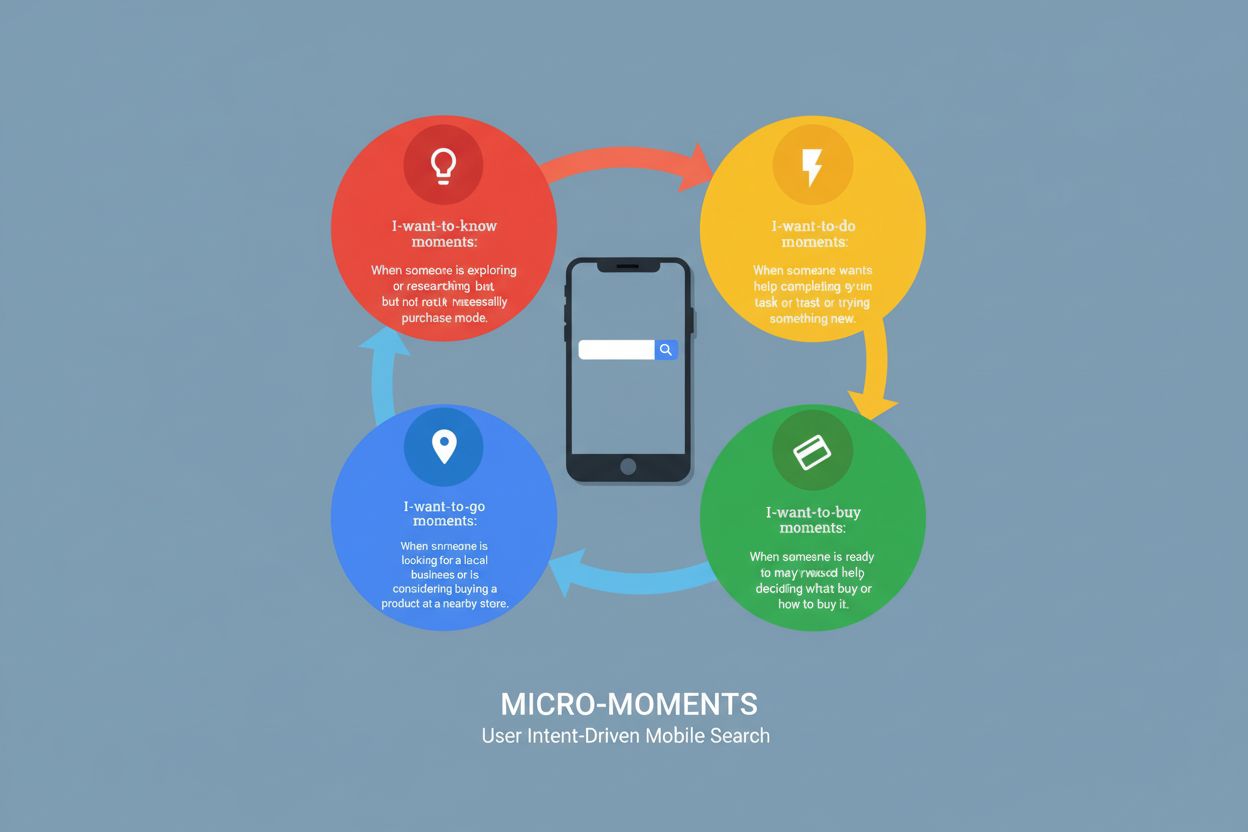
Micro-Moment
Micro-Moment definition: intent-rich mobile search interactions where users seek immediate answers. Learn the four types and how to optimize for AI search visib...

A touchpoint is any moment of interaction or point of contact between a customer and a brand, occurring across digital, physical, or virtual channels throughout the customer journey. Touchpoints encompass all moments before, during, and after a purchase that shape customer perception and influence brand loyalty.
A touchpoint is any moment of interaction or point of contact between a customer and a brand, occurring across digital, physical, or virtual channels throughout the customer journey. Touchpoints encompass all moments before, during, and after a purchase that shape customer perception and influence brand loyalty.
A touchpoint is any moment of interaction or point of contact between a customer and a brand, occurring across digital, physical, or virtual channels throughout the customer journey. Touchpoints represent the individual moments where customers engage with a brand’s products, services, messaging, or representatives—whether through a website visit, social media interaction, email communication, in-store experience, or customer service engagement. These interactions are fundamental to shaping customer perception, influencing purchasing decisions, and building long-term brand loyalty. Understanding and optimizing touchpoints has become essential for modern businesses seeking to deliver consistent, personalized experiences that drive customer satisfaction and retention.
The significance of touchpoints extends beyond simple transaction points. Each interaction represents an opportunity for brands to reinforce their value proposition, demonstrate their commitment to customer success, and differentiate themselves from competitors. According to research from Salesforce, 88% of customers believe that the experience a brand provides is just as important as the product itself, underscoring the critical role that well-designed touchpoints play in overall business success. In today’s omnichannel environment, where customers interact with brands across multiple platforms simultaneously, the strategic management of touchpoints has become a cornerstone of effective marketing and customer experience strategies.
The concept of touchpoints emerged from customer experience management and marketing attribution research, gaining prominence as businesses recognized that customer journeys were rarely linear. Historically, marketing focused on individual campaigns or channels in isolation, but the evolution toward customer journey mapping revealed that success depended on orchestrating multiple interactions across the entire customer lifecycle. This shift was driven by data showing that customers typically interact with brands through 5-10 different touchpoints before making a purchase decision, and many more after the sale.
The rise of digital marketing accelerated the importance of touchpoint strategy. As customers gained access to more channels—social media, mobile apps, email, websites, and messaging platforms—brands faced the challenge of maintaining consistency and relevance across these diverse interaction points. According to a 2023 Statista survey, social media and video-sharing platforms emerged as the leading digital touchpoints among US consumers, with 54% of consumers using search engines as their primary source of pre-purchase information. This fragmentation of customer attention across channels made touchpoint management not just beneficial but essential for competitive survival.
The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced analytics has further transformed how brands approach touchpoints. Modern platforms now enable real-time tracking of customer interactions, sentiment analysis, and predictive modeling to anticipate customer needs at specific touchpoints. The global customer journey mapping software market, valued at $14.2 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $16.46 billion by 2025, reflecting the growing investment in touchpoint optimization and measurement. This expansion demonstrates that businesses increasingly recognize touchpoints as strategic assets that directly impact revenue, customer lifetime value, and competitive positioning.
Touchpoints can be classified across multiple dimensions, each offering distinct strategic implications for brand management. The most common classification divides touchpoints into three stages aligned with the customer journey: pre-purchase, during-purchase, and post-purchase touchpoints. Pre-purchase touchpoints include social media posts, online advertisements, blog content, customer reviews, and referrals—all designed to build awareness and consideration. During-purchase touchpoints encompass website checkout experiences, sales conversations, product demonstrations, and point-of-sale interactions that facilitate the transaction. Post-purchase touchpoints include thank-you emails, customer service interactions, loyalty programs, and feedback surveys that nurture relationships and encourage repeat business.
Another critical classification distinguishes between digital touchpoints and physical touchpoints. Digital touchpoints include website interactions, email campaigns, social media engagement, mobile app usage, chatbot conversations, and online customer service. Physical touchpoints involve in-store experiences, face-to-face sales interactions, product packaging, events, and direct mail. The emergence of virtual touchpoints—such as video consultations, virtual events, and augmented reality experiences—represents a third category that blends digital and physical elements. Understanding this taxonomy helps brands allocate resources effectively and ensure consistent messaging across all interaction channels.
Touchpoints can also be classified as direct or indirect. Direct touchpoints involve immediate interaction between the customer and the brand, such as visiting a website or calling customer service. Indirect touchpoints involve third parties, such as social media influencers, review platforms, or industry publications that shape customer perception without direct brand involvement. This distinction is particularly important for brand monitoring and reputation management, as indirect touchpoints often carry significant influence over customer decisions despite being outside direct brand control.
| Touchpoint Type | Channel | Customer Stage | Primary Goal | Measurement Metric |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Post | Digital | Awareness | Build brand awareness | Engagement rate, reach |
| Search Engine Ad | Digital | Consideration | Drive website traffic | Click-through rate (CTR) |
| Product Review | Digital/Indirect | Consideration | Provide social proof | Review rating, conversion impact |
| Website Checkout | Digital | Purchase | Facilitate transaction | Conversion rate, cart abandonment |
| In-Store Experience | Physical | Purchase | Enable direct purchase | Sales volume, customer satisfaction |
| Customer Service Chat | Digital | Post-Purchase | Resolve issues | Customer satisfaction score (CSAT) |
| Email Newsletter | Digital | Post-Purchase | Drive repeat business | Open rate, click rate |
| Loyalty Program | Digital/Physical | Post-Purchase | Increase retention | Customer lifetime value (CLV) |
| Product Packaging | Physical | Post-Purchase | Reinforce brand | Unboxing experience, social sharing |
| AI-Generated Response | Digital/Indirect | All Stages | Brand visibility in AI | Citation frequency, positioning |
Optimizing touchpoints has become a core business imperative because each interaction directly influences customer perception and behavior. Research from McKinsey found that companies excelling at touchpoint management achieve 40% higher customer satisfaction and 25% higher customer retention rates compared to peers. This performance gap reflects the compounding effect of positive experiences across multiple touchpoints—each successful interaction builds trust and increases the likelihood of the next interaction being positive.
The concept of touchpoint consistency is particularly crucial in omnichannel environments. When customers experience inconsistent messaging, branding, or service quality across different touchpoints, it erodes trust and increases the likelihood of abandonment. Conversely, brands that maintain consistent value propositions, visual identity, and service standards across all touchpoints create a cohesive brand experience that reinforces customer loyalty. This consistency requirement extends to tone of voice, product information accuracy, pricing transparency, and customer service responsiveness—all elements that customers evaluate at each touchpoint.
Touchpoint attribution—the process of assigning credit to specific interactions for driving conversions—has become increasingly sophisticated with the adoption of multi-touch attribution models. Rather than crediting only the final click before purchase (last-click attribution), modern attribution recognizes that multiple touchpoints contribute to conversion. Linear attribution assigns equal value to all touchpoints, while position-based attribution gives greater weight to first and last interactions. Time-decay attribution credits more recent touchpoints more heavily, reflecting the assumption that interactions closer to purchase have greater influence. Understanding which attribution model best reflects your business dynamics enables more accurate resource allocation and ROI measurement.
The digital transformation of customer interactions has fundamentally reshaped touchpoint strategy and execution. Traditional businesses that once relied primarily on physical touchpoints now must integrate digital channels seamlessly into their customer experience. This evolution has created both opportunities and challenges: opportunities to reach customers across more channels and gather richer data about their preferences, and challenges in maintaining consistency and managing the complexity of omnichannel operations.
Artificial intelligence is increasingly transforming how brands manage touchpoints. AI-powered chatbots now handle initial customer service touchpoints, providing 24/7 availability and instant responses. Personalization engines analyze customer data to deliver tailored content at each touchpoint, increasing relevance and engagement. Predictive analytics identify which touchpoints are most likely to drive conversions for specific customer segments, enabling more strategic resource allocation. Machine learning algorithms continuously optimize touchpoint sequences, testing different interaction patterns to identify the most effective customer journey paths.
The emergence of AI-generated content platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has created an entirely new category of touchpoints that brands must monitor and optimize. When customers ask AI systems for product recommendations, company information, or industry insights, the AI’s response represents a critical touchpoint that can significantly influence customer perception and purchasing decisions. Brands that fail to monitor their presence in these AI-generated touchpoints risk losing visibility and influence in an increasingly important channel. This development underscores the evolving nature of touchpoints and the need for continuous adaptation to emerging technologies and customer behaviors.
Touchpoint mapping is the process of identifying, documenting, and analyzing all interactions between customers and a brand throughout the entire customer lifecycle. This strategic exercise involves creating visual representations of the customer journey that highlight each touchpoint, the customer’s emotional state at that moment, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. Effective touchpoint maps reveal gaps in the customer experience, redundancies in communication, and moments of truth where customer satisfaction is most vulnerable.
Creating a comprehensive touchpoint map requires cross-functional collaboration involving marketing, sales, customer service, product, and operations teams. Each department typically manages different touchpoints, but without coordination, these interactions can feel disjointed and inconsistent to customers. The mapping process forces organizations to view the customer experience holistically rather than through departmental silos. This perspective shift often reveals surprising insights—such as how a negative customer service touchpoint can undo the positive impact of months of marketing efforts, or how a small improvement in the checkout touchpoint can significantly increase conversion rates.
Touchpoint maps typically include quantitative data (conversion rates, engagement metrics, customer satisfaction scores) alongside qualitative insights (customer emotions, pain points, unmet needs). This combination enables data-driven decision-making while maintaining focus on the human experience. Advanced organizations use dynamic touchpoint maps that update in real-time as customer behavior data flows in, allowing for continuous optimization rather than static, annual reviews. The sophistication of touchpoint mapping tools has increased dramatically, with platforms now offering AI-powered analysis that identifies patterns and recommends optimizations automatically.
Measuring touchpoint effectiveness requires a comprehensive set of metrics that capture both immediate interaction quality and longer-term impact on customer relationships. Cost-per-click (CPC) measures the efficiency of paid touchpoints like search ads and social media advertising, with global averages around $0.62 and UK averages around $1.22. Click-through rate (CTR) indicates how compelling a touchpoint is in motivating customer action, while engagement rate measures the depth of interaction beyond simple clicks—including comments, shares, and time spent.
Conversion-focused metrics become increasingly important as customers move through the purchase stage. Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action at a touchpoint, while cost per conversion reveals the efficiency of different touchpoints in driving actual sales. These metrics are essential for understanding which touchpoints deliver the best return on marketing investment and where budget reallocation might improve overall performance.
Post-purchase metrics shift focus to retention and loyalty. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) measures satisfaction with specific touchpoints or overall experience, while Net Promoter Score (NPS) indicates likelihood to recommend based on touchpoint experiences. Customer Effort Score (CES) measures how easily customers can accomplish their goals at each touchpoint, with research showing that reduced effort is a key driver of retention. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) aggregates the impact of all touchpoints over the entire customer relationship, providing the ultimate measure of touchpoint strategy effectiveness. According to Gartner research, 61.1% of marketing teams report email open rates exceeding 20%, demonstrating the continued effectiveness of email as a touchpoint channel.
The future of touchpoints will be shaped by accelerating technological change, evolving customer expectations, and the emergence of new interaction channels. Voice-activated touchpoints through smart speakers and voice assistants represent a growing category that brands must optimize for, as voice search and voice commerce continue to expand. Unlike text-based touchpoints, voice interactions require different optimization strategies, including conversational language, featured snippet optimization, and voice-specific branding approaches.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) touchpoints are emerging as immersive alternatives to traditional digital interactions. Brands are experimenting with virtual showrooms, AR product try-ons, and immersive brand experiences that create memorable touchpoints differentiating them from competitors. These technologies enable customers to interact with products in ways previously impossible, reducing purchase hesitation and increasing satisfaction. As AR/VR technology becomes more accessible and mainstream, these touchpoints will likely become standard expectations rather than novelties.
The integration of blockchain and Web3 technologies is creating new touchpoint possibilities through NFTs, decentralized communities, and tokenized loyalty programs. These emerging touchpoints appeal particularly to tech-savvy and younger customer segments, offering novel ways to build community and reward loyalty. However, brands must approach these touchpoints thoughtfully, ensuring they deliver genuine value rather than appearing as opportunistic trend-chasing.
Sustainability and ethical touchpoints are becoming increasingly important as customers demand transparency about environmental and social impact. Touchpoints that communicate a brand’s sustainability efforts, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility initiatives are becoming competitive differentiators. Brands that authentically integrate sustainability messaging across all touchpoints build stronger connections with values-conscious customers, while those perceived as greenwashing face reputational damage.
The role of AI in personalizing touchpoints will continue to expand, with machine learning algorithms becoming increasingly sophisticated at predicting customer needs and delivering hyper-personalized experiences. However, this advancement raises important questions about privacy, data security, and customer consent that brands must navigate carefully. The future touchpoint landscape will likely be characterized by a balance between personalization and privacy, with customers increasingly demanding transparency about how their data is used across touchpoints.
For brands operating in the modern digital ecosystem, understanding touchpoints extends beyond traditional marketing channels to include AI-generated response touchpoints. When customers query AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, or Claude, the AI’s response represents a critical touchpoint that can significantly influence customer perception and purchasing decisions. These AI touchpoints differ from traditional touchpoints in that brands have limited direct control over the interaction, yet the quality and accuracy of the AI’s response directly impacts brand reputation and customer trust.
Monitoring AI touchpoints has become essential for comprehensive brand management. Brands need visibility into how frequently their products, services, and company information appear in AI-generated responses, what context they appear in, and how they compare to competitor mentions. This monitoring reveals gaps in brand visibility, opportunities to improve AI citations, and potential reputation risks from inaccurate or negative AI-generated content. Platforms like AmICited enable brands to track their presence across multiple AI systems, providing the data necessary to optimize their visibility in this emerging touchpoint category.
The strategic importance of AI touchpoints will only increase as AI systems become more integrated into customer decision-making processes. Brands that proactively monitor and optimize their presence in AI-generated responses gain competitive advantages in visibility, credibility, and customer acquisition. This requires ensuring that brand information is accurate, comprehensive, and easily discoverable by AI systems—a challenge that extends traditional SEO and content strategy into new domains. As AI continues to evolve, the ability to manage touchpoints across both traditional and AI-driven channels will become a core competency for marketing and brand management teams.
A channel is the medium through which communication occurs (such as email or social media), while a touchpoint is the specific interaction or moment of contact within that channel. For example, email is a channel, but a promotional email sent to a customer is a touchpoint. Multiple touchpoints can exist within a single channel, and understanding this distinction helps brands optimize each interaction point strategically.
There is no universal number, as it depends on your industry, customer preferences, and business model. However, research shows that customers expect consistent experiences across 5-10 key touchpoints on average. The goal is quality over quantity—each touchpoint should add value and move customers closer to their goals without overwhelming them with excessive contact.
Touchpoint mapping is critical for AI monitoring because it helps brands track where their brand mentions, products, and services appear in AI-generated responses across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. By understanding all touchpoints, brands can monitor their visibility and influence across the entire AI ecosystem, ensuring consistent representation and identifying gaps in AI citations.
The most critical touchpoint varies by business, but research indicates that the point-of-sale (POS) and post-purchase customer service touchpoints have the highest impact on retention and loyalty. However, pre-purchase touchpoints like product reviews and social proof are equally vital for initial conversion. The key is ensuring all touchpoints work cohesively to create a seamless experience.
Brands measure touchpoint effectiveness using metrics like conversion rates, customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer effort score (CES), engagement rates, and attribution modeling. Advanced analytics platforms track which touchpoints drive the most conversions and customer loyalty, allowing brands to allocate resources to high-performing interactions and optimize underperforming ones.
Yes, many touchpoints can be automated through marketing automation, chatbots, email workflows, and AI-driven personalization. Automated touchpoints like triggered emails, chatbot responses, and personalized product recommendations can improve efficiency and consistency. However, human touchpoints like customer service interactions and sales conversations remain essential for building genuine relationships and handling complex customer needs.
Omnichannel strategies are built on the foundation of integrated touchpoints across all channels—online and offline. An omnichannel approach ensures customers have a seamless experience whether they interact with a brand via social media, website, mobile app, or physical store. This requires coordinating touchpoints so that customer data, messaging, and brand experience remain consistent across all interaction points.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Micro-Moment definition: intent-rich mobile search interactions where users seek immediate answers. Learn the four types and how to optimize for AI search visib...
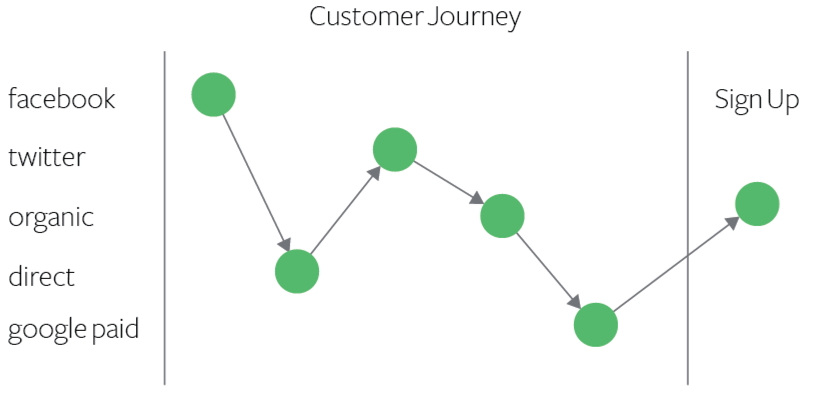
Multi-touch attribution assigns credit to all customer touchpoints in the conversion journey. Learn how this data-driven approach optimizes marketing budgets an...

Last-click attribution credits the final customer interaction for conversions. Learn how this single-touch model works, its limitations, and why marketers are s...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.