
Agentic Commerce
Learn how agentic commerce uses AI agents to autonomously complete purchases. Explore how intelligent systems are revolutionizing e-commerce and consumer shoppi...

AI agents that independently research, compare, and complete purchases for users without human intervention. These intelligent systems use advanced machine learning and natural language processing to understand customer needs, navigate e-commerce platforms, and execute transactions autonomously while maintaining security and trust guardrails.
AI agents that independently research, compare, and complete purchases for users without human intervention. These intelligent systems use advanced machine learning and natural language processing to understand customer needs, navigate e-commerce platforms, and execute transactions autonomously while maintaining security and trust guardrails.
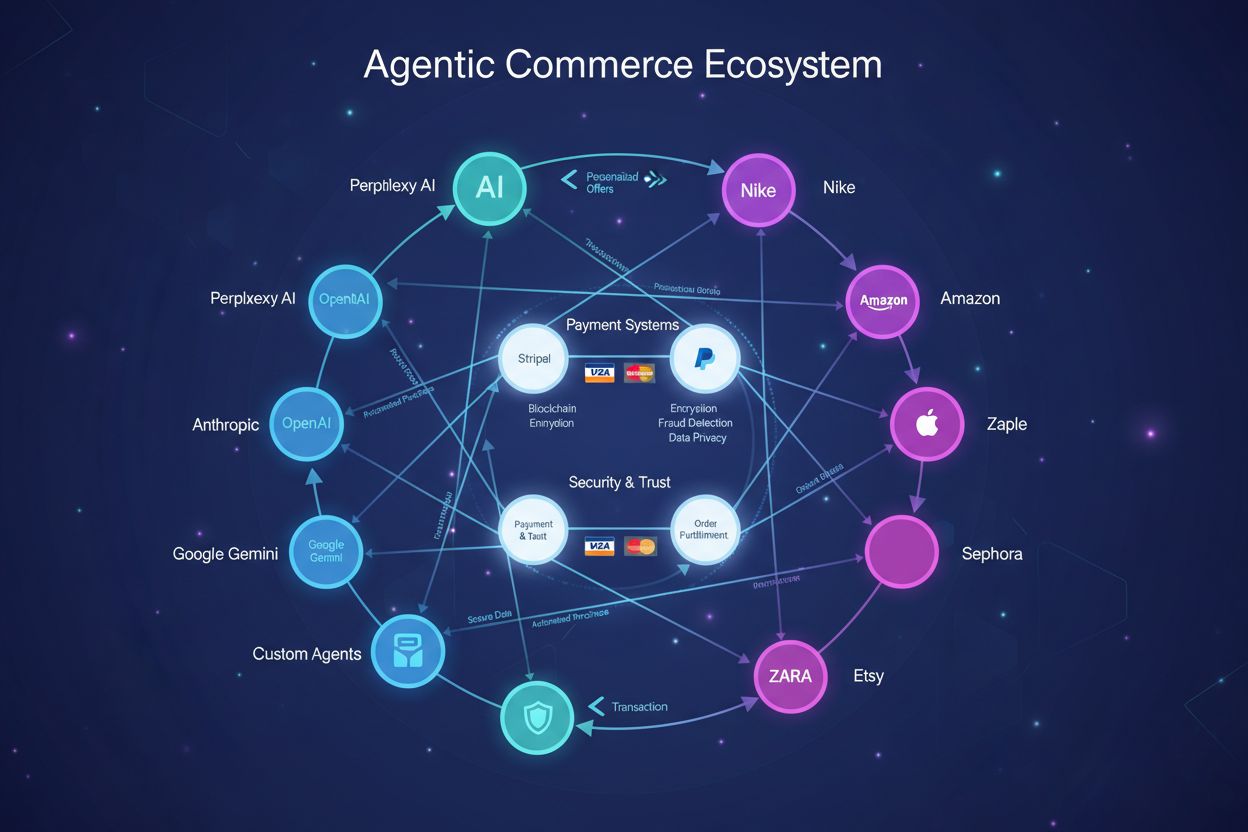
Autonomous AI Commerce refers to the use of artificial intelligence agents that independently conduct shopping transactions, product discovery, and purchasing decisions on behalf of consumers without requiring real-time human intervention. These AI systems leverage advanced language models and decision-making algorithms to navigate e-commerce platforms, compare products, negotiate prices, and complete purchases autonomously. Unlike traditional chatbots that provide recommendations, autonomous AI commerce agents actively execute transactions and manage the entire customer journey from product search to post-purchase support. This represents a fundamental shift in how consumers interact with digital marketplaces, moving from passive browsing to active AI-driven procurement.

Autonomous AI commerce operates through a sophisticated multi-step process where AI agents interpret user preferences, search across multiple retailers, evaluate options based on predefined criteria, and execute transactions with appropriate authorization protocols. The system begins by understanding consumer intent through natural language processing, then accesses retailer APIs and product databases to gather real-time information about availability, pricing, and specifications. Decision-making algorithms evaluate options against user-defined parameters such as price range, brand preferences, sustainability criteria, and delivery timeframes. The agent then communicates with payment systems and fulfillment networks to complete the transaction, often utilizing emerging protocols like the Visa Trusted Agent Protocol and OpenAI Agentic Commerce Protocol to ensure secure, standardized interactions. These protocols establish trust frameworks and standardized communication methods between AI agents and merchant systems, enabling seamless integration across diverse e-commerce platforms.
| Aspect | Traditional E-Commerce | Autonomous AI Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| User Role | Active decision-maker | Sets preferences, AI executes |
| Search Process | Manual browsing | Automated comparison across retailers |
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to hours | Seconds to minutes |
| Decision Criteria | Human judgment | Algorithm-based optimization |
| Integration | Single platform | Multi-platform aggregation |
| Authorization | Per-transaction approval | Pre-authorized parameters |
Modern autonomous AI commerce platforms deliver a comprehensive suite of capabilities that fundamentally transform the shopping experience. Product discovery functionality enables agents to search across thousands of SKUs simultaneously, identifying items that match specific requirements with precision that exceeds human capability. Price comparison algorithms monitor real-time pricing across competing retailers, identifying optimal purchase opportunities and executing transactions when predetermined price thresholds are met. Autonomous checkout processes eliminate friction by automating payment processing, address verification, and shipping method selection based on user preferences. Order tracking and management features provide continuous monitoring of shipments, automatically handling returns, managing refunds, and coordinating with customer service when issues arise. Additional capabilities include:
Retailers and e-commerce platforms are rapidly integrating autonomous AI commerce to capture market share and enhance customer lifetime value. Walmart, Amazon, Alibaba, and Flipkart have launched or are developing agentic shopping capabilities, recognizing that 25% of young Americans (18-39) already use AI to shop, indicating strong consumer demand for this technology. Enterprise adoption is accelerating, with Gartner projecting that 33% of enterprises will include agentic AI by 2028, representing a fundamental restructuring of B2B and B2C commerce operations. Major AI platforms including ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Amazon Rufus, and Salesforce Agentforce have integrated commerce capabilities directly into their interfaces, enabling seamless shopping experiences within conversational AI environments. For brands and retailers, this shift creates both opportunities to reach consumers through new channels and challenges in ensuring their products are accurately represented and recommended by autonomous agents—a critical area where AmICited.com’s AI monitoring capabilities help track how brands are cited and represented in AI-driven shopping recommendations.
Autonomous AI commerce delivers substantial value to consumers through time savings, cost optimization, and personalized shopping experiences. By delegating routine purchasing decisions to AI agents, consumers reclaim hours previously spent on product research, price comparison, and transaction management, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities. Cost optimization becomes automatic, as AI agents continuously monitor prices and execute purchases at optimal moments, often achieving savings that exceed what individual consumers could negotiate manually. Personalization reaches new levels of sophistication, with agents learning individual preferences, dietary restrictions, sustainability values, and budget constraints to make increasingly refined recommendations over time. The convenience factor is transformative—consumers can specify needs in natural language and receive completed purchases without navigating multiple websites or managing complex checkout processes.

Despite its transformative potential, autonomous AI commerce faces significant technical, regulatory, and ethical challenges that must be addressed for sustainable growth. Data privacy concerns emerge as AI agents require access to detailed consumer preferences, purchase history, payment information, and behavioral data to function effectively, creating expanded attack surfaces for cybercriminals and potential misuse by platforms. Transparency and explainability remain problematic, as consumers often cannot understand why an AI agent selected a particular product or retailer, undermining trust and making it difficult to identify when recommendations are influenced by undisclosed commercial relationships. Algorithmic bias can perpetuate discrimination in product recommendations, pricing, and service quality, potentially disadvantaging certain demographic groups or reinforcing existing market inequalities. Fraud and security risks multiply when autonomous agents have authorization to execute transactions, requiring robust authentication mechanisms and continuous monitoring to prevent unauthorized purchases or account compromise. Accountability frameworks remain underdeveloped—when an AI agent makes a poor purchasing decision or executes a fraudulent transaction, determining liability between the consumer, the AI platform provider, and the retailer becomes legally complex and contested.
The autonomous AI commerce market is experiencing explosive growth, with a 4,700% year-over-year increase in AI-driven retail traffic demonstrating the rapid adoption trajectory. Leading technology providers including OpenAI, Google, Amazon, and Salesforce have positioned themselves at the forefront of this transformation, embedding commerce capabilities directly into their flagship AI platforms and establishing themselves as gatekeepers for consumer-to-retailer interactions. Protocol standardization efforts through initiatives like the Visa Trusted Agent Protocol and OpenAI Agentic Commerce Protocol are creating interoperability frameworks that enable AI agents to operate across diverse merchant ecosystems without requiring custom integrations for each retailer. Retail adaptation is accelerating across all major e-commerce segments, from luxury goods to grocery delivery, as retailers recognize that failing to integrate with autonomous AI agents risks losing market share to competitors who embrace the technology. The competitive landscape is consolidating around platform ecosystems where AI providers control both the agent interface and merchant access, creating potential monopolistic dynamics that regulators are beginning to scrutinize.
Autonomous AI commerce will likely become the dominant shopping paradigm within the next 3-5 years as consumer adoption accelerates and technical capabilities mature. Integration depth will expand beyond simple product purchasing to encompass complex services including financial products, insurance, travel bookings, and subscription management, creating comprehensive AI-driven procurement platforms. Regulatory frameworks will emerge to address privacy, transparency, and accountability concerns, potentially requiring AI commerce platforms to implement standardized disclosure mechanisms and consumer protection guarantees. Competitive dynamics will intensify as retailers and technology providers compete for control over the agent-consumer relationship, potentially leading to fragmentation where different AI platforms favor different merchant ecosystems. The convergence of autonomous AI commerce with other emerging technologies like blockchain-based verification, advanced biometric authentication, and real-time supply chain visibility will create increasingly sophisticated and trustworthy shopping experiences that fundamentally reshape consumer behavior and retail economics.
Traditional e-commerce requires active consumer participation in browsing, comparing, and purchasing decisions. Autonomous AI Commerce delegates these tasks to AI agents that independently research products, compare prices across retailers, and execute purchases based on pre-defined consumer preferences and authorization parameters. The consumer sets criteria and the AI agent handles the entire transaction process autonomously.
Autonomous AI agents employ multiple security layers including encrypted communication protocols, multi-factor authentication, transaction authorization limits, and real-time fraud detection algorithms. Emerging standards like the Visa Trusted Agent Protocol and OpenAI Agentic Commerce Protocol establish security frameworks and verification mechanisms. Additionally, agents operate within defined guardrails that escalate suspicious transactions to human review.
Current autonomous AI commerce systems primarily execute transactions at listed prices and identify optimal purchase timing based on price monitoring. However, advanced agents are beginning to negotiate volume discounts and exclusive pricing with retailers. Future iterations are expected to develop sophisticated negotiation capabilities, potentially engaging in real-time price discussions with merchant systems.
Autonomous AI agents require access to structured product data (specifications, pricing, availability), customer preference profiles, purchase history, behavioral patterns, and real-time inventory information. They also need access to payment systems, shipping logistics data, and retailer APIs. The quality and consistency of this data directly impacts agent performance and recommendation accuracy.
Retailers should prioritize data structuring and standardization using schema.org markup and GS1 standards to ensure AI agents can accurately interpret product information. Implementing robust APIs for inventory, pricing, and fulfillment systems is essential. Additionally, retailers should develop strategies for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) to ensure their products are prominently featured in AI agent recommendations.
Key risks include data privacy breaches, algorithmic bias in recommendations, lack of transparency in agent decision-making, fraud and unauthorized transactions, and unclear accountability frameworks. Additionally, concentrated control by major AI platforms over the agent-consumer relationship creates potential monopolistic dynamics. Regulatory frameworks are still developing to address these concerns.
Major technology providers including OpenAI (ChatGPT with Instant Checkout), Google (Gemini shopping features), Amazon (Rufus agent), and Salesforce (Agentforce Commerce) are leading the market. Retailers like Walmart, Amazon, Alibaba, and Flipkart are integrating autonomous shopping capabilities into their platforms. Payment providers like Visa are establishing standardized protocols for secure agent-merchant interactions.
Autonomous AI commerce will transform retail employment by automating routine purchasing decisions and customer service interactions. However, it will create new roles in AI agent management, data quality assurance, merchant optimization, and customer relationship management. The net employment impact will depend on how quickly retailers adopt the technology and whether they invest in reskilling existing workforce members.
AmICited tracks how your brand is cited and recommended by AI shopping agents across ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity, and other AI platforms. Ensure your products are accurately represented in autonomous AI commerce systems.

Learn how agentic commerce uses AI agents to autonomously complete purchases. Explore how intelligent systems are revolutionizing e-commerce and consumer shoppi...
Learn how to prepare your brand for agentic commerce. Discover essential steps to make your systems AI agent-ready and stay competitive in the evolving e-commer...

Discover how agentic AI is transforming shopping and what it means for brand visibility. Learn how AI agents make autonomous purchases and how to prepare your b...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.