
Synthetic Data Training
Learn about synthetic data training for AI models, how it works, benefits for machine learning, challenges like model collapse, and implications for brand repre...

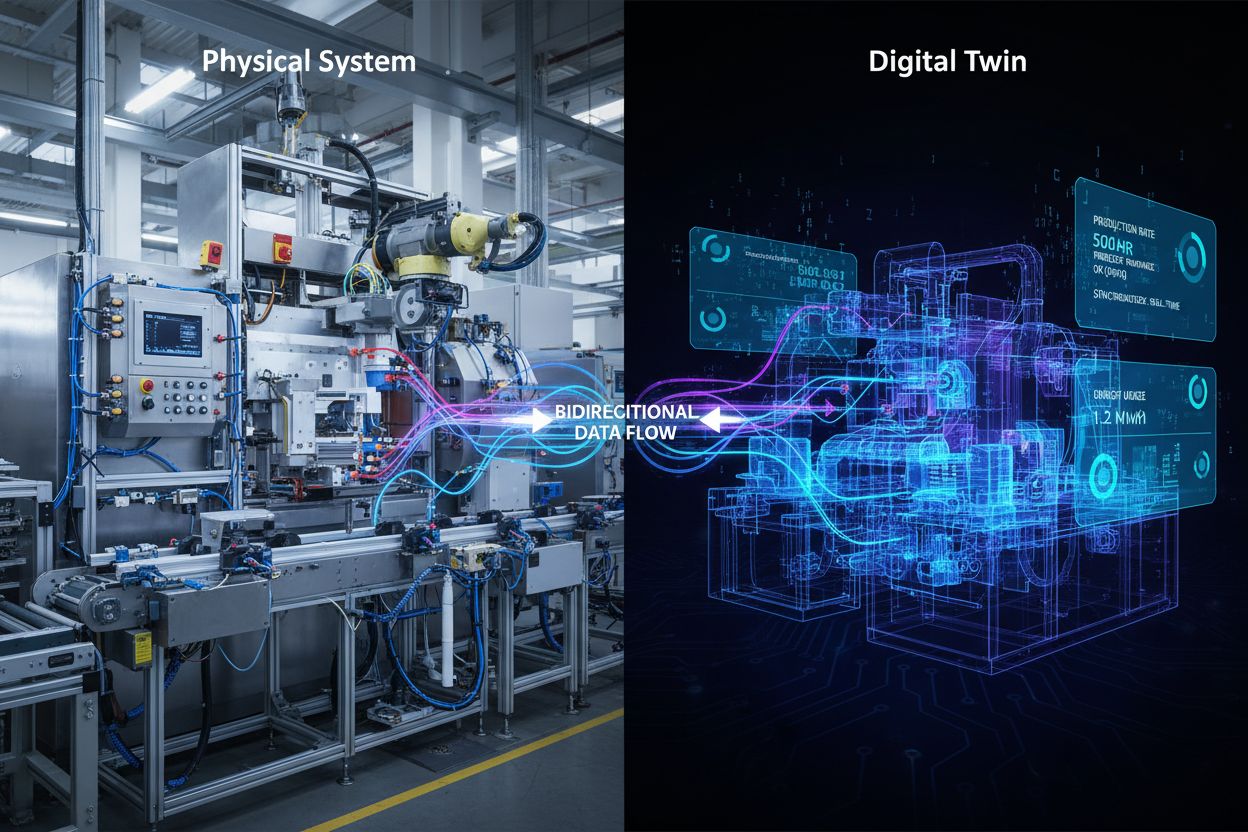
An AI Digital Twin is a virtual representation of a physical or digital system that uses real-time data and machine learning to create a dynamic, continuously updated model for monitoring, testing, and optimization. Unlike static simulations, digital twins maintain live connections to their real-world counterparts, enabling organizations to predict outcomes, optimize performance, and test changes risk-free. These virtual replicas are increasingly used for brand monitoring, customer behavior simulation, and AI system testing across industries. Digital twins integrate data collection, modeling, synchronization, and AI-powered analytics to deliver predictive insights and autonomous optimization capabilities.
An AI Digital Twin is a virtual representation of a physical or digital system that uses real-time data and machine learning to create a dynamic, continuously updated model for monitoring, testing, and optimization. Unlike static simulations, digital twins maintain live connections to their real-world counterparts, enabling organizations to predict outcomes, optimize performance, and test changes risk-free. These virtual replicas are increasingly used for brand monitoring, customer behavior simulation, and AI system testing across industries. Digital twins integrate data collection, modeling, synchronization, and AI-powered analytics to deliver predictive insights and autonomous optimization capabilities.
An AI Digital Twin is a virtual representation of a physical or digital system that uses real-time data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to create a dynamic, continuously updated model. Unlike static simulations, digital twins maintain a live connection to their real-world counterparts, receiving constant streams of data that keep the virtual model synchronized with actual conditions. This synchronization enables organizations to monitor, analyze, and predict system behavior with unprecedented accuracy. The concept gained prominence during NASA’s Apollo 13 mission, when engineers created a virtual replica of the spacecraft to troubleshoot problems in real-time—a foundational example of digital twin technology in action.
Digital twins differ fundamentally from traditional simulations in their dynamic nature and continuous evolution. While simulations are typically static models created for specific scenarios and run independently, digital twins maintain bidirectional communication with their physical counterparts. They receive live sensor data, environmental inputs, and operational metrics, which feed into sophisticated algorithms that update the virtual model in real-time. This continuous feedback loop allows digital twins to reflect the actual state of systems at any given moment, making them invaluable for monitoring, optimization, and predictive analysis. The integration of AI and machine learning transforms these virtual replicas into intelligent systems capable of learning from historical patterns, identifying anomalies, and recommending optimizations without human intervention.
The key characteristics that define an effective AI Digital Twin include real-time data integration, continuous synchronization, predictive capabilities, and autonomous optimization. Real-time data collection ensures the virtual model remains accurate and current, while synchronization mechanisms keep the digital and physical systems aligned. The predictive dimension—powered by machine learning algorithms—enables organizations to forecast failures, optimize performance, and make data-driven decisions before problems occur. These characteristics make digital twins particularly valuable for brand monitoring and testing environments, where organizations need to understand how AI systems interact with and reference their brands across digital channels.
| Aspect | Digital Twin | Traditional Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Data Flow | Bidirectional, real-time | Unidirectional, static |
| Updates | Continuous, dynamic | Periodic or one-time |
| Connection | Live link to physical system | Independent model |
| Learning | Adaptive, learns from data | Fixed parameters |
| Use Case | Ongoing monitoring & optimization | Scenario testing |
| Accuracy | Improves over time | Depends on initial parameters |
The operational framework of an AI Digital Twin involves a sophisticated multi-stage process that begins with comprehensive data collection from sensors, APIs, databases, and user interactions embedded throughout the physical or digital system. This data flows into a centralized platform where it’s processed, cleaned, and normalized to ensure consistency and accuracy. The collected data feeds into a detailed virtual model that replicates the structure, behavior, and dynamics of the real system. Machine learning algorithms continuously analyze incoming data streams, identifying patterns, correlations, and deviations from expected behavior. The system then uses these insights to update its predictive models, refine its understanding of system dynamics, and generate recommendations for optimization or intervention.
The synchronization mechanism is critical to digital twin functionality. Real-time data pipelines maintain constant communication between the physical system and its virtual counterpart, ensuring the digital model reflects current conditions within milliseconds. This synchronization enables closed-loop feedback systems where insights generated by the digital twin can trigger automated actions in the physical system, creating a continuous cycle of monitoring, analysis, and optimization. The AI component processes vast amounts of historical and real-time data to identify patterns that humans might miss, enabling predictive analytics that forecast failures, performance degradation, or market opportunities before they materialize.
The operational workflow of an AI Digital Twin typically follows these key stages:
Consider a practical example: a financial services company might create a digital twin of its mobile banking application to monitor how AI-powered recommendation systems reference and interact with customer data. The digital twin would collect data on user interactions, AI decision-making processes, and system performance metrics. Machine learning algorithms would analyze this data to identify patterns in how the AI system references customer information, whether recommendations align with brand values, and how users respond to AI-generated suggestions. This continuous monitoring enables the organization to optimize the AI system’s behavior, ensure brand consistency, and improve customer experience—functions that platforms like AmICited.com help organizations accomplish through comprehensive AI monitoring and analysis.
AI Digital Twins have emerged as powerful tools for virtual brand representation and testing, enabling organizations to understand and optimize how their brands are perceived, referenced, and interacted with by AI systems and customers. In the context of brand monitoring, digital twins create risk-free environments where companies can simulate customer interactions, test marketing messages, and evaluate how AI systems reference their brands across digital channels. These virtual environments allow marketers and brand managers to conduct extensive A/B testing, scenario analysis, and predictive modeling without affecting real customers or risking brand reputation.
One critical application involves customer behavior simulation within digital twin environments. Organizations can model how different customer segments respond to brand messaging, product recommendations, and AI-driven personalization strategies. By simulating thousands of customer interactions within the digital twin, companies gain insights into which messaging resonates most effectively, which product recommendations drive conversion, and how different customer personas perceive brand values. This simulation capability enables data-driven optimization of marketing campaigns before they reach real audiences, significantly reducing the risk of ineffective or misaligned messaging.
Marketing campaign optimization represents another powerful use case for AI Digital Twins. Rather than launching campaigns and measuring results reactively, organizations can use digital twins to predict campaign performance, test variations, and optimize targeting parameters before deployment. The digital twin simulates how different audience segments will respond to various creative approaches, messaging frameworks, and channel strategies. Machine learning algorithms identify the optimal combination of variables that maximizes engagement, conversion, and brand alignment. This predictive capability accelerates time-to-market while improving campaign effectiveness and ROI.
Key applications of AI Digital Twins in brand monitoring and testing include:
For organizations using platforms like AmICited.com, AI Digital Twins provide enhanced capabilities for monitoring how AI systems reference and represent brands. The digital twin can simulate various scenarios where AI systems might reference brand information, test how different AI models handle brand-related queries, and predict potential issues before they impact real customers. This integration of digital twin technology with AI monitoring platforms creates a comprehensive ecosystem for brand protection and optimization in an increasingly AI-driven digital landscape.
AI Digital Twins have revolutionized operations across diverse industries, each leveraging the technology to address unique challenges and unlock competitive advantages. The versatility of digital twin technology stems from its ability to model complex systems, predict outcomes, and optimize performance regardless of industry context. From manufacturing floors to hospital corridors, from retail stores to software development environments, digital twins are transforming how organizations operate, innovate, and compete.
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Benefit | Typical Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, quality control, production optimization | Reduced downtime and maintenance costs | 20-25% reduction in unplanned downtime |
| Healthcare | Patient care optimization, facility management, treatment planning | Improved patient outcomes and resource efficiency | 15-30% improvement in patient outcomes |
| Retail | Customer journey optimization, store layout design, inventory management | Enhanced customer experience and sales | 10-20% increase in conversion rates |
| Software Testing | Environment replication, continuous validation, performance testing | Faster deployment and higher quality | 40-50% reduction in bugs in production |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Safety testing, performance validation, design optimization | Enhanced safety and reduced development time | 30-40% faster development cycles |
Manufacturing represents one of the most mature applications of digital twin technology. Manufacturers create virtual replicas of production lines, equipment, and facilities to monitor performance in real-time and predict maintenance needs before failures occur. Predictive maintenance powered by digital twins reduces unplanned downtime by 20-25%, significantly lowering operational costs. Quality control processes benefit from continuous monitoring and analysis, enabling manufacturers to identify defects earlier in production cycles. Digital twins also optimize production scheduling, resource allocation, and supply chain coordination, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and throughput. Companies like Siemens and GE have pioneered digital twin implementations that have transformed manufacturing efficiency and competitiveness.
Healthcare organizations leverage digital twins to optimize patient care delivery and facility operations. Hospital administrators create digital replicas of facilities to simulate patient flows, optimize staff scheduling, and improve resource allocation. Clinical teams use digital twins of patient populations to predict disease progression, test treatment protocols, and personalize care plans. Pharmaceutical companies employ digital twins in drug development to simulate how compounds interact with biological systems, accelerating research timelines and reducing development costs. These applications have demonstrated improvements in patient outcomes ranging from 15-30%, while simultaneously reducing operational costs and improving staff efficiency.
Retail businesses use digital twins to enhance customer experience and optimize store operations. Retailers simulate customer journeys through physical and digital channels, identifying friction points and optimization opportunities. Store layout optimization through digital twins has increased conversion rates by 10-20% by improving product discovery and reducing customer navigation friction. Inventory management systems powered by digital twins predict demand patterns, optimize stock levels, and reduce both stockouts and excess inventory. E-commerce platforms use digital twins to simulate customer interactions with recommendation systems, testing how AI-driven personalization impacts purchase behavior and customer satisfaction.
Software Testing and Quality Assurance have been transformed by digital twin technology. Development teams create virtual replicas of production environments, enabling comprehensive testing before deployment. Continuous validation through digital twins identifies performance bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and compatibility issues in controlled environments. This approach has reduced production bugs by 40-50% while accelerating deployment cycles. Digital twins enable teams to simulate various user scenarios, load conditions, and edge cases without impacting real users. The ability to test extensively in virtual environments before production deployment has become essential for organizations delivering mission-critical software.
Aerospace and Automotive industries rely heavily on digital twins for safety validation and performance optimization. Aircraft manufacturers create detailed digital replicas of aircraft systems to simulate flight conditions, test safety protocols, and validate design changes. Automotive companies use digital twins to simulate crash scenarios, test autonomous driving algorithms, and optimize vehicle performance across various conditions. These applications have reduced development cycles by 30-40% while improving safety outcomes. The ability to conduct extensive virtual testing before physical prototyping has dramatically reduced development costs and accelerated innovation in these safety-critical industries.

The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning transforms digital twins from static models into intelligent, adaptive systems capable of autonomous learning and optimization. AI algorithms process vast volumes of real-time and historical data, identifying complex patterns and relationships that would be impossible for humans to detect manually. Machine learning models continuously improve their accuracy and predictive power as they process more data, creating a virtuous cycle where the digital twin becomes increasingly valuable over time. This AI-powered evolution enables digital twins to move beyond simple monitoring into sophisticated predictive analytics and autonomous optimization.
Predictive analytics represents one of the most valuable capabilities enabled by AI integration in digital twins. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical patterns, current conditions, and external variables to forecast future outcomes with remarkable accuracy. In manufacturing, predictive models forecast equipment failures weeks or months in advance, enabling preventive maintenance that eliminates costly downtime. In healthcare, predictive algorithms identify patients at risk of adverse events, enabling early intervention. In retail, predictive models forecast demand patterns, enabling optimal inventory management. These predictive capabilities transform organizations from reactive problem-solvers into proactive optimizers, fundamentally changing how they operate and compete.
Pattern recognition algorithms powered by deep learning and neural networks identify subtle correlations and anomalies within complex datasets. These algorithms can detect equipment degradation patterns that precede failures, identify customer behavior changes that signal churn risk, or recognize market trends before they become obvious. The sophistication of modern machine learning enables digital twins to understand not just what is happening, but why it’s happening and what will happen next. This understanding enables autonomous decision-making where the digital twin recommends or automatically implements optimizations without human intervention.
Real-time optimization capabilities emerge when AI algorithms continuously analyze system performance and recommend adjustments to improve outcomes. In manufacturing, optimization algorithms adjust production parameters to maximize throughput while maintaining quality. In software systems, optimization algorithms adjust resource allocation to maintain performance under varying load conditions. In customer-facing systems, optimization algorithms personalize experiences based on individual preferences and behavior patterns. These continuous optimizations compound over time, creating significant performance improvements and competitive advantages.
The connection between AI Digital Twins and AI monitoring platforms like AmICited.com becomes particularly relevant in this context. As organizations deploy increasingly sophisticated AI systems to interact with customers and manage brand representation, they need comprehensive monitoring to ensure these systems behave appropriately and reference brands accurately. Digital twins of AI systems enable organizations to simulate various scenarios, test how AI models respond to edge cases, and predict potential issues before they impact real customers. This integration of digital twin technology with AI monitoring creates a powerful framework for ensuring AI systems operate safely, ethically, and in alignment with organizational values and brand guidelines.
AI Digital Twins deliver substantial business value across multiple dimensions, from cost reduction and efficiency improvements to risk mitigation and competitive advantage. Organizations implementing digital twin technology report transformative impacts on their operations, financial performance, and market position. The benefits extend beyond immediate operational improvements to include strategic advantages in innovation, customer experience, and organizational agility.
Cost reduction represents one of the most tangible benefits of digital twin implementation. Predictive maintenance enabled by digital twins reduces unplanned downtime by 20-25%, eliminating expensive emergency repairs and production interruptions. Optimized operations reduce energy consumption, material waste, and resource inefficiency. Simulation capabilities reduce the need for physical prototyping, accelerating development cycles while reducing costs. Organizations implementing digital twins typically see return on investment within 12-24 months, with ongoing benefits accumulating over time.
Improved efficiency and productivity emerge from continuous optimization enabled by digital twins. Manufacturing facilities optimize production schedules, reduce cycle times, and improve equipment utilization. Healthcare facilities optimize staff scheduling, reduce patient wait times, and improve resource allocation. Retail operations optimize inventory management, reduce stockouts, and improve customer service levels. Software development teams reduce testing cycles, accelerate deployment, and improve code quality. These efficiency improvements compound across operations, creating significant productivity gains.
Faster time-to-market becomes possible when organizations can test and validate innovations in digital environments before physical deployment. Product development cycles accelerate when teams can simulate designs, test performance, and validate safety in virtual environments. Marketing campaigns launch faster when they’ve been optimized through digital twin simulations. Software releases accelerate when comprehensive testing occurs in digital replicas of production environments. This speed advantage translates directly into competitive advantage, enabling organizations to respond faster to market opportunities and customer needs.
Risk mitigation capabilities protect organizations from costly failures and reputation damage. Digital twins enable extensive testing of safety-critical systems before real-world deployment, reducing accident risk in aerospace, automotive, and healthcare applications. Simulation of crisis scenarios enables organizations to develop effective response strategies before emergencies occur. Testing of AI systems in digital environments ensures they behave appropriately before interacting with real customers. This proactive risk management prevents costly failures and protects organizational reputation.
Enhanced customer experience results from optimization enabled by digital twins. Personalization algorithms refined through digital twin simulations deliver more relevant recommendations and experiences. Customer journey optimization reduces friction and improves satisfaction. AI systems tested and optimized in digital environments provide better service when deployed to real customers. These improvements in customer experience drive loyalty, increase lifetime value, and generate positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Key benefits of AI Digital Twin implementation include:
Despite their transformative potential, AI Digital Twins face significant challenges that organizations must address to achieve successful implementation and realize expected benefits. Understanding these challenges enables organizations to develop mitigation strategies and set realistic expectations for digital twin initiatives.
Data quality and scarcity represent fundamental challenges for digital twin effectiveness. Digital twins require vast amounts of high-quality, consistent data to train accurate models and maintain synchronization with physical systems. Many organizations struggle with data fragmentation across legacy systems, inconsistent data formats, and missing historical data. Poor data quality leads to inaccurate models that generate unreliable predictions and recommendations. Organizations must invest in data infrastructure, governance, and quality assurance to ensure digital twins have access to the data they need. Mitigation strategies include implementing comprehensive data collection systems, establishing data quality standards, and gradually building historical datasets over time.
Privacy and security concerns intensify as digital twins collect and process sensitive operational and customer data. Creating detailed virtual replicas of systems requires capturing information about operations, customer behavior, and system vulnerabilities. This data becomes an attractive target for cyberattacks, and breaches could expose sensitive information. Organizations must implement robust security measures, encryption protocols, and access controls to protect digital twin data. Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA add complexity to data handling requirements. Mitigation approaches include implementing zero-trust security architectures, encrypting data in transit and at rest, and conducting regular security audits.
Complexity of implementation challenges many organizations attempting digital twin projects. Creating accurate virtual replicas of complex systems requires deep technical expertise, sophisticated modeling capabilities, and integration with multiple data sources and systems. Organizations often underestimate the complexity of synchronizing digital and physical systems in real-time, managing data pipelines, and training machine learning models. The learning curve is steep, and many organizations lack internal expertise. Mitigation strategies include partnering with experienced consultants, investing in team training, and starting with pilot projects on less complex systems before scaling.
Cost of infrastructure and implementation can be substantial, particularly for organizations new to digital twin technology. Building the necessary data infrastructure, implementing real-time synchronization systems, and deploying machine learning platforms requires significant capital investment. Ongoing operational costs for data storage, processing, and model maintenance add to the total cost of ownership. Organizations must carefully evaluate ROI and ensure digital twin investments align with strategic priorities. Mitigation approaches include starting with high-impact use cases that deliver clear ROI, leveraging cloud-based platforms to reduce infrastructure costs, and phasing implementation across multiple projects.
Validation challenges arise from the difficulty of ensuring digital twins accurately represent physical systems. Validating that a virtual model truly reflects real-world behavior requires extensive testing and comparison of predictions against actual outcomes. Incomplete or inaccurate models can generate misleading predictions and recommendations. Organizations must establish rigorous validation processes and continuously monitor prediction accuracy. Mitigation strategies include implementing comprehensive testing protocols, maintaining feedback loops that compare predictions to actual outcomes, and continuously refining models based on validation results.
Skills gap in organizations limits the ability to develop, deploy, and maintain digital twins effectively. Digital twin projects require expertise in data engineering, machine learning, systems modeling, and domain-specific knowledge. Many organizations struggle to find and retain talent with these specialized skills. The shortage of qualified professionals increases hiring costs and extends project timelines. Mitigation approaches include investing in employee training and development, partnering with external experts, and building communities of practice to share knowledge and best practices.
Integration with existing systems presents technical and organizational challenges. Digital twins must integrate with legacy systems, databases, and applications that may not have been designed for real-time data sharing or API-based integration. Organizations often face resistance to change from teams invested in existing processes and systems. Mitigation strategies include investing in integration platforms and middleware, establishing clear governance structures for digital twin initiatives, and securing executive sponsorship to drive organizational alignment.
The digital twin market is experiencing explosive growth, with projections indicating the market will reach $16 billion by 2025-2026, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38%. This rapid expansion reflects increasing recognition of digital twin value across industries and growing maturity of underlying technologies. Organizations that successfully implement digital twins today are positioning themselves as leaders in their industries, while those that delay risk falling behind competitors who leverage these capabilities for innovation and optimization.
Emerging use cases continue to expand the applicability of digital twin technology beyond traditional manufacturing and engineering domains. Healthcare organizations are creating digital twins of entire hospital systems to optimize operations and improve patient outcomes. Retail companies are using digital twins to simulate store experiences and optimize customer journeys. Financial services firms are creating digital twins of trading systems and customer interactions to improve performance and manage risk. Smart cities are implementing digital twins of urban infrastructure to optimize traffic flow, energy consumption, and emergency response. These diverse applications demonstrate the versatility of digital twin technology and its potential to transform virtually every industry.
Integration with IoT and edge computing is expanding digital twin capabilities and enabling real-time processing at the edge of networks. As IoT devices proliferate, they generate vast amounts of data that feed into digital twins, enabling more accurate and responsive virtual models. Edge computing enables processing and analysis to occur closer to data sources, reducing latency and enabling faster decision-making. This integration creates more responsive digital twins capable of real-time optimization and autonomous decision-making. Organizations are increasingly deploying digital twins across distributed networks rather than centralizing all processing in cloud environments.
Autonomous digital twins represent an emerging frontier where digital twins operate with minimal human intervention, making decisions and implementing optimizations independently. These systems combine advanced machine learning, real-time data processing, and autonomous decision-making to continuously optimize system performance. Autonomous digital twins could revolutionize how organizations operate, enabling systems to self-optimize, self-heal, and adapt to changing conditions without human oversight. However, autonomous systems also raise important questions about accountability, transparency, and control that organizations must address.
Industry 4.0 integration positions digital twins as central to the next industrial revolution. Smart factories, connected supply chains, and autonomous systems all rely on digital twins for coordination, optimization, and decision-making. As manufacturing becomes increasingly digital and connected, digital twins will become essential infrastructure rather than optional tools. Organizations that embrace digital twin technology will gain significant competitive advantages in Industry 4.0 environments.
Cookieless marketing and privacy-first approaches are creating new opportunities for digital twins in customer experience optimization. As third-party cookies disappear and privacy regulations tighten, organizations need new ways to understand customer behavior and optimize marketing. Digital twins of customer populations enable organizations to simulate customer behavior and test marketing approaches without relying on invasive tracking. This privacy-respecting approach to customer understanding will become increasingly important as regulations tighten and consumer expectations for privacy increase.
AI system monitoring and brand protection will increasingly leverage digital twin technology. As organizations deploy more sophisticated AI systems to interact with customers and manage brand representation, they need comprehensive monitoring to ensure appropriate behavior. Digital twins of AI systems enable organizations to simulate various scenarios, test how AI models handle edge cases, and predict potential issues before they impact real customers. This integration of digital twin technology with AI monitoring platforms creates a comprehensive ecosystem for ensuring AI systems operate safely and in alignment with organizational values. Platforms like AmICited.com will increasingly incorporate digital twin capabilities to provide organizations with deeper insights into how their AI systems reference and represent brands across digital channels.
The convergence of digital twin technology with artificial intelligence, IoT, edge computing, and advanced analytics is creating unprecedented opportunities for organizations to understand, optimize, and innovate. Organizations that invest in digital twin capabilities today will be well-positioned to compete in increasingly digital and AI-driven markets. The future belongs to organizations that can leverage data, simulation, and artificial intelligence to make faster, better decisions and continuously optimize their operations and customer experiences.
Digital twins maintain bidirectional, real-time connections to physical systems and continuously update based on live data, while simulations are typically static models created for specific scenarios. Digital twins learn and adapt over time, becoming more accurate as they process more data. Simulations run independently with fixed parameters and don't evolve based on new information. This fundamental difference makes digital twins superior for ongoing monitoring, optimization, and predictive analytics.
AI and machine learning transform digital twins from static models into intelligent, adaptive systems. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast volumes of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend optimizations. These algorithms continuously improve their accuracy as they process more data, enabling digital twins to move beyond simple monitoring into sophisticated predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making. AI integration enables digital twins to understand not just what is happening, but why and what will happen next.
Digital twins deliver value across diverse industries including manufacturing (predictive maintenance), healthcare (patient care optimization), retail (customer journey optimization), software testing (environment replication), aerospace (safety validation), and automotive (performance optimization). Manufacturing and aerospace have the most mature implementations, but emerging applications in healthcare, retail, and smart cities demonstrate the technology's versatility. Any industry with complex systems, high costs of failure, or need for continuous optimization can benefit from digital twins.
Digital twins create risk-free environments where organizations can simulate customer interactions, test marketing messages, and evaluate how AI systems reference their brands. They enable A/B testing of campaigns, simulation of customer behavior, and prediction of how different audiences will respond to brand messaging. For organizations using platforms like AmICited.com, digital twins provide enhanced capabilities for monitoring how AI systems reference brands and predicting potential issues before they impact real customers.
Key challenges include data quality and scarcity (requiring vast amounts of high-quality data), privacy and security concerns (protecting sensitive operational data), complexity of implementation (requiring specialized expertise), infrastructure costs (significant capital investment), validation challenges (ensuring accuracy), skills gaps (shortage of qualified professionals), and integration with existing systems (technical and organizational barriers). Organizations can mitigate these challenges through phased implementation, investment in training, partnerships with experts, and starting with high-impact use cases.
Digital twins enable extensive testing in virtual environments before real-world deployment, reducing bugs by 40-50% and accelerating development cycles. They allow simulation of various scenarios, load conditions, and edge cases without impacting real users. Organizations can test safety-critical systems, validate design changes, and optimize performance parameters in controlled environments. This capability is particularly valuable for software development, aerospace, automotive, and healthcare applications where failure costs are high.
The digital twin market is experiencing explosive growth, with projections indicating the market will reach $16 billion by 2025-2026, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38%. This rapid expansion reflects increasing recognition of digital twin value across industries and growing maturity of underlying technologies. Organizations implementing digital twins today are positioning themselves as leaders in their industries, while those that delay risk falling behind competitors who leverage these capabilities.
Digital twins require robust security measures including encryption protocols, access controls, and zero-trust security architectures to protect sensitive operational and customer data. Organizations must comply with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA when handling personal data. Mitigation strategies include encrypting data in transit and at rest, conducting regular security audits, implementing comprehensive access controls, and using synthetic data where appropriate. Privacy-respecting approaches to digital twins are becoming increasingly important as regulations tighten.
Discover how AmICited.com tracks your brand mentions across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Ensure your brand is accurately represented in AI-generated answers and optimize your digital presence.

Learn about synthetic data training for AI models, how it works, benefits for machine learning, challenges like model collapse, and implications for brand repre...
Learn how AI deduplication logic identifies and handles duplicate data sources. Explore algorithms, techniques, and real-world applications for maintaining data...
Learn what AI-generated images are, how they're created using diffusion models and neural networks, their applications in marketing and design, and the ethical ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.