
Understanding Your Current AI Visibility: A Self-Assessment Guide
Learn how to conduct a baseline AI visibility audit to understand how ChatGPT, Google AI, and Perplexity mention your brand. Step-by-step assessment guide for b...

The degree to which AI platforms disclose how they select and rank sources when generating responses. AI ranking transparency refers to the visibility of algorithms and criteria that determine which sources appear in AI-generated answers, distinguishing it from traditional search engine ranking. This transparency is critical for content creators, publishers, and users who need to understand how information is selected and prioritized. Without transparency, users cannot verify source credibility or understand potential biases in AI-generated content.
The degree to which AI platforms disclose how they select and rank sources when generating responses. AI ranking transparency refers to the visibility of algorithms and criteria that determine which sources appear in AI-generated answers, distinguishing it from traditional search engine ranking. This transparency is critical for content creators, publishers, and users who need to understand how information is selected and prioritized. Without transparency, users cannot verify source credibility or understand potential biases in AI-generated content.
AI ranking transparency refers to the disclosure of how artificial intelligence systems select, prioritize, and present sources when generating responses to user queries. Unlike traditional search engines that display ranked lists of links, modern AI platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google’s AI Overviews integrate source selection into their response generation process, making the ranking criteria largely invisible to users. This opacity creates a critical gap between what users see (a synthesized answer) and how that answer was constructed (which sources were chosen, weighted, and cited). For content creators and publishers, this lack of transparency means their visibility depends on algorithms they cannot understand or influence through traditional optimization methods. The distinction from traditional search engine transparency is significant: while Google publishes general ranking factors and quality guidelines, AI platforms often treat their source selection mechanisms as proprietary trade secrets. Key stakeholders affected include content creators seeking visibility, publishers concerned about traffic attribution, brand managers monitoring reputation, researchers verifying information sources, and users who need to understand the credibility of AI-generated responses. Understanding AI ranking transparency has become essential for anyone producing, distributing, or relying on digital content in an increasingly AI-mediated information landscape.
AI platforms employ Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems that combine language models with real-time information retrieval to ground responses in actual sources rather than relying solely on training data. The RAG process involves three primary stages: retrieval (finding relevant documents), ranking (ordering sources by relevance), and generation (synthesizing information while maintaining citations). Different platforms implement distinct ranking approaches—Perplexity prioritizes source authority and recency, Google’s AI Overviews emphasize topical relevance and E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), while ChatGPT Search balances source quality with response comprehensiveness. The factors influencing source selection typically include domain authority (established reputation and backlink profile), content recency (freshness of information), topical relevance (semantic alignment with the query), engagement signals (user interaction metrics), and citation frequency (how often sources are referenced by other authoritative sites). AI systems weight these signals differently depending on query intent—factual queries may prioritize authority and recency, while opinion-based queries might emphasize diverse perspectives and engagement. The ranking algorithms remain largely undisclosed, though platform documentation provides limited insight into their weighting mechanisms.
| Platform | Citation Transparency | Source Selection Criteria | Ranking Algorithm Disclosure | User Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perplexity | High - inline citations with links | Authority, recency, relevance, topical expertise | Moderate - some documentation | Medium - source filtering options |
| Google AI Overviews | Medium - cited sources listed | E-E-A-T, topical relevance, freshness, engagement | Low - minimal disclosure | Low - limited customization |
| ChatGPT Search | Medium - sources listed separately | Quality, relevance, comprehensiveness, authority | Low - proprietary algorithm | Low - no ranking customization |
| Brave Leo | Medium - source attribution | Privacy-respecting sources, relevance, authority | Low - privacy-focused opacity | Medium - source selection options |
| Consensus | Very High - academic focus with metrics | Citation count, peer review status, recency, field relevance | High - academic standards transparent | High - filter by study type and quality |
The AI industry lacks standardized disclosure practices for how ranking systems operate, creating a fragmented landscape where each platform determines its own level of transparency. OpenAI’s ChatGPT Search provides minimal explanation of source selection, Meta’s AI systems offer limited documentation, and Google’s AI Overviews disclose more than competitors but still withhold critical algorithmic details. Platforms resist full disclosure citing competitive advantage, proprietary concerns, and the complexity of explaining machine learning systems to general audiences—yet this opacity prevents external auditing and accountability. The “source laundering” problem emerges when AI systems cite sources that themselves aggregate or rewrite original content, obscuring the true origin of information and potentially amplifying misinformation through multiple layers of synthesis. Regulatory pressure is mounting: the EU AI Act requires high-risk AI systems to maintain documentation of training data and decision-making processes, while the NTIA AI Accountability Policy calls for companies to disclose AI system capabilities, limitations, and appropriate use cases. Specific disclosure failures include Perplexity’s initial struggles with proper attribution (later improved), Google’s vague explanation of how AI Overviews select sources, and ChatGPT’s limited transparency about why certain sources appear in responses while others don’t. The absence of standardized metrics for measuring transparency makes it difficult for users and regulators to compare platforms objectively.
The opacity of AI ranking systems creates significant visibility challenges for content creators, as traditional SEO strategies designed for search engines don’t directly translate to AI platform optimization. Publishers cannot easily understand why their content appears in some AI responses but not others, making it impossible to develop targeted strategies for improving visibility in AI-generated answers. Citation bias emerges when AI systems disproportionately favor certain sources—established news outlets, academic institutions, or high-traffic websites—while marginalizing smaller publishers, independent creators, and niche experts who may have equally valuable information. Smaller publishers face particular disadvantages because AI ranking systems often weight domain authority heavily, and newer or specialized sites lack the backlink profiles and brand recognition that established outlets possess. Research from Search Engine Land indicates that AI Overviews have reduced click-through rates to traditional search results by 18-64% depending on query type, with traffic concentrated among the few sources cited in AI responses. The distinction between SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) is becoming critical—while SEO focuses on ranking in traditional search, GEO requires understanding and optimizing for AI platform selection criteria, which remain largely opaque. Content creators need tools like AmICited.com to monitor where their content appears in AI responses, track citation frequency, and understand their visibility across different AI platforms.
The AI industry has developed several frameworks for documenting and disclosing system behavior, though adoption remains inconsistent across platforms. Model Cards provide standardized documentation of machine learning model performance, intended use cases, limitations, and bias analysis—similar to nutritional labels for AI systems. Datasheets for Datasets document the composition, collection methodology, and potential biases in training data, addressing the principle that AI systems are only as good as their training information. System Cards take a broader approach, documenting end-to-end system behavior including how components interact, potential failure modes, and real-world performance across different user groups. The NTIA AI Accountability Policy recommends that companies maintain detailed documentation of AI system development, testing, and deployment, with particular emphasis on high-risk applications affecting public welfare. The EU AI Act mandates that high-risk AI systems maintain technical documentation, training data records, and performance logs, with requirements for transparency reports and user notification. Industry best practices increasingly include:
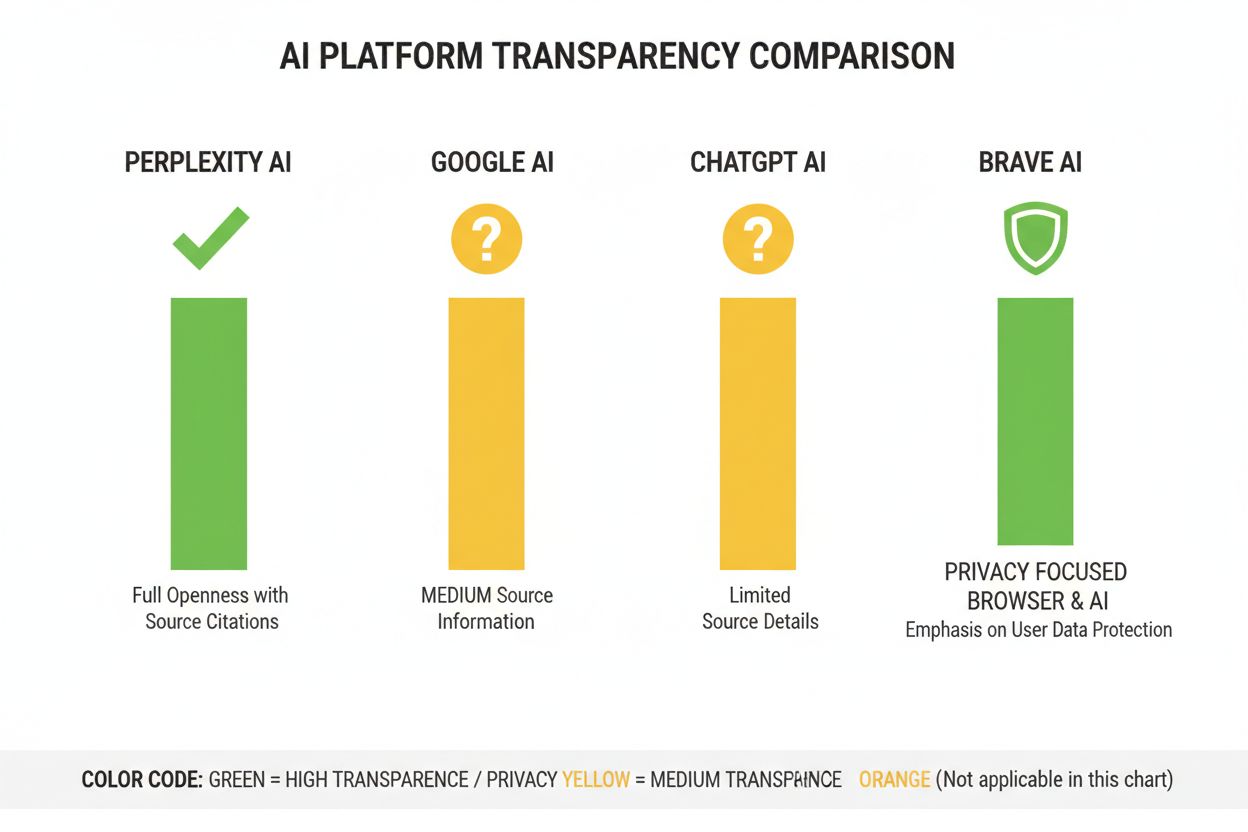
Perplexity has positioned itself as the most citation-transparent AI platform, displaying inline source links throughout responses and allowing users to see exactly which sources contributed to each statement. The platform provides relatively clear documentation of its ranking approach, emphasizing source authority, topical expertise, and content recency, though the precise weighting of these factors remains proprietary. Google’s AI Overviews offer moderate transparency by listing cited sources at the end of responses, but provide limited explanation of why certain sources were selected over others or how the ranking algorithm weights different signals. Google’s documentation emphasizes E-E-A-T principles but doesn’t fully disclose how these are measured or weighted in the AI ranking process. OpenAI’s ChatGPT Search represents a middle ground, displaying sources separately from the response text and allowing users to click through to original content, yet offering minimal explanation of source selection criteria or ranking methodology. Brave Leo prioritizes privacy-focused transparency, disclosing that it uses privacy-respecting sources and doesn’t track user queries, though this comes at the cost of less detailed explanation of ranking mechanisms. Consensus stands apart by focusing exclusively on academic research, providing high transparency through citation metrics, peer review status, and study quality indicators—making it the most algorithmically transparent platform for research-focused queries. User control varies significantly: Perplexity allows source filtering, Consensus enables filtering by study type and quality, while Google and ChatGPT offer minimal customization of ranking preferences. The variation in transparency approaches reflects different business models and target audiences, with academic-focused platforms prioritizing disclosure while consumer-facing platforms balance transparency with proprietary concerns.
Trust and credibility depend fundamentally on users understanding how information reaches them—when AI systems obscure their sources or ranking logic, users cannot independently verify claims or assess source reliability. Transparency enables verification and fact-checking, allowing researchers, journalists, and informed users to trace claims back to original sources and evaluate their accuracy and context. The misinformation and bias prevention benefits of transparency are substantial: when ranking algorithms are visible, researchers can identify systematic biases (such as favoring certain political perspectives or commercial interests), and platforms can be held accountable for amplifying false information. Algorithmic accountability represents a fundamental user right in democratic societies—people deserve to understand how systems that shape their information environment make decisions, particularly when those systems influence public opinion, purchasing decisions, and access to knowledge. For research and academic work, transparency is essential because scholars need to understand source selection to properly contextualize AI-generated summaries and ensure they’re not inadvertently relying on biased or incomplete source sets. The business implications for content creators are profound: without understanding ranking factors, publishers cannot optimize their content strategy, smaller creators cannot compete fairly with established outlets, and the entire ecosystem becomes less meritocratic. Transparency also protects users from manipulation—when ranking criteria are hidden, bad actors can exploit unknown vulnerabilities to promote misleading content, while transparent systems can be audited and improved.
Regulatory trends are pushing toward mandatory transparency: the EU AI Act’s implementation in 2025-2026 will require detailed documentation and disclosure for high-risk AI systems, while similar regulations are emerging in the UK, California, and other jurisdictions. The industry is moving toward standardization of transparency practices, with organizations like the Partnership on AI and academic institutions developing common frameworks for documenting and disclosing AI system behavior. User demand for transparency is increasing as awareness grows about AI’s role in information distribution—surveys indicate that 70%+ of users want to understand how AI systems select sources and rank information. Technical innovations in explainable AI (XAI) are making it increasingly feasible to provide detailed explanations of ranking decisions without fully exposing proprietary algorithms, using techniques like LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) and SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations). Monitoring tools like AmICited.com will become increasingly important as platforms implement transparency measures, helping content creators and publishers track their visibility across multiple AI systems and understand how ranking changes affect their reach. The convergence of regulatory requirements, user expectations, and technical capabilities suggests that 2025-2026 will be pivotal years for AI ranking transparency, with platforms likely adopting more standardized disclosure practices, implementing better user controls over source selection, and providing clearer explanations of ranking logic. The future landscape will likely feature tiered transparency—academic and research-focused platforms leading with high disclosure, consumer platforms offering moderate transparency with user customization options, and regulatory compliance becoming a baseline expectation across the industry.
AI ranking transparency refers to how openly AI platforms disclose their algorithms for selecting and ranking sources in generated responses. It matters because users need to understand source credibility, content creators need to optimize for AI visibility, and researchers need to verify information sources. Without transparency, AI systems can amplify misinformation and create unfair advantages for established outlets over smaller publishers.
AI platforms use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems that combine language models with real-time information retrieval. They rank sources based on factors like domain authority, content recency, topical relevance, engagement signals, and citation frequency. However, the exact weighting of these factors remains largely proprietary and undisclosed by most platforms.
Traditional SEO focuses on ranking in search engine link lists, where Google publishes general ranking factors. AI ranking transparency concerns how AI platforms select sources for synthesized answers, which involves different criteria and is largely undisclosed. While SEO strategies are well-documented, AI ranking factors remain mostly opaque.
You can click through to original sources to verify claims in their full context, check if sources are from authoritative domains, look for peer review status (especially in academic content), and cross-reference information across multiple sources. Tools like AmICited help track which sources appear in AI responses and how frequently your content is cited.
Consensus leads in transparency by focusing exclusively on peer-reviewed academic research with clear citation metrics. Perplexity provides inline source citations and moderate documentation of ranking factors. Google's AI Overviews offer medium transparency, while ChatGPT Search and Brave Leo provide limited disclosure of their ranking algorithms.
Model cards are standardized documentation of AI system performance, intended uses, limitations, and bias analysis. Datasheets document training data composition, collection methods, and potential biases. System cards describe end-to-end system behavior. These tools help make AI systems more transparent and comparable, similar to nutritional labels for food.
The EU AI Act requires high-risk AI systems to maintain detailed technical documentation, training data records, and performance logs. It mandates transparency reports and user notification about AI system use. These requirements are pushing AI platforms toward greater disclosure of ranking mechanisms and source selection criteria.
AmICited.com is an AI citation monitoring platform that tracks how AI systems like Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and ChatGPT cite your brand and content. It provides visibility into which sources appear in AI responses, how frequently your content is cited, and how your ranking transparency compares across different AI platforms.
Track how AI platforms like Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and ChatGPT cite your content. Understand your ranking transparency and optimize your visibility across AI search engines with AmICited.

Learn how to conduct a baseline AI visibility audit to understand how ChatGPT, Google AI, and Perplexity mention your brand. Step-by-step assessment guide for b...

Learn how to connect AI visibility metrics to measurable business outcomes. Track brand mentions in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews with actionable...

Learn proven strategies to maintain and improve your content's visibility in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.