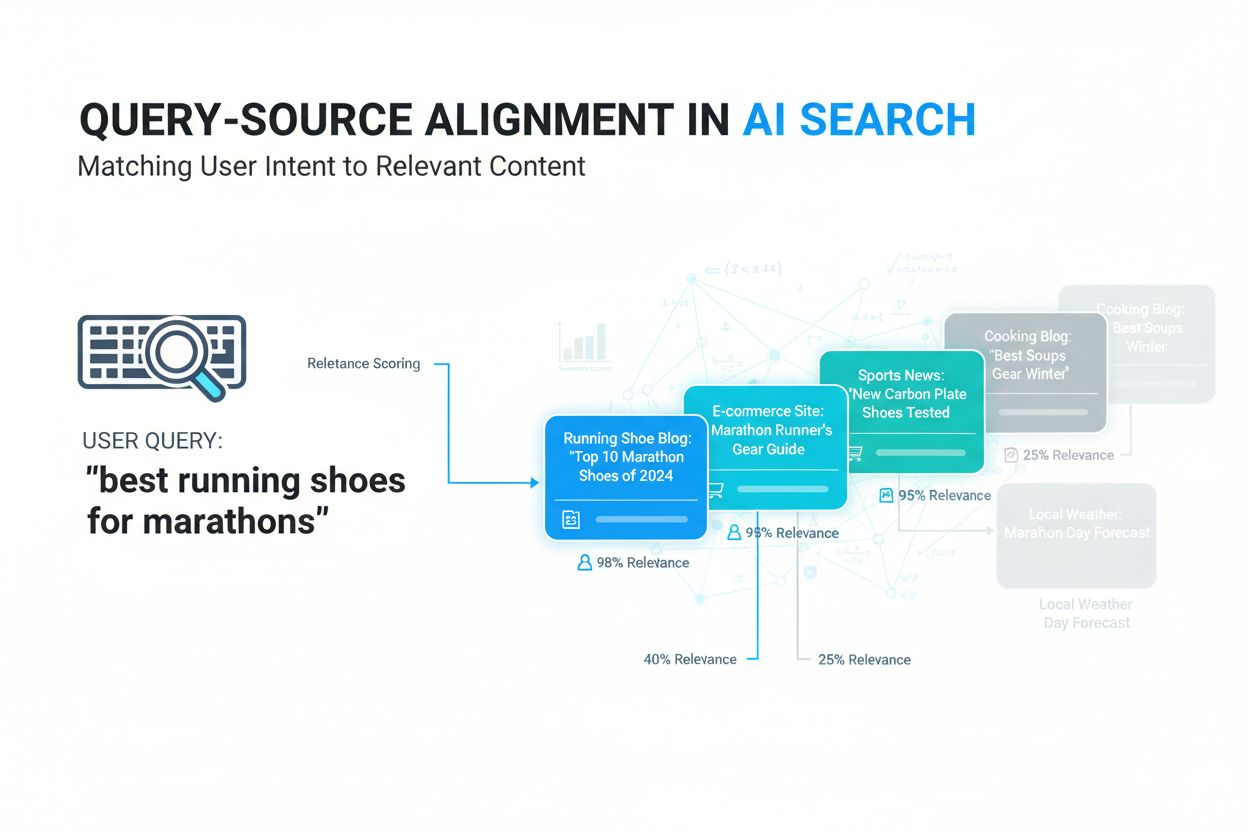
Query-source alignment is the process of matching user search queries with the most relevant information sources based on semantic meaning and contextual relevance. It uses AI and machine learning to understand the intent behind queries and connect them to sources that genuinely address user information needs, rather than relying on simple keyword matching. This technology is fundamental to modern AI search systems like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. Effective alignment ensures that AI systems return accurate, relevant results that improve user satisfaction and content visibility.
Query-source alignment is the process of matching user search queries with the most relevant information sources based on semantic meaning and contextual relevance. It uses AI and machine learning to understand the intent behind queries and connect them to sources that genuinely address user information needs, rather than relying on simple keyword matching. This technology is fundamental to modern AI search systems like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. Effective alignment ensures that AI systems return accurate, relevant results that improve user satisfaction and content visibility.
Query-source alignment refers to the process of matching user search queries with the most relevant information sources based on semantic meaning and contextual relevance rather than simple keyword overlap. At its core, this concept addresses a fundamental challenge in information retrieval: ensuring that when users search for information, the results they receive are not just technically related to their search terms, but genuinely address their underlying information needs.
Traditionally, search systems relied on keyword matching—finding documents that contained the exact words or phrases a user typed. While straightforward, this approach frequently produced irrelevant results because it ignored context, intent, and the deeper meaning behind queries. Query-source alignment solves this problem by employing semantic matching techniques that understand the conceptual relationship between what users are asking and what information sources contain. This means a search for “vehicle maintenance” can effectively retrieve articles about “car upkeep” or “automobile servicing,” even without exact keyword matches.
In the context of modern AI search systems, query-source alignment has become increasingly important as artificial intelligence enables more sophisticated understanding of language nuance and user intent. Rather than treating queries as mere collections of words, AI-powered alignment systems analyze the semantic content of both the user’s question and available sources, creating meaningful connections based on relevance rather than surface-level similarity.
This distinction matters significantly because it directly impacts search quality and user satisfaction. Effective query-source alignment ensures that information retrieval systems return results that genuinely answer user questions, reduce irrelevant noise in search results, and help users discover information they might not have found using traditional keyword-based approaches. As AI search technology continues to evolve, query-source alignment remains a cornerstone principle for building systems that truly understand and respond to user information needs.
The technical process of query-source alignment involves several sophisticated steps that transform user queries into meaningful connections with relevant sources:
Query Processing and Tokenization - When a user submits a search query, the system first breaks it down into individual tokens (words and phrases) and analyzes the grammatical structure. Natural language processing algorithms identify the core concepts, entities, and intent behind the query, removing stop words and identifying the most meaningful components that will guide the alignment process.
Query Embedding Generation - The processed query is converted into a semantic vector—a mathematical representation that captures the meaning and context of the query in multi-dimensional space. This embedding is created using neural language models trained on vast amounts of text data, allowing the system to represent the query’s semantic essence rather than just its literal words.
Source Document Vectorization - Simultaneously, all available source documents in the system are converted into semantic vectors using the same embedding model. This ensures that both queries and sources are represented in the same semantic space, making direct comparison possible. Each document’s vector captures its overall meaning, topics, and relevance signals.
Vector Similarity Calculations - The system calculates the similarity between the query vector and each source document vector using mathematical distance metrics, most commonly cosine similarity. This calculation determines how closely the semantic meaning of each source aligns with the semantic meaning of the query, producing a similarity score between 0 and 1.
Relevance Scoring and Ranking - Beyond semantic similarity, the system applies additional ranking factors including domain authority, content freshness, user engagement metrics, and topical relevance. These factors are combined with semantic similarity scores to produce a comprehensive relevance score for each source, determining its position in the ranked results.
Content Matching Validation - The system validates that the selected sources actually contain relevant information by analyzing specific sections of the content. This ensures that sources aren’t ranked highly just because they mention relevant keywords, but because they genuinely address the user’s information need with substantive, accurate content.
Final Source Selection and Ranking - The top-ranked sources are selected for presentation to the user or for citation in AI-generated answers. The final ranking reflects the combined assessment of semantic alignment, authority, relevance, and content quality, ensuring that users receive the most appropriate sources for their specific query.
| Method/Approach | How It Works | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword Matching (Traditional) | Searches for exact words or phrases in documents; ranks based on frequency and position | Simple to implement; fast processing; transparent matching logic | Ignores context and intent; produces irrelevant results; fails with synonyms | Simple, factual queries; legacy systems |
| Semantic Similarity (Vector-based) | Converts queries and documents to semantic vectors; calculates similarity using mathematical distance metrics | Understands meaning beyond keywords; handles synonyms and context; highly accurate | Computationally expensive; requires large training datasets; less transparent | Complex queries; intent-driven search; modern AI systems |
| Entity Recognition | Identifies and classifies key entities (people, places, organizations, products) in queries and content | Improves understanding of specific subjects; disambiguates terms; enables knowledge graph integration | Requires extensive entity databases; struggles with new or niche entities | Queries about specific entities; knowledge-based search |
| Contextual Understanding | Analyzes surrounding context, user history, and query patterns to infer meaning | Captures nuanced intent; personalizes results; improves accuracy for ambiguous queries | Privacy concerns with user data; requires historical data; complex implementation | Conversational search; personalized recommendations |
| Hybrid Approach | Combines multiple methods (semantic similarity, entity recognition, contextual understanding) for comprehensive matching | Leverages strengths of multiple methods; more robust and accurate; handles diverse query types | Complex to implement and maintain; higher computational costs; harder to debug | Enterprise search; AI search platforms |
| Knowledge Graph-based | Uses interconnected entities and relationships to understand queries and match relevant sources | Captures real-world relationships; enables sophisticated reasoning; supports complex queries | Requires extensive knowledge graph construction; maintenance intensive; domain-specific | Complex research queries; semantic web applications |
Query-source alignment is fundamental to how modern AI search systems operate and select sources for their answers:
Google AI Overviews - Uses query-source alignment to select the most relevant sources to cite when generating AI-powered search summaries. The system analyzes semantic alignment between the user’s query and available web pages, prioritizing sources with strong semantic relevance and high authority. Research shows that approximately 70% of sources in AI Overviews come from the top 10 organic search results, indicating that traditional ranking and semantic alignment work together.
ChatGPT with Browsing - When ChatGPT’s browsing feature is enabled, it uses query-source alignment to identify and fetch the most relevant web pages for answering user questions. The system prioritizes authoritative sources with strong semantic alignment to the query, ensuring that generated answers are grounded in reliable, relevant information from the web.
Perplexity AI - Implements query-source alignment to select sources for its conversational answers. The platform displays cited sources alongside its responses, making the alignment process transparent to users. Strong semantic alignment between queries and sources ensures that Perplexity’s answers are well-grounded and verifiable.
Bing AI Chat - Leverages query-source alignment to integrate search results into conversational responses. The system matches user queries to relevant Bing search results using semantic understanding, then synthesizes information from multiple aligned sources into coherent answers.
Core Sources Concept - AI systems identify “core sources”—URLs that consistently appear across multiple responses for related queries. These sources have exceptionally strong semantic alignment with query topics and are considered highly authoritative. Becoming a core source for your niche is a major goal for content visibility in AI search.
Semantic Relevance Scoring - AI platforms assign relevance scores based on how well source content semantically aligns with query intent. Sources with higher semantic alignment scores are more likely to be selected, cited, and featured prominently in AI-generated answers.
Multi-Query Alignment - When AI systems generate answers, they often break down user queries into multiple sub-queries (fan-out queries). Query-source alignment is applied to each sub-query, and sources that align well with multiple related queries are prioritized, creating more comprehensive and well-sourced answers.
AmICited Monitoring - AmICited tracks query-source alignment by monitoring which of your pages are selected as sources for specific queries across AI platforms. The platform shows your semantic alignment scores, tracks core source status, and identifies opportunities to improve alignment with high-value queries in your niche.
Authority and Semantic Balance - While domain authority remains important, research indicates that semantic alignment is increasingly critical. Sources with strong semantic alignment but moderate authority can outrank high-authority sources with weak semantic alignment, showing that meaning matters as much as reputation.
Real-time Alignment Tracking - Modern AI monitoring platforms track how query-source alignment changes over time as content is updated and new sources emerge. This enables marketers to understand which content updates improve alignment and which queries represent the best opportunities for visibility.
Understanding and optimizing query-source alignment has become essential for content creators, marketers, and brands in the age of AI search:
Brand Citation Tracking - Query-source alignment directly determines whether your brand and content are cited in AI-generated answers. Platforms like AmICited monitor this alignment, showing you which queries your content ranks for in AI answers and how often your brand is mentioned across AI search platforms.
Semantic Relevance and Discovery - Strong semantic alignment with user queries increases the likelihood that your content will be discovered and cited by AI systems. This is especially important for long-tail queries and niche topics where traditional SEO competition may be lower but semantic relevance is critical.
Competitive Advantage in AI Search - As AI search becomes more prevalent, brands with strong query-source alignment for high-value queries gain significant competitive advantages. Early optimization for semantic alignment positions your content to capture visibility before competitors adapt their strategies.
Source Tracking and Attribution - Understanding query-source alignment helps you track which of your pages are selected as sources for specific queries. This attribution data reveals which content performs best in AI answers and which topics represent opportunities for improvement.
Optimization for AI Answers - Rather than optimizing solely for traditional search rankings, modern content strategy must account for query-source alignment. Content that ranks well in traditional search but has weak semantic alignment may not be selected by AI systems, missing opportunities for visibility.
Risk Mitigation and Brand Control - Monitoring query-source alignment helps you understand how your brand is represented in AI answers. If competitors’ content has stronger alignment for important queries, you can identify gaps and create content that better addresses user intent.
Content Strategy Refinement - Query-source alignment metrics reveal which topics, keywords, and content formats resonate most strongly with AI systems. This data guides content strategy, helping you focus on topics where semantic alignment is achievable and valuable.
Competitive Intelligence - By analyzing query-source alignment across your industry, you can identify which competitors’ content is most frequently cited in AI answers. This competitive intelligence reveals gaps in your content strategy and opportunities to capture visibility.
Long-term Visibility Planning - Query-source alignment is more stable than traditional search rankings because it’s based on semantic meaning rather than algorithmic factors that change frequently. Strong semantic alignment provides more durable visibility in AI search over time.
Measurable ROI for Content Investment - Tracking query-source alignment and resulting visibility in AI answers provides clear metrics for measuring content ROI. You can see directly how content investments translate into brand citations and traffic from AI search platforms.
Optimizing for query-source alignment requires a strategic approach that goes beyond traditional SEO. The goal is to ensure your content has strong semantic alignment with the queries your target audience uses, making it more likely to be selected by AI systems as a relevant source.
Understanding Semantic Optimization - Semantic optimization focuses on ensuring that your content deeply addresses specific user intents and questions, not just ranking for keywords. This involves understanding the semantic relationships between concepts, using consistent terminology, and structuring content to clearly communicate meaning to both humans and AI systems.
Best Practices for Query-Source Alignment:
Conduct Semantic Keyword Research - Go beyond traditional keyword research to identify semantic clusters of related terms and concepts. Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to find not just high-volume keywords, but semantic variations and related queries that address the same user intent. Group these into semantic clusters and create comprehensive content that addresses all variations.
Implement Semantic HTML5 Markup - Use semantic HTML5 elements like <article>, <section>, <header>, <nav>, and <main> to clearly structure your content. These elements help AI systems understand the organization and hierarchy of your content, improving semantic interpretation. Use heading tags (<h1>, <h2>, etc.) hierarchically to establish clear topic relationships.
Create Entity-Rich Content - Identify key entities (people, organizations, products, concepts) relevant to your topic and mention them explicitly in your content. Use consistent terminology and provide context that helps AI systems understand which entities you’re discussing. For example, if discussing “Apple,” clarify whether you mean the technology company or the fruit through contextual clues.
Use Structured Data (JSON-LD) - Implement schema.org markup using JSON-LD format to provide explicit semantic information about your content. Use appropriate schema types like Article, NewsArticle, HowTo, FAQPage, or Product depending on your content type. This helps AI systems understand exactly what your content is about and how it relates to user queries.
Optimize for Search Intent Variations - Identify the different ways users express the same information need and create content that addresses all variations. For example, users might search for “how to fix a leaky faucet,” “faucet repair guide,” or “leaky tap solutions.” Create comprehensive content that addresses all these intent variations with consistent semantic meaning.
Develop Comprehensive Topic Coverage - Rather than creating multiple shallow articles on similar topics, develop comprehensive guides that thoroughly address specific topics. AI systems favor in-depth content that provides complete answers to user questions. Use topic clustering to ensure your content covers all aspects of a topic with strong semantic relationships between sections.
Maintain Consistent Terminology - Use consistent language and terminology throughout your content and across your website. If you introduce a concept with a specific term, use that same term consistently rather than switching to synonyms. This consistency helps AI systems recognize that you’re discussing the same concepts throughout your content.
Create Clear Content Hierarchies - Structure your content with clear hierarchies that show how concepts relate to each other. Use heading tags, bullet points, and numbered lists to establish relationships between ideas. This structure helps AI systems understand the semantic organization of your content and how different concepts connect.
Optimize Meta Descriptions and Titles - Write meta descriptions and page titles that clearly communicate the semantic content of your page. These elements are often used by AI systems to understand page content, so ensure they accurately reflect the page’s main topic and key concepts. Include relevant entities and concepts in titles and descriptions.
Monitor Semantic Alignment Scores - Use AI monitoring platforms like AmICited to track your semantic alignment scores for important queries. Monitor how your alignment changes as you update content and identify which content updates improve alignment. Track which queries show the strongest alignment and focus on expanding content in those areas.
Real-World Examples Across Industries:
E-commerce - An online retailer selling running shoes can optimize for query-source alignment by creating comprehensive guides about “marathon training shoes,” “best running shoes for different foot types,” and “shoe technology comparison.” By addressing semantic variations of user intent and using consistent terminology about shoe features, the retailer increases the likelihood of being selected as a source in AI answers about running footwear.
Healthcare - A medical practice can improve query-source alignment by creating detailed content about specific conditions, treatments, and practitioners. Using proper medical terminology, entity recognition for conditions and treatments, and structured data markup helps AI systems understand the semantic content and match it to relevant health-related queries.
Technology - A software company can optimize alignment by creating comprehensive documentation and guides that address semantic variations of user problems. Using consistent terminology for features, clear hierarchies of concepts, and structured data helps AI systems recognize the content as a relevant source for technology-related queries.
Traditional keyword matching simply looks for exact words or phrases in documents, while query-source alignment uses semantic understanding to match the meaning and intent behind queries. This means a search for 'vehicle maintenance' can retrieve articles about 'car upkeep' even without exact keyword matches. Query-source alignment produces more relevant results because it understands context and user intent rather than just surface-level word similarity.
AI search platforms use query-source alignment to select the most relevant sources to cite in their generated answers. The system analyzes both the semantic meaning of the user's query and the content of available sources, then ranks sources based on relevance, authority, and semantic alignment. This ensures that AI-generated answers are grounded in high-quality, relevant sources that genuinely address the user's information need.
Query-source alignment directly impacts whether your content gets selected as a source in AI-generated answers. If your content has strong semantic alignment with common queries in your niche, it's more likely to be cited by AI systems. This visibility in AI answers drives traffic and builds brand authority. Understanding and optimizing for query-source alignment is essential for maintaining visibility in the age of AI search.
To optimize for query-source alignment, focus on creating content that deeply addresses specific user intents and questions. Use semantic HTML markup, implement structured data (JSON-LD), ensure clear entity recognition, and maintain consistent terminology. Write comprehensive, solution-focused content that answers questions thoroughly. Monitor your semantic alignment scores and track how your content performs in AI answers using tools like AmICited.
Semantic similarity is the core mechanism of query-source alignment. It measures how closely the meaning of a query matches the meaning of content in sources. This is calculated using vector embeddings—mathematical representations of text that capture semantic meaning. Sources with higher semantic similarity scores to the query are ranked higher and more likely to be selected by AI systems as relevant sources for answering user questions.
AmICited is an AI monitoring platform that tracks how your brand and content are cited across AI search platforms. It monitors query-source alignment by showing which of your pages are selected as sources for specific queries, how often your brand is mentioned in AI answers, and how your semantic alignment compares to competitors. This data helps you understand and optimize your content strategy for better visibility in AI search.
Core sources are URLs that consistently appear across multiple AI-generated answers for the same or related queries. These sources have strong semantic alignment with the query topics and are considered highly relevant by AI systems. Core sources typically rank higher in traditional search results and have better semantic alignment with query intent. Becoming a core source for your niche queries is a key goal for content visibility in AI search.
Entity recognition helps AI systems identify and understand key concepts, people, organizations, and topics in both queries and source content. By recognizing entities, AI systems can better understand what a query is really asking about and match it to sources that discuss the same entities in relevant contexts. For example, recognizing that 'Apple' refers to the technology company rather than the fruit helps align queries about Apple products with relevant tech sources.
Track how your content is cited across AI search platforms and optimize for better query-source alignment with AmICited's AI monitoring platform.

Learn how semantic query matching enables AI systems to understand user intent and deliver relevant results beyond keyword matching. Explore NLP, embeddings, an...

Learn how semantic search uses AI to understand user intent and context. Discover how it differs from keyword search and why it's essential for modern AI system...
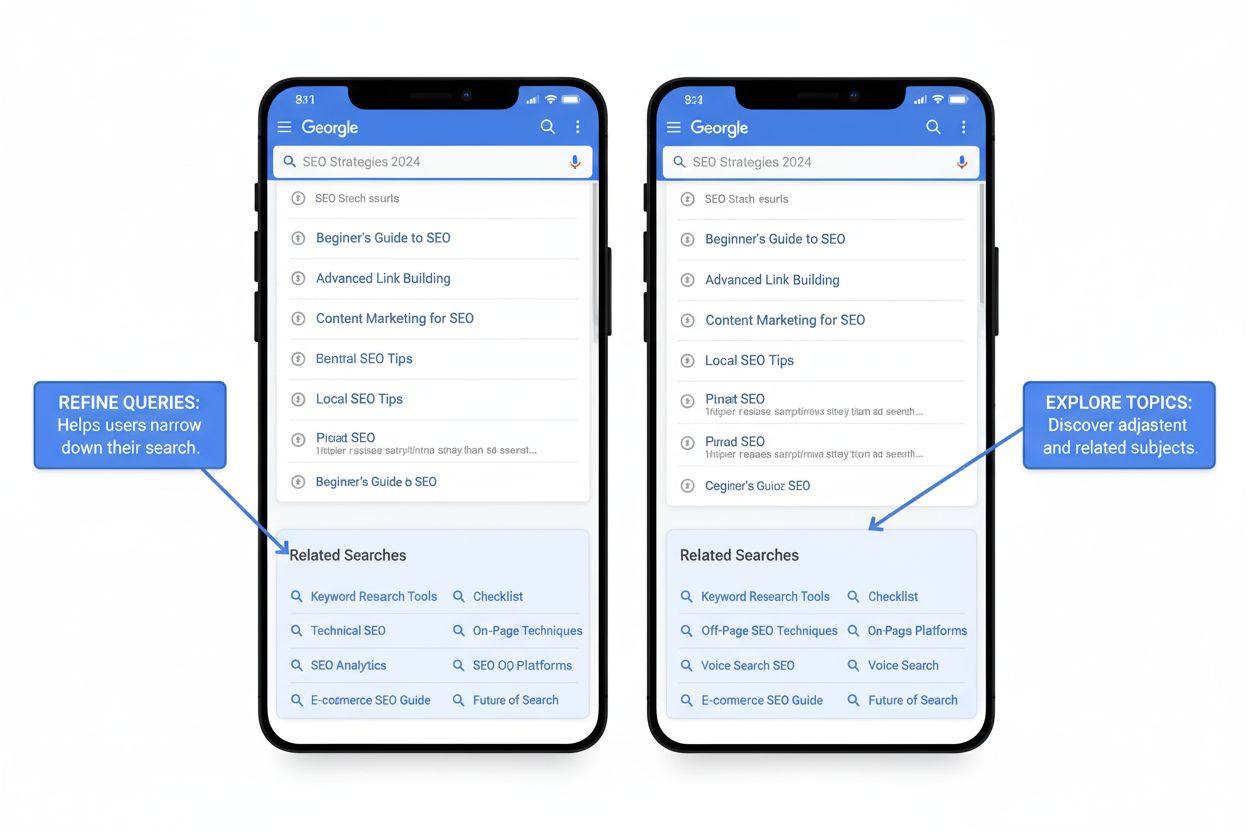
Related Searches are suggested queries at the bottom of Google SERPs. Learn how this SERP feature works, its prevalence, and how to leverage it for keyword rese...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.