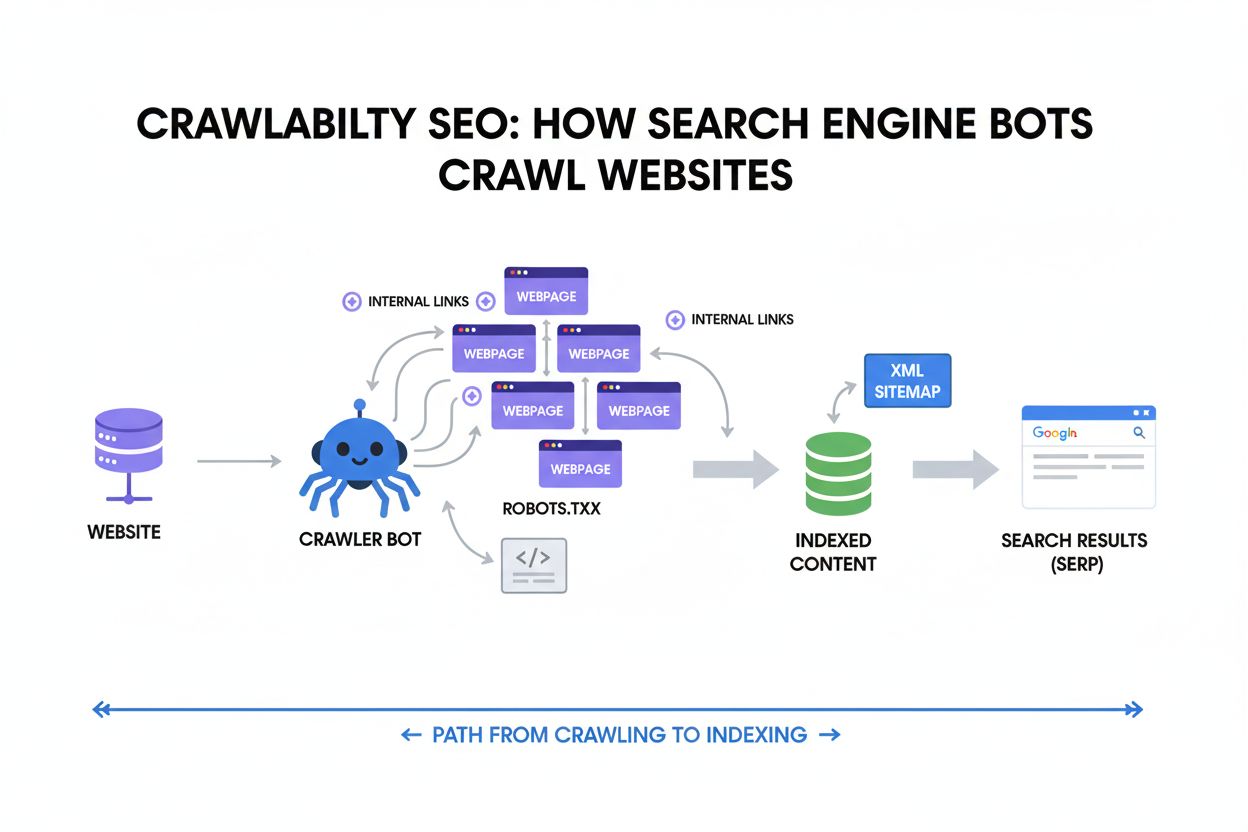
Crawlability
Crawlability is the ability of search engines to access and navigate website pages. Learn how crawlers work, what blocks them, and how to optimize your site for...
Technical issues preventing AI crawlers from accessing or properly indexing content. These errors occur when artificial intelligence-powered systems cannot retrieve, interpret, or understand website content due to technical barriers such as JavaScript dependencies, missing structured data, robots.txt restrictions, or server configuration problems. Unlike traditional search engine crawl errors, AI crawl errors can prevent language models and AI assistants from accurately representing your content in their systems.
Technical issues preventing AI crawlers from accessing or properly indexing content. These errors occur when artificial intelligence-powered systems cannot retrieve, interpret, or understand website content due to technical barriers such as JavaScript dependencies, missing structured data, robots.txt restrictions, or server configuration problems. Unlike traditional search engine crawl errors, AI crawl errors can prevent language models and AI assistants from accurately representing your content in their systems.
AI crawl errors occur when artificial intelligence-powered crawlers fail to properly access, retrieve, or interpret content from websites during their indexing processes. These errors represent a critical gap between what your website displays to human visitors and what AI systems can actually understand and utilize for training, retrieval, or analysis purposes. Unlike traditional search engine crawl errors that primarily affect visibility in search results, AI crawl errors can prevent language models, AI assistants, and content aggregation platforms from accurately representing your content in their systems. The consequences range from misrepresentation of your brand in AI-generated responses to complete exclusion from AI training datasets and retrieval systems. Understanding and resolving these errors is essential for maintaining your digital presence in an increasingly AI-driven information ecosystem.

AI crawlers operate fundamentally differently from traditional search engine crawlers like Googlebot, requiring distinct technical approaches to ensure proper content accessibility. While search engines have invested heavily in JavaScript rendering capabilities and can execute dynamic content, most AI crawlers retrieve and analyze the raw HTML response without rendering JavaScript, meaning they only see what’s delivered in the initial server response. This distinction creates a critical technical divide: a website might render perfectly for Google’s crawler but remain completely inaccessible to AI systems that cannot execute client-side code. Additionally, AI crawlers typically operate at different frequencies and with different user-agent patterns, and some—like those used by Perplexity—employ stealth crawling techniques to bypass traditional robots.txt restrictions, while others like OpenAI’s crawler follow more conventional ethical crawling practices. The table below illustrates these key differences:
| Characteristic | Search Engine Crawlers | AI Crawlers |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript Rendering | Full rendering capability | Limited or no rendering |
| Crawl Frequency | Periodic, based on authority | Often more frequent |
| Robots.txt Compliance | Strict adherence | Variable (some bypass) |
| User-Agent Transparency | Clearly identified | Sometimes stealth/obfuscated |
| Content Interpretation | Keyword and link-based | Semantic understanding required |
| Response Type Needed | Rendered HTML | Raw HTML or API access |
AI crawl errors manifest in several distinct categories, each requiring different diagnostic and remediation approaches. The most prevalent errors include:
JavaScript rendering represents one of the most significant barriers between websites and AI crawlers, as the vast majority of AI systems cannot execute client-side code to reveal dynamically generated content. When your website relies on JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular to populate content after the initial page load, AI crawlers receive an empty or minimal HTML shell that contains no actual content to analyze. This creates a fundamental accessibility problem: your website might display beautifully and function perfectly for human users, but AI systems see only the JavaScript code itself rather than the rendered output. The distinction is critical because AI crawlers analyze the raw HTTP response—what the server sends before any browser processing—rather than the final rendered DOM that users see. To address this issue, websites should implement server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG) to ensure content is present in the initial HTML response, use dynamic rendering services that pre-render content for crawlers, or provide alternative content delivery methods such as APIs that AI crawlers can access directly.
The robots.txt file serves as the primary mechanism for communicating crawling preferences to automated systems, yet its effectiveness varies significantly across different AI crawlers with different ethical standards and business models. Traditional search engines like Google respect robots.txt directives and will not crawl content explicitly blocked by these rules, making it a reliable tool for controlling search engine access. However, the AI crawler landscape is more fragmented: some AI companies like OpenAI have committed to respecting robots.txt and provide mechanisms for content creators to opt out of training data collection, while others employ stealth crawlers that deliberately bypass robots.txt restrictions to gather training data. This creates a complex situation where website owners cannot rely solely on robots.txt to control AI crawler access, particularly for companies seeking to prevent their content from being used in AI training datasets. The most effective approach combines robots.txt rules with additional technical measures such as monitoring tools that track which AI crawlers are accessing your site, implementing user-agent specific rules for known AI crawlers, and using tools like AmICited.com to monitor and verify actual crawler behavior against stated policies.
Structured data and semantic markup have become increasingly critical for AI system comprehension, as these elements provide explicit context that helps AI crawlers understand content meaning, relationships, and entity information far more effectively than raw text alone. When you implement Schema.org markup, JSON-LD structured data, or other semantic formats, you’re essentially creating a machine-readable layer that describes what your content is about, who created it, when it was published, and how it relates to other entities and concepts. AI systems rely heavily on this structured information to accurately represent content in their systems, generate more relevant responses, and understand the authoritative source of information. For example, a news article with proper NewsArticle schema markup allows AI systems to identify the publication date, author, headline, and article body with certainty, whereas the same content without markup requires the AI system to infer this information through natural language processing, which is far more error-prone. The absence of structured data forces AI crawlers to make assumptions about content, often resulting in misrepresentation, incorrect attribution, or failure to recognize important content distinctions. Implementing comprehensive Schema.org markup for your content type—whether articles, products, organizations, or events—significantly improves how AI systems interpret and utilize your content.
Beyond JavaScript and robots.txt, numerous technical infrastructure issues can prevent AI crawlers from successfully accessing and processing your website content. Server-side problems such as misconfigured SSL certificates, expired HTTPS certificates, or improper HTTP header configurations can cause crawlers to abandon requests entirely, particularly AI crawlers that may have stricter security requirements than traditional browsers. Rate limiting and IP blocking mechanisms designed to prevent abuse can inadvertently block legitimate AI crawlers, especially if your security systems don’t recognize the crawler’s user-agent or IP ranges. Improper Content-Type headers, missing or incorrect character encoding declarations, and malformed HTML can cause AI crawlers to misinterpret content or fail to parse it correctly. Additionally, overly aggressive caching strategies that serve identical content regardless of user-agent can prevent crawlers from receiving appropriate content variations, while insufficient server resources that cause timeouts or slow response times may exceed the timeout thresholds of AI crawling systems.
Detecting AI crawl errors requires a multi-layered monitoring approach that goes beyond traditional search engine crawl error reporting, as most website analytics and SEO tools focus exclusively on search engine crawlers rather than AI systems. Server log analysis provides the foundational layer, allowing you to identify which AI crawlers are accessing your site, how frequently they’re crawling, what content they’re requesting, and what HTTP status codes they’re receiving in response. By examining user-agent strings in your access logs, you can identify specific AI crawlers like GPTBot, Perplexity’s crawler, or other AI systems and analyze their crawling patterns and success rates. Tools like AmICited.com provide specialized monitoring specifically designed for AI crawler tracking and error detection, offering insights into how different AI systems are accessing and interpreting your content. Additionally, you can perform manual testing by simulating AI crawler behavior—disabling JavaScript in your browser, using curl or wget to fetch pages as raw HTML, and analyzing what content is actually available to non-rendering crawlers. Monitoring your website’s appearance in AI-generated responses and search results from AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude can reveal whether your content is being properly indexed and represented, providing real-world validation of your crawlability status.
Resolving AI crawl errors requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses both the technical infrastructure and content delivery mechanisms of your website. First, audit your website’s crawlability by testing pages with JavaScript disabled to identify content that’s inaccessible to non-rendering crawlers, then prioritize converting JavaScript-dependent content to server-side rendering or providing alternative content delivery methods. Implement comprehensive Schema.org structured data markup across all content types, ensuring that AI systems can understand content context, authorship, publication dates, and entity relationships without relying solely on natural language processing. Review and optimize your robots.txt file to explicitly allow AI crawlers you want to index your content while blocking those you don’t, though recognize that this approach has limitations with non-compliant crawlers. Ensure your website’s technical infrastructure is robust: verify SSL certificates are valid and properly configured, implement appropriate HTTP headers, use correct Content-Type and character encoding declarations, and ensure server response times are adequate. Monitor your website’s actual appearance in AI systems and use specialized tools like AmICited.com to track how different AI crawlers are accessing your content and identify errors in real-time. Establish a regular crawl error monitoring routine that checks server logs for AI crawler activity, analyzes response codes and patterns, and identifies emerging issues before they significantly impact your AI visibility. Finally, stay informed about evolving AI crawler standards and best practices, as the landscape continues to develop rapidly with new crawlers, updated ethical guidelines, and changing technical requirements.
AI crawl errors specifically affect how artificial intelligence systems access and interpret your content, while traditional SEO crawl errors impact search engine visibility. The key difference is that AI crawlers typically don't render JavaScript and have different crawling patterns, user-agents, and compliance standards than search engines like Google. A page might be perfectly crawlable by Googlebot but completely inaccessible to AI systems.
Yes, you can use robots.txt to block AI crawlers, but effectiveness varies. Some AI companies like OpenAI respect robots.txt directives, while others like Perplexity have been documented using stealth crawlers to bypass these restrictions. For more reliable control, use specialized monitoring tools like AmICited.com to track actual crawler behavior and implement additional technical measures beyond robots.txt.
Monitor your server logs for AI crawler user-agents (GPTBot, Perplexity, ChatGPT-User, etc.) and analyze their HTTP response codes. Use specialized tools like AmICited.com that provide real-time tracking of AI crawler activity. Additionally, test your website with JavaScript disabled to see what content is actually available to non-rendering crawlers, and monitor how your content appears in AI-generated responses.
Yes, significantly. Most AI crawlers cannot render JavaScript and only see the raw HTML response from your server. Content that loads dynamically through JavaScript frameworks like React or Vue will be invisible to AI systems. To ensure AI crawlability, implement server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), or provide alternative content delivery methods like APIs.
Robots.txt serves as the primary mechanism for communicating crawling preferences to AI systems, but its effectiveness is inconsistent. Ethical AI companies respect robots.txt directives, while others bypass them. The most effective approach combines robots.txt rules with real-time monitoring tools to verify actual crawler behavior and implement additional technical controls.
Structured data is critical for AI crawlers. Schema.org markup, JSON-LD, and other semantic formats help AI systems understand content meaning, authorship, publication dates, and entity relationships. Without structured data, AI systems must rely on natural language processing to infer this information, which is error-prone and can result in misrepresentation of your content in AI-generated responses.
AI crawl errors can result in your content being excluded from AI training datasets, misrepresented in AI-generated responses, or completely invisible to language models and AI assistants. This impacts your brand's visibility in answer engines, reduces citation opportunities, and can damage your authority in AI search results. The consequences are particularly severe because AI crawlers often don't return to re-crawl content after initial failures.
Implement server-side rendering to ensure content is in the initial HTML response, add comprehensive Schema.org structured data markup, optimize your robots.txt for AI crawlers, ensure robust server infrastructure with proper SSL certificates and HTTP headers, monitor Core Web Vitals, and use tools like AmICited.com to track actual AI crawler behavior and identify errors in real-time.
Track how AI crawlers like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI systems are accessing your content. Identify crawl errors before they impact your AI visibility and brand citations.

Crawlability is the ability of search engines to access and navigate website pages. Learn how crawlers work, what blocks them, and how to optimize your site for...
Learn how to audit AI crawler access to your website. Discover which bots can see your content and fix blockers preventing AI visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity,...

Learn how to allow AI bots like GPTBot, PerplexityBot, and ClaudeBot to crawl your site. Configure robots.txt, set up llms.txt, and optimize for AI visibility.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.