
How to Conduct an AI Visibility Audit: Complete Methodology
Learn the complete step-by-step methodology for conducting an AI visibility audit. Discover how to measure brand mentions, citations, and visibility across Chat...
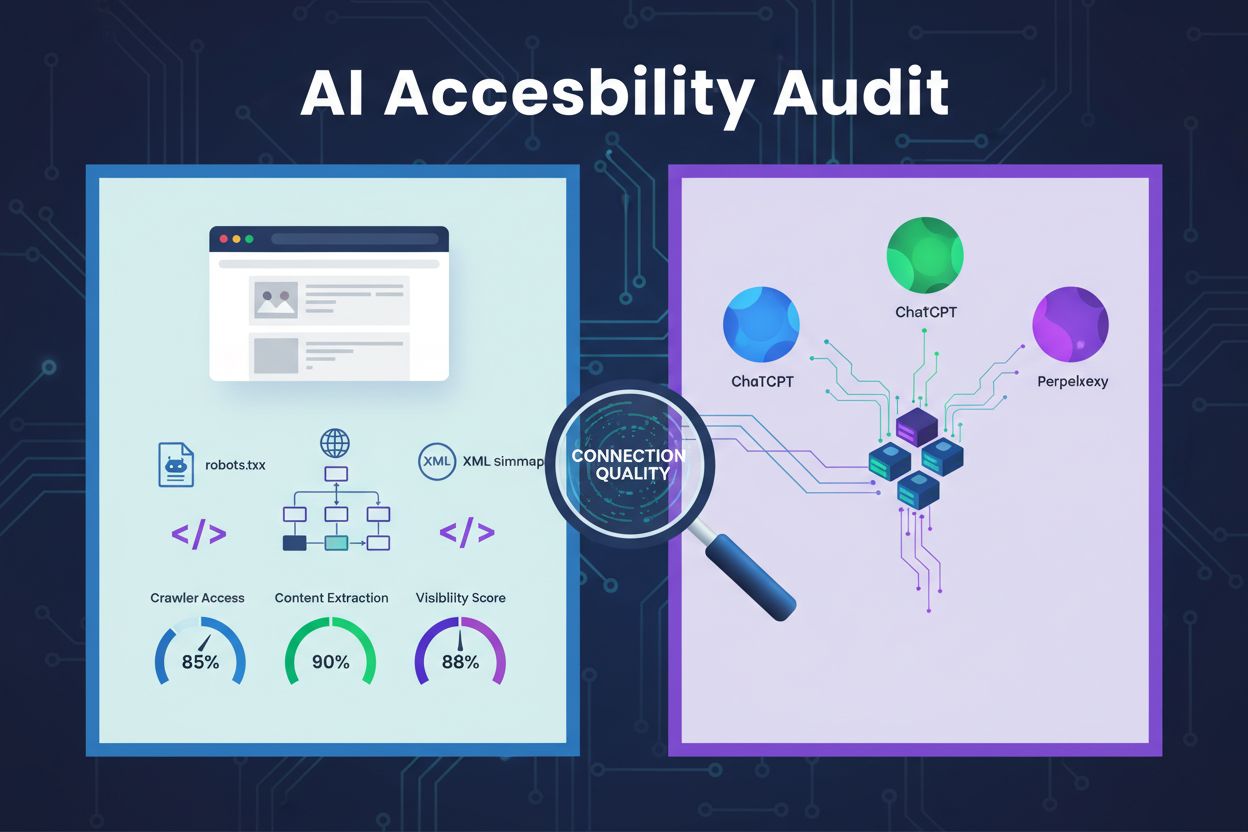
A technical review of website architecture, configuration, and content structure to determine whether AI crawlers can effectively access, understand, and extract content. Evaluates robots.txt configuration, XML sitemaps, site crawlability, JavaScript rendering, and content extraction capability to ensure visibility across AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity.
A technical review of website architecture, configuration, and content structure to determine whether AI crawlers can effectively access, understand, and extract content. Evaluates robots.txt configuration, XML sitemaps, site crawlability, JavaScript rendering, and content extraction capability to ensure visibility across AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity.
An AI accessibility audit is a technical review of your website’s architecture, configuration, and content structure to determine whether AI crawlers can effectively access, understand, and extract your content. Unlike traditional SEO audits that focus on keyword rankings and backlinks, AI accessibility audits examine the technical foundations that enable AI systems like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity to discover and cite your content. This audit evaluates critical components including robots.txt configuration, XML sitemaps, site crawlability, JavaScript rendering, and content extraction capability to ensure your website is fully visible to the AI-powered search ecosystem.
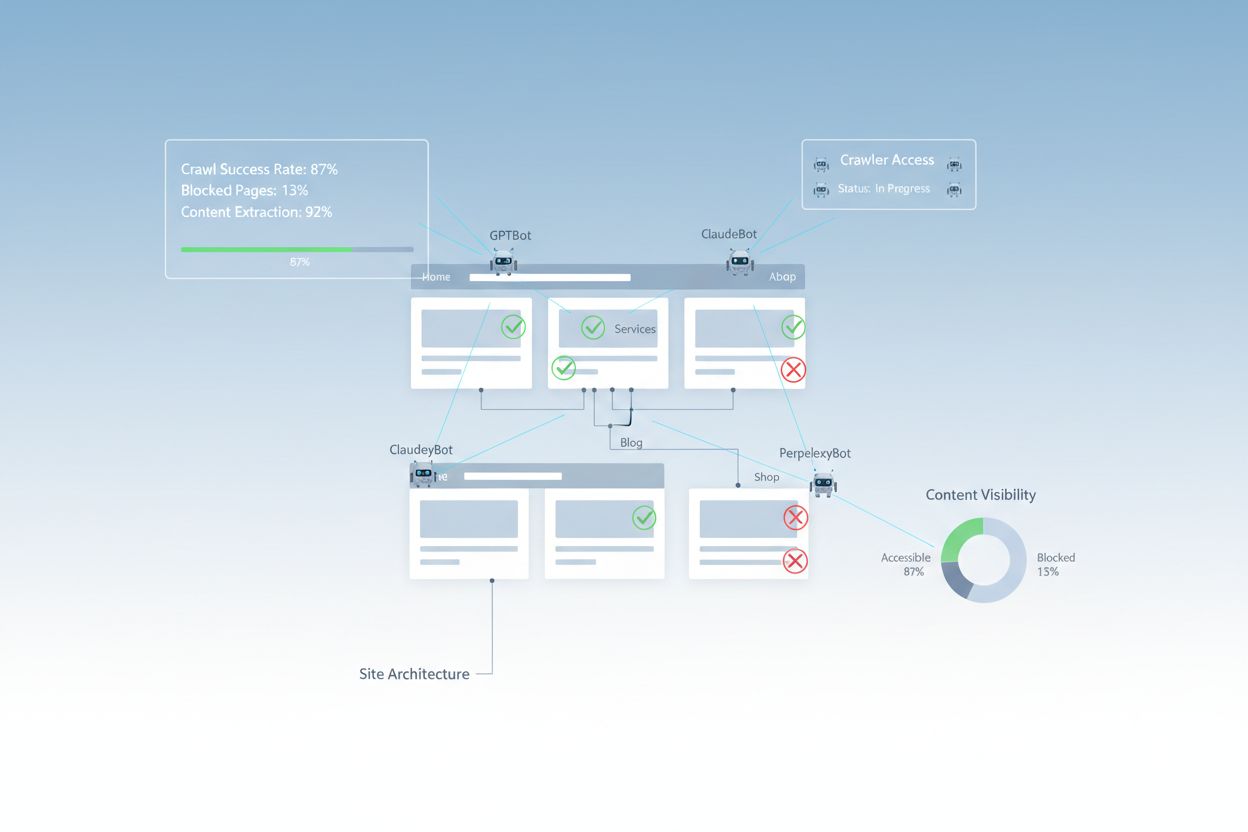
Despite advances in web technology, AI crawlers face significant barriers when attempting to access modern websites. The primary challenge is that many contemporary websites rely heavily on JavaScript rendering to display content dynamically, but most AI crawlers cannot execute JavaScript code. This means that approximately 60-90% of modern website content remains invisible to AI systems, even though it displays perfectly in user browsers. Additionally, security tools like Cloudflare block AI crawlers by default, treating them as potential threats rather than legitimate indexing bots. Research shows that 35% of enterprise sites inadvertently block AI crawlers, preventing valuable content from being discovered and cited by AI systems.
Common barriers preventing AI crawler access include:
A comprehensive AI accessibility audit examines multiple technical and structural elements that influence how AI systems interact with your website. Each component plays a distinct role in determining whether your content becomes visible to AI-powered search platforms. The audit process involves testing crawlability, verifying configuration files, assessing content structure, and monitoring actual crawler behavior. By systematically evaluating these components, you can identify specific barriers and implement targeted solutions to improve your AI visibility.
| Component | Purpose | Impact on AI Visibility |
|---|---|---|
| Robots.txt Configuration | Controls which crawlers can access specific site sections | Critical - Misconfiguration blocks AI crawlers entirely |
| XML Sitemaps | Guides crawlers to important pages and content structure | High - Helps AI systems prioritize and discover content |
| Site Crawlability | Ensures pages are accessible without authentication or complex navigation | Critical - Blocked pages are invisible to AI systems |
| JavaScript Rendering | Determines if dynamic content is visible to crawlers | Critical - 60-90% of content may be missed without pre-rendering |
| Content Extraction | Evaluates how easily AI systems can parse and understand content | High - Poor structure reduces citation probability |
| Security Tool Configuration | Manages firewall and protection rules affecting crawler access | Critical - Overly restrictive rules block legitimate AI bots |
| Schema Markup Implementation | Provides machine-readable context about content | Medium - Improves AI comprehension and citation likelihood |
| Internal Linking Structure | Establishes semantic relationships between pages | Medium - Helps AI understand topic authority and relevance |
Your robots.txt file is the primary mechanism for controlling which crawlers can access your website. Located at the root of your domain, this simple text file contains directives that tell crawlers whether they’re allowed to access specific sections of your site. For AI accessibility, proper robots.txt configuration is essential because misconfigured rules can completely block major AI crawlers like GPTBot (OpenAI), ClaudeBot (Anthropic), and PerplexityBot (Perplexity). The key is to explicitly allow these crawlers while maintaining security by blocking malicious bots and protecting sensitive areas.
Example robots.txt configuration for AI crawlers:
# Allow all AI crawlers
User-agent: GPTBot
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
User-agent: ClaudeBot
User-agent: Claude-Web
User-agent: PerplexityBot
User-agent: Google-Extended
Allow: /
# Block sensitive areas
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /api/
# Sitemaps
Sitemap: https://yoursite.com/sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://yoursite.com/ai-sitemap.xml
This configuration explicitly permits major AI crawlers to access your public content while protecting administrative and private sections. The Sitemap directives help crawlers discover your most important pages efficiently.
An XML sitemap acts as a roadmap for crawlers, listing the URLs you want indexed and providing metadata about each page. For AI systems, sitemaps are particularly valuable because they help crawlers understand your site’s structure, prioritize important content, and discover pages that might otherwise be missed through standard crawling. Unlike traditional search engines that can infer site structure through links, AI crawlers benefit significantly from explicit guidance about which pages matter most. A well-structured sitemap with proper metadata increases the likelihood that your content will be discovered, understood, and cited by AI systems.
Example XML sitemap structure for AI optimization:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<!-- High-priority content for AI crawlers -->
<url>
<loc>https://yoursite.com/about</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-03</lastmod>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://yoursite.com/products</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-03</lastmod>
<priority>0.9</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://yoursite.com/blog/ai-guide</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-02</lastmod>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://yoursite.com/faq</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-01</lastmod>
<priority>0.7</priority>
</url>
</urlset>
The priority attribute signals to AI crawlers which pages are most important, while lastmod indicates content freshness. This helps AI systems allocate crawl resources effectively and understand your content hierarchy.
Beyond configuration files, several technical barriers can prevent AI crawlers from accessing your content effectively. JavaScript rendering remains the most significant challenge, as modern web frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular render content dynamically in the browser, leaving AI crawlers with empty HTML. Cloudflare and similar security tools often block AI crawlers by default, treating their high request volumes as potential attacks. Rate limiting can prevent comprehensive indexing, while complex site architecture and dynamic content loading further complicate crawler access. Fortunately, multiple solutions exist to overcome these barriers.
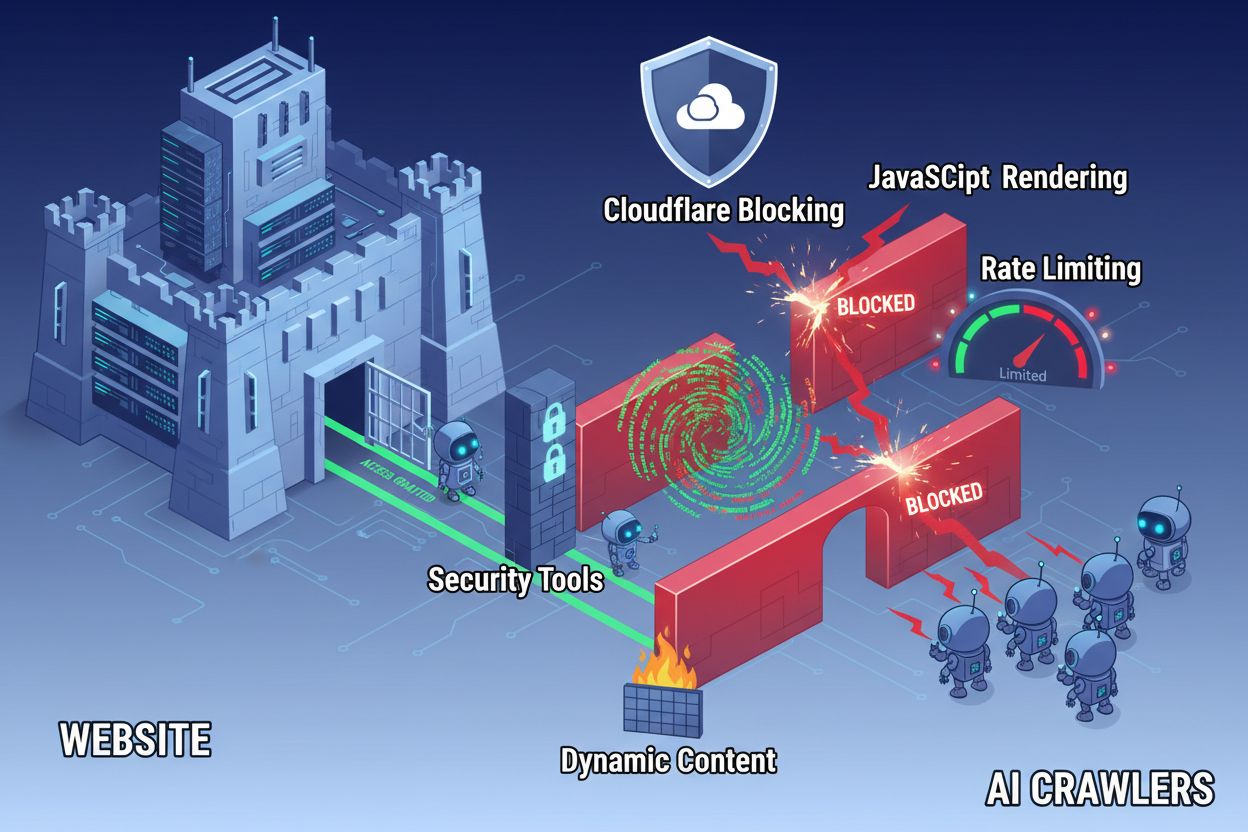
Solutions to improve AI crawler access:
AI systems don’t just need to access your content—they need to understand it. Content extraction refers to how effectively AI crawlers can parse, comprehend, and extract meaningful information from your pages. This process depends heavily on semantic HTML structure, which uses proper heading hierarchies, descriptive text, and logical organization to convey meaning. When your content is well-structured with clear headings (H1, H2, H3), descriptive paragraphs, and logical flow, AI systems can more easily identify key information and understand context. Additionally, schema markup provides machine-readable metadata that explicitly tells AI systems what your content is about, dramatically improving comprehension and citation probability.
Proper semantic structure also includes using semantic HTML elements like <article>, <section>, <nav>, and <aside> instead of generic <div> tags. This helps AI systems understand the purpose and importance of different content sections. When combined with structured data like FAQ schema, Product schema, or Organization schema, your content becomes significantly more accessible to AI systems, increasing the likelihood of being featured in AI-generated responses and answers.
After implementing improvements, you need to verify that AI crawlers can actually access your content and monitor ongoing performance. Server logs provide direct evidence of crawler activity, showing which bots visited your site, which pages they accessed, and whether they encountered errors. Google Search Console offers insights into how Google’s crawlers interact with your site, while specialized AI visibility monitoring tools track how your content appears across different AI platforms. AmICited.com specifically monitors how AI systems reference your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, providing visibility into which of your pages are being cited and how frequently.
Tools and methods for monitoring AI crawler access:
Optimizing your website for AI crawler access requires a strategic, ongoing approach. Rather than treating AI accessibility as a one-time project, successful organizations implement continuous monitoring and improvement processes. The most effective strategy combines proper technical configuration with content optimization, ensuring that both your infrastructure and your content are AI-ready.
Do’s for AI accessibility:
Don’ts for AI accessibility:
The most successful AI accessibility strategy treats crawlers as partners in content distribution rather than threats to be blocked. By ensuring your website is technically sound, properly configured, and semantically clear, you maximize the likelihood that AI systems will discover, understand, and cite your content in their responses to users.
AI accessibility audits focus on semantic structure, machine-readable content, and citation-worthiness for AI systems, whereas traditional SEO audits emphasize keywords, backlinks, and search rankings. AI audits examine whether crawlers can access and understand your content, while SEO audits focus on ranking factors for Google's search results.
Check your server logs for AI crawler user agents like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot. Use Google Search Console to monitor crawl activity, test your robots.txt file with validation tools, and use specialized platforms like AmICited to track how AI systems reference your content across different platforms.
The most common barriers include JavaScript rendering limitations (AI crawlers can't execute JavaScript), Cloudflare and security tool blocking (35% of enterprise sites block AI crawlers), rate limiting that prevents comprehensive indexing, complex site architecture, and dynamic content loading. Each barrier requires different solutions.
Most businesses benefit from allowing AI crawlers, as they increase brand visibility in AI-powered search results and conversational interfaces. However, the decision depends on your content strategy, competitive positioning, and business goals. You can use robots.txt to selectively allow certain crawlers while blocking others based on your specific needs.
Conduct a comprehensive audit quarterly or whenever you make significant changes to your site architecture, content strategy, or security configuration. Monitor crawler activity continuously using server logs and specialized tools. Update your robots.txt and sitemaps whenever you launch new content sections or modify URL structures.
Robots.txt is your primary mechanism for controlling AI crawler access. Proper configuration explicitly allows major AI crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, PerplexityBot) while protecting sensitive areas. Misconfigured robots.txt can completely block AI crawlers, making your content invisible to AI systems regardless of its quality.
While technical optimization is important, you can also improve AI visibility through content optimization—using semantic HTML structure, implementing schema markup, improving internal linking, and ensuring content completeness. However, technical barriers like JavaScript rendering and security tool blocking typically require technical solutions for full AI accessibility.
Use server log analysis to track crawler activity, Google Search Console for crawl statistics, robots.txt validators to verify configuration, schema markup validators for structured data, and specialized platforms like AmICited to monitor AI citations. Many SEO tools like Screaming Frog also provide crawler simulation capabilities for testing AI accessibility.
Track how ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems reference your brand with AmICited. Get real-time insights into your AI search visibility and optimize your content strategy.

Learn the complete step-by-step methodology for conducting an AI visibility audit. Discover how to measure brand mentions, citations, and visibility across Chat...

Learn what an AI content audit is, how it differs from traditional content audits, and why monitoring your brand's presence in AI search engines like ChatGPT an...

Learn how to audit your content for AI visibility and prioritize updates. Complete framework for ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews with actionable st...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.