
What is Conversational Commerce and AI? Definition, Benefits & Implementation
Learn what conversational commerce and AI are, how they work together, their benefits for businesses and customers, and best practices for implementation in you...
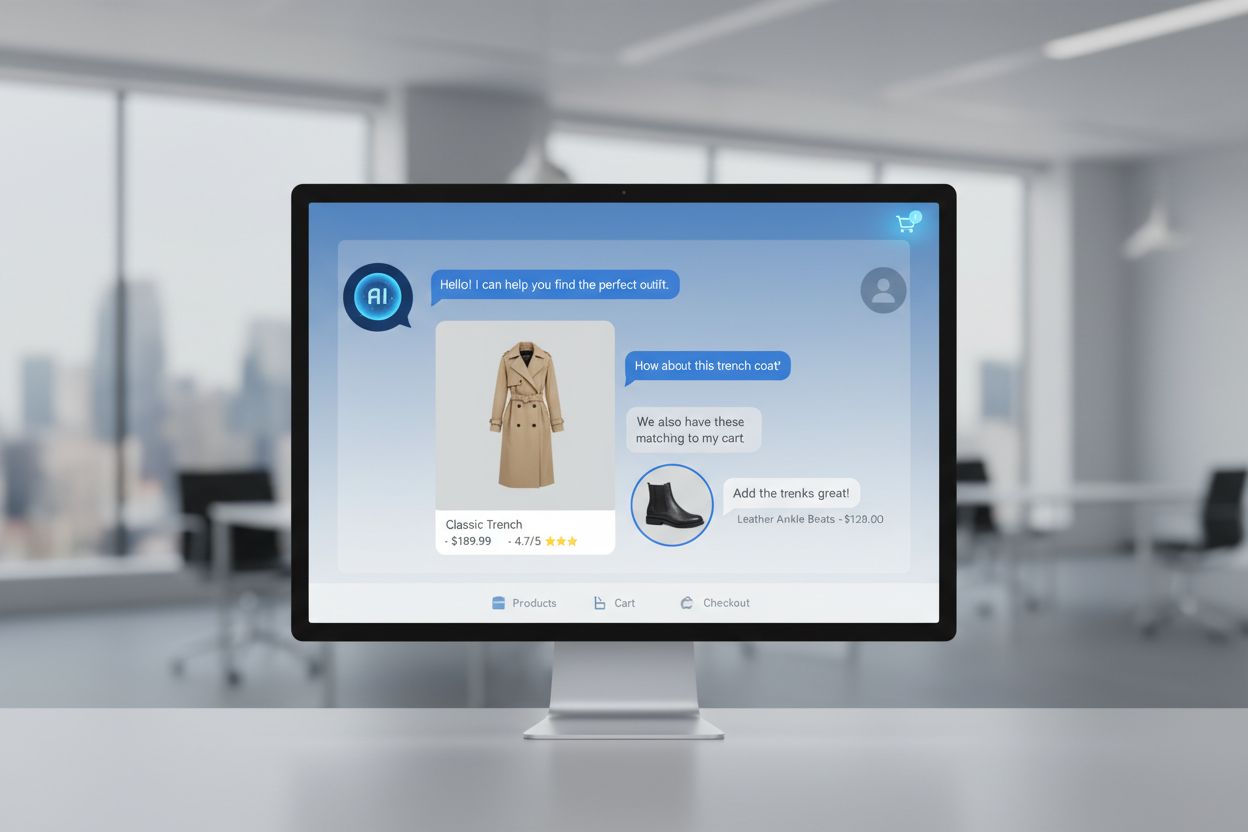
Conversational commerce is the practice of conducting shopping transactions through AI chatbot interactions, messaging apps, and voice assistants rather than traditional e-commerce interfaces. It enables customers to discover, evaluate, and purchase products through natural language conversations with AI-powered systems. This technology leverages natural language processing, machine learning, and generative AI to create personalized, seamless shopping experiences. The global market is projected to reach $290 billion by 2025, with chatbots driving $142 billion in retail sales.
Conversational commerce is the practice of conducting shopping transactions through AI chatbot interactions, messaging apps, and voice assistants rather than traditional e-commerce interfaces. It enables customers to discover, evaluate, and purchase products through natural language conversations with AI-powered systems. This technology leverages natural language processing, machine learning, and generative AI to create personalized, seamless shopping experiences. The global market is projected to reach $290 billion by 2025, with chatbots driving $142 billion in retail sales.
Conversational commerce represents a fundamental shift in how consumers interact with brands and make purchases through natural language conversations. Unlike traditional e-commerce, which relies on browsing product catalogs and filling out forms, conversational commerce enables customers to discover, evaluate, and purchase products through dialogue with AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, or live agents. This technology leverages three core pillars: Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand customer intent, Machine Learning (ML) to improve responses over time, and Generative AI to create contextually relevant, human-like interactions. The distinction from traditional e-commerce is profound—while conventional platforms require customers to navigate multiple pages and complete lengthy checkout processes, conversational commerce compresses the entire customer journey into a single, seamless dialogue. Intent classification algorithms analyze what customers actually want, whether that’s product recommendations, order tracking, or customer support. The technology understands context, remembers previous interactions, and adapts responses based on individual preferences. This shift represents a move from transactional interactions to relational experiences, where the platform becomes a knowledgeable shopping assistant rather than a static storefront. Conversational commerce operates across multiple channels—messaging apps, voice assistants, social media, and websites—creating a unified experience regardless of where customers initiate contact. The underlying AI continuously learns from millions of conversations, becoming increasingly sophisticated at predicting customer needs and delivering personalized recommendations without explicit requests.

The conversational commerce market is experiencing explosive growth, driven by increasing consumer comfort with AI interactions and business recognition of its ROI potential. The sector demonstrates remarkable expansion across multiple dimensions, with enterprises investing heavily in conversational technologies to enhance customer engagement and drive revenue growth.
| Metric | Value | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Global Conversational Commerce Market Size (2025) | $290 Billion | 25% YoY |
| Chatbot & Virtual Assistant Revenue (2024) | $142 Billion | 35% YoY |
| Consumer Preference for Conversational Shopping | 70% | +15% annually |
| Enterprise Adoption Rate | 80% | +20% annually |
| Average Conversation-to-Purchase Rate | 35-45% | +12% YoY |
| Customer Satisfaction with Chatbots | 68% | +8% annually |
This explosive growth reflects fundamental changes in consumer behavior and business strategy. 70% of consumers now prefer conversational interactions for customer service and shopping, particularly among younger demographics who view chatbots as convenient and efficient. 80% of enterprises have implemented or plan to implement conversational commerce solutions within the next 18 months, recognizing the competitive advantage these technologies provide. The market expansion is fueled by improvements in generative AI capabilities, reduced implementation costs, and proven ROI metrics. Businesses report 35-45% conversation-to-purchase conversion rates, significantly outperforming traditional digital channels. The revenue opportunity extends beyond direct sales—enterprises capture substantial value through reduced customer service costs, improved customer lifetime value, and enhanced data collection. Regional variations exist, with North America and Asia-Pacific leading adoption, though European markets are rapidly catching up driven by regulatory clarity around AI governance.
Conversational commerce operates through an integrated technology stack that combines multiple AI disciplines to create seamless customer interactions. Natural Language Processing (NLP) forms the foundation, enabling systems to parse customer messages, extract meaning, and identify linguistic patterns that indicate purchase intent or support needs. Advanced NLP models can understand colloquialisms, typos, and context-dependent language, making interactions feel natural rather than robotic. Machine Learning algorithms continuously analyze conversation data to identify patterns, predict customer behavior, and optimize response strategies. These systems learn which conversation paths lead to successful purchases, which questions customers ask most frequently, and how to personalize recommendations based on individual browsing and purchase history. Generative AI, particularly large language models, creates contextually appropriate responses that feel conversational and human-like rather than templated. Intent classification represents a critical capability—the system must accurately determine whether a customer wants product recommendations, order status updates, returns processing, or general information. Session persistence maintains conversation context across multiple interactions, allowing customers to reference previous messages and continue conversations days or weeks later without repeating information. CRM integration connects conversational systems with customer relationship management platforms, enabling access to purchase history, preferences, loyalty status, and previous support interactions. Sentiment analysis monitors customer emotions throughout conversations, triggering escalation to human agents when frustration levels rise. Entity recognition identifies specific products, brands, prices, and other relevant information within natural language, enabling precise product matching and accurate order processing.
Conversational commerce delivers measurable business value across multiple dimensions, from revenue growth to operational efficiency and customer loyalty enhancement.
Increased Conversion Rates: Businesses implementing conversational commerce report 20-35% increases in conversion rates compared to traditional e-commerce channels, as the guided dialogue reduces friction and addresses customer objections in real-time.
Reduced Customer Service Costs: Automated conversational systems handle 60-70% of routine inquiries without human intervention, reducing customer service expenses by 30-40% while maintaining or improving satisfaction scores.
Enhanced Customer Retention: Personalized conversational experiences increase customer lifetime value by 25-40%, as customers appreciate the individualized attention and are more likely to return for repeat purchases.
Improved Personalization & Recommendations: AI-driven conversations enable real-time product recommendations based on expressed preferences and browsing behavior, increasing average order value by 15-25% through intelligent upselling and cross-selling.
Valuable Data Insights: Every conversation generates structured data about customer preferences, pain points, and decision-making processes, enabling businesses to refine product offerings, improve marketing messaging, and optimize inventory management.
Faster Customer Resolution: Conversational systems resolve customer inquiries 3-5x faster than traditional support channels, improving customer satisfaction while reducing operational overhead and enabling support teams to focus on complex issues requiring human judgment.
Competitive Differentiation: Early adopters of conversational commerce establish brand loyalty and market positioning advantages, as customers increasingly expect seamless, intelligent interactions and view companies without these capabilities as outdated.
Conversational commerce transforms customer interactions across diverse industries, each leveraging the technology to address unique business challenges and customer needs. In Retail & Fashion, conversational systems function as personal stylists, asking about preferences, body type, and occasion to recommend clothing items, check inventory across locations, and process returns through natural dialogue. Brands like major fashion retailers use conversational commerce to reduce return rates by 15% through better fit guidance and increase repeat purchases through personalized recommendations. In Travel & Hospitality, chatbots handle flight searches, hotel bookings, itinerary planning, and customer support, reducing booking friction and enabling customers to modify reservations through conversation rather than navigating complex websites. Hotels use conversational systems to handle guest requests, restaurant reservations, and local recommendations, improving guest satisfaction while reducing front-desk workload. In Financial Services, conversational commerce enables account inquiries, transaction history reviews, loan applications, and investment advice through secure, compliant dialogue, with banks reporting 40% reduction in call center volume. Quick Service Restaurants (QSR) leverage conversational ordering through messaging apps and voice assistants, enabling customers to place orders, customize items, and track delivery status through natural conversation, increasing order frequency by 20-30%. In Healthcare, patient-facing chatbots handle appointment scheduling, prescription refills, symptom assessment, and post-visit follow-up, reducing administrative burden on medical staff while improving patient engagement. In E-commerce, conversational systems serve as intelligent shopping assistants, answering product questions, comparing options, and guiding customers through checkout, with some platforms reporting 45% of transactions initiated through conversational interfaces.
The distinction between conversational commerce and traditional e-commerce represents a fundamental reimagining of the customer journey and interaction model. Traditional e-commerce relies on form-based navigation, requiring customers to browse product categories, apply filters, read descriptions, and complete multi-step checkout processes—a fragmented experience where customers must independently evaluate options and make decisions. In contrast, conversational commerce creates a seamless, guided dialogue where customers express needs in natural language and receive personalized recommendations, immediate answers to questions, and streamlined purchasing without navigating multiple pages. Traditional platforms present static product information that applies equally to all customers, while conversational systems deliver dynamic, personalized content tailored to individual preferences, purchase history, and expressed needs. The customer effort differs dramatically—traditional e-commerce requires customers to invest significant time and cognitive effort in product discovery and comparison, whereas conversational commerce compresses this process into a brief dialogue. Session persistence distinguishes the two approaches: traditional e-commerce sessions are often isolated, requiring customers to restart searches if they return days later, while conversational systems maintain continuous context across multiple interactions, remembering preferences and previous conversations. Friction points proliferate in traditional e-commerce—customers abandon carts due to complex checkout, forgotten passwords, and unclear shipping policies—while conversational commerce addresses these issues proactively through dialogue. The data collection differs fundamentally: traditional platforms capture behavioral data through page views and clicks, while conversational systems gather rich intent data through natural language, enabling deeper understanding of customer motivations and preferences. Customer support in traditional e-commerce requires customers to navigate help sections or contact support separately, whereas conversational commerce integrates support seamlessly into the shopping experience.
Successfully implementing conversational commerce requires strategic planning, technical integration, and continuous optimization to maximize ROI and customer satisfaction.
Target High-Intent Touchpoints: Deploy conversational systems at moments when customers are most likely to engage—product pages, checkout flows, post-purchase support, and customer service inquiries—rather than attempting to force conversations in low-intent contexts where customers prefer traditional browsing.
Integrate with Existing Technology Stack: Ensure seamless integration with CRM systems, inventory management, payment processors, and fulfillment platforms so conversational systems access real-time data and can execute transactions without manual handoffs or data delays.
Establish Clear Measurement Frameworks: Define KPIs including conversation-to-purchase conversion rates, average order value, customer satisfaction scores, resolution rates, and cost-per-interaction, with regular monitoring and optimization based on performance data.
Implement Robust Personalization: Leverage customer data to deliver individualized recommendations, reference previous interactions, and adapt communication style to customer preferences, creating experiences that feel tailored rather than generic.
Plan for Seamless Escalation: Design clear pathways for escalating complex issues to human agents, ensuring customers never feel trapped in conversations with AI systems unable to resolve their needs, and enabling human agents to access full conversation context.
Prioritize Privacy & Data Security: Implement encryption, secure data storage, and transparent privacy policies that comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, building customer trust through responsible data handling and clear communication about how information is used.
Establish Governance & Quality Standards: Create processes for monitoring conversation quality, identifying and correcting errors, updating training data, and ensuring brand voice consistency across all conversational touchpoints and channels.
Scale Gradually with Testing: Begin with limited deployments on specific products or customer segments, gather performance data, optimize based on results, and gradually expand to additional channels and use cases as confidence and capabilities increase.
Conversational commerce continues evolving rapidly, with emerging technologies and shifting consumer expectations reshaping how businesses engage customers. Voice commerce represents a significant growth frontier, with the market projected to reach $40 billion by 2026, as consumers increasingly use smart speakers and voice assistants for shopping, driven by convenience and hands-free interaction capabilities. Agentic AI represents the next evolution beyond conversational systems—autonomous agents that can independently execute complex tasks like comparing prices across competitors, negotiating terms, and managing entire purchase workflows without human intervention. Augmented Reality (AR) integration will enable customers to visualize products in their environment through conversational guidance, asking “show me how this furniture looks in my living room” and receiving AR-rendered previews that dramatically improve purchase confidence. Social commerce integration will deepen conversational experiences within messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Instagram, and WeChat, where customers increasingly expect to discover and purchase products without leaving their preferred communication channels. Omnichannel persistence will become standard, with conversation history and context seamlessly flowing across devices, channels, and platforms, enabling customers to start conversations on mobile, continue on desktop, and complete on voice assistants without repetition. Privacy-preserving AI will advance, enabling personalization and recommendations while maintaining strict data privacy through techniques like federated learning and on-device processing. Multimodal interactions will combine text, voice, images, and video within single conversations, enabling richer communication and more sophisticated product discovery. The competitive landscape will intensify as conversational commerce becomes table-stakes rather than differentiator, with success determined by implementation quality, personalization sophistication, and seamless integration with broader customer experience strategies.

Conversational commerce is the practice of using AI chatbots, messaging apps, and voice assistants to enable customers to discover, evaluate, and purchase products through natural language conversations. Unlike traditional e-commerce that requires browsing and form-filling, conversational commerce compresses the entire customer journey into a seamless dialogue where customers express needs and receive personalized recommendations and guidance.
Traditional chatbots follow pre-programmed rules and scripts, while conversational commerce systems use advanced AI, natural language processing, and machine learning to understand context, remember previous interactions, and deliver truly personalized experiences. Modern conversational commerce leverages generative AI to create human-like conversations that adapt to individual customer needs and preferences.
Conversational commerce relies on natural language processing (NLP) to understand customer intent, machine learning to improve responses over time, generative AI to create contextually relevant interactions, intent classification to determine what customers want, and CRM integration to access customer history and preferences. These technologies work together to create seamless, personalized shopping experiences.
Key benefits include 20-35% increases in conversion rates, 30-40% reduction in customer service costs, 25-40% improvement in customer lifetime value, 15-25% increase in average order value through intelligent recommendations, and valuable data insights about customer preferences. Businesses also achieve faster customer resolution and competitive differentiation in the market.
Customers benefit from convenience (shopping through familiar messaging apps), personalized recommendations tailored to their preferences, faster resolution of questions and issues, 24/7 availability without waiting for human support, and seamless experiences across devices and channels. The guided dialogue reduces decision-making friction and helps customers find exactly what they need.
Retail and fashion benefit through personalized styling advice, travel and hospitality through booking and itinerary management, financial services through account inquiries and loan applications, quick-service restaurants through order placement, healthcare through appointment scheduling, and e-commerce through product discovery and checkout assistance. Essentially, any industry with customer interactions can benefit.
Start by identifying high-intent touchpoints like product pages and checkout flows, integrate with your existing CRM and inventory systems, establish clear measurement frameworks for success, implement robust personalization, plan for seamless escalation to human agents, prioritize privacy and data security, and scale gradually with testing before full deployment.
Yes, when implemented properly. Secure conversational commerce systems use encryption, tokenization for payment data, secure data storage, and compliance with regulations like PCI-DSS, GDPR, and CCPA. Payments are processed through secure gateways, and sensitive information is never stored in conversation logs. Always ensure your provider implements enterprise-grade security measures.
AmICited tracks how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews mention your brand in conversational shopping contexts. Understand your AI visibility and optimize your presence in the conversational commerce ecosystem.

Learn what conversational commerce and AI are, how they work together, their benefits for businesses and customers, and best practices for implementation in you...
Conversational AI is a collection of AI technologies enabling natural dialogue between humans and machines. Learn how NLP, machine learning, and dialogue manage...

Discover how AI shopping and conversational commerce are transforming retail. Learn about chat-based shopping trends, real-world success stories, and how to imp...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.