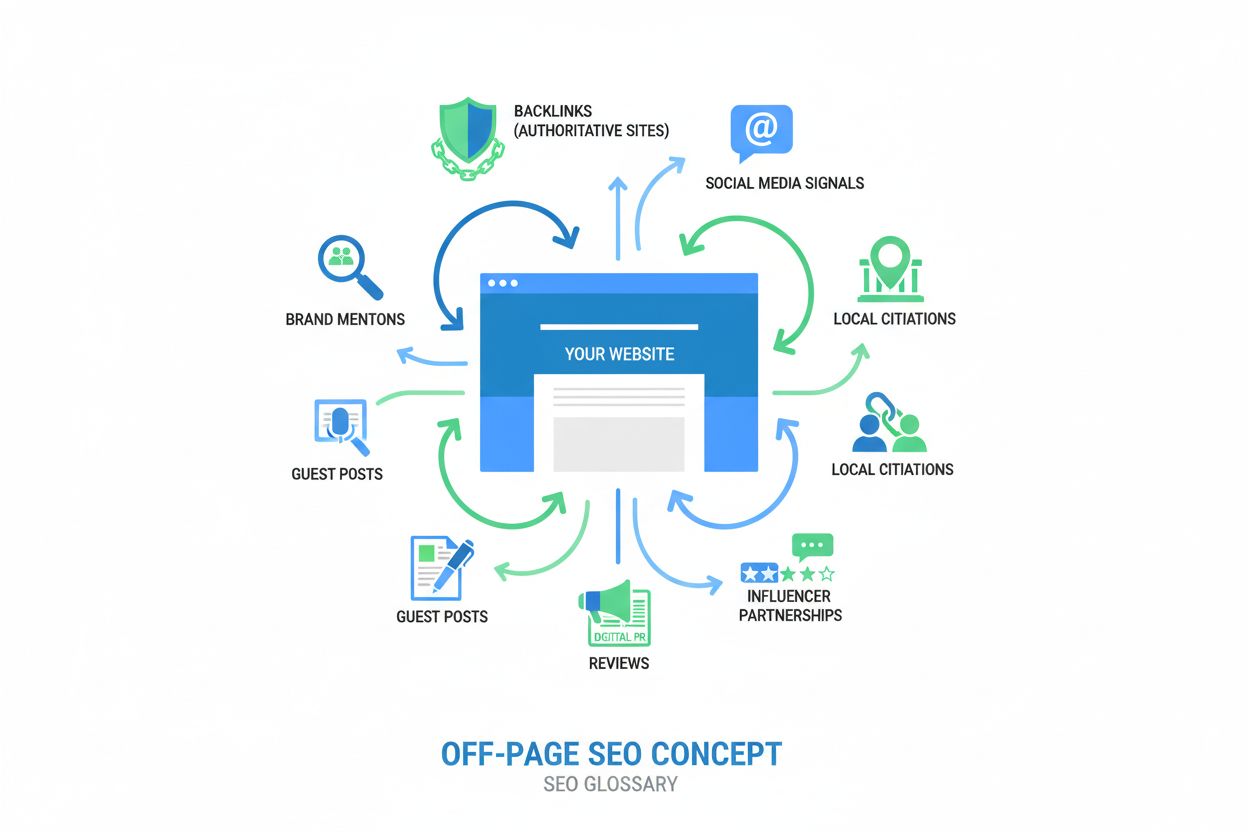
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO definition: external optimization strategies including backlinks, brand mentions, and authority building. Learn how off-site signals impact search ...
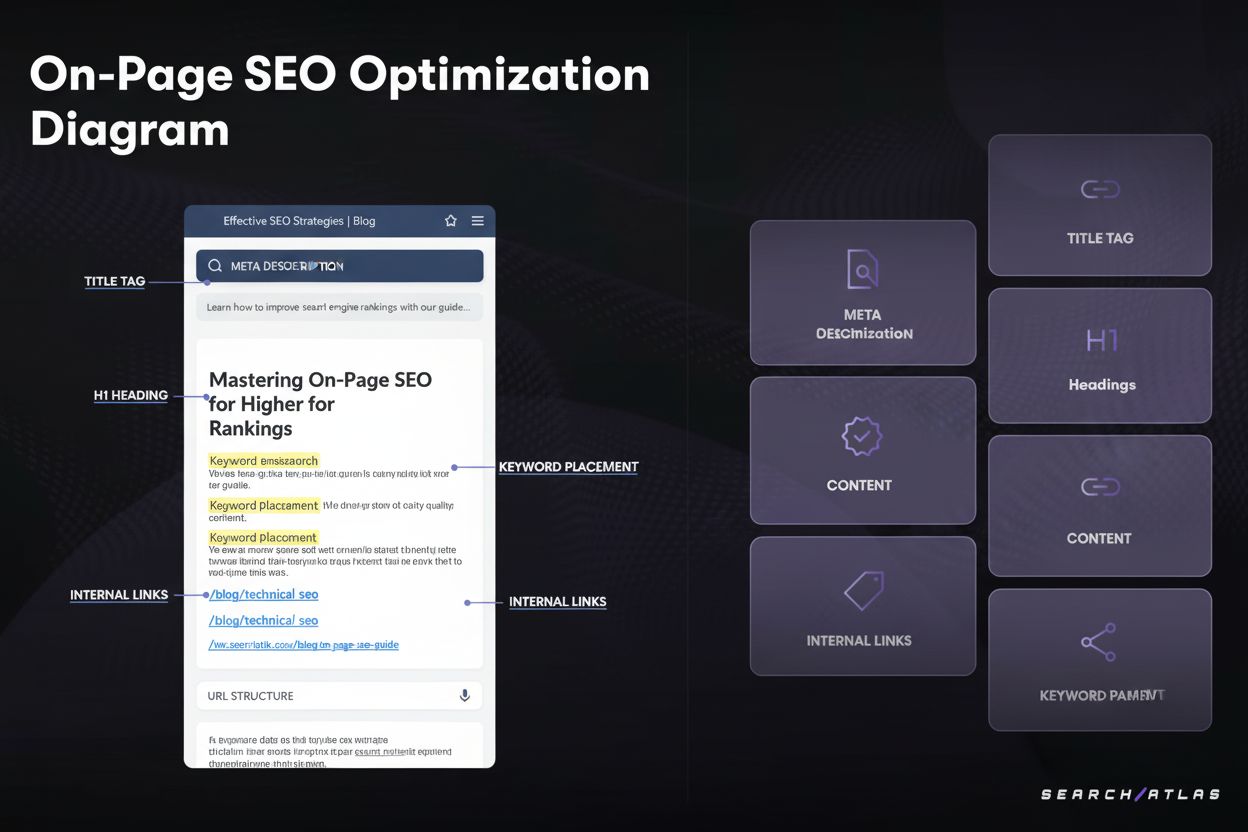
On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing individual webpage elements—including content, HTML source code, title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and internal links—to improve search engine rankings and user experience. It focuses on making webpages more relevant to specific search queries and easier for search engines to understand and index.
On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing individual webpage elements—including content, HTML source code, title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and internal links—to improve search engine rankings and user experience. It focuses on making webpages more relevant to specific search queries and easier for search engines to understand and index.
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, refers to the practice of optimizing individual webpage elements to improve search engine rankings and earn more relevant organic traffic. This encompasses optimizing both the visible content and the underlying HTML source code of a page to make it more relevant to specific search queries and easier for search engines to understand. Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on external signals like backlinks and social media, on-page SEO concentrates entirely on elements within your direct control. The primary objective is to create a clear connection between user search intent and your webpage content, ensuring that search engines can accurately interpret what your page is about and match it with relevant search queries. According to HubSpot’s State of Marketing Report, 39% of marketers identify optimizing on-page content based on keywords as their top SEO strategy, underscoring the continued importance of this foundational practice.
On-page SEO has evolved dramatically since the early days of search engine optimization. In the 1990s and early 2000s, on-page SEO was primarily about keyword placement and density—marketers would strategically repeat target keywords in specific locations like title tags, headings, and body text to signal relevance to search engines. However, as search algorithms became increasingly sophisticated, this approach became less effective and even counterproductive. Google’s Panda algorithm update in 2011 specifically targeted “thin content” and keyword stuffing, marking a significant shift in how search engines evaluated pages. Today’s search engines employ advanced natural language processing and machine learning to understand content meaning, context, and user intent far beyond simple keyword matching. This evolution means that modern on-page SEO emphasizes content quality, semantic relevance, and user experience rather than mechanical keyword optimization. Research from Backlinko indicates that pages ranking in the top three positions have an average of 3.8 times more backlinks than lower-ranking pages, but on-page factors remain critical for establishing initial relevance and ensuring content is discoverable and properly indexed.
The foundation of effective on-page SEO rests on several interconnected elements that work together to optimize webpage performance. Title tags serve as the primary headline in search results and should be concise (50-60 characters), include the primary keyword, and accurately describe page content. Meta descriptions provide a brief summary (150-160 characters) that appears below the title in search results and should entice users to click while incorporating relevant keywords. Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) create a hierarchical structure that helps both users and search engines understand content organization and importance. The H1 tag should appear only once per page and typically match or closely relate to the page title. Content quality remains paramount—pages should provide comprehensive, original, and valuable information that thoroughly addresses user queries. URL structure should be descriptive, concise, and hierarchical, helping users and search engines understand page context at a glance. Internal linking connects related pages within your site, distributing authority and helping search engines understand content relationships. Keyword optimization involves naturally incorporating target keywords and semantic variations throughout content where they make contextual sense. Finally, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and Core Web Vitals have become increasingly important ranking factors that directly impact user experience and search visibility.
| Factor | On-Page SEO | Technical SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Content and visible page elements | Website infrastructure and backend | External signals and authority |
| Primary Control | Direct (website owner) | Direct (website owner) | Partial (external factors) |
| Key Elements | Title tags, meta descriptions, content, headings, internal links | Site speed, mobile optimization, XML sitemaps, robots.txt, structured data | Backlinks, social signals, brand mentions, citations |
| Main Goal | Improve relevance and user experience | Ensure crawlability and indexability | Build domain authority and trust |
| Timeline to Impact | Days to weeks | Weeks to months | Months to years |
| Ranking Influence | High (direct relevance signals) | High (accessibility and performance) | Very High (authority signals) |
| Tools Used | Content editors, meta tag generators, keyword research tools | Site auditors, page speed tools, schema markup generators | Backlink analyzers, citation trackers, PR tools |
| Maintenance Frequency | Monthly to quarterly | Quarterly to annually | Ongoing (continuous link building) |
On-page SEO has become increasingly critical as search engines prioritize user experience and content quality above all else. Google’s algorithm updates consistently reward websites that provide valuable, well-structured content that genuinely satisfies user intent. Unlike off-page factors such as backlinks, which can take months or years to accumulate, on-page optimizations provide immediate opportunities to improve search visibility and drive traffic. For businesses of all sizes, a comprehensive on-page SEO strategy represents one of the most cost-effective marketing investments available. While paid advertising stops generating results the moment campaigns end, properly optimized content continues driving organic traffic and conversions indefinitely. This sustainable approach to visibility makes on-page SEO essential for building lasting online presence and authority. Research from Search Atlas indicates that SEO delivers leads that are 8.5 times more likely to convert compared to other marketing channels, and 91% of marketers reported that SEO improved their website performance in 2024. The direct correlation between on-page optimization and business results underscores why this practice remains fundamental to digital marketing strategy.
Implementing on-page SEO requires both strategic thinking and technical execution. Title tag optimization involves researching target keywords, understanding user intent, and crafting compelling headlines that include primary keywords near the beginning while remaining under 60 characters. Meta description writing requires balancing keyword inclusion with persuasive copy that encourages click-through rates—a good meta description should be unique to each page, include the primary keyword naturally, and clearly communicate the page’s value proposition. Content creation should begin with thorough keyword research to identify what users are actually searching for, followed by analysis of top-ranking competitors to understand content depth and structure expectations. The content itself should be comprehensive (typically 1,500-2,500+ words for competitive topics), well-organized with clear headings, and written naturally without forced keyword repetition. Internal linking should connect semantically related pages using descriptive anchor text that provides context about the linked page. URL optimization involves creating logical, hierarchical structures that reflect site organization and include relevant keywords where appropriate. Image optimization requires using descriptive file names, adding alt text that describes images and includes relevant keywords, compressing files for faster loading, and ensuring images are contextually relevant to surrounding content. Schema markup implementation involves adding structured data that helps search engines better understand content type, which can enable rich results like star ratings, FAQs, and other enhanced search features.
Beyond basic optimization, advanced on-page SEO techniques can provide significant competitive advantages in crowded search landscapes. Featured snippet optimization involves structuring content to directly answer common user questions in clear, concise formats—typically 40-60 words for paragraph snippets, 3-8 items for list snippets, or well-organized tables for comparison snippets. This technique is particularly valuable because featured snippets appear in “position zero” at the top of search results, often generating substantial traffic even when your page ranks below position one. Voice search optimization requires understanding that voice queries tend to be longer (7+ words) and more conversational than text queries, often phrased as questions beginning with “who,” “what,” “where,” “when,” “why,” or “how.” Optimizing for voice search means creating content that answers these specific questions naturally and conversationally. Semantic content optimization goes beyond keyword matching to create content that thoroughly explores topics from multiple angles, addressing related concepts and answering follow-up questions users might have. Page speed optimization has become critical, with Google’s Core Web Vitals now directly influencing rankings—this involves image optimization, code minification, browser caching, and server-side improvements. Mobile-first optimization ensures that pages are fully functional and provide excellent user experience on mobile devices, which now account for the majority of search traffic. Schema markup implementation for specific content types (Article, FAQ, HowTo, Product, etc.) can significantly increase search visibility by enabling rich results and helping search engines better understand content context.
Research and industry data consistently identify six primary on-page SEO ranking factors that have the most significant impact on search visibility:
Each of these factors contributes to a comprehensive on-page SEO strategy, and their combined effect is more powerful than any single element. Pages that excel across all these dimensions consistently outrank competitors that optimize only a few factors.
As AI-powered search systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become increasingly prominent, on-page SEO takes on new significance. These AI systems rely on well-structured, authoritative content to generate responses and citations. Pages with clear definitions, comprehensive information, proper heading hierarchy, and schema markup are more likely to be cited by AI systems when generating answers to user queries. This creates a new dimension to on-page SEO optimization—not only must content rank well in traditional search results, but it must also be discoverable and citable by AI systems. Platforms like AmICited help marketers monitor where their optimized content appears in AI-generated responses, providing insights into how on-page SEO efforts translate to visibility in the emerging AI search landscape. The combination of traditional on-page SEO best practices with AI-friendly content structure—such as clear topic definitions, well-organized information, and authoritative sourcing—ensures maximum visibility across both traditional and AI search channels.
Implementing an effective on-page SEO strategy requires a systematic approach that prioritizes high-impact optimizations. Begin with comprehensive keyword research to identify target keywords with adequate search volume and reasonable competition levels. Analyze top-ranking competitors to understand content depth, structure, and keyword usage expectations. Create or update title tags and meta descriptions to be compelling, keyword-rich, and accurately descriptive of page content. Develop high-quality content that thoroughly addresses user intent, incorporates target keywords naturally, and provides genuine value that competitors don’t offer. Implement proper heading hierarchy with a single H1 tag and logical H2-H3 structure that guides readers through content. Add internal links to related pages using descriptive anchor text that provides context. Optimize images with descriptive file names and alt text. Implement schema markup appropriate to your content type. Test and optimize page speed to ensure fast loading across devices. Finally, establish a regular review schedule—monthly for keyword performance, quarterly for content updates, and semi-annually for comprehensive audits. This systematic approach ensures that on-page SEO remains effective as algorithms evolve and competitive landscapes shift.
The future of on-page SEO will likely emphasize user experience signals, content authenticity, and AI compatibility even more strongly than today. As search engines continue to prioritize E-E-A-T signals (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), on-page SEO will increasingly require demonstrating genuine expertise through comprehensive content, author credentials, and authoritative sourcing. The rise of AI search systems means that on-page SEO must evolve to serve both traditional search engines and AI systems simultaneously—this requires clear definitions, well-structured information, and proper schema markup that AI systems can easily parse and cite. Core Web Vitals and page experience metrics will likely become even more important ranking factors as user experience becomes central to search quality. The integration of voice search, visual search, and conversational AI will require on-page SEO to adapt to new query formats and content consumption patterns. Additionally, as AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, search engines will likely place even greater emphasis on authenticity signals and original research, making genuine expertise and unique perspectives increasingly valuable ranking factors. Marketers who stay ahead of these trends by combining traditional on-page SEO best practices with emerging technologies and user experience innovations will maintain competitive advantages in search visibility and AI discoverability.
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing elements within your website that you directly control, such as content quality, title tags, meta descriptions, and internal linking. Off-page SEO involves external factors outside your website, including backlinks, social media signals, and brand authority. While on-page SEO emphasizes relevance signals, off-page SEO builds domain authority and trustworthiness through external endorsements and citations.
On-page SEO changes can take anywhere from a few hours to several weeks to be reflected in search results, depending on the scope of changes and how frequently Google crawls your site. Some optimizations like title tag updates may show impact within days, while comprehensive content rewrites might take 4-8 weeks. Consistency and patience are essential, as search algorithms continuously evaluate and re-rank pages based on updated signals.
The six most critical on-page SEO factors are: keyword optimization (strategic placement of relevant terms), content quality (comprehensive and valuable information), meta title tags (compelling and keyword-rich headlines), URLs (descriptive and hierarchical structure), headings (proper H1-H6 hierarchy), and internal linking (strategic connections between related pages). These elements work together to signal relevance to search engines and improve user experience.
Keyword density is no longer a primary ranking factor in modern SEO. Search engines like Google have evolved to understand content meaning through context, synonyms, and semantic relationships rather than exact keyword repetition. What matters now is natural keyword integration that serves user intent—keywords should appear where they make sense contextually without forced repetition or 'keyword stuffing,' which can actually harm rankings.
On-page SEO directly impacts whether your content appears in AI-generated responses from systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Well-optimized pages with clear definitions, structured data, and authoritative content are more likely to be cited by AI systems. Platforms like AmICited help monitor where your optimized content appears in AI responses, providing insights into how your on-page SEO efforts translate to AI visibility and brand mentions.
Yes, optimizing for featured snippets is an advanced on-page SEO technique that can significantly increase visibility. Featured snippets appear in 'position zero' at the top of search results and drive substantial traffic. To optimize for snippets, structure your content with clear question-answer formats, use concise definitions in the first paragraph, organize information in lists or tables, and ensure your answers directly address common user queries related to your target keywords.
On-page SEO should be reviewed and updated every 1-2 months to maintain optimal performance. New pages should be optimized before publication, keyword performance should be monitored regularly, and a comprehensive on-page audit should be conducted every 6 months. Regular updates ensure your content remains aligned with evolving search algorithms, user intent, and competitive landscape changes.
No, on-page SEO alone cannot guarantee top rankings. While it's a critical foundation, search rankings depend on multiple factors including off-page signals (backlinks, domain authority), technical SEO (site speed, mobile-friendliness), and overall website authority. However, strong on-page SEO significantly improves your chances of ranking well, especially when combined with quality backlinks and technical optimization. According to research, 39% of marketers list on-page content optimization as their top SEO strategy.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Off-page SEO definition: external optimization strategies including backlinks, brand mentions, and authority building. Learn how off-site signals impact search ...
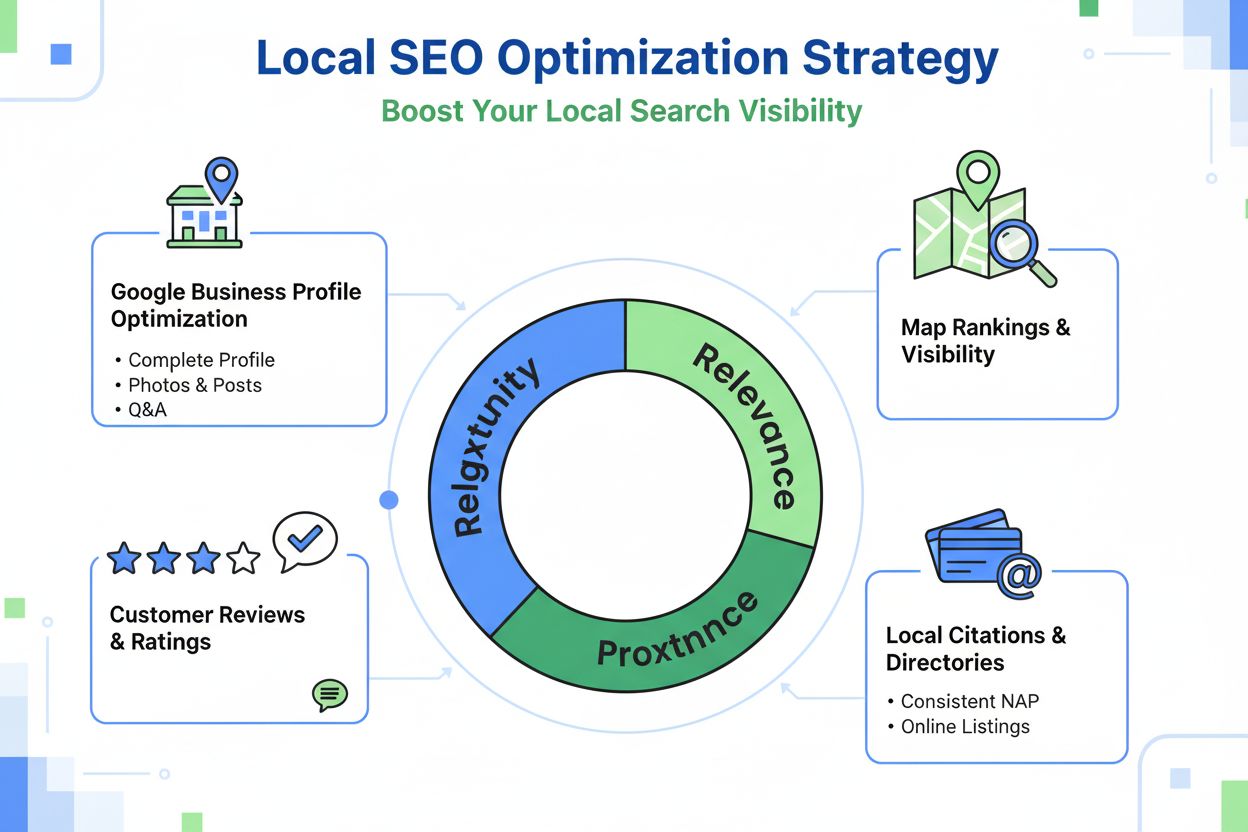
Local SEO is the practice of optimizing a business's online presence for location-based search results. Learn how to rank higher in Google Maps, local pack, and...
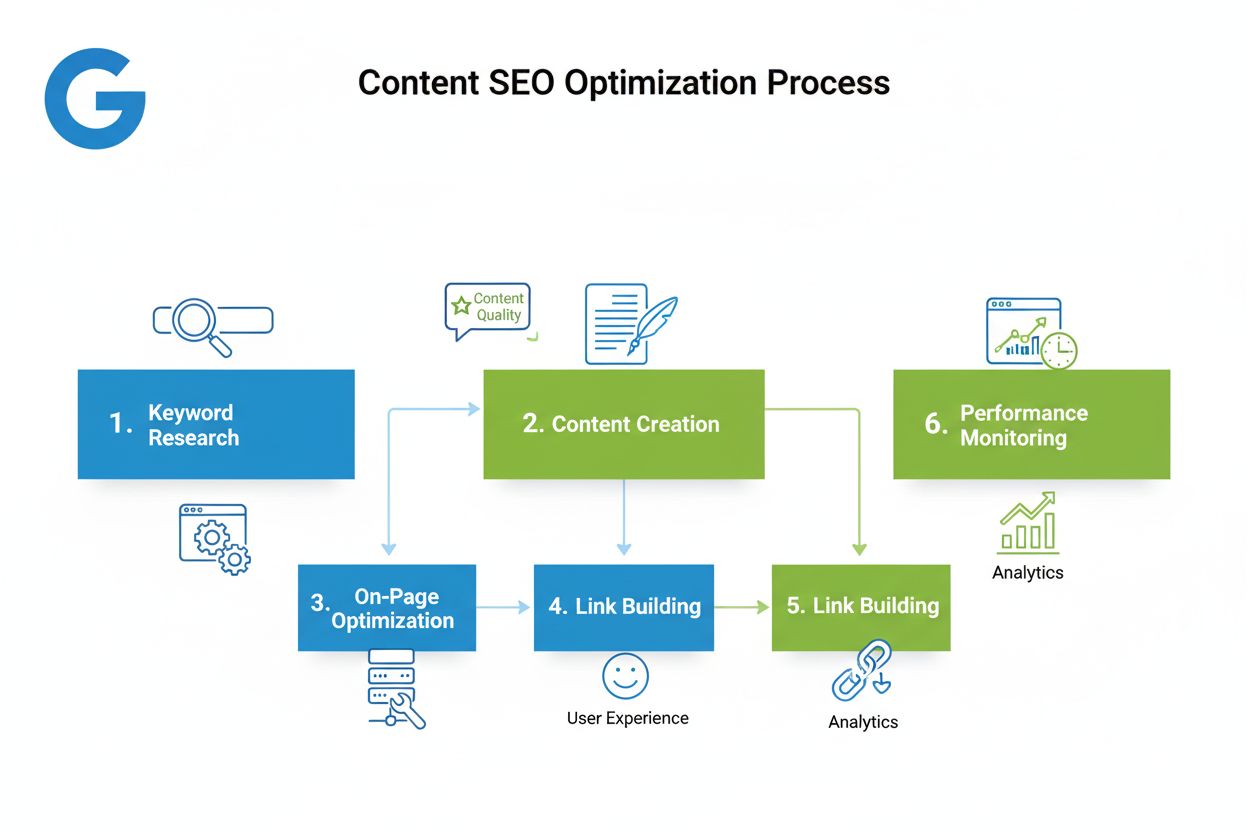
Content SEO is the strategic creation and optimization of high-quality content to improve search engine rankings and organic visibility. Learn how to optimize c...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.