
FAQ Expansion
Learn how FAQ Expansion develops comprehensive question-answer pairs for AI systems. Discover strategies to improve AI citations, platform-specific optimization...
Query expansion optimization is the process of enhancing user search queries with related terms, synonyms, and contextual variations to improve AI system retrieval accuracy and content relevance. It bridges vocabulary gaps between user queries and relevant documents, ensuring AI systems like GPTs and Perplexity can find and reference more appropriate content. This technique is essential for improving both the comprehensiveness and accuracy of AI-generated responses. By expanding queries intelligently, AI platforms can dramatically improve how they discover and cite relevant sources.
Query expansion optimization is the process of enhancing user search queries with related terms, synonyms, and contextual variations to improve AI system retrieval accuracy and content relevance. It bridges vocabulary gaps between user queries and relevant documents, ensuring AI systems like GPTs and Perplexity can find and reference more appropriate content. This technique is essential for improving both the comprehensiveness and accuracy of AI-generated responses. By expanding queries intelligently, AI platforms can dramatically improve how they discover and cite relevant sources.

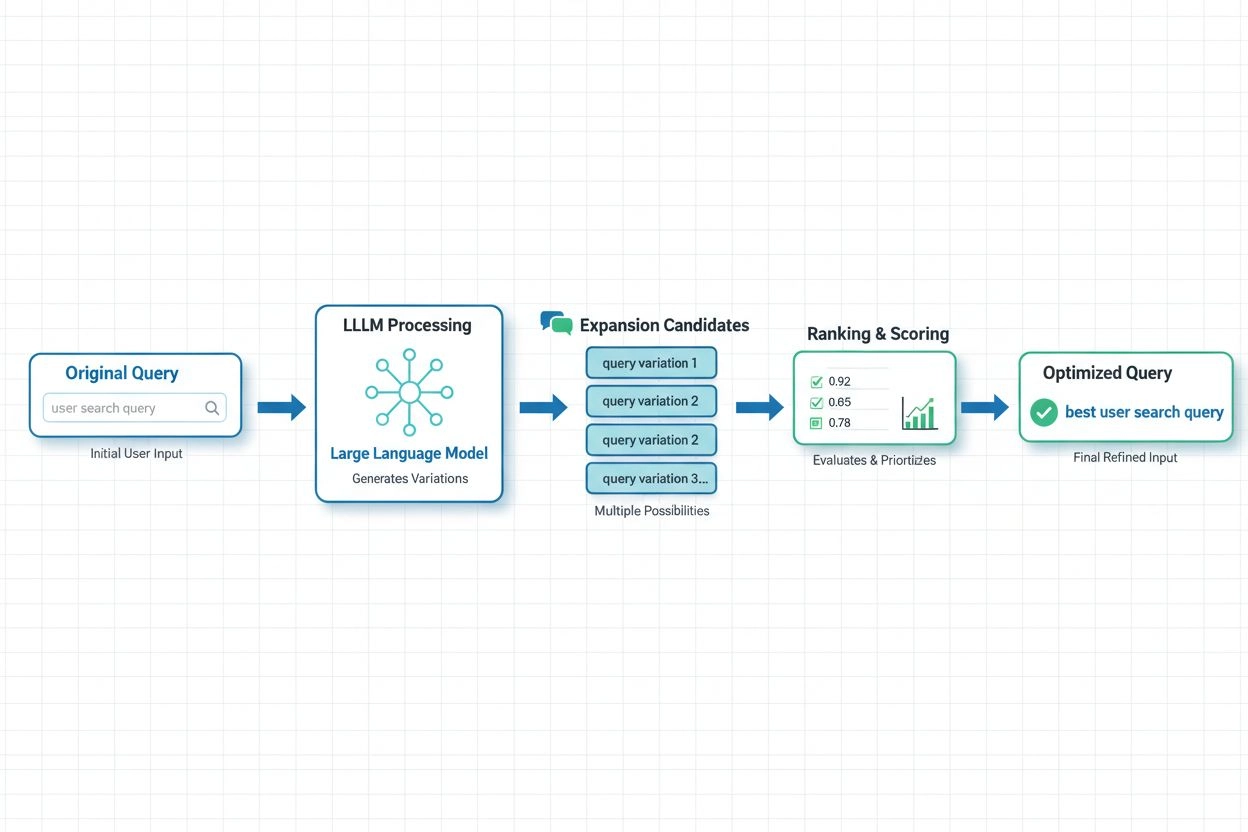
Query Expansion Optimization is the process of reformulating and enhancing search queries by adding related terms, synonyms, and semantic variations to improve retrieval performance and answer quality. At its core, query expansion addresses the vocabulary mismatch problem—the fundamental challenge that users and AI systems often use different terminology to describe the same concepts, leading to missed relevant results. This technique is critical for AI systems because it bridges the gap between how people naturally express their information needs and how content is actually indexed and stored. By expanding queries intelligently, AI platforms can dramatically improve both the relevance and comprehensiveness of their responses.
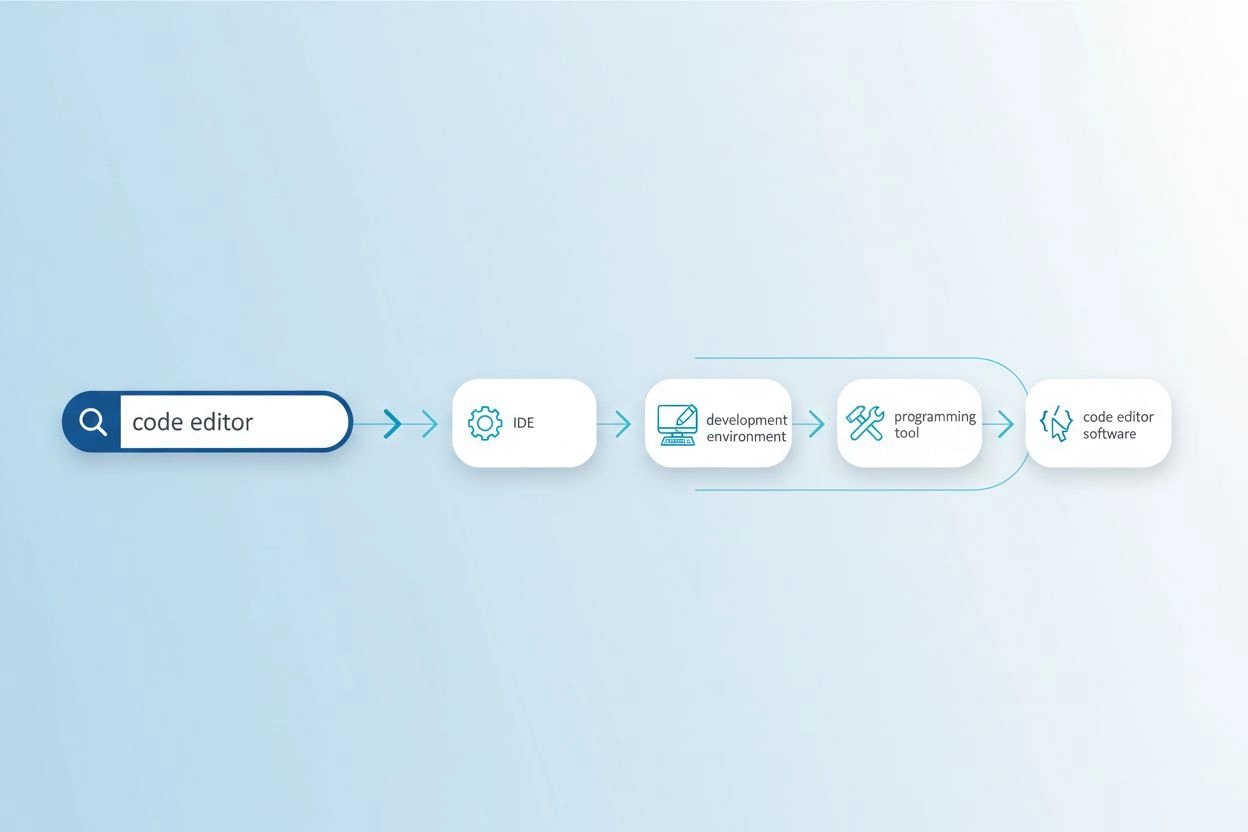
The vocabulary mismatch problem occurs when the exact words used in a query don’t match the terminology found in relevant documents, causing search systems to miss valuable information. For example, a user searching for “code editor” might miss results about “IDEs” (Integrated Development Environments) or “text editors,” even though these are highly relevant alternatives. Similarly, someone querying “vehicle” might not find results tagged with “car,” “automobile,” or “motor vehicle,” despite clear semantic overlap. This problem becomes increasingly severe in specialized domains where multiple technical terms describe the same concept, and it directly impacts the quality of AI-generated responses by limiting the source material available for synthesis. Query expansion solves this by automatically generating related query variations that capture different ways the same information might be expressed.
| Original Query | Expanded Query | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| code editor | IDE, text editor, development environment, source code editor | Finds 3-5x more relevant results |
| machine learning | AI, artificial intelligence, deep learning, neural networks | Captures domain-specific terminology variations |
| vehicle | car, automobile, motor vehicle, transportation | Includes common synonyms and related terms |
| headache | migraine, tension headache, pain relief, headache treatment | Addresses medical terminology variations |
Modern query expansion employs several complementary techniques, each with distinct advantages depending on the use case and domain:
Each technique offers different trade-offs between computational cost, expansion quality, and domain specificity, with LLM-based approaches providing the highest quality but requiring more resources.
Query expansion improves AI responses by providing language models and retrieval systems with a richer, more comprehensive set of source materials to draw from when generating answers. When a query is expanded to include synonyms, related concepts, and alternative phrasings, the retrieval system can access documents that use different terminology but contain equally relevant information, dramatically increasing the recall of the search process. This expanded context allows AI systems to synthesize more complete and nuanced answers, as they’re no longer limited by the specific vocabulary choices in the original query. However, query expansion introduces a precision vs. recall trade-off: while expanded queries retrieve more relevant documents, they can also introduce noise and less-relevant results if expansion is too aggressive. The key to optimization is calibrating expansion intensity to maximize relevance improvements while minimizing irrelevant noise, ensuring that AI responses become more comprehensive without sacrificing accuracy.
In modern AI systems, LLM-based query expansion has emerged as the most sophisticated approach, leveraging the semantic understanding capabilities of large language models to generate contextually appropriate query variations. Recent research from Spotify demonstrates the power of this approach: their implementation using preference alignment techniques (combining RSFT and DPO methods) achieved approximately 70% reduction in processing time while simultaneously improving top-1 retrieval accuracy. These systems work by training language models to understand user preferences and intent, then generating expansions that align with what users actually find valuable rather than just adding arbitrary synonyms. Real-time optimization approaches continuously adapt expansion strategies based on user feedback and retrieval outcomes, allowing systems to learn which expansions work best for specific query types and domains. This dynamic approach is particularly valuable for AI monitoring platforms, as it enables systems to track how query expansion affects citation accuracy and content discovery across different topics and industries.
Despite its benefits, query expansion presents significant challenges that require careful optimization strategies. The over-expansion problem occurs when too many query variations are added, introducing noise and retrieving irrelevant documents that dilute answer quality and increase computational costs. Domain-specific tuning is essential because expansion techniques that work well for general web search may fail in specialized fields like medical research or legal documentation, where terminology precision is critical. Organizations must balance coverage versus accuracy—expanding enough to capture relevant variations without expanding so much that irrelevant results overwhelm the signal. Effective validation approaches include A/B testing different expansion strategies against human-rated relevance judgments, monitoring metrics like precision@k and recall@k, and continuously analyzing which expansions actually improve downstream task performance. The most successful implementations use adaptive expansion that adjusts intensity based on query characteristics, domain context, and observed retrieval quality, rather than applying uniform expansion rules across all queries.
For AmICited.com and AI monitoring platforms, query expansion optimization is fundamental to accurately tracking how AI systems cite and reference sources across different topics and search contexts. When AI systems use expanded queries internally, they access a broader range of potential source materials, which directly affects which citations appear in their responses and how comprehensively they cover available information. This means that monitoring AI answer quality requires understanding not just what users ask, but what expanded query variations the AI system might be using behind the scenes to retrieve supporting information. Brands and content creators should optimize their content strategy by considering how their material might be discovered through query expansion—using multiple terminology variations, synonyms, and related concepts throughout their content to ensure visibility across different query formulations. AmICited helps organizations track this by monitoring how their content appears in AI-generated responses across various query types and expansions, revealing gaps where content might be missed due to vocabulary mismatches and providing insights into how query expansion strategies affect citation patterns and content discovery in AI systems.
Query expansion adds related terms and synonyms to the original query while keeping the core intent intact, whereas query rewriting reformulates the entire query to better match the search system's capabilities. Query expansion is additive—it broadens the search scope—while rewriting is transformative, changing how the query is expressed. Both techniques improve retrieval, but expansion is typically less risky as it preserves the original query intent.
Query expansion directly impacts which sources AI systems discover and cite because it changes the documents available for retrieval. When AI systems use expanded queries internally, they access a broader range of potential sources, which affects which citations appear in their responses. This means monitoring AI answer quality requires understanding not just what users ask, but what expanded query variations the AI system might be using behind the scenes.
Yes, over-expansion can introduce noise and retrieve irrelevant documents that dilute answer quality. This occurs when too many query variations are added without proper filtering. The key is balancing expansion intensity to maximize relevance improvements while minimizing irrelevant noise. Effective implementations use adaptive expansion that adjusts intensity based on query characteristics and observed retrieval quality.
Large Language Models have revolutionized query expansion by enabling semantic understanding of user intent and generating contextually appropriate query variations. LLM-based expansion uses preference alignment techniques to train models to generate expansions that actually improve retrieval outcomes, rather than just adding arbitrary synonyms. Recent research shows LLM-based approaches can reduce processing time by ~70% while improving retrieval accuracy.
Brands should use multiple terminology variations, synonyms, and related concepts throughout their content to ensure visibility across different query formulations. This means considering how your material might be discovered through query expansion—using both technical and colloquial terms, including alternative phrasings, and addressing related concepts. This strategy ensures your content is discoverable regardless of which query variations AI systems use.
Key metrics include precision@k (relevance of top-k results), recall@k (coverage of relevant content in top-k results), Mean Reciprocal Rank (position of first relevant result), and downstream task performance. Organizations also monitor processing time, computational costs, and user satisfaction metrics. A/B testing different expansion strategies against human-rated relevance judgments provides the most reliable validation.
No, they are complementary but distinct techniques. Query expansion modifies the input query to improve retrieval, while semantic search uses embeddings and vector representations to find conceptually similar content. Query expansion can be part of a semantic search pipeline, but semantic search can also work without explicit query expansion. Both techniques address vocabulary mismatch but through different mechanisms.
AmICited tracks how AI systems cite and reference sources across different topics and search contexts, revealing which expanded queries lead to your brand being referenced. By monitoring citation patterns across various query types and expansions, AmICited provides insights into how query expansion strategies affect content discovery and citation accuracy in AI systems like GPTs and Perplexity.
Query expansion optimization affects how AI systems like GPTs and Perplexity discover and cite your content. Use AmICited to track which expanded queries lead to your brand being referenced in AI answers.

Learn how FAQ Expansion develops comprehensive question-answer pairs for AI systems. Discover strategies to improve AI citations, platform-specific optimization...
Learn how query reformulation helps AI systems interpret and enhance user queries for better information retrieval. Understand the techniques, benefits, and imp...
Query refinement is the iterative process of optimizing search queries for better results in AI search engines. Learn how it works across ChatGPT, Perplexity, G...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.