Google Search Console
Google Search Console is Google's free webmaster platform for monitoring search performance, tracking indexing status, and fixing SEO issues. Learn how GSC help...
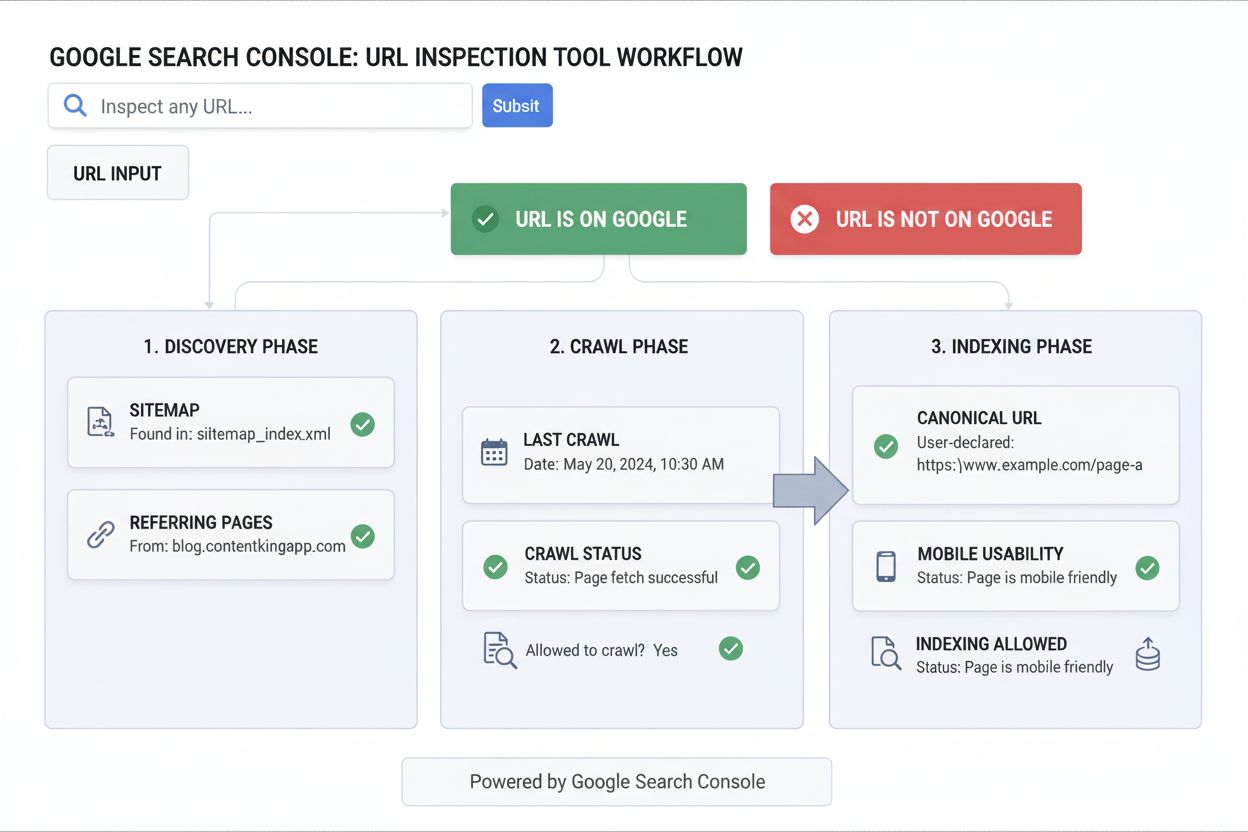
The URL Inspection Tool is a Google Search Console feature that provides detailed information about Google’s indexed version of a specific page and allows webmasters to test whether a URL is indexable. It enables SEO professionals to diagnose crawling, indexing, and rendering issues while monitoring how their content appears in Google’s search index.
The URL Inspection Tool is a Google Search Console feature that provides detailed information about Google's indexed version of a specific page and allows webmasters to test whether a URL is indexable. It enables SEO professionals to diagnose crawling, indexing, and rendering issues while monitoring how their content appears in Google's search index.
The URL Inspection Tool is a powerful feature within Google Search Console that provides webmasters and SEO professionals with detailed information about how Google views and indexes specific pages on their websites. This tool enables users to check the indexing status of individual URLs, diagnose crawling and indexing issues, and test whether pages are eligible to appear in Google Search results. By entering a fully-qualified URL into the inspection search bar, users can access comprehensive data about Google’s indexed version of that page, including discovery information, crawl details, indexing status, and any enhancements or issues detected. The tool also offers a live testing feature that allows real-time inspection of the current state of a page, making it invaluable for verifying fixes and troubleshooting technical SEO problems before they impact search visibility.
The URL Inspection Tool was introduced by Google in 2018 as a successor to the older Fetch as Google feature, representing a significant evolution in how webmasters interact with Google’s indexing systems. Prior to this tool’s introduction, SEO professionals relied on limited diagnostic capabilities and had to wait for Google’s natural crawl cycle to discover indexing problems. The tool emerged during a period when Google was increasingly emphasizing transparency and providing webmasters with more direct access to indexing data. Over the past six years, the URL Inspection Tool has become an essential component of the Google Search Console ecosystem, with adoption rates among SEO professionals reaching approximately 87% according to industry surveys. The tool has continuously evolved to include new features such as live URL testing, enhanced structured data validation, and improved mobile usability reporting. Today, it serves as the primary diagnostic instrument for thousands of enterprises managing large-scale websites, with studies showing that approximately 92% of professional SEO teams use the URL Inspection Tool at least weekly as part of their technical SEO workflows.
The URL Inspection Tool operates through a sophisticated multi-phase analysis process that mirrors Google’s actual crawling and indexing workflow. When a URL is submitted for inspection, the tool retrieves information from three distinct phases: Discovery, Crawl, and Indexing. During the Discovery phase, the tool identifies how Google found the URL, whether through XML sitemaps, referring pages, or other discovery mechanisms. The Crawl phase reveals whether Google was able to access the page, what user agent was used (desktop or mobile), and whether any robots.txt rules blocked access. The Indexing phase shows the canonical URL Google selected, whether indexing was allowed, and any issues that prevented indexing. The tool displays this information through a clear status indicator at the top showing whether the URL is “on Google,” “not on Google,” or has specific issues. Additionally, the live test feature allows users to run real-time inspections that simulate how Google’s crawler would currently see a page, providing immediate feedback on whether recent changes have resolved technical issues. This dual approach—combining historical indexed data with real-time testing—makes the URL Inspection Tool uniquely powerful for both diagnostic and verification purposes.
| Feature | URL Inspection Tool | Index Coverage Report | Rich Results Test | AMP Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single URL Analysis | Yes, detailed per-URL | No, aggregate data only | Yes, limited scope | Yes, AMP-specific |
| Indexing Status | Complete with reasons | Yes, categorized by status | No | No |
| Live Testing | Yes, real-time | No, historical only | Yes, real-time | Yes, real-time |
| Crawl Data | Yes, detailed | No | No | No |
| Structured Data Validation | Yes, comprehensive | No | Yes, focused | No |
| Mobile Usability | Yes | No | No | Yes, AMP-specific |
| Canonical Detection | Yes, user and Google-selected | No | No | No |
| Request Indexing | Yes, direct submission | No | No | No |
| Requires Property Ownership | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Best Use Case | Individual page diagnosis | Site-wide pattern analysis | Rich snippet validation | AMP page validation |
The URL Inspection Tool functions as a real-time diagnostic interface that communicates directly with Google’s indexing infrastructure. When a user enters a URL, the tool first checks whether that URL exists in Google’s index and retrieves the most recent indexed version of the page. The tool then displays the page indexing status at the top, which can show one of five primary statuses: “URL is on Google,” “URL is on Google, but has issues,” “URL is not on Google,” “URL is not on Google: Indexing errors,” or “URL is an alternate version.” Each status provides specific information about why the page is or isn’t indexed. The tool’s View Crawled Page section reveals the actual HTML that Google received, HTTP response headers, and page resources that loaded or failed. The Coverage section breaks down the discovery, crawl, and indexing phases, showing details like the last crawl date, whether crawling was allowed, page fetch success, and whether indexing was permitted. For pages with structured data, the tool validates schema markup and reports any errors or warnings that might prevent rich results from displaying. The live test feature operates differently by fetching the current version of the page in real-time, simulating how Google’s crawler would see it today, which is particularly useful for verifying that recent fixes have resolved issues.
SEO professionals use the URL Inspection Tool for multiple critical workflows that directly impact search visibility and organic traffic. When launching new content, professionals use the tool to verify that pages are discoverable and indexable before they’re promoted, catching technical issues before they affect search performance. After implementing technical SEO fixes—such as removing noindex tags, fixing robots.txt rules, or correcting canonical URLs—the live test feature allows immediate verification that changes have taken effect. The tool is also essential for troubleshooting missing pages, where the detailed coverage information helps identify whether a page wasn’t indexed due to crawl blocks, indexing restrictions, or other technical issues. For e-commerce sites and large-scale publishers, the URL Inspection Tool helps diagnose why important pages aren’t appearing in search results, often revealing issues like soft 404 errors, redirect chains, or mobile usability problems. The tool’s ability to show Google-selected canonical URLs is particularly valuable for managing duplicate content and ensuring that the correct version of a page is being indexed. Additionally, professionals use the tool to validate structured data implementation, ensuring that schema markup for products, recipes, job postings, and other rich result types is correctly formatted and recognized by Google. The tool’s request indexing feature allows professionals to expedite the indexing of newly published or updated content, though it’s subject to daily limits and should be used strategically for high-priority pages.
In the emerging landscape of AI-powered search, the URL Inspection Tool serves as a foundational component of comprehensive content visibility strategies. While the tool specifically monitors Google Search indexing, platforms like AmICited extend this monitoring to track how content appears in AI-generated responses from systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. The relationship between these systems is symbiotic: pages that are properly indexed and structured with high-quality content through the URL Inspection Tool’s verification are more likely to be discovered and cited by AI systems. When a page shows “URL is on Google” status with proper structured data and mobile usability, it signals to AI systems that the content is authoritative and trustworthy. Conversely, pages that fail URL inspection—showing indexing errors or missing from Google’s index—are unlikely to be cited by AI systems that rely on Google’s index as a primary source. For organizations monitoring their brand presence in AI search, the URL Inspection Tool becomes the first diagnostic step: ensuring pages are indexed and properly formatted increases the likelihood of AI citation. This integration means that technical SEO work done through URL inspection directly impacts AI visibility, making the tool essential for modern GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) strategies that account for both traditional search and AI-powered discovery.
The URL Inspection Tool provides several critical status indicators that communicate the health and indexability of a page. The primary overall page status appears at the top and determines whether a page can appear in Google Search results. “URL is on Google” indicates the page is indexed and eligible for search results, though this doesn’t guarantee ranking. “URL is on Google, but has issues” means the page is indexed but has problems with enhancements like structured data or AMP pages that might prevent rich results from displaying. “URL is not on Google” indicates the page wasn’t indexed, often due to intentional blocks like noindex tags or robots.txt restrictions. “URL is not on Google: Indexing errors” shows that Google encountered technical problems preventing indexing, such as 4xx or 5xx HTTP status codes. Within the Coverage section, the tool shows whether a page is “Submitted and indexed,” “Crawled but not indexed,” “Discovered but not indexed,” or has specific error statuses. The Crawl allowed? field indicates whether robots.txt permitted Google to access the page, while Page fetch shows whether Google could successfully retrieve the page from the server. The Indexing allowed? field reveals whether the page had a noindex directive or other indexing restrictions. The User-declared canonical shows what canonical URL the webmaster specified, while Google-selected canonical reveals which URL Google actually chose as the authoritative version. These metrics collectively provide a complete picture of a page’s indexability and search eligibility.
The URL Inspection Tool is evolving to meet the demands of modern search ecosystems that increasingly include AI-powered search engines and generative AI systems. Google has indicated plans to enhance the tool with better integration of Core Web Vitals data at the URL level, providing more comprehensive performance metrics directly within the inspection interface. The tool is also expected to provide deeper insights into how pages perform in AI Overviews, Google’s AI-generated search results feature, helping webmasters understand not just whether their content is indexed, but how it’s being surfaced in AI-generated responses. As GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) becomes increasingly important alongside traditional SEO, the URL Inspection Tool will likely expand to show how content is being cited and used by AI systems. The integration of URL inspection data with broader AI monitoring platforms like AmICited represents the future direction of content visibility tracking, where webmasters can see a unified view of how their pages perform across Google Search, AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI systems. Additionally, the tool is expected to provide better diagnostic capabilities for JavaScript-rendered content, as more websites rely on client-side rendering. The strategic importance of the URL Inspection Tool will only increase as search behavior continues to shift toward AI-powered discovery, making it an essential component of any comprehensive digital visibility strategy that accounts for both traditional search engines and emerging AI search systems.
The URL Inspection Tool provides detailed information about a single specific URL, including its indexed version, crawl data, and live testing capabilities. The Index Coverage report, by contrast, shows aggregate data across all pages on your site, categorizing them by indexing status. The URL Inspection Tool is ideal for diagnosing individual page issues, while the Index Coverage report helps identify site-wide patterns and problems affecting multiple pages.
No, the URL Inspection Tool cannot guarantee ranking. It only confirms whether a page is indexed and eligible to appear in search results. Even if the tool shows 'URL is on Google,' the page must still meet Google's quality guidelines, avoid manual actions, and compete with other pages for ranking positions. Ranking depends on content quality, relevance, authority, and many other ranking factors beyond indexing status.
You should use the URL Inspection Tool regularly, especially after publishing new content, making significant updates, or fixing technical issues. For ongoing monitoring, check critical pages weekly or monthly. After implementing fixes for crawling or indexing issues, use the live test feature immediately to verify the corrections. Many SEO professionals integrate URL inspection into their routine site audits and post-launch verification processes.
This status means Google has indexed your page, but detected problems with enhancements like structured data, AMP pages, or mobile usability. These issues may prevent the page from displaying rich results or appearing with all intended features. To fix it, expand the Enhancements section to see specific warnings or errors, then address them according to Google's recommendations. Use the live test feature to verify your fixes before resubmitting.
The URL Inspection Tool displays data from Google's most recent crawl and index of your page, which can be days or weeks old. If you've recently made changes, the tool won't reflect them immediately. To see current information, click 'Test Live URL' to run a real-time test of your page. This live test shows how Google would see your page right now, helping you verify that recent fixes are working correctly.
No, you can only use the URL Inspection Tool on properties you own and have verified in Google Search Console. For pages on other websites, you can use non-owner testing tools like the Rich Results Test or AMP Test. These alternative tools provide limited diagnostic information without requiring property ownership, making them useful for competitive analysis or testing third-party content.
While the URL Inspection Tool focuses on Google Search indexing, modern AI monitoring platforms like AmICited track how your content appears in AI-generated responses from systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. The URL Inspection Tool ensures your pages are discoverable by Google's crawler, which is foundational for AI visibility. When pages are properly indexed and structured with quality content, they're more likely to be cited by AI systems, making URL inspection a critical first step in comprehensive AI monitoring strategies.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Google Search Console is Google's free webmaster platform for monitoring search performance, tracking indexing status, and fixing SEO issues. Learn how GSC help...

Discover the best tools for checking AI crawlability. Learn how to monitor GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot access to your website with free and enterprise ...
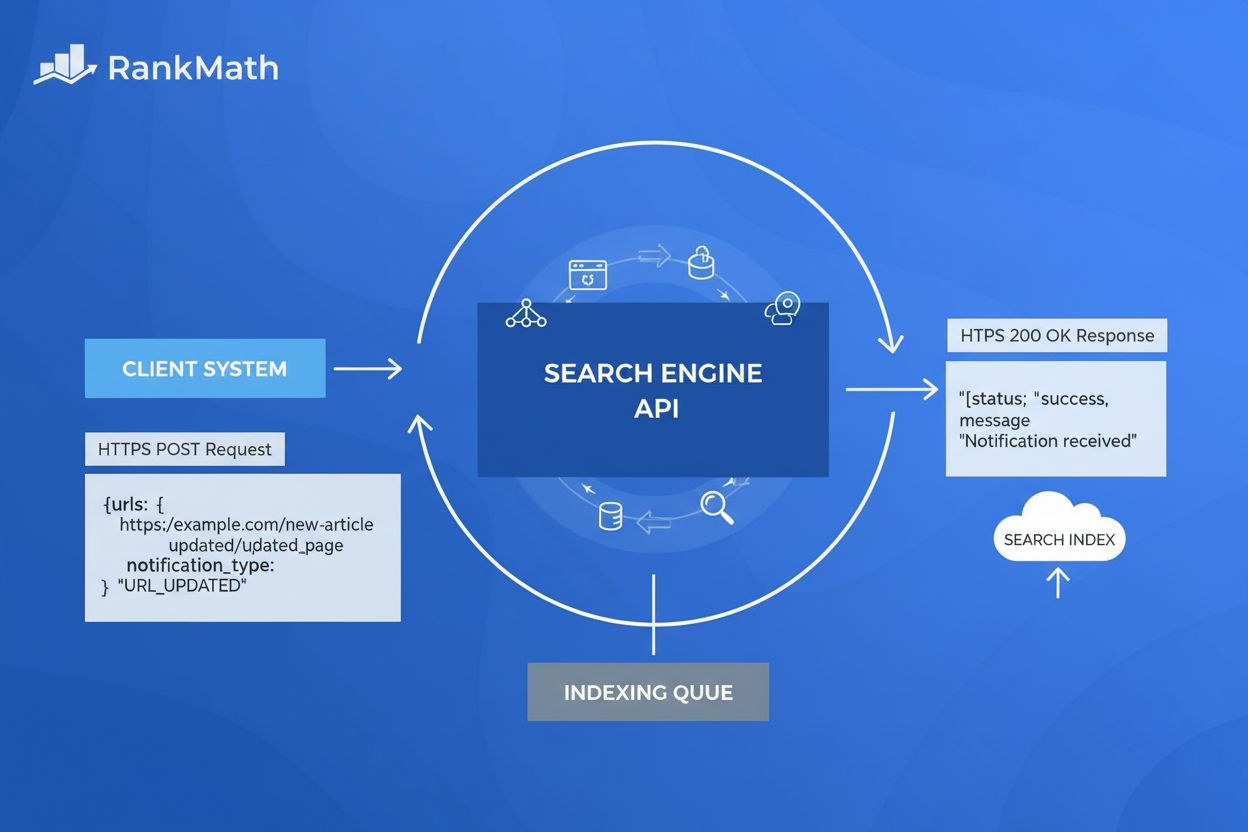
Learn what the Indexing API is, how it works for direct URL submission to Google, and how it accelerates indexing compared to traditional sitemaps and crawling ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.