
What is Real-Time Search in AI?
Learn how real-time search in AI works, its benefits for users and businesses, and how it differs from traditional search engines and static AI models.

APIs that provide AI systems with current content updates for time-sensitive information, enabling immediate access to fresh data through persistent streaming connections. These APIs deliver information in milliseconds rather than requiring periodic polling, ensuring AI models always have the most recent context available for accurate decision-making and response generation.
APIs that provide AI systems with current content updates for time-sensitive information, enabling immediate access to fresh data through persistent streaming connections. These APIs deliver information in milliseconds rather than requiring periodic polling, ensuring AI models always have the most recent context available for accurate decision-making and response generation.
A Real-Time Content API is an application programming interface that provides AI systems with current content updates and information as it becomes available, enabling immediate access to time-sensitive data without delay. Unlike traditional request-response APIs that require clients to poll for updates at intervals, real-time content APIs establish persistent connections that push new information to AI systems the moment it’s generated or updated. These APIs are fundamental to modern AI applications that require up-to-date context, such as large language models (LLMs), AI agents, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems. By delivering fresh, relevant content in milliseconds, real-time content APIs ensure that AI systems can make informed decisions based on the latest available information rather than stale or outdated data.

Real-time content APIs operate on fundamentally different principles than traditional REST APIs, prioritizing continuous data delivery over discrete request-response cycles. The core architecture relies on persistent connections that remain open between the client (AI system) and server, allowing data to flow bidirectionally or unidirectionally depending on the protocol. These APIs employ event-driven architecture, where updates are triggered immediately when new content becomes available rather than waiting for scheduled batch processes. The technical implementation emphasizes low-latency delivery, typically measured in milliseconds, ensuring that AI systems receive information with minimal delay. Scalability is built into the design through distributed streaming platforms that can handle millions of concurrent connections and process enormous volumes of data simultaneously.
| Characteristic | Real-Time Content API | Traditional REST API | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Persistent/Streaming | Request-Response | Scheduled Jobs |
| Data Delivery | Push (Server-initiated) | Pull (Client-initiated) | Periodic Batches |
| Latency | Milliseconds | Seconds to Minutes | Hours to Days |
| Data Freshness | Always Current | Depends on Polling | Significantly Delayed |
| Scalability | High Concurrency | Limited Connections | Batch-dependent |
| Use Case | Real-time AI, Live Updates | Standard Web Services | Analytics, Reporting |
| Cost Model | Connection-based | Request-based | Compute-based |
The operational flow of a real-time content API begins with data ingestion, where content from various sources—databases, message queues, external APIs, or user-generated events—is captured and normalized into a standardized format. Once ingested, the data enters a processing pipeline where it may be enriched, filtered, or transformed to add context and relevance for AI systems. The processed content is then made available through streaming endpoints that maintain open connections with subscribed AI clients. When new or updated content arrives, the API immediately transmits it through these persistent connections to all interested consumers. This architecture eliminates the need for AI systems to repeatedly query for updates, reducing network overhead and ensuring that critical information reaches AI models within milliseconds of becoming available. The entire process is designed for fault tolerance, with mechanisms to handle connection failures, ensure message delivery, and maintain data consistency across distributed systems.
The importance of data freshness in AI systems cannot be overstated, as the accuracy and relevance of AI outputs directly depend on the currency of the information available to the model. When AI systems like LLMs or AI agents operate with outdated information, they risk providing inaccurate recommendations, missing critical context, or making decisions based on superseded facts. Real-time content APIs solve this problem by ensuring that AI systems always have access to the most current information available, enabling them to provide more accurate responses and make better-informed decisions. For applications like financial trading, fraud detection, or personalized recommendations, even a delay of seconds can result in significant errors or missed opportunities. By maintaining continuous access to fresh data, real-time content APIs enable AI systems to understand the current state of the world, adapt to changing conditions, and provide responses that reflect the latest developments. This freshness is particularly critical for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, where the quality of retrieved context directly impacts the quality of generated responses.
Real-time content APIs leverage several key streaming protocols and technologies, each optimized for different use cases and requirements:
WebSockets: Provides full-duplex communication over a single TCP connection, enabling bidirectional real-time data exchange. Ideal for interactive applications requiring low-latency, two-way communication between client and server.
Server-Sent Events (SSE): Allows servers to push data to clients over HTTP connections in a unidirectional manner. Simpler to implement than WebSockets and well-suited for scenarios where only server-to-client updates are needed.
gRPC: A high-performance RPC framework using Protocol Buffers for efficient serialization. Supports multiple streaming modes and is particularly effective for microservices communication and AI model serving.
Apache Kafka: A distributed streaming platform that acts as a message broker, enabling reliable, scalable event streaming. Commonly used as the backbone for real-time data pipelines feeding AI systems.
MQTT: A lightweight publish-subscribe protocol designed for IoT and mobile applications. Provides efficient bandwidth usage and is ideal for scenarios with constrained network resources.
AMQP: Advanced Message Queuing Protocol offering reliable message delivery with support for complex routing patterns. Suitable for enterprise applications requiring guaranteed message delivery and transaction support.
Real-time content APIs enable a diverse range of AI applications that depend on current information. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems use real-time content APIs to fetch the latest documents, articles, or knowledge base entries, ensuring that generated responses incorporate the most recent information available. AI agents leverage real-time APIs to access current market data, inventory levels, customer information, and operational metrics, enabling them to make timely decisions and take appropriate actions. Personalization engines use real-time content APIs to track user behavior, preferences, and context, allowing AI systems to deliver customized experiences that adapt to changing user needs. Fraud detection systems rely on real-time content APIs to access transaction data, user profiles, and historical patterns, enabling immediate identification of suspicious activities. Recommendation systems use real-time APIs to incorporate trending content, user interactions, and contextual information, ensuring that recommendations remain relevant and timely. Chatbots and conversational AI benefit from real-time access to knowledge bases, FAQs, and product information, enabling them to provide accurate and up-to-date responses to user queries.
Real-time content APIs play a crucial role in enabling AI visibility and monitoring, allowing organizations to track how AI systems access, process, and utilize content. By instrumenting real-time content APIs with monitoring capabilities, organizations can observe which content AI systems are retrieving, how frequently they access specific information, and how this content influences AI outputs. This visibility is essential for understanding AI behavior, ensuring compliance with data governance policies, and detecting when AI systems are relying on outdated or incorrect information. Content attribution tracking through real-time APIs enables organizations to understand which sources AI systems are using to generate responses, supporting transparency and accountability. Real-time monitoring of API usage patterns helps identify performance bottlenecks, optimize data delivery, and ensure that AI systems have access to the information they need. For organizations using platforms like AmICited.com, real-time content APIs provide the foundation for monitoring how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews reference and cite brand content, enabling real-time visibility into AI-generated mentions and citations.
The distinction between real-time content APIs and batch processing represents a fundamental difference in how data is delivered to AI systems. Batch processing collects data over a period of time and processes it in scheduled intervals, typically hours or days later, making it suitable for historical analysis and reporting but unsuitable for time-sensitive AI applications. Real-time content APIs, by contrast, deliver data immediately as it becomes available, enabling AI systems to respond to current conditions and make decisions based on the latest information. For AI applications requiring immediate responses—such as fraud detection, trading systems, or customer service chatbots—the latency of batch processing is prohibitive. Real-time APIs also enable continuous learning and adaptation, where AI systems can adjust their behavior based on immediate feedback and changing conditions. While batch processing excels at processing large volumes of historical data cost-effectively, real-time content APIs are essential for applications where timeliness and accuracy are paramount. Many modern AI architectures employ a hybrid approach, using real-time APIs for immediate decision-making while batch processing handles deeper analysis and model training on historical data.
Implementing real-time content APIs for AI systems introduces several technical and operational challenges. Scalability remains a primary concern, as maintaining millions of concurrent connections while delivering consistent performance requires sophisticated infrastructure and careful resource management. Data consistency across distributed systems becomes more complex in real-time environments, where ensuring that all AI systems receive updates in the correct order and without duplication requires careful coordination. Error handling and resilience are critical, as network failures, service outages, or data corruption can impact AI system performance; robust mechanisms for connection recovery, message replay, and state synchronization are essential. Cost implications can be significant, as real-time streaming infrastructure often requires more resources than batch processing, though the value delivered through improved AI accuracy and responsiveness often justifies the investment. Security and access control must be carefully implemented to ensure that AI systems only access authorized content and that sensitive information is protected during transmission. Monitoring and observability become increasingly important in real-time systems, where rapid data flows and complex interactions make it essential to have comprehensive visibility into system behavior and performance.
Several mature platforms and technologies enable organizations to build and deploy real-time content APIs for AI systems. Confluent provides a comprehensive data streaming platform built on Apache Kafka, offering managed services for ingesting, processing, and serving real-time data to AI applications through its Real-Time Context Engine and Confluent Intelligence features. Tinybird specializes in real-time data processing and API generation, enabling organizations to ingest streaming data and instantly expose it through low-latency APIs suitable for AI applications. OpenAI’s Realtime API enables direct real-time communication with AI models, supporting speech-to-speech interactions and multimodal inputs with minimal latency. Apache Kafka remains the industry standard for distributed event streaming, providing the foundation for countless real-time data pipelines. AmICited.com stands out as a leading platform for AI monitoring and visibility, using real-time content APIs to track how AI systems reference and cite brand content across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. These platforms collectively enable organizations to build sophisticated AI systems that leverage real-time content for improved accuracy, responsiveness, and decision-making quality.
Real-Time Content APIs establish persistent connections that push data to clients as it becomes available, while traditional REST APIs require clients to send requests and wait for responses. Real-Time Content APIs deliver information in milliseconds with continuous updates, whereas REST APIs have higher latency and require polling for new data. This makes real-time APIs ideal for AI systems that need current information, while REST APIs are better suited for standard web services.
AI systems like LLMs and AI agents make decisions based on the information available to them. Outdated or stale data can lead to inaccurate responses, missed opportunities, and poor decision-making. Real-time content APIs ensure AI systems always have access to the most current information, enabling them to provide accurate responses, understand current conditions, and adapt to changing circumstances. This is especially critical for applications like fraud detection, trading, and personalized recommendations where delays can result in significant errors.
Common protocols include WebSockets for bidirectional communication, Server-Sent Events (SSE) for unidirectional server-to-client updates, gRPC for high-performance microservices communication, Apache Kafka for distributed event streaming, MQTT for IoT applications, and AMQP for enterprise messaging. Each protocol has different strengths and is optimized for specific use cases, from interactive applications to large-scale data pipelines.
Real-Time Content APIs improve accuracy by ensuring AI models have access to the most current and relevant information when generating responses. This is particularly important for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, where the quality of retrieved context directly impacts response quality. With fresh data, AI systems can provide more accurate recommendations, detect fraud more effectively, and make better-informed decisions based on current conditions rather than outdated information.
Key challenges include managing scalability for millions of concurrent connections, ensuring data consistency across distributed systems, implementing robust error handling and recovery mechanisms, controlling costs of real-time infrastructure, securing sensitive data during transmission, and maintaining comprehensive monitoring and observability. These challenges require sophisticated infrastructure, careful architectural design, and ongoing operational management.
Real-Time Content APIs enable organizations to track which content AI systems are accessing, how frequently they retrieve specific information, and how this content influences AI outputs. By instrumenting APIs with monitoring capabilities, organizations can observe AI behavior, ensure compliance with data governance policies, track content attribution, and understand which sources AI systems rely on. This visibility is essential for transparency, accountability, and understanding AI system performance.
Real-time content APIs typically require more infrastructure resources than batch processing, as they must maintain persistent connections and deliver data with minimal latency. However, the value delivered through improved AI accuracy, faster decision-making, and better user experiences often justifies the higher cost. Many organizations use a hybrid approach, employing real-time APIs for immediate decisions while batch processing handles deeper analysis and model training on historical data.
AmICited.com leverages real-time content APIs to monitor how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews reference and cite brand content. The platform provides real-time visibility into AI-generated mentions, citations, and content attribution, enabling organizations to track how their content is being used by AI systems. This real-time monitoring helps brands understand their presence in AI outputs and ensure accurate representation across AI platforms.
Track and monitor how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews cite and reference your brand with AmICited.com's real-time content monitoring platform.

Learn how real-time search in AI works, its benefits for users and businesses, and how it differs from traditional search engines and static AI models.
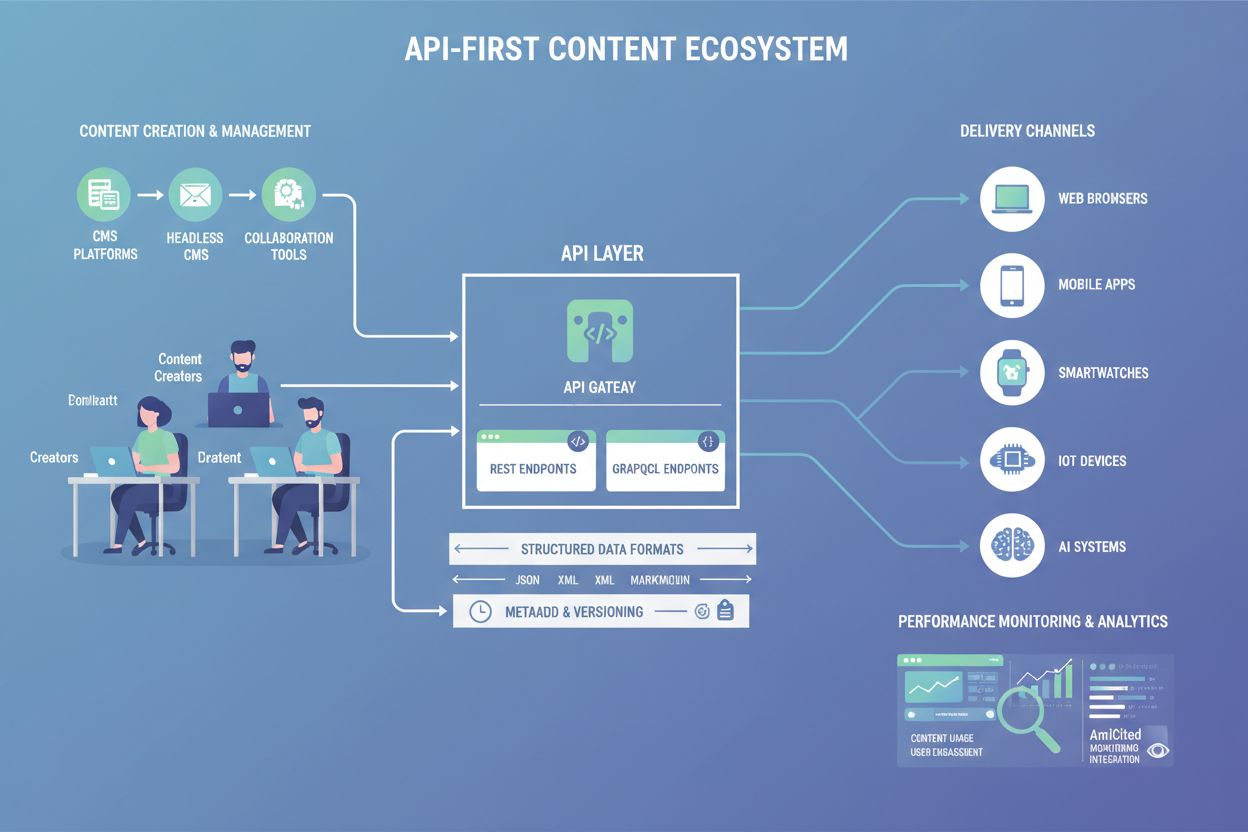
Learn what API-First Content is, how it enables AI visibility, and why it matters for content architecture. Discover how structured APIs improve content accessi...

Community discussion explaining how RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) works and what it means for content creators. Non-technical explanations from AI practi...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.