Freshness Signal
Freshness signal is a ranking factor measuring content recency and update frequency. Learn how publication dates, update frequency, and content changes impact S...
Technical indicators such as timestamps and modification dates that AI systems use to assess how recently content was created or updated. These signals help determine content currency and relevance for citation in AI-generated responses. Content freshness signals include datePublished, dateModified, crawl timestamps, and schema markup metadata. They directly influence whether AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity cite your content in their responses.
Technical indicators such as timestamps and modification dates that AI systems use to assess how recently content was created or updated. These signals help determine content currency and relevance for citation in AI-generated responses. Content freshness signals include datePublished, dateModified, crawl timestamps, and schema markup metadata. They directly influence whether AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity cite your content in their responses.
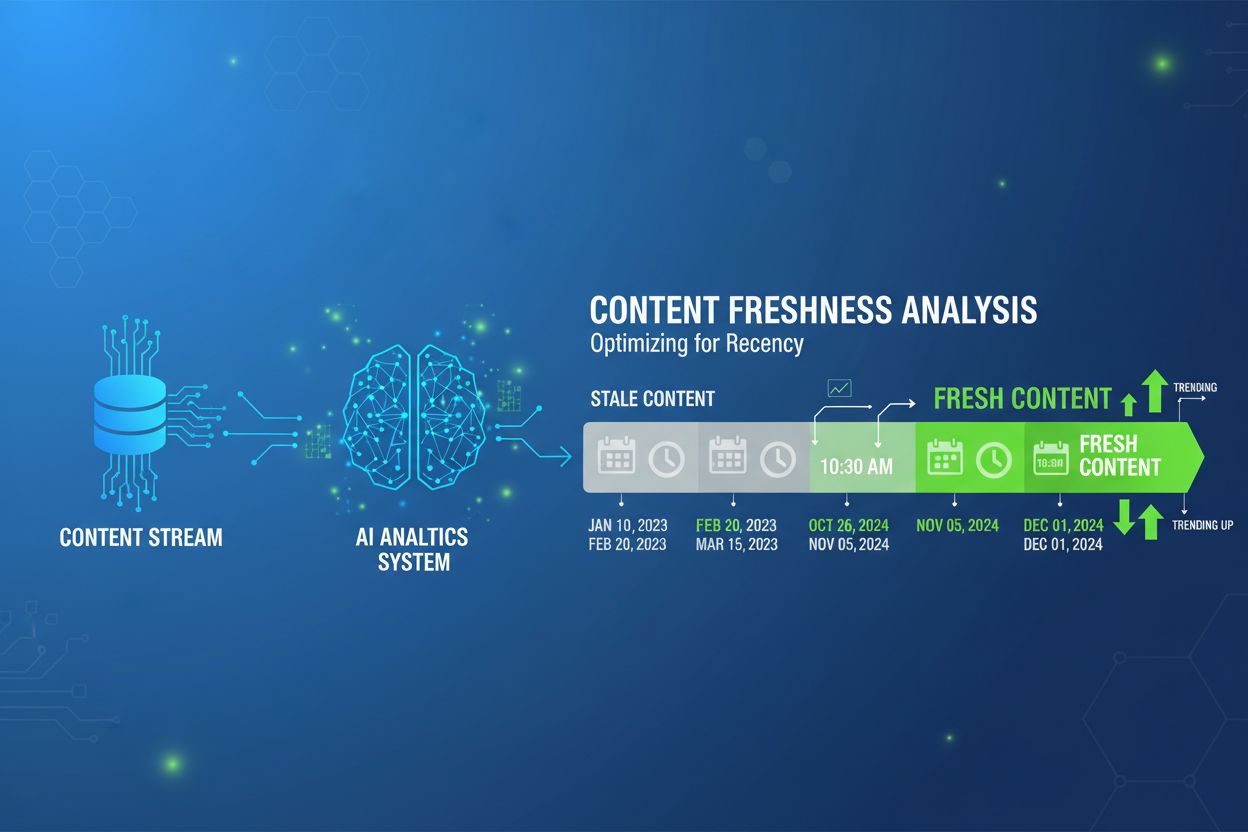
Content freshness signals are indicators that search engines, AI systems, and citation algorithms use to determine how recently content was created, updated, or remains relevant to current information needs. These signals encompass both explicit metadata (such as publication dates and modification timestamps) and implicit indicators (like the recency of linked sources and the currency of referenced data). AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity increasingly rely on freshness signals to prioritize sources that reflect the latest information, with research showing that AI-cited content is 25.7% fresher than average web content. Unlike traditional search engines that primarily use freshness as a ranking factor, modern large language models (LLMs) treat freshness as a credibility and relevance indicator, directly influencing which sources are selected for citations and responses. Understanding and implementing robust freshness signals has become essential for content creators seeking visibility in AI-powered search and citation systems. The strategic use of these signals can significantly improve a content piece’s likelihood of being cited by AI systems and discovered through modern search interfaces.
AI systems evaluate content currency through mechanisms that differ substantially from traditional search engine freshness algorithms, creating distinct advantages for strategically updated content. While Google’s freshness algorithm primarily considers publication date and update frequency as ranking signals, LLMs like ChatGPT employ a more nuanced approach that weighs the recency of cited sources against the knowledge cutoff date of the model itself—ChatGPT, for instance, demonstrates a documented preference for sources published one or more years newer than competing alternatives when evaluating topical relevance. Gemini integrates real-time web access to evaluate freshness dynamically, allowing it to prioritize recently updated content for queries about current events, product releases, and breaking news with greater precision than traditional search. Perplexity combines freshness evaluation with source attribution transparency, explicitly showing users the publication dates of cited sources and allowing the system to weight recent content more heavily in its response generation. The distinction matters critically: traditional search freshness is primarily a ranking signal, while AI freshness evaluation is a source selection mechanism that directly determines whether your content appears in citations at all. This fundamental difference means that content freshness strategies must now account for how LLMs assess currency rather than solely optimizing for search engine crawl patterns and index updates.
Technical freshness signals provide machine-readable indicators that AI systems and search engines parse to understand content recency and update patterns with precision. The datePublished schema markup property establishes the original publication timestamp, while dateModified indicates when content was last substantively updated—both critical for AI systems that need to distinguish between evergreen content and time-sensitive information. The lastmod tag in XML sitemaps communicates update frequency to crawlers, helping systems understand whether content receives regular maintenance or represents a static resource. Structured data markup using Schema.org vocabulary allows publishers to explicitly declare freshness metadata in machine-readable formats that AI systems can reliably parse, reducing ambiguity about content currency. Crawl timestamps and index refresh rates provide implicit signals about how actively a piece of content is being maintained, with frequently crawled pages suggesting ongoing updates and relevance. The following table outlines the primary technical signals, their purposes, and implementation approaches:
| Signal Type | Purpose | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| datePublished | Establish original publication date | Schema.org markup in article/newsarticle schema |
| dateModified | Indicate substantive content updates | Update schema property and visible date display |
| lastmod | Communicate crawl frequency | XML sitemap lastmod tag |
| Schema.org markup | Machine-readable freshness metadata | Implement Article, NewsArticle, or BlogPosting schema |
| Crawl frequency | Signal active maintenance | Regular updates trigger more frequent crawls |
| Content versioning | Track iteration history | Version numbers or revision dates in metadata |
Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) is a concept that recognizes certain search queries inherently require current information, making freshness signals disproportionately important for visibility and citation in AI systems. QDF operates on the principle that not all queries benefit equally from fresh content—some topics demand the most recent information available, while others remain relevant regardless of age. AI systems apply QDF logic when evaluating which sources to cite, prioritizing recently updated content for queries that fall into specific categories where currency directly impacts usefulness and accuracy. Understanding which query types trigger QDF requirements helps content creators prioritize freshness efforts on high-impact topics rather than applying uniform update strategies across all content. The following categories represent query types where freshness signals significantly influence AI citation patterns:
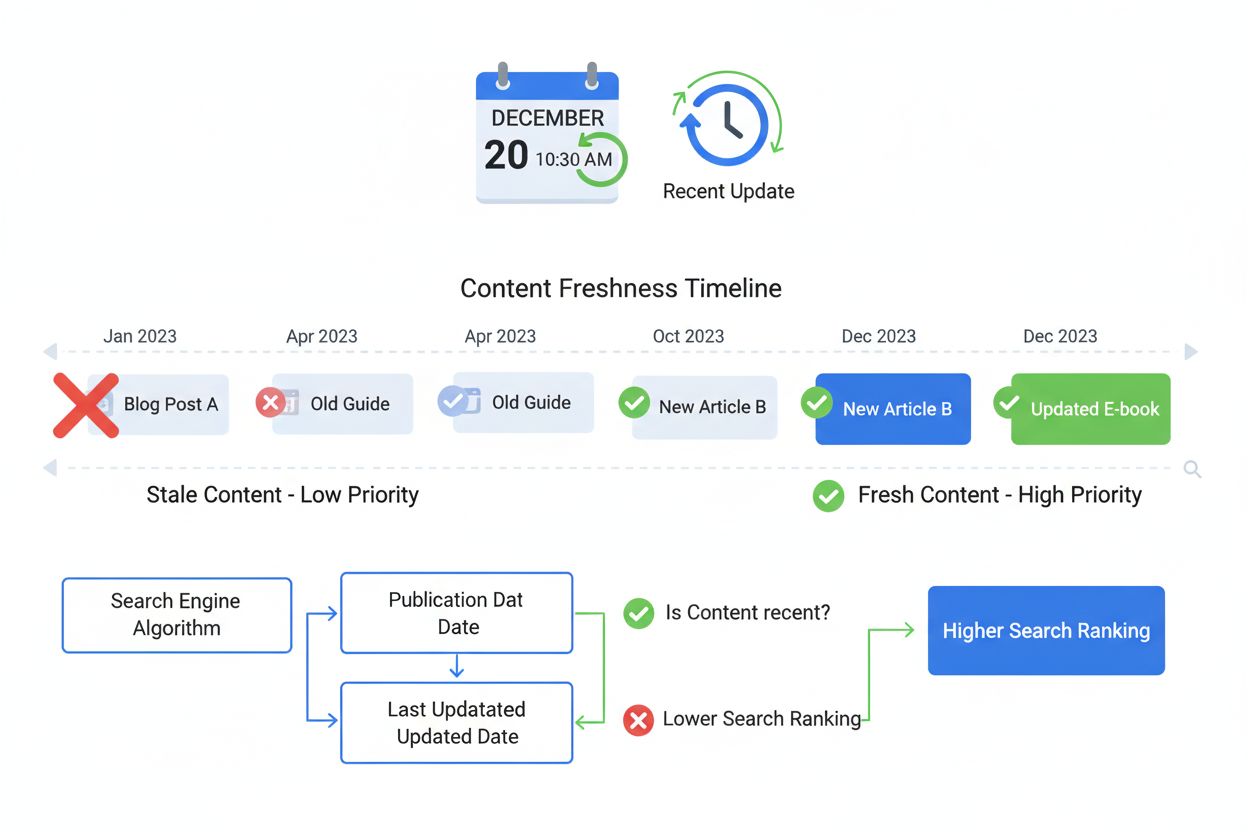
Content experiences predictable decay patterns in AI citation visibility, with freshness signals directly influencing how long a piece remains discoverable and citable by LLMs. Research indicates that approximately 30% of content cited by AI systems receives substantive refreshes within six months of initial publication, while 70% of ChatGPT citations come from sources updated within the past year—demonstrating that active maintenance significantly extends citation lifespan. The visibility lifecycle typically follows a pattern where newly published content receives initial citation attention, visibility plateaus during the “evergreen” phase, and then declines as content ages without updates unless it addresses timeless topics. Content that receives regular updates experiences extended visibility windows and higher citation probability, as freshness signals reset the decay clock and signal to AI systems that information remains current and reliable. Strategic refresh timing—updating content before it reaches critical decay thresholds—can extend citation visibility by 40-60% compared to static content, making maintenance schedules as important as initial publication quality. Understanding this lifecycle allows content creators to implement proactive refresh strategies that maintain visibility rather than waiting for citation decline to trigger updates.
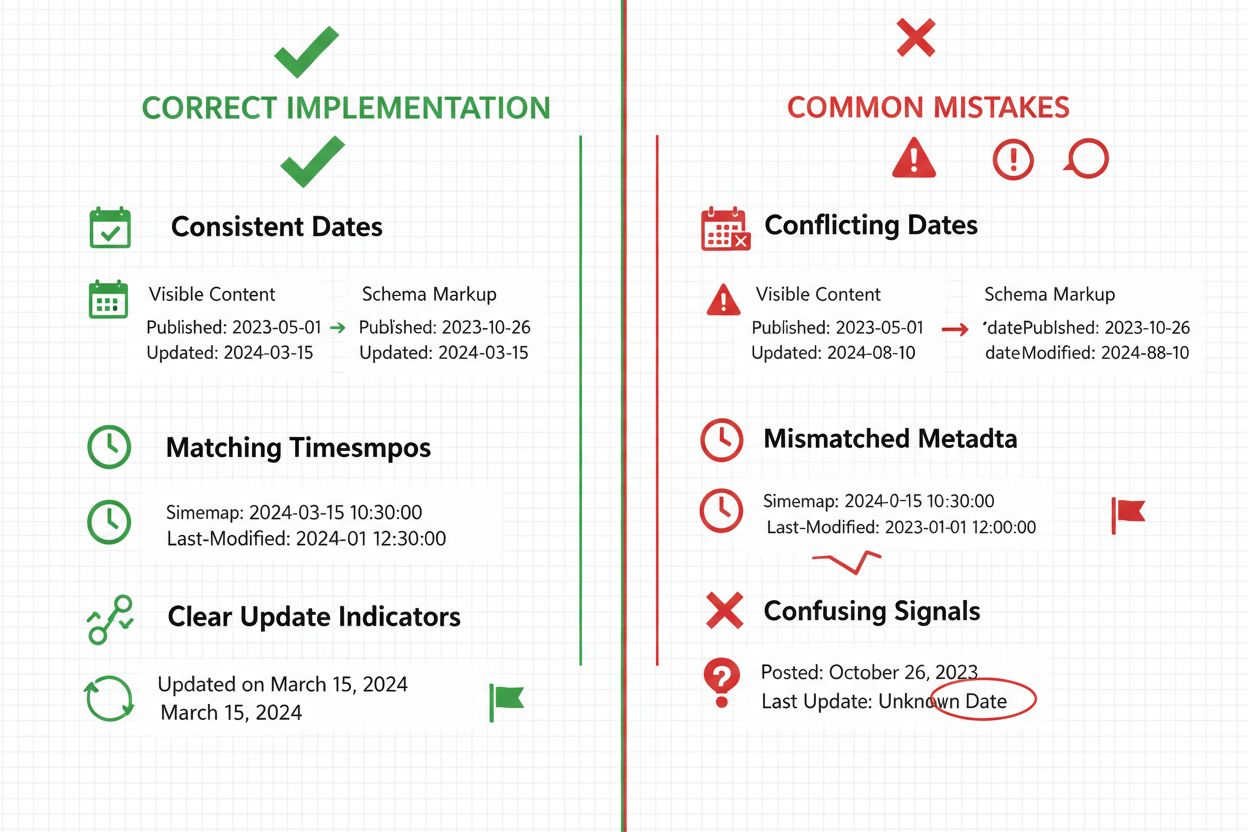
Freshness signals manifest in two distinct forms: textual signals that human readers recognize and technical signals that machines parse, with both contributing to AI citation decisions but through different mechanisms. Textual freshness signals include visible date displays, references to current events, mentions of recent statistics, and language that explicitly acknowledges when information was last verified—for example, a sentence stating “As of March 2024, the current market rate is…” provides clear temporal context that readers and AI systems both recognize. Technical freshness signals operate invisibly to human readers but communicate directly with AI systems through schema markup, HTTP headers, sitemap metadata, and structured data that explicitly declare publication and modification dates. A content piece might display “Updated: January 15, 2024” as a textual signal while simultaneously embedding "dateModified": "2024-01-15" in its schema markup as a technical signal—both serve freshness purposes but reach different audiences. AI systems increasingly weight technical signals more heavily than textual signals because metadata cannot be manipulated as easily as visible text, making schema markup and structured data more reliable indicators of genuine content updates. Effective freshness strategies implement both signal types consistently, ensuring that visible dates match embedded metadata and that update claims in body text correspond to actual modification timestamps. Inconsistencies between textual and technical signals can trigger credibility penalties in AI evaluation systems, as mismatches suggest either negligent maintenance or intentional date manipulation.
Implementing freshness signals effectively requires a systematic approach that integrates schema markup, visible date displays, and update workflows into content management processes. Begin by implementing Article or NewsArticle schema markup on all content, ensuring that datePublished reflects the original publication date and dateModified updates automatically whenever content receives substantive changes—this provides the machine-readable foundation that AI systems rely on for freshness evaluation. Display publication and modification dates prominently in content headers or footers, using clear language that distinguishes between “Published” and “Updated” dates to help both human readers and AI systems understand content history. Establish a content refresh schedule based on topic decay rates and QDF requirements, with high-priority topics (breaking news, product reviews, market data) receiving monthly or quarterly reviews and evergreen content receiving annual audits. When updating content, ensure that modifications are substantive rather than cosmetic—changing a single word or date without meaningful content revision can trigger credibility penalties if AI systems detect the mismatch between modification timestamps and actual content changes. Implement automated schema markup generation through your content management system to eliminate manual date entry errors and ensure consistency across all published content. Monitor how freshness signals correlate with AI citation rates using tools that track which of your content pieces appear in LLM responses, allowing you to refine refresh strategies based on actual citation performance rather than assumptions about freshness importance.
Freshness signal strategies must adapt to industry-specific content lifecycles and information decay rates, as different sectors experience vastly different freshness requirements. News and media organizations require near-real-time freshness signals, with publication timestamps accurate to the minute and continuous updates reflecting breaking developments—AI systems cite news sources with extreme recency bias, often preferring articles published within hours of query time. SaaS and software companies benefit from quarterly or semi-annual refresh cycles that update feature descriptions, pricing information, and integration lists as products evolve, with schema markup clearly indicating when documentation was last verified against current product versions. Healthcare and medical content demands rigorous freshness practices because outdated medical information can pose safety risks; content should include expert review dates, citations to current clinical guidelines, and clear indicators when information reflects current medical consensus. E-commerce and retail requires dynamic freshness signals that update product availability, pricing, and inventory status in real-time, with schema markup reflecting current product information and modification timestamps updating whenever inventory or pricing changes. Financial services and investment content must balance evergreen educational content with time-sensitive market analysis, using clear date indicators to distinguish between timeless principles and current market commentary that requires frequent updates. Technology and software reviews benefit from seasonal refresh cycles aligned with product release schedules, with major version updates triggering content refreshes and schema markup updates that signal to AI systems when comparisons reflect current product capabilities.
Monitoring freshness impact requires tracking how content freshness correlates with AI citation rates, visibility in LLM responses, and overall content performance across AI-powered search interfaces. Implement tracking mechanisms that capture when your content appears in ChatGPT responses, Gemini citations, Perplexity sources, and other AI systems, then correlate citation frequency with content age and freshness signal implementation—this data reveals whether freshness improvements actually drive citation increases for your specific content categories. Use tools that monitor your content’s presence in AI search results and track citation patterns over time, noting whether recently updated content receives more citations than static content on similar topics. Analyze the relationship between modification date frequency and citation rate by comparing citation metrics for content updated monthly versus quarterly versus annually, establishing baseline freshness requirements for your industry and content types. Create dashboards that display freshness metrics alongside citation metrics, allowing you to identify which content pieces would benefit most from refresh efforts based on their citation potential and current visibility gaps. Track not just whether content is cited, but how prominently it appears in AI responses—content cited in opening paragraphs versus mentioned in supporting context indicates different levels of freshness signal effectiveness. Establish feedback loops where citation performance data informs refresh prioritization, ensuring that freshness efforts focus on high-impact content pieces rather than applying uniform update schedules across all content.
Common freshness signal mistakes undermine citation potential and can trigger credibility penalties from AI systems that detect inconsistencies or manipulation attempts. Date manipulation—updating modification timestamps without making substantive content changes—represents the most serious error, as AI systems increasingly detect mismatches between claimed update dates and actual content changes, penalizing sources that appear to artificially inflate freshness signals. Inconsistent date displays occur when visible publication dates conflict with schema markup dates or when modification timestamps appear in some content pieces but not others, creating confusion about which dates represent actual updates versus display errors. Over-updating evergreen content wastes resources and can backfire when AI systems detect that “updated” content contains no meaningful changes, potentially triggering penalties for apparent manipulation rather than rewarding freshness efforts. Ignoring dateModified entirely represents a missed opportunity, as many content creators implement datePublished schema markup but fail to update dateModified when content changes, leaving AI systems unable to recognize that content has been refreshed. Failing to distinguish between minor and major updates leads to modification timestamps that update for typo corrections or formatting changes, diluting the signal value of dates that should indicate substantive content revisions. Neglecting to update supporting data and statistics creates a common scenario where publication dates appear current but referenced statistics, prices, or product information remain outdated, causing AI systems to downweight citations despite fresh timestamps. Inconsistent refresh schedules that update some content regularly while leaving other pieces static create unpredictable freshness signals that prevent AI systems from developing reliable expectations about your content’s maintenance patterns and currency.
Traditional search engines like Google use freshness primarily as a ranking factor that influences page position in search results. AI systems like ChatGPT and Gemini use freshness signals as a source selection mechanism that determines whether your content gets cited at all. This fundamental difference means AI systems may completely exclude older content from consideration, while traditional search might still rank it on page 2 or 3. For AI visibility, freshness is a credibility and relevance indicator rather than just a ranking boost.
The dateModified schema markup property is the most critical freshness signal for AI systems because it provides machine-readable, verifiable evidence of when content was last substantively updated. Unlike visible dates that can be manipulated, schema markup is parsed directly by AI systems and harder to fake. Consistency between dateModified and actual content changes is essential—AI systems detect mismatches and penalize sources that appear to artificially inflate freshness signals without meaningful updates.
Update frequency depends on your industry and content type. High-velocity topics like news, technology, and finance benefit from monthly or even weekly updates. Medium-velocity content like SaaS documentation and digital marketing guides should refresh quarterly or semi-annually. Low-velocity evergreen content like historical information or foundational education can update annually. Research shows that approximately 30% of AI-cited content receives updates within 6 months, and 70% within a year, suggesting quarterly updates as a baseline for maintaining competitive AI visibility.
Technically yes, but it's a serious mistake that damages credibility. AI systems increasingly detect mismatches between modification timestamps and actual content changes, treating date manipulation as a credibility red flag. If you update a modification date without substantive content changes, AI systems may downweight or exclude your content from citations. Only update dateModified when you make meaningful changes like adding new information, updating statistics, revising outdated sections, or improving clarity. Minor changes like typo fixes don't warrant date updates.
Start by implementing Article or NewsArticle schema markup with datePublished and dateModified properties. Configure your CMS to automatically update dateModified only when substantive changes occur, not on every save. Display publication and modification dates prominently in your content headers using clear labels like 'Published' and 'Updated.' Update your XML sitemap's lastmod tag to reflect genuine content updates. Create editorial guidelines that define what constitutes a substantive update worthy of a date change. Use tools that monitor schema markup accuracy across your site to catch implementation errors.
Content freshness is a component of the Trust (T) pillar in Google's E-E-A-T framework. Regular updates signal that you actively maintain your content and care about accuracy, which builds trust with both users and AI systems. Outdated content, especially in high-stakes domains like healthcare and finance, suggests neglect and reduces perceived trustworthiness. Combining fresh content with clear author credentials, expert review dates, and citations to current sources creates a comprehensive trust signal that improves both traditional search rankings and AI citation likelihood.
Monitor your content's appearance in ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other AI systems using tools that track AI citations. Create a baseline by documenting which of your content pieces currently appear in AI responses. After implementing freshness improvements, retest the same queries monthly to see if citation frequency increases. Correlate citation metrics with content age and modification dates to establish whether freshness improvements drive citation increases for your specific content categories. Track not just whether content is cited, but how prominently it appears—opening paragraph citations indicate stronger freshness signal effectiveness than supporting mentions.
Yes, but with strategic clarity. Display both dates when content has been meaningfully updated, using clear labels like 'Published: January 15, 2024' and 'Updated: December 20, 2024.' This transparency helps readers understand content history and signals to AI systems that you actively maintain content. However, for evergreen content that hasn't changed, showing only the publication date avoids creating false impressions of freshness. Never show conflicting dates or hide modification dates when updates have occurred—inconsistency damages credibility with both users and AI systems.
Track how AI systems reference your content with AmICited.com. Get real-time insights into your brand's presence in ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.

Freshness signal is a ranking factor measuring content recency and update frequency. Learn how publication dates, update frequency, and content changes impact S...
Learn when and how to update your content for AI visibility. Discover freshness signals that help ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews cite your brand.

Learn how to balance evergreen and news content for maximum AI visibility. Discover freshness strategies that work with ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.