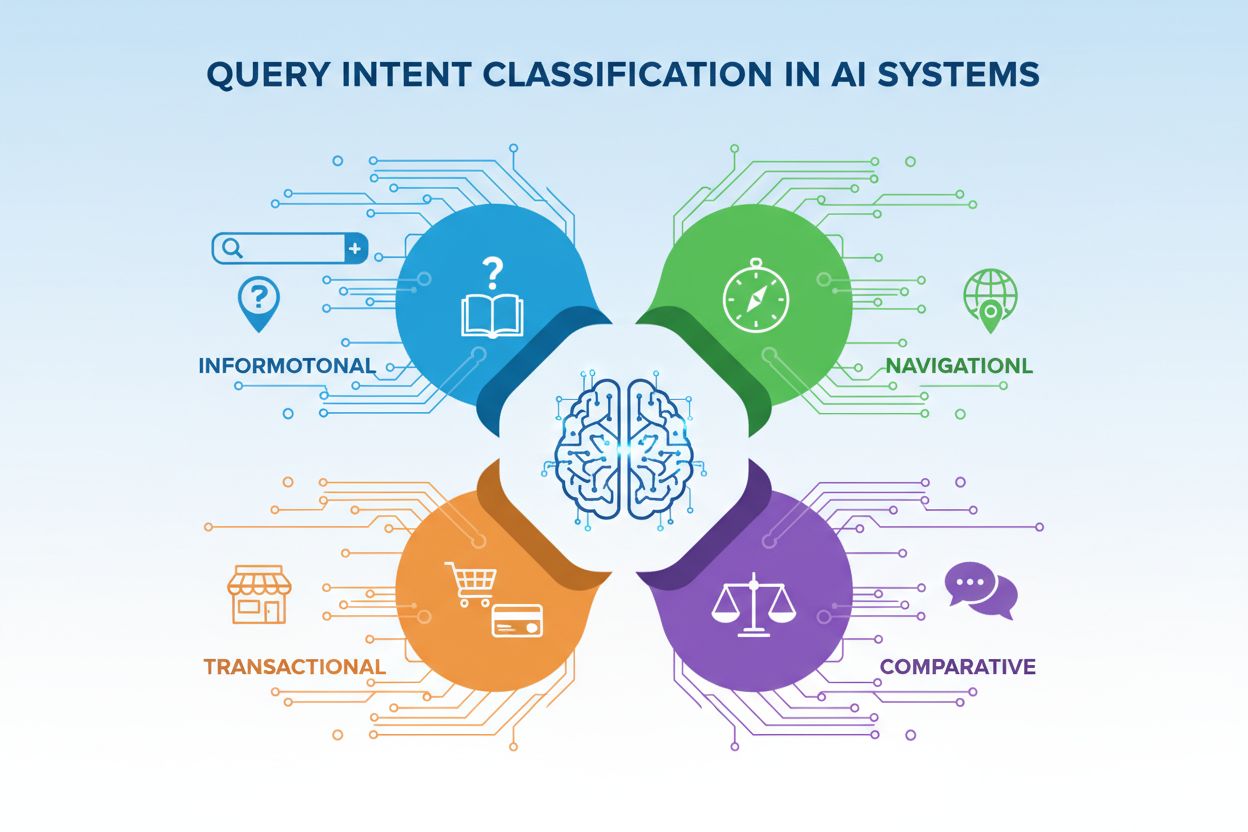
Query Intent Classification
Learn about Query Intent Classification - how AI systems categorize user queries by intent (informational, navigational, transactional, comparative). Understand...
AI systems’ ability to understand user needs beyond explicit query wording. Implicit intent detection infers underlying goals from subtle cues, context, and behavioral patterns without users directly stating their complete needs. This capability enables AI to deliver more relevant, personalized experiences by recognizing hidden intentions beneath surface-level queries.
AI systems' ability to understand user needs beyond explicit query wording. Implicit intent detection infers underlying goals from subtle cues, context, and behavioral patterns without users directly stating their complete needs. This capability enables AI to deliver more relevant, personalized experiences by recognizing hidden intentions beneath surface-level queries.
Implicit intent detection refers to the AI capability to understand what users truly want without them explicitly stating it. Unlike explicit intent—where users directly express their needs through clear keywords or direct questions—implicit intent operates beneath the surface of user behavior, requiring systems to infer underlying goals from subtle cues, context, and patterns. This distinction is crucial because users often don’t articulate their complete needs; they may ask “What’s the weather like?” when they actually want to know if they should bring an umbrella, or search for “best restaurants” when they’re really looking for a place to celebrate an anniversary. Implicit intent detection has become increasingly important as AI systems move beyond simple keyword matching toward genuine understanding of user needs. By recognizing these hidden intentions, AI systems can deliver more relevant, personalized, and satisfying experiences. This capability transforms how businesses interact with customers, enabling proactive assistance rather than reactive responses.
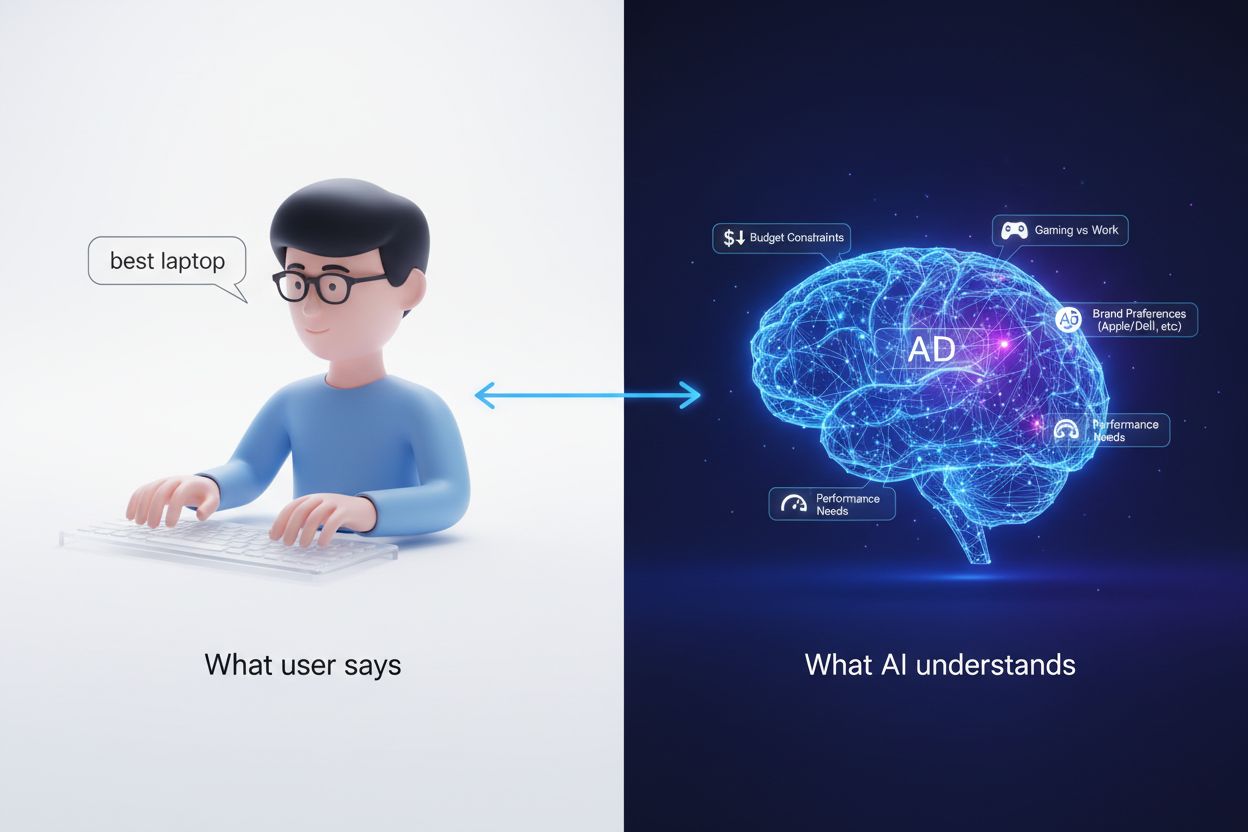
Understanding the distinction between explicit and implicit intent is fundamental to designing effective AI systems. Explicit intent occurs when users directly communicate their needs through clear, unambiguous language—they know what they want and say it plainly. Implicit intent, conversely, requires AI systems to read between the lines, analyzing context, user history, behavioral patterns, and environmental factors to determine what users actually need. The difference becomes apparent when examining how users interact with technology; explicit intent is straightforward to process, while implicit intent demands sophisticated analysis. Consider a user who searches for “running shoes” on an e-commerce platform—their explicit intent is to find running shoes, but their implicit intent might be to prepare for a marathon, find shoes for a specific terrain, or replace worn-out athletic footwear. AI systems that recognize only explicit intent miss opportunities to provide superior recommendations, while those that detect implicit intent can suggest complementary products, training guides, or nutrition advice. This deeper understanding creates competitive advantages in customer satisfaction and business outcomes.
| Intent Type | Definition | Example Query | What AI Must Infer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explicit Intent | Directly stated user need or goal | “Show me blue running shoes size 10” | User wants blue running shoes in size 10 |
| Implicit Intent | Underlying need inferred from context and behavior | “I have a 5K race next month” | User needs training plans, nutrition advice, race-day preparation tips, performance tracking |
| Contextual Intent | Intent derived from user’s situation and environment | “It’s raining outside” | User may need waterproof gear, indoor activities, or weather-appropriate clothing |
| Behavioral Intent | Intent inferred from past actions and patterns | User frequently browses hiking gear | User is likely interested in outdoor activities, adventure travel, or fitness-related products |
AI systems employ sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) techniques to move beyond surface-level keyword analysis and uncover deeper user intentions. These systems analyze linguistic patterns, semantic relationships, and contextual clues embedded within user queries and interactions. Contextual analysis plays a vital role, as AI examines surrounding information—previous searches, browsing history, time of day, location data, and user profile characteristics—to build a comprehensive understanding of what users truly seek. Machine learning models trained on vast datasets of user interactions learn to recognize patterns that correlate with specific implicit intents, enabling them to make accurate predictions about unstated needs. Sentiment analysis helps systems understand emotional undertones that reveal intent; a user asking “How do I fix my broken laptop?” with frustrated language may implicitly need urgent support rather than a detailed technical guide. Advanced systems also incorporate behavioral analytics, tracking how users interact with recommendations and results to continuously refine their understanding of implicit intent. The combination of these approaches enables AI to transform vague or indirect user inputs into actionable insights that drive meaningful interactions.
Several cutting-edge technologies work in concert to enable effective implicit intent detection:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Breaks down user input into meaningful components, identifying grammatical structures, semantic relationships, and linguistic nuances that reveal underlying intentions beyond literal word meanings.
Word Embeddings: Converts words and phrases into numerical vectors that capture semantic meaning, allowing AI systems to understand that “automobile,” “car,” and “vehicle” represent similar concepts and may indicate related implicit intents.
Transformer Models: Advanced neural network architectures like BERT and GPT that understand context by analyzing relationships between all words in a sequence, enabling sophisticated comprehension of complex, multi-layered user intentions.
Sentiment Analysis: Evaluates emotional tone and attitude in user language, revealing whether requests stem from frustration, curiosity, urgency, or other emotional states that indicate different implicit needs.
Contextual Embeddings: Generates dynamic word representations that change based on surrounding context, allowing systems to understand that the same word carries different implicit meanings in different situations.
Behavioral Analytics: Tracks user interactions, click patterns, dwell time, and navigation flows to identify implicit preferences and intentions that emerge from actual behavior rather than stated preferences.
Reinforcement Learning: Enables AI systems to learn from outcomes of intent predictions, continuously improving accuracy by understanding which inferred intentions led to successful user satisfaction and engagement.
Implicit intent detection has revolutionized how businesses across industries serve their customers more effectively. In e-commerce, when a customer searches for “winter coat,” AI systems detect implicit intents like “I need something waterproof,” “I’m looking for a specific style,” or “I want the best value,” then tailor product recommendations accordingly. Customer service platforms use implicit intent detection to route inquiries to appropriate departments before customers explicitly state their problem—recognizing frustration signals or technical language patterns that indicate the nature of their issue. Search engines leverage this technology to return results that match what users actually want rather than just what they typed, understanding that “best restaurants near me” implicitly means “restaurants I can reach easily that match my cuisine preferences and budget.” Recommendation systems across streaming platforms, social media, and retail sites detect implicit preferences from viewing history, engagement patterns, and demographic data to suggest content users didn’t know they wanted. Voice assistants use implicit intent detection to understand conversational context, recognizing that “It’s cold” might mean “Turn up the heat” or “What should I wear?” depending on the situation. Healthcare applications detect implicit patient needs by analyzing symptom descriptions and medical history to recommend preventive care or lifestyle changes. These applications demonstrate how implicit intent detection transforms user experiences from transactional to genuinely personalized.

Despite significant advances, implicit intent detection remains fraught with challenges that limit AI accuracy and reliability. Ambiguity represents the fundamental obstacle—human language is inherently ambiguous, and the same query can legitimately indicate multiple different implicit intents depending on context that AI systems may not possess. Context scarcity occurs when AI lacks sufficient information about user circumstances, preferences, or history to make accurate inferences; a new user with no browsing history provides minimal data for intent detection. Language variations across dialects, slang, cultural references, and evolving terminology create moving targets for AI systems trained on historical data that may not reflect current usage patterns. Data quality issues plague many systems, as training data may contain biases, errors, or unrepresentative samples that lead to incorrect intent predictions. Privacy constraints limit the contextual information systems can ethically collect and analyze, forcing implicit intent detection to operate with incomplete information. Temporal dynamics mean that user intentions change over time—someone interested in “pregnancy information” has vastly different implicit needs depending on whether they’re planning, expecting, or postpartum. Successfully navigating these challenges requires continuous refinement, diverse training data, and transparent acknowledgment of system limitations.
As AI systems become increasingly central to business operations, monitoring their implicit intent detection capabilities has become essential for maintaining quality and trustworthiness. AI monitoring platforms track how accurately systems infer user intentions, measuring whether detected intents lead to satisfactory outcomes or missed opportunities. Organizations must monitor whether their AI systems exhibit bias in intent detection—for example, inferring different implicit needs from identical queries based on user demographics—which can perpetuate discrimination and reduce service quality for underrepresented groups. Brand citation tracking through platforms like AmICited.com helps organizations understand how their AI systems are being referenced and discussed in the context of intent detection capabilities, providing insights into market perception and competitive positioning. The rise of AI-powered search and content platforms like Google AI, Perplexity, and specialized GPTs has intensified the need for monitoring, as these systems make implicit intent inferences that directly influence what information users encounter. Organizations must establish clear monitoring frameworks that track intent detection accuracy, user satisfaction with inferred needs, and alignment between detected intentions and actual user outcomes. Effective monitoring also requires understanding how different user segments experience intent detection—whether the system serves all users equitably or whether certain groups receive systematically worse inferences. This monitoring becomes increasingly critical as AI systems make higher-stakes decisions based on inferred intentions, from healthcare recommendations to financial advice.
Quantifying the impact of implicit intent detection requires establishing clear key performance indicators (KPIs) that connect improved intent understanding to business outcomes. Engagement metrics serve as primary indicators—systems that accurately detect implicit intent typically show increased click-through rates, longer session durations, and higher conversion rates as users find more relevant content and recommendations. Customer satisfaction scores directly reflect whether implicit intent detection improves user experience; surveys and feedback mechanisms reveal whether users feel understood and whether their actual needs are being met. Recommendation accuracy can be measured through A/B testing, comparing outcomes when systems use explicit intent only versus when they incorporate implicit intent detection, quantifying the improvement in relevance and user satisfaction. Revenue impact provides the ultimate ROI measure—organizations can track whether improved intent detection increases average order value, reduces cart abandonment, improves customer lifetime value, or drives higher subscription renewal rates. Operational efficiency gains emerge as implicit intent detection reduces support tickets by proactively addressing needs, decreases search friction by delivering better results faster, and enables more efficient resource allocation. Retention metrics demonstrate long-term value, as users who feel understood by AI systems exhibit higher loyalty and lower churn rates. Forward-thinking organizations establish comprehensive measurement frameworks that connect implicit intent detection capabilities to strategic business objectives, ensuring that investments in this technology deliver measurable returns.
Explicit intent is when users directly state what they want, like searching for 'blue running shoes size 10.' Implicit intent is the underlying need inferred from context and behavior—the same user might implicitly need training plans, nutrition advice, or race-day preparation tips. AI systems that detect implicit intent provide superior, more personalized experiences.
AI systems use machine learning models trained on vast datasets of user interactions, learning to recognize patterns that correlate with specific implicit intents. They employ natural language processing, contextual analysis, sentiment analysis, and behavioral analytics to understand what users truly need beyond their literal words.
Key challenges include language ambiguity (the same query can indicate multiple intents), context scarcity (insufficient user information), language variations and slang, data quality issues, privacy constraints, and temporal dynamics (user intentions change over time). These obstacles require continuous refinement and diverse training data.
Search engines use implicit intent detection to return results matching what users actually want rather than just what they typed. When someone searches 'best restaurants near me,' the system infers they want accessible restaurants matching their cuisine preferences and budget, not just any restaurant listing.
Yes, significantly. Customer service platforms use implicit intent detection to route inquiries to appropriate departments before customers explicitly state their problem, recognizing frustration signals or technical language patterns. This proactive approach reduces resolution time and improves customer satisfaction.
Machine learning is fundamental—models learn from historical user interactions to recognize patterns indicating specific implicit intents. These models continuously improve through reinforcement learning, understanding which inferred intentions led to successful outcomes and adjusting predictions accordingly.
Current systems achieve 75-85% accuracy for well-defined intent categories, with performance varying based on data quality, language complexity, and available context. Accuracy continues improving as models become more sophisticated and training datasets more comprehensive and representative.
AmICited tracks how AI systems like GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews infer and represent your brand's implicit intent. The platform monitors whether AI systems accurately understand your brand's positioning, values, and offerings, ensuring your brand is represented correctly in AI-generated content and recommendations.
AmICited tracks how AI systems reference and understand your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Detect implicit intent patterns in AI responses and ensure your brand is accurately represented in AI-generated content.

Learn about Query Intent Classification - how AI systems categorize user queries by intent (informational, navigational, transactional, comparative). Understand...

Learn how to align your content with AI query intent to increase citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Master content-prompt matching strategies ...

Learn what informational search intent means for AI systems, how AI recognizes these queries, and why understanding this intent matters for content visibility i...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.