Preparing for Agentic Commerce: What Brands Need to Do Now
Learn how to prepare your brand for agentic commerce. Discover essential steps to make your systems AI agent-ready and stay competitive in the evolving e-commer...

Agentic commerce refers to AI systems that autonomously complete purchases on behalf of users based on preferences and permissions. These intelligent agents can discover products, compare prices, negotiate deals, and execute transactions without continuous human intervention, fundamentally transforming how consumers shop online.
Agentic commerce refers to AI systems that autonomously complete purchases on behalf of users based on preferences and permissions. These intelligent agents can discover products, compare prices, negotiate deals, and execute transactions without continuous human intervention, fundamentally transforming how consumers shop online.
Agentic commerce represents a fundamental shift in how consumers shop online by leveraging autonomous AI agents to make purchasing decisions independently on behalf of users. Unlike traditional e-commerce platforms where customers manually browse, compare, and purchase products, or basic AI chatbots that simply provide recommendations, agentic commerce systems possess true autonomous decision-making capabilities that enable them to execute complete transactions without continuous human intervention. These intelligent agents analyze customer preferences, budget constraints, and historical behavior patterns to identify and purchase products that align with user needs—much like having a personal shopper who understands your tastes and financial boundaries. The core distinction lies in the agent’s ability to act proactively rather than reactively; instead of waiting for user commands, these systems monitor markets, identify opportunities, and execute purchases autonomously. Autonomous transactions occur seamlessly across multiple retailers and platforms, with agents negotiating prices, comparing options, and finalizing purchases in real-time. This represents a departure from both traditional e-commerce, where humans control every step, and from basic AI chatbots, which merely suggest products without executing purchases. Agentic commerce fundamentally reimagines the shopping experience by removing friction, saving time, and optimizing purchasing decisions through continuous, intelligent automation.

The operational framework of agentic commerce involves a sophisticated multi-stage process that combines data analysis, decision-making algorithms, and secure transaction execution. When a user establishes preferences and parameters—such as “purchase household essentials when inventory runs low” or “find me flights under $500 departing within the next two weeks”—the autonomous AI agent begins continuous monitoring of relevant markets and inventory levels. The agent collects real-time data from multiple sources, analyzing prices, product availability, customer reviews, and market trends to identify optimal purchasing opportunities. Using real-time processing capabilities, the system evaluates options against the user’s established criteria, learning from past purchases and feedback to refine its decision-making process. Once the agent identifies a suitable product or service, it initiates the transaction through secure payment gateways, employing cryptographic authentication and tokenization to protect sensitive financial information. The system maintains detailed transaction logs and can provide users with complete visibility into all autonomous purchases, including reasoning behind each decision. Integration with existing payment infrastructure—including credit card networks, digital wallets, and bank systems—ensures seamless execution while maintaining security standards. The agent continuously adapts its behavior based on outcomes, user feedback, and changing market conditions, creating a self-improving system that becomes increasingly effective over time.
| Aspect | Traditional E-commerce | Agentic Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| User Role | Active decision-maker and executor | Preference setter and monitor |
| Decision Making | Manual comparison and selection | Autonomous AI-driven analysis |
| Purchase Execution | User-initiated transactions | Agent-initiated autonomous transactions |
| Personalization | Rule-based recommendations | Adaptive, learning-based personalization |
| Speed | Limited by user availability | 24/7 continuous operation |
| Learning | Static algorithms | Real-time adaptation and improvement |
Agentic commerce systems deliver a comprehensive suite of autonomous capabilities that transform how consumers interact with digital marketplaces. These intelligent platforms excel at several critical functions:
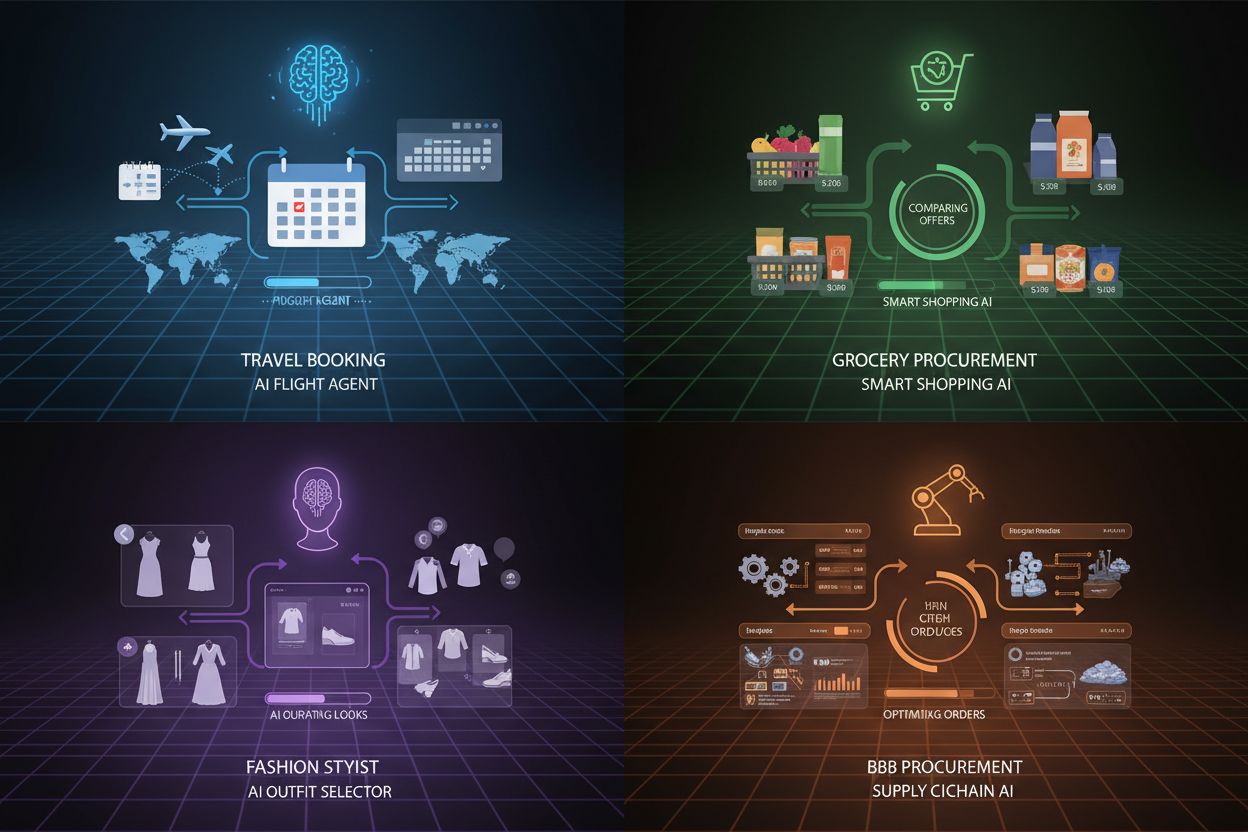
The practical applications of agentic commerce span numerous consumer and business scenarios, demonstrating the technology’s versatility across different shopping contexts. Practical applications include travel booking, where agents can autonomously search for and purchase flights matching specific criteria—such as “find me the cheapest red-eye flight from New York to Los Angeles under $500 departing within the next three weeks.” Household essentials represent another prime use case, with agents automatically reordering groceries, toiletries, and supplies based on consumption patterns and inventory levels, eliminating the need for manual replenishment. Fashion and personal shopping benefit significantly from agentic systems that learn individual style preferences, body measurements, and budget constraints to autonomously discover and purchase clothing items from preferred retailers. B2B procurement processes become dramatically more efficient when agents handle routine purchasing of office supplies, raw materials, and equipment, negotiating with suppliers and optimizing costs across organizational needs. Grocery shopping transforms through agents that compare prices across multiple stores, identify weekly deals, and compile optimized shopping lists that minimize costs while meeting dietary preferences. Price tracking and deal hunting represent continuous background operations where agents monitor products of interest, alerting users to price drops and automatically purchasing when predetermined thresholds are met. These diverse applications demonstrate how agentic commerce adapts to different purchasing contexts while maintaining core principles of autonomy, optimization, and user preference alignment.
Consumers experience transformative advantages through agentic commerce systems that fundamentally improve the shopping experience across multiple dimensions. Time savings represent perhaps the most immediate benefit, as agents eliminate hours spent browsing, comparing products, and executing transactions—shopping occurs continuously in the background without requiring active user participation. Better deal discovery emerges naturally from agents’ ability to monitor thousands of products and retailers simultaneously, identifying price reductions and promotional opportunities that individual shoppers would never find manually. The reduction of decision fatigue proves particularly valuable in categories with overwhelming choices; agents handle the cognitive burden of evaluating options, allowing users to focus on higher-level preferences rather than granular product comparisons. Improved personalization develops as agents learn individual preferences, creating increasingly tailored shopping experiences that anticipate needs and align purchases with personal values and budgets. The 24/7 shopping capability means purchases occur at optimal times regardless of user availability, capturing limited-time deals and ensuring products are purchased when prices are lowest. Cost optimization becomes systematic rather than occasional, with agents consistently finding better prices, bundling opportunities, and loyalty rewards that reduce overall spending. Industry data reveals that 70% cart abandonment rate in traditional e-commerce reflects consumer frustration with the shopping process—agentic commerce eliminates this friction entirely. Furthermore, studies indicate a 4,700% increase in AI-driven traffic when intelligent shopping agents are deployed, demonstrating consumer enthusiasm for autonomous purchasing capabilities.
Retailers and merchants gain substantial competitive and operational advantages by embracing agentic commerce infrastructure and integrating with autonomous agent networks. Increased conversion rates result directly from agents completing purchases that would otherwise be abandoned, as the friction of manual shopping disappears and transactions occur automatically when conditions align with user preferences. Better customer data insights emerge from the detailed behavioral information agents collect, providing merchants with unprecedented understanding of consumer preferences, price sensitivity, and purchasing patterns that inform product development and marketing strategies. Operational efficiency improves dramatically as agents handle routine transactions, reducing the burden on customer service teams and allowing human staff to focus on complex issues and relationship building. Inventory optimization becomes more precise when merchants can predict demand patterns based on agent purchasing behavior, reducing overstock situations and stockouts through better demand forecasting. The reduced customer service burden translates directly to cost savings, as agents handle transaction inquiries, order tracking, and routine support without human intervention. New revenue opportunities emerge through agent-specific features such as premium placement in agent search results, sponsored recommendations, and exclusive agent-only deals that create additional monetization channels. Merchants who successfully integrate with agentic commerce networks gain significant competitive advantage by capturing market share from retailers who remain dependent on traditional e-commerce models, positioning themselves as forward-thinking brands aligned with consumer preferences for convenience and optimization.
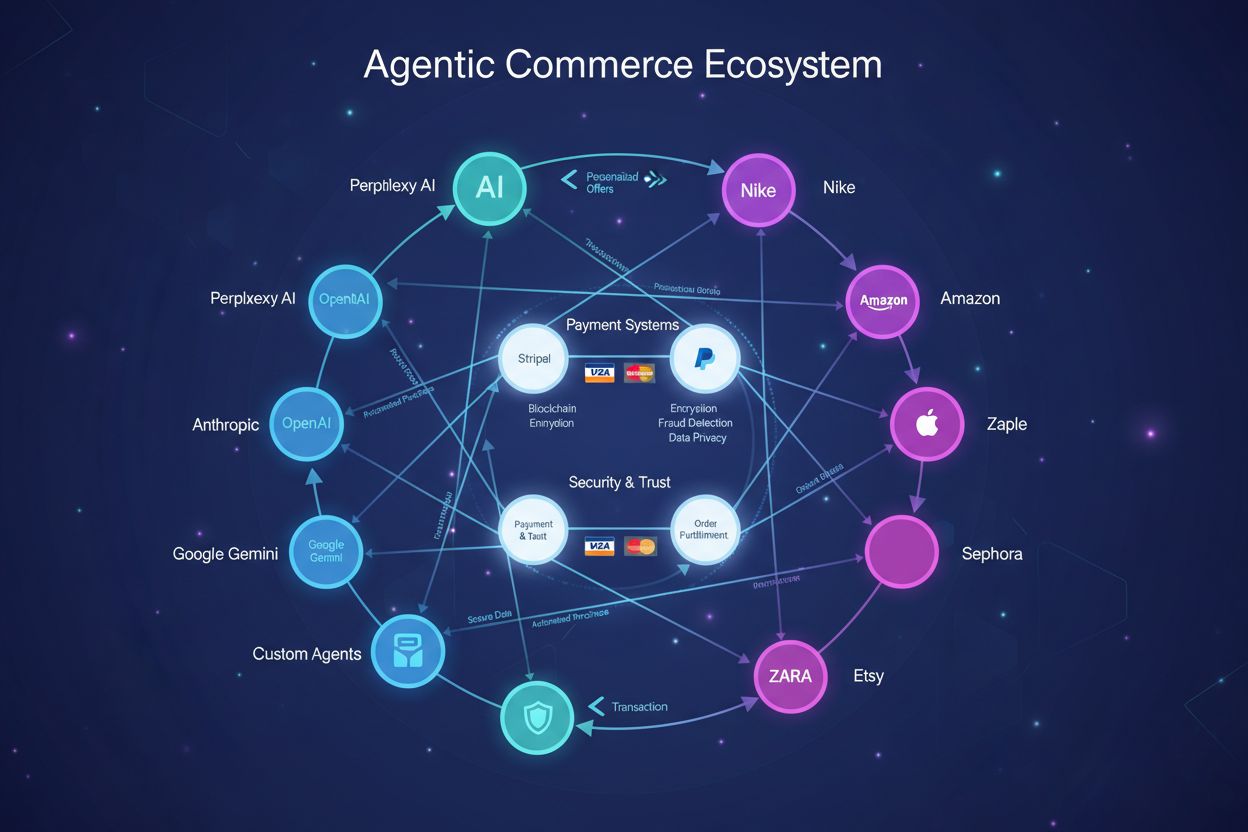
The agentic commerce market remains in early stages of development, with major technology and financial services companies actively investing in infrastructure and pilot programs to establish market leadership. Market leaders include OpenAI, which has demonstrated autonomous shopping capabilities through its AI agents, Google, which integrates agentic features into its Shopping platform, Microsoft, which leverages its Copilot technology for autonomous commerce applications, and Perplexity, which combines search and purchasing capabilities. Payment infrastructure companies including Visa and Mastercard are developing protocols and security frameworks specifically designed for autonomous transactions, recognizing that existing payment systems require enhancement to support agent-initiated purchases at scale. Retail implementations are beginning to emerge, with Amazon exploring “Buy For Me” functionality that enables autonomous purchasing based on user preferences, and Google Shopping integrating AI-driven product discovery and purchasing capabilities. The timeline for widespread commercial availability is expected around 2026, when regulatory frameworks mature and security standards become established across major markets. Current activity focuses on pilot programs and early adoption among tech-forward consumers and enterprises, with companies testing agent capabilities in controlled environments before broader rollout. AmICited.com serves as a critical monitoring solution for tracking AI references and market developments in agentic commerce, helping stakeholders understand competitive positioning and technology evolution. Market predictions suggest explosive growth once consumer trust reaches critical mass, with some analysts projecting agentic commerce could represent 15-20% of total e-commerce transactions within five years of mainstream adoption.
Despite significant potential, agentic commerce faces substantial obstacles that must be resolved before widespread adoption becomes feasible, particularly around security, liability, and regulatory frameworks. Security and data privacy represent paramount concerns, as agents require access to payment information, personal preferences, and purchase history—creating expanded attack surfaces that malicious actors could exploit to commit fraud or steal sensitive data. Authentication and fraud prevention mechanisms must evolve significantly to verify that purchase requests genuinely originate from authorized agents rather than compromised systems or unauthorized actors attempting to exploit user accounts. Liability and dispute resolution frameworks remain undefined; when an agent makes a poor purchasing decision or executes an unauthorized transaction, determining responsibility between user, agent provider, and merchant becomes legally complex. Regulatory uncertainty persists across most jurisdictions, with governments still developing frameworks governing autonomous financial transactions, consumer protection standards, and merchant obligations when dealing with agent-initiated purchases. Consumer trust building requires demonstrating that agents operate reliably, transparently, and in users’ best interests—a challenge given historical concerns about algorithmic bias and corporate data practices. Error handling and refund processes must be streamlined to address situations where agents make mistakes, purchase wrong items, or encounter technical failures that result in unintended transactions. Integration complexity emerges from the need to connect agents with diverse retailer systems, payment networks, and data sources while maintaining security and performance standards. Advanced security protocols including agentic tokens, Trusted Agent Protocol implementations, and cryptographic authentication mechanisms are under development to address these concerns, though widespread standardization remains incomplete.
Agentic commerce represents an inevitable evolution in how consumers and businesses conduct transactions, with transformative market disruption expected as the technology matures and adoption accelerates. Market disruption will fundamentally reshape e-commerce by eliminating traditional shopping friction, shifting competitive advantage toward merchants who integrate seamlessly with agent networks, and creating entirely new business models around agent-specific services and premium features. Consumer expectations will evolve dramatically as agentic shopping becomes normalized; users will increasingly expect autonomous purchasing capabilities as standard features rather than innovations, similar to how e-commerce itself became expected rather than novel. Merchants must adapt their strategies to succeed in an agentic-dominated landscape, focusing on agent-friendly product data, transparent pricing, and integration capabilities rather than relying on traditional marketing and user interface design. The technology maturation timeline suggests that core infrastructure will stabilize by 2025-2026, with regulatory frameworks following shortly thereafter and mainstream adoption accelerating through 2027-2028. Integration with emerging AI capabilities—including advanced reasoning, multimodal understanding, and real-time learning—will enable agents to handle increasingly complex purchasing scenarios and provide more sophisticated decision-making. The competitive landscape will consolidate around platforms that successfully combine agent technology, merchant networks, and consumer trust, creating winner-take-most dynamics similar to other digital platform markets. Organizations that recognize agentic commerce as inevitable and begin preparing now will establish sustainable competitive advantages, while those that resist or delay adaptation risk obsolescence as consumer preferences and market dynamics shift irreversibly toward autonomous, intelligent shopping experiences.
Regular AI chatbots provide recommendations and answer questions, but users must manually execute purchases. Agentic commerce systems go further by autonomously making purchasing decisions and completing transactions without user intervention. While chatbots assist humans, agentic systems act independently on behalf of users within established permission boundaries.
No. Agentic commerce operates within strict permission-based boundaries that users establish beforehand. Users define specific parameters—such as budget limits, product preferences, and acceptable price ranges—and agents only execute purchases that align with these pre-established rules. Users maintain complete control over what agents can and cannot do.
Security is a primary focus for agentic commerce developers. Systems employ multiple protective measures including tokenization (replacing actual credit card numbers with harmless digital codes), encrypted connections, secure storage systems, and cryptographic authentication. Payment companies like Visa and Mastercard are developing specialized security protocols specifically designed for autonomous transactions.
Commercial availability is expected around 2026, with pilot programs and early adoption already underway. Major companies including OpenAI, Google, Visa, and Mastercard are actively developing infrastructure and testing capabilities. Mainstream adoption will likely accelerate through 2027-2028 as regulatory frameworks mature and consumer trust increases.
Retailers should focus on making product information machine-readable through structured data and schema markup, creating API connections for direct agent access to catalogs and inventory, standardizing product descriptions for consistency, building customer trust through transparent policies and reviews, and redesigning checkout processes to support automated transactions. Starting with an on-site AI shopping assistant provides valuable testing ground.
Liability and dispute resolution frameworks are still being developed, but the expectation is that users will have clear recourse for agent errors. This may include automatic refunds for incorrect purchases, return processes similar to traditional e-commerce, and potentially compensation from agent providers for significant mistakes. These protections are being formalized as the industry matures.
Major technology companies including OpenAI (ChatGPT), Google (Gemini), Microsoft, and Perplexity are developing agentic capabilities. Payment infrastructure leaders Visa and Mastercard are building security protocols and frameworks. Retailers like Amazon and Google Shopping are implementing autonomous purchasing features. AmICited.com monitors how these platforms reference brands in agentic commerce contexts.
Agentic commerce will shift shopping from an active, time-consuming process to a passive, background operation. Instead of spending hours comparing products, you'll set preferences once and let agents handle continuous monitoring and purchasing. This enables better deal discovery, eliminates decision fatigue, and ensures purchases occur at optimal times. Consumer expectations will evolve to expect autonomous shopping as standard rather than innovative.
Track how AI systems like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Perplexity mention your products and brand in autonomous shopping scenarios. AmICited helps you understand your presence in AI-powered commerce.

Learn how to prepare your brand for agentic commerce. Discover essential steps to make your systems AI agent-ready and stay competitive in the evolving e-commer...

Discover how agentic AI is transforming shopping and what it means for brand visibility. Learn how AI agents make autonomous purchases and how to prepare your b...

Discover agentic commerce: how autonomous AI agents are revolutionizing online shopping with 30% higher conversion rates, personalized experiences, and seamless...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.