
What is Real-Time Search in AI?
Learn how real-time search in AI works, its benefits for users and businesses, and how it differs from traditional search engines and static AI models.
Real-Time AI Adaptation refers to AI systems that continuously learn from and adjust to current events and incoming data without requiring manual retraining. These systems update their recommendations, decisions, and behaviors dynamically as new information becomes available, enabling organizations to respond instantly to changing market conditions, customer behavior, and operational needs.
Real-Time AI Adaptation refers to AI systems that continuously learn from and adjust to current events and incoming data without requiring manual retraining. These systems update their recommendations, decisions, and behaviors dynamically as new information becomes available, enabling organizations to respond instantly to changing market conditions, customer behavior, and operational needs.
Real-time AI adaptation refers to machine learning systems that continuously learn and adjust their behavior based on incoming data streams without requiring manual retraining cycles. Unlike traditional static AI models that operate on fixed parameters until scheduled retraining, adaptive systems process new information instantaneously and update their decision-making logic in milliseconds. The fundamental difference lies in continuous learning versus batch learning—real-time systems ingest and respond to data as it arrives, while conventional approaches accumulate data for periodic offline updates. Key enabling technologies include online learning algorithms, stream processing platforms, and federated learning frameworks that distribute computation across edge devices.
Real-time AI adaptation operates through a sophisticated pipeline of data ingestion, processing, and feedback mechanisms. Systems employ online learning algorithms that update model parameters incrementally as new data points arrive, stream processing engines like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink that handle high-velocity data flows, and federated learning architectures that train models across distributed nodes without centralizing sensitive data. The decision-making process occurs in real-time, with models generating predictions while simultaneously incorporating feedback signals that refine future outputs. This creates self-reinforcing feedback loops where each prediction and outcome improve subsequent model performance.
| Feature | Traditional AI | Real-Time Adaptive AI |
|---|---|---|
| Model Updates | Weekly/Monthly scheduled retraining | Continuous, millisecond-level updates |
| Learning Speed | Hours to days for new patterns | Immediate pattern recognition |
| Context Awareness | Static historical context | Dynamic, current-moment context |
| Adaptation Capability | Limited to predefined scenarios | Unlimited scenario adaptation |
| Best Use Cases | Stable, predictable environments | Dynamic, rapidly changing markets |
Real-time AI adaptation leverages several critical technologies and methodologies:
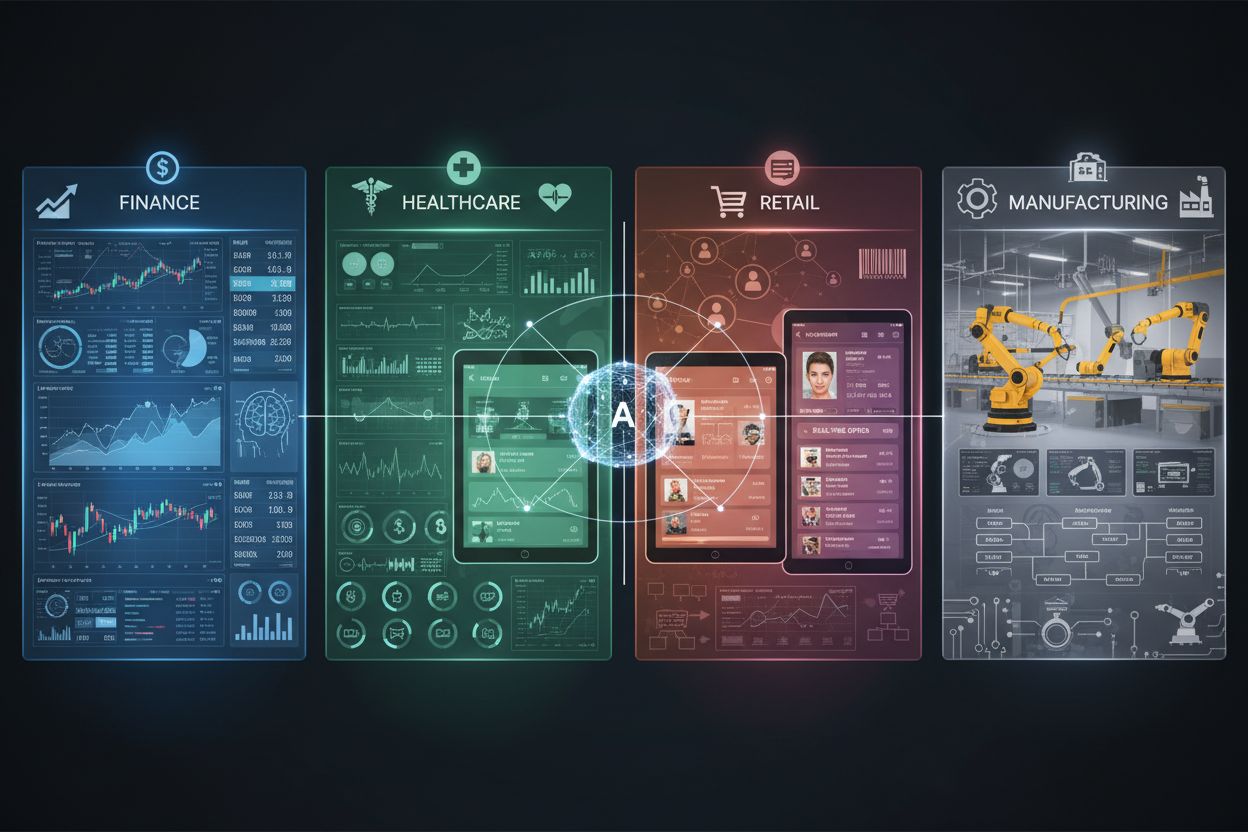

Real-time AI adaptation transforms operations across diverse industries with measurable impact. Finance institutions deploy adaptive fraud detection systems achieving 94.2% accuracy with AUC-ROC scores of 0.96, while algorithmic trading systems adjust strategies within microseconds to market fluctuations. Healthcare providers implement patient monitoring systems that adapt treatment recommendations based on real-time vital signs and lab results, with diagnostic systems continuously improving accuracy through clinical feedback. E-commerce platforms leverage adaptive recommendation engines that increase conversion rates from 2.5% to 4.2% and boost order values by 30%—Netflix’s personalization engine drives 80% of viewer activity through real-time adaptation. Manufacturing facilities employ predictive maintenance systems that reduce equipment breakdowns by 70% and cut planning time by 50%. Customer service chatbots improve response quality with each interaction, learning customer preferences and communication patterns. Autonomous vehicles make split-second navigation decisions by processing sensor data and adapting to road conditions, weather, and traffic patterns instantaneously.
Adaptive AI systems deliver substantial business advantages through accelerated decision-making and continuous performance improvement. Real-time adaptation enables decisions in milliseconds rather than hours or days, critical for fraud prevention, trading, and autonomous systems where delays create financial or safety risks. Continuous learning mechanisms improve accuracy exponentially—models trained on yesterday’s data become obsolete in dynamic markets, while adaptive systems maintain peak performance by incorporating today’s patterns immediately. Organizations reduce operational costs by automating retraining cycles and minimizing manual model maintenance, with some implementations cutting ML operations overhead by 40%. Customer experience improves dramatically as systems learn individual preferences, behavior patterns, and needs in real-time, driving loyalty and retention. Businesses implementing adaptive AI are projected to outperform competitors by 25%, with the real-time AI market valued at $1.04B in 2024 and expected to reach $30.51B by 2034, reflecting explosive demand for adaptive capabilities.
Implementing real-time AI adaptation presents significant technical and organizational challenges requiring careful management. Data quality and noise become critical issues at scale—streaming data contains errors, duplicates, and anomalies that corrupt models if not filtered properly, requiring robust data validation pipelines. Computational resource requirements escalate dramatically; processing millions of events per second demands specialized infrastructure, GPUs, and distributed systems that increase capital and operational expenses. Latency constraints create engineering complexity—systems must process data, update models, and generate predictions within strict time windows (often under 100 milliseconds), leaving minimal margin for error. Model drift and concept drift occur when data distributions shift unexpectedly, causing previously accurate models to degrade without warning, necessitating continuous monitoring and automatic retraining triggers. Privacy and security concerns intensify with continuous data collection and model updates, particularly in regulated industries like healthcare and finance where data governance becomes exponentially more complex. Explainability challenges worsen as models continuously evolve—understanding why a system made a specific decision becomes difficult when parameters change constantly. Legacy system integration proves costly and time-consuming, as existing infrastructure often lacks the streaming capabilities and real-time processing architecture that adaptive AI requires.
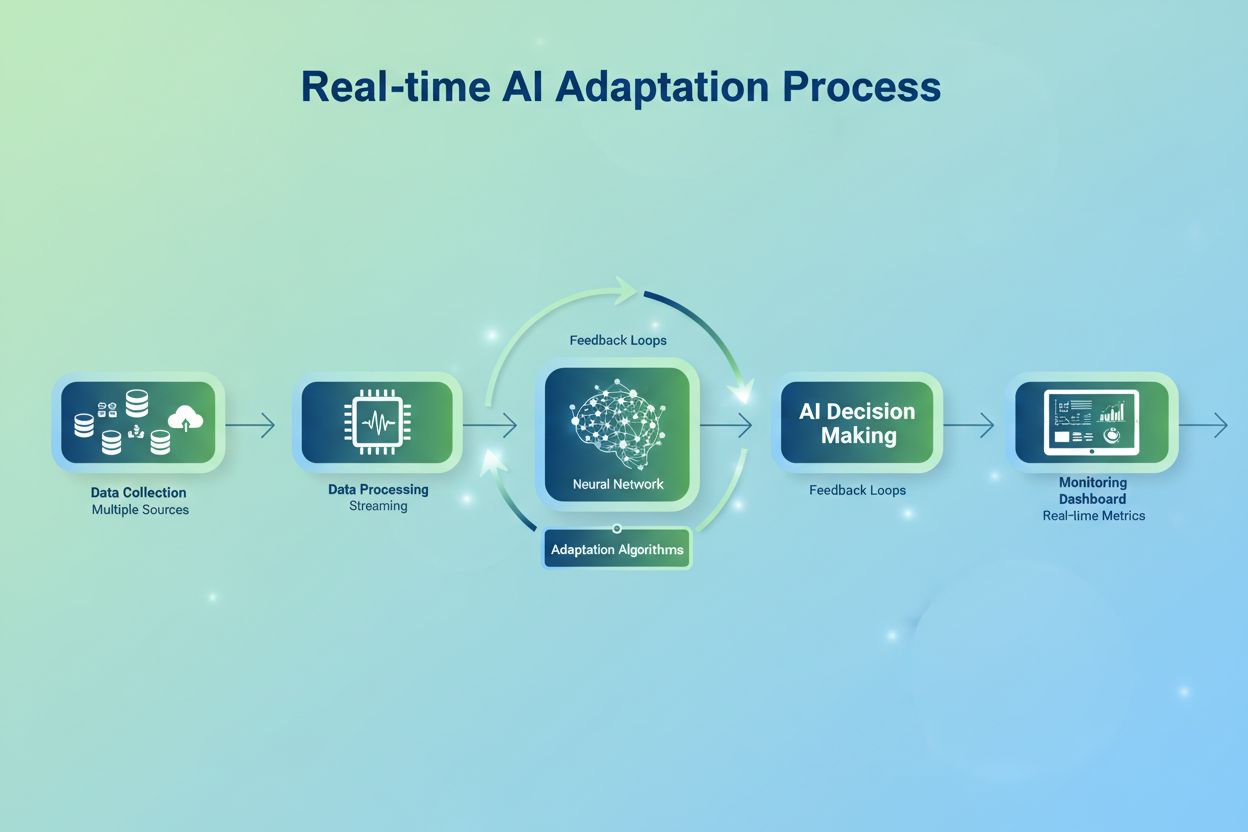
Successful real-time AI adaptation implementations follow proven best practices that balance innovation with operational stability. Start with high-impact use cases where real-time adaptation delivers measurable ROI—fraud detection, recommendation engines, and predictive maintenance typically show faster payback than experimental applications. Ensure robust data infrastructure by investing in stream processing platforms, data validation systems, and monitoring tools before deploying adaptive models; poor data quality undermines all downstream benefits. Implement comprehensive monitoring and governance frameworks that track model performance, detect drift, and trigger alerts when accuracy degrades below acceptable thresholds. Deploy edge computing strategically to reduce latency for latency-sensitive applications while maintaining cloud connectivity for complex computations and data aggregation. Establish feedback mechanisms that capture ground truth labels, user interactions, and outcome data to fuel continuous learning loops. Plan for scalability from inception—design systems that handle 10x current data volumes without architectural redesign. Consider hybrid approaches combining real-time adaptation for critical decisions with batch learning for non-urgent pattern discovery, optimizing cost and performance simultaneously.
Real-time AI adaptation continues evolving toward more sophisticated, autonomous, and integrated systems. Edge AI and 5G integration will enable ultra-low-latency adaptive systems operating directly on mobile devices and IoT sensors, eliminating cloud dependency for time-critical applications. Multi-agent adaptive systems will coordinate learning across thousands of distributed agents, creating emergent intelligence that solves complex problems through collective adaptation. Self-healing AI systems will automatically detect failures, recalibrate models, and recover from degradation without human intervention, reducing operational overhead. Improved explainability techniques including attention mechanisms and causal inference will make continuously evolving models interpretable, addressing regulatory and trust concerns. Industry-specific adaptations will emerge as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing develop domain-specialized adaptive architectures optimized for their unique constraints and requirements. Convergence with generative AI will enable adaptive systems that not only learn from data but generate synthetic training examples, accelerating learning in data-scarce scenarios. Regulatory frameworks are emerging globally to govern adaptive AI systems, establishing standards for transparency, fairness, and accountability that will shape implementation approaches across industries.
Traditional AI models operate on fixed parameters until scheduled retraining, while real-time adaptive systems continuously learn and adjust their behavior based on incoming data streams. Real-time systems process new information instantaneously and update decision-making logic in milliseconds, whereas traditional approaches accumulate data for periodic offline updates. This fundamental difference enables adaptive systems to maintain accuracy in dynamic, rapidly changing environments where traditional models quickly become obsolete.
Real-time AI systems can adapt in milliseconds to seconds, depending on the application and infrastructure. Online learning algorithms update model parameters with each new data point, while stream processing platforms like Apache Kafka and Flink handle millions of events per second with sub-second latency. For critical applications like fraud detection and autonomous vehicles, adaptation occurs within 100 milliseconds or less, enabling immediate response to changing conditions.
Finance, healthcare, e-commerce, manufacturing, and autonomous vehicles benefit significantly from real-time AI adaptation. Finance uses it for fraud detection (94.2% accuracy) and algorithmic trading. Healthcare applies it to patient monitoring and treatment adaptation. E-commerce leverages it for recommendation engines (increasing conversion rates from 2.5% to 4.2%) and dynamic pricing. Manufacturing uses predictive maintenance (70% reduction in breakdowns). Each industry gains competitive advantage through instant responsiveness to changing conditions.
Key challenges include data quality and noise in streaming data, high computational resource requirements for processing millions of events per second, strict latency constraints (often under 100 milliseconds), model drift when data distributions shift unexpectedly, privacy and security concerns with continuous data collection, explainability difficulties as models continuously evolve, and integration complexity with legacy systems lacking streaming capabilities. Addressing these challenges requires robust infrastructure, monitoring systems, and governance frameworks.
Real-time AI systems employ multiple data quality mechanisms including validation pipelines that filter errors and duplicates, anomaly detection algorithms that identify suspicious data points, concept drift detection that recognizes when data distributions shift, and continuous monitoring that tracks data quality metrics. These systems use feedback loops to learn from ground truth labels and user interactions, automatically recalibrating when quality degrades. Robust data infrastructure and governance frameworks are essential for maintaining model accuracy.
Yes, with proper governance, monitoring, and human oversight. Real-time AI systems can improve consistency and reliability compared to manual decision-making, particularly in high-volume scenarios like fraud detection. However, critical applications require comprehensive monitoring frameworks that track model performance, detect drift, and trigger alerts when accuracy degrades. Explainability techniques, audit trails, and human-in-the-loop approaches ensure accountability and enable quick intervention when needed.
Real-time AI refers to systems that continuously learn and adapt to incoming data with minimal latency, while edge AI specifically refers to processing data at network edges (IoT devices, mobile phones, local servers) rather than in centralized cloud systems. These technologies are complementary—edge AI enables real-time adaptation by reducing latency and eliminating cloud dependency, while real-time AI principles can be applied at the edge. Together, they create ultra-responsive systems for time-critical applications.
Real-time AI improves customer experience by learning individual preferences and behavior patterns instantaneously, enabling personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing, and responsive customer service. Netflix's personalization engine drives 80% of viewer activity through real-time adaptation, while e-commerce platforms increase order values by 30% through adaptive recommendations. Chatbots improve response quality with each interaction, and recommendation systems increase conversion rates from 2.5% to 4.2%. This continuous learning creates experiences that feel natural and anticipate customer needs.
Real-time AI adaptation is transforming how AI systems respond to current events. AmICited tracks how AI mentions your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews as they happen. Stay informed about your AI presence.

Learn how real-time search in AI works, its benefits for users and businesses, and how it differs from traditional search engines and static AI models.

Learn how to request corrections from AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude. Understand correction mechanisms, feedback processes, and strategies to...
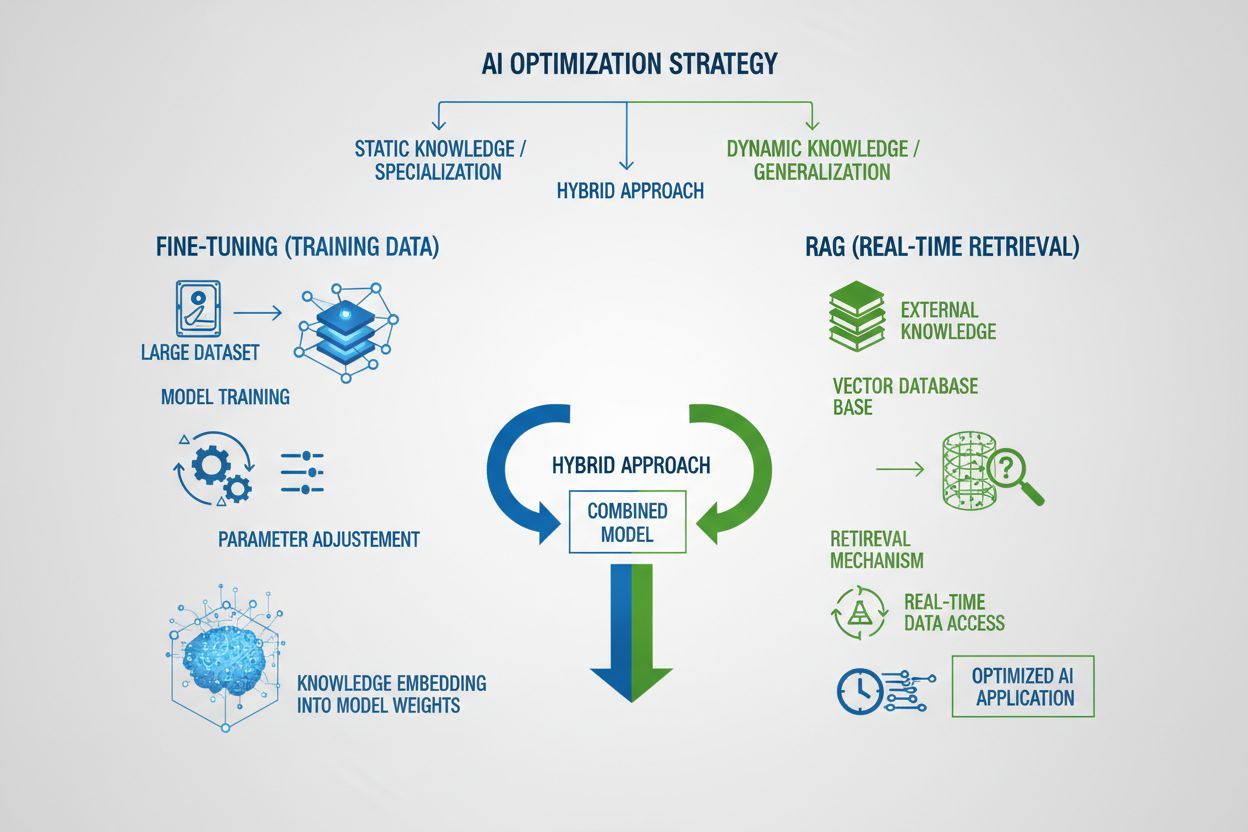
Compare training data optimization and real-time retrieval strategies for AI. Learn when to use fine-tuning vs RAG, cost implications, and hybrid approaches for...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.