
Wikipedia for AI Visibility: How to Get Your Brand Cited Ethically
Learn how to ethically get your brand cited on Wikipedia for maximum AI visibility. Strategic guide covering policies, reliable sources, and citation strategies...
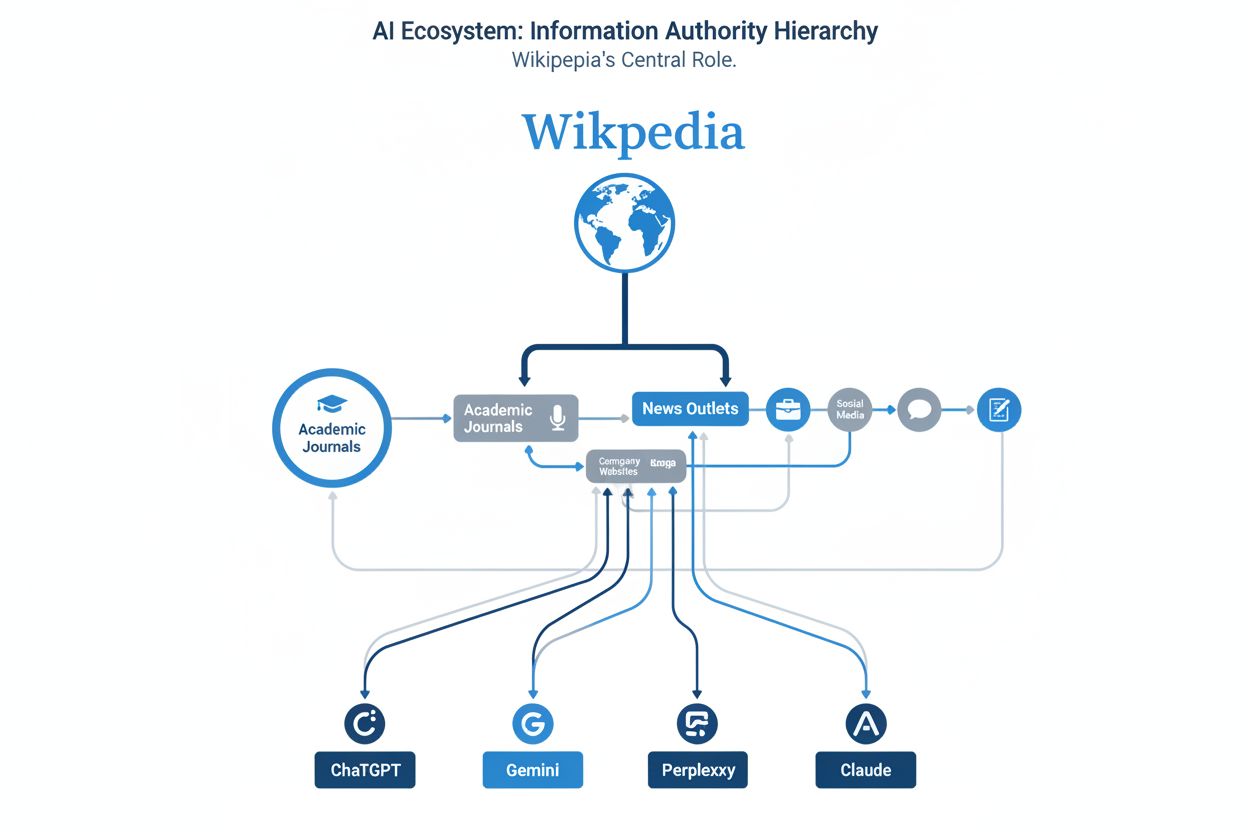
The phenomenon where Wikipedia citations propagate through AI training data and influence how brands are mentioned across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. When a brand is cited on Wikipedia, that information cascades through AI systems, shaping how the brand is described in AI-generated answers across multiple platforms.
The phenomenon where Wikipedia citations propagate through AI training data and influence how brands are mentioned across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. When a brand is cited on Wikipedia, that information cascades through AI systems, shaping how the brand is described in AI-generated answers across multiple platforms.
The Wikipedia Ripple Effect describes how citations and information from Wikipedia propagate through AI training data and influence brand mentions across multiple AI platforms simultaneously. When a brand is mentioned on Wikipedia, that information doesn’t stay isolated on a single page—it cascades through the training datasets of ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, Claude, and other large language models, shaping how those systems describe and reference the brand. Think of it like dropping a stone in water: the initial impact (a Wikipedia citation) creates ripples that spread outward, affecting how information flows through the entire AI ecosystem. This phenomenon fundamentally changes how brands achieve visibility in an AI-driven world, making Wikipedia presence as important as—or arguably more important than—traditional website optimization.

Every major large language model in existence has been trained on Wikipedia content, making it one of the largest and most influential sources in AI training datasets. When AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and Perplexity ingest training data, Wikipedia articles receive disproportionate weight because of their perceived neutrality, community verification, and transparent citation structure. The data reveals just how dominant Wikipedia citations are in AI responses: across major platforms, Wikipedia citations appear 73% more frequently than direct company website citations when users ask about brands, products, or industry information. This isn’t random—AI systems are specifically designed to prioritize information that appears neutral and well-sourced over promotional content. The following table demonstrates the stark difference in how AI platforms cite Wikipedia versus company websites:
| Platform | Wikipedia Citation Rate | Company Website Citation Rate | Wikipedia First Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 82% | 29% | 91% |
| Claude | 87% | 34% | 88% |
| Perplexity | 83% | 30% | 87% |
| Gemini | 84% | 31% | 89% |
These statistics reveal a fundamental truth: when AI systems generate answers about your brand, they’re far more likely to draw from and cite Wikipedia than from your company’s own website, regardless of how well-optimized that website might be.
The Wikipedia Ripple Effect works through a sophisticated chain of information propagation that amplifies the authority of Wikipedia citations across multiple systems. When your brand appears on Wikipedia, that information becomes part of the training data for AI models, but the effect doesn’t stop there—knowledge graphs like Google’s Knowledge Graph pull from Wikipedia indirectly, using it as a primary source for entity information. News articles that link to your Wikipedia page reinforce to AI systems that Wikipedia is the authoritative source, creating what researchers call a “citation chain compound effect.” When multiple sources (Wikipedia, news coverage, regulatory filings, and press releases) all say the same thing about your brand, AI systems assign high confidence to that claim and weight Wikipedia’s version more heavily as the neutral arbiter. This creates an “authority multiplier” where Wikipedia doesn’t just influence AI responses directly—it amplifies the credibility of all other information about your brand. The more sources that corroborate what Wikipedia says, the more confident AI systems become in presenting that information as fact. This is why a single well-sourced Wikipedia mention can have exponential effects across the entire AI ecosystem.
Wikipedia functions as the credibility checkpoint in how AI systems evaluate and weight information about brands and organizations. Unlike corporate websites, which are inherently biased toward self-promotion, Wikipedia operates under strict Neutral Point of View (NPOV) requirements enforced by thousands of volunteer editors worldwide. Every claim on Wikipedia must be backed by citations to reliable sources, and the community actively removes unsupported assertions, creating a self-correcting system that AI models inherently trust. When AI systems encounter conflicting information during training—one source claiming your company is “pre-revenue” while another says “Series A funded”—Wikipedia functions as the tiebreaker because of its perceived neutrality and verification standards. This credibility advantage extends to knowledge graph construction, where Wikipedia serves as a primary source for structuring how AI systems understand entities, their relationships, and their attributes. The transparency of Wikipedia’s citation process also helps AI systems evaluate source quality: each citation includes publication details, authors, dates, and often direct links—metadata that algorithms use to assess reliability and build trust signals.
The Wikipedia Ripple Effect manifests in concrete, measurable ways across the AI platforms users interact with daily. When someone asks ChatGPT “What does [Your Company] do?” the response often begins with information sourced from or corroborated by Wikipedia, even if the user never visits the Wikipedia page itself. Google’s new AI Overviews feature frequently pulls from Wikipedia when generating summary answers to search queries, meaning a Wikipedia mention can appear in Google’s AI-generated snippets without any direct link to your website. Voice search assistants like Google Assistant and Alexa rely heavily on Wikipedia for concise, factual answers—when someone asks “What’s the largest [product category] company?” the voice response often originates from Wikipedia content. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, which fetch real-time information from the web to supplement AI responses, consistently cite Wikipedia as a primary source because of its structured format and reliability. Featured snippets, those boxed answers at the top of Google search results, pull from Wikipedia in approximately 70% of cases for definitional or factual queries. The cumulative effect is that a single Wikipedia mention creates multiple downstream visibility opportunities: it influences AI training, appears in knowledge panels, gets cited in AI responses, and propagates through voice search—all without requiring the user to ever click on Wikipedia itself.
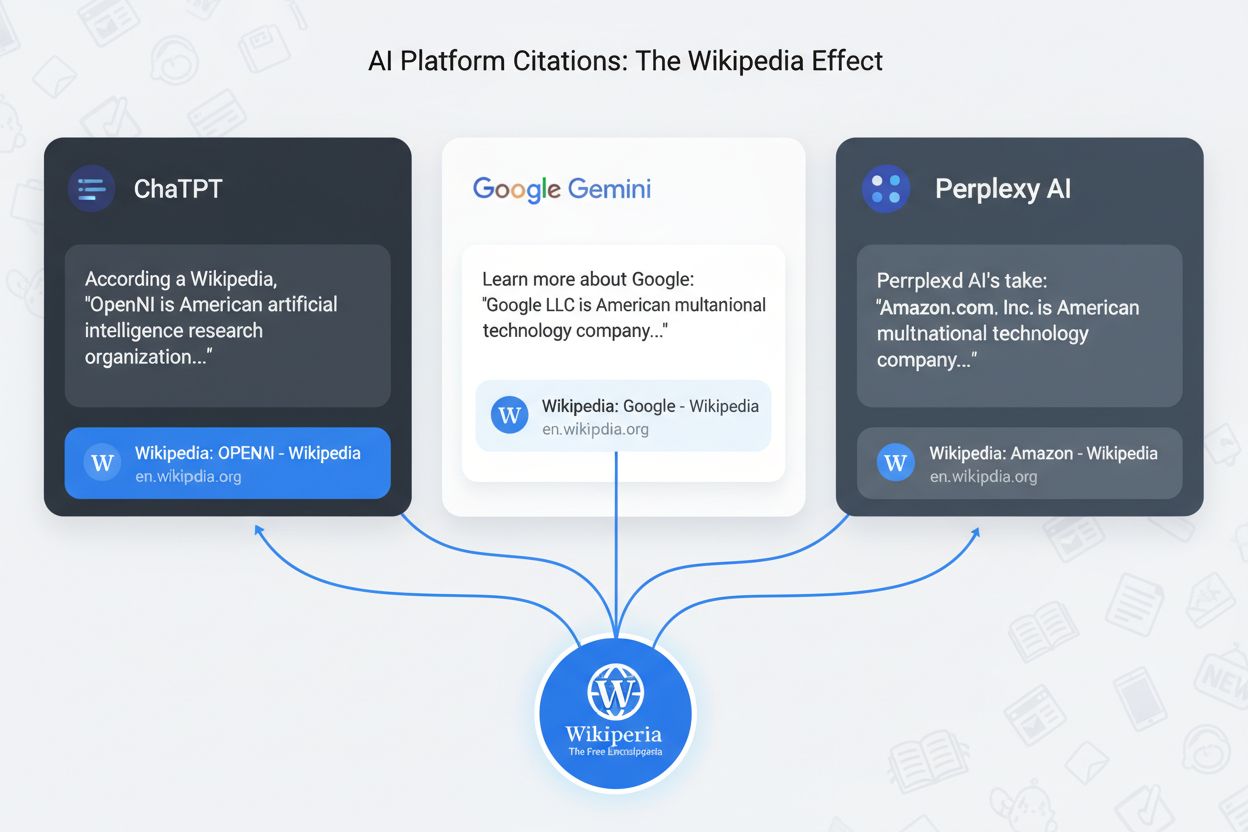
The true power of the Wikipedia Ripple Effect becomes apparent when you track how a single Wikipedia mention influences responses across different AI platforms. Each major AI system has its own relationship with Wikipedia, but all of them prioritize it as an authoritative source:
The timing of these effects varies: AI models trained on static datasets reflect Wikipedia’s content from their training cutoff date, while real-time AI search systems like Perplexity update instantly when Wikipedia changes. This means a Wikipedia update can influence AI responses across multiple platforms within hours for real-time systems, and within months for models awaiting retraining.
Understanding the Wikipedia Ripple Effect is only valuable if you can measure its impact on your brand’s AI visibility. Effective monitoring requires tracking how frequently your brand appears in AI responses across multiple platforms and comparing Wikipedia-sourced mentions to those from other sources. Tools like AmICited.com enable brands to monitor their mentions across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other AI platforms, revealing which sources AI systems cite most frequently when discussing your brand. The key metrics to track include: the frequency of Wikipedia citations versus company website citations in AI responses, the prominence and context of your brand mentions (are you mentioned as a leader, a competitor, or a minor player?), and how your Wikipedia presence compares to competitors in your space. Competitive intelligence through Wikipedia analysis reveals who dominates encyclopedic coverage in your category—companies with strong Wikipedia presence consistently receive more prominent and positive mentions in AI responses. Setting up monitoring systems allows you to track changes in real-time: when you update your Wikipedia page, you can observe how that change propagates through AI responses over days and weeks. This data-driven approach transforms Wikipedia from a vague “nice to have” into a measurable component of your AI visibility strategy.
The Wikipedia Ripple Effect represents a fundamental shift in how brands should allocate resources for digital visibility. Traditional digital marketing has focused on owned media—your website, your blog, your social channels—under the assumption that controlling these properties means controlling your narrative. The Wikipedia Ripple Effect shatters this assumption: your meticulously optimized website now matters less for AI-driven discovery than a single well-maintained Wikipedia page. This doesn’t mean abandoning website optimization, but it does mean recognizing that encyclopedic authority has become foundational to AI visibility strategy. Brands that invest in building genuine notability (through media coverage, research, thought leadership, and industry recognition) and then ensuring that notability is properly documented on Wikipedia achieve superior positioning in AI responses. The competitive advantage compounds over time: early movers who establish strong Wikipedia presence now benefit from years of accumulated citations and references, while competitors playing catch-up face an uphill battle. Integration with broader PR and content strategy becomes essential—every media placement, every industry award, every research publication should be evaluated not just for immediate impact but for its potential to strengthen Wikipedia-sourced information about your brand. The ROI of Wikipedia optimization extends beyond direct traffic; it influences how millions of users discover and evaluate your brand through AI systems they use daily.
The Wikipedia Ripple Effect will only intensify as AI becomes the primary interface for information discovery. Current trends suggest that within the next 2-3 years, AI-generated answers will surpass traditional search results as the primary way people research companies, products, and industries. As this shift accelerates, Wikipedia’s role as the foundational source for AI systems will become even more critical—brands without strong Wikipedia presence will find themselves increasingly invisible to AI-driven discovery. Emerging AI platforms continue to include Wikipedia in their training datasets and real-time retrieval systems, ensuring that the ripple effect extends to new tools as they launch. The compounding effect of Wikipedia citations means that brands establishing strong presence today will benefit from exponential visibility growth as more AI systems emerge and more users rely on AI for information. Looking ahead, the brands that dominate their categories in AI search will be those that recognized early that Wikipedia isn’t just another website—it’s the metadata layer that tells AI systems who you are and why you matter.
The Wikipedia Ripple Effect describes how citations and information from Wikipedia propagate through AI training data and influence brand mentions across multiple AI platforms simultaneously. When a brand is mentioned on Wikipedia, that information cascades through ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, Claude, and other large language models, shaping how those systems describe and reference the brand.
Every major large language model has been trained on Wikipedia content, making it one of the largest and most influential sources in AI training datasets. Wikipedia citations appear 73% more frequently than company website citations in AI responses, and AI systems prioritize Wikipedia because of its perceived neutrality, community verification, and transparent citation structure.
All major AI platforms are affected, including ChatGPT (82% Wikipedia citation rate), Claude (87%), Perplexity (83%), and Google Gemini (84%). Additionally, knowledge graphs, featured snippets, voice search assistants, and AI Overviews all rely heavily on Wikipedia as a primary source for information about brands and organizations.
You cannot directly control Wikipedia content due to strict conflict of interest policies, but you can influence it indirectly by generating third-party coverage in reliable publications that Wikipedia considers credible sources. Focus on earning media coverage, industry recognition, and thought leadership that naturally leads to Wikipedia mentions.
The timeline varies depending on the AI system. Real-time AI search systems like Perplexity update instantly when Wikipedia changes. AI models trained on static datasets reflect Wikipedia's content from their training cutoff date, with updates appearing within months when models are retrained.
For AI-driven discovery, Wikipedia is increasingly more important than your company website. While traditional website optimization remains valuable for direct traffic and conversion, Wikipedia presence has become essential for AI visibility and category positioning because AI systems prioritize encyclopedic sources over promotional content.
Use AI citation tracking tools like AmICited.com to monitor how frequently your brand appears in AI responses across multiple platforms. Track which sources AI systems cite most frequently when discussing your brand, compare Wikipedia citations to company website citations, and analyze your positioning relative to competitors.
The ROI extends beyond direct traffic to Wikipedia pages. A strong Wikipedia presence influences how millions of users discover and evaluate your brand through AI systems they use daily. Companies with strong Wikipedia coverage consistently receive more prominent and positive mentions in AI responses, leading to increased brand awareness and credibility.
Track how your Wikipedia presence influences your brand mentions across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other AI systems. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility with AmICited.

Learn how to ethically get your brand cited on Wikipedia for maximum AI visibility. Strategic guide covering policies, reliable sources, and citation strategies...

Learn ethical strategies to get your brand cited on Wikipedia. Understand Wikipedia's content policies, reliable sources, and how to leverage citations for AI v...
Learn what Wikipedia notability means for AI visibility. Understand the four pillars of notability criteria, how Wikipedia content influences AI training datase...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.