
AI Brand Sentiment: What LLMs Really Think About Your Company
Discover how LLMs perceive your brand and why AI sentiment monitoring is critical for your business. Learn to measure and improve your brand's AI perception.

AI Reputation Repair encompasses techniques and strategies for improving negative or neutral brand sentiment in AI-generated responses from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. It involves monitoring how AI systems describe your brand, identifying sources of negative sentiment, and implementing targeted fixes through content optimization, product improvements, and source authority building. Unlike traditional reputation management, AI reputation repair addresses how large language models synthesize and present brand information from diverse sources including reviews, forums, and third-party content.
AI Reputation Repair encompasses techniques and strategies for improving negative or neutral brand sentiment in AI-generated responses from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. It involves monitoring how AI systems describe your brand, identifying sources of negative sentiment, and implementing targeted fixes through content optimization, product improvements, and source authority building. Unlike traditional reputation management, AI reputation repair addresses how large language models synthesize and present brand information from diverse sources including reviews, forums, and third-party content.
AI brand sentiment refers to how often and in what tone a brand is described across AI-generated responses from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Unlike traditional search engines that primarily return brand-owned websites, modern AI engines cast a much wider net—scanning user reviews, Reddit discussions, social media posts, and third-party content to synthesize answers about brands. This fundamental shift means that negative or neutral sentiment from any source can now be amplified to millions of users in AI-generated answers. Traditional reputation management focused on controlling your own web presence and responding to reviews on known platforms; AI reputation repair requires monitoring and influencing how AI systems interpret and present your brand across all available data sources. The stakes are high: when an AI engine describes your brand negatively or neutrally, it directly impacts customer perception and purchasing decisions before they ever visit your website.
Large language models determine brand sentiment through a sophisticated process that goes far beyond simple keyword matching. When an LLM encounters text about your brand, it first converts that text into token embeddings—numerical representations that capture semantic meaning. A classification mechanism then analyzes these embeddings using attention mechanisms that examine the entire context of the text, allowing the model to understand tone shifts, sarcasm, and nuance that simpler systems would miss. The model assigns probability scores to sentiment classes (positive, neutral, negative), and the class with the highest probability becomes the output. However, this process has inherent challenges: subjectivity in language, ambiguous context, sarcasm, and cultural idioms can all lead to misclassification. Early LLMs showed a “positive bias,” but newer instruction-tuned models like GPT-4 reduce this by calibrating against more balanced training data.
| Aspect | Description | Impact on Reputation |
|---|---|---|
| Token Encoding | Converting text to numerical representations | Captures semantic meaning and context |
| Attention Mechanisms | Analyzing entire context and relationships | Reduces false negatives and improves accuracy |
| Fine-tuning | Adjusting models for balanced sentiment data | Reduces positive bias and improves fairness |
| Challenges | Sarcasm, idioms, subjectivity, ambiguity | May misclassify sentiment and harm brand perception |
Spotting sentiment problems requires a systematic, data-driven approach rather than guessing based on overall scores. Begin by examining your sentiment mix—the ratio of positive, neutral, and negative mentions across all AI platforms. A healthy brand typically shows a majority of positive mentions, moderate neutral mentions (from users researching or comparing), and minimal negative mentions. However, even small negative percentages can harm your brand if neutral sentiment is high, signaling that a large audience remains undecided. Next, break sentiment down by topic or product line to identify which specific areas confuse or disappoint customers. For example, one product category might have 5% negative sentiment while another has only 1%, revealing where to focus repair efforts. Analyze the actual user prompts that trigger negative responses—these questions reveal real pain points. Then benchmark your sentiment scores against competitors on the same topics; if competitors score significantly higher on key topics, it indicates customers perceive them more favorably. Finally, monitor sentiment regularly (weekly or monthly) to detect spikes caused by news events, product changes, or competitor campaigns, allowing you to respond quickly before misinformation spreads.
Negative sentiment in AI responses stems from several distinct causes, each requiring different repair strategies:
Confusion or lack of information: Users don’t understand your pricing structure, feature set, or how your product solves their specific problem. AI engines amplify this confusion when authoritative sources don’t clearly explain your offering.
Product or service problems: Real issues like hidden fees, poor customer service, limited availability, or quality problems generate legitimate complaints that AI systems pick up from reviews and forums.
Inaccurate or hallucinated AI outputs: LLMs sometimes cite outdated information, misinterpret facts, or invent features you don’t offer—especially when reliable sources don’t mention your brand, forcing the model to fill gaps with speculation.
Brand safety risks and negative associations: Your brand may appear alongside controversial topics or inappropriate content due to ambiguous language or unvetted third-party partnerships, damaging perception without your knowledge.
Negative citations from unreliable sources: High-influence websites that AI engines rely on may present biased, outdated, or incomplete comparisons that emphasize your weaknesses while omitting your strengths.
When negative sentiment stems from confusion or missing information, your primary strategy is creating authoritative, intent-driven content that AI systems can cite. Develop comprehensive FAQs and guides that answer the exact questions users ask in AI prompts—if sentiment analysis reveals users asking “What are the hidden fees?” or “How does pricing compare?”, publish detailed pages answering these questions with transparent pricing tables and fee breakdowns. Use structured data markup (FAQ schema, how-to schema, breadcrumb schema) on these pages, as LLMs reference structured data more confidently than unstructured text. Create niche-specific landing pages for different audience segments; if users ask “Which tool is best for remote teams?” or “What’s the best solution for startups?”, build dedicated pages addressing these specific use cases. Beyond your own site, identify the high-influence domains that AI engines cite most frequently for your industry—these sites have outsized impact on how generative models answer questions about your category. If these authoritative sites omit your brand or present outdated information, reach out to their editors with accurate data, propose guest posts, or collaborate on updated comparisons. Tools like AmICited.com help you identify exactly which domains are cited in AI responses, allowing you to prioritize outreach efforts where they’ll have maximum impact on sentiment.
When negative sentiment reflects real product or service issues, fixing sentiment requires fixing the underlying problem. Start by triangulating the issue: cross-reference negative sentiment data with the actual user prompts and complaints to understand what’s driving dissatisfaction. If multiple prompts ask about “unlimited mileage options” or “young driver fees,” investigate whether your policies genuinely lack these features or if your communication simply fails to highlight them. Improve onboarding and self-service resources by creating interactive wizards, booking tools, and transparent pricing calculators that walk users through your offering and set realistic expectations. Enhance customer support visibility by ensuring live chat, community forums, and knowledge bases are accessible to AI crawlers—when users ask about support quality, generative answers should cite your official support resources rather than third-party complaints. Communicate improvements clearly through your website and high-authority industry sites; when you solve a problem, publicize it so AI models learn about the fix. Feature positive customer stories on weak topics—if sentiment lags on a specific product category, encourage satisfied customers to share testimonials on influential review and comparison sites, using review schema markup to help AI systems capture positive sentiment. Transparency about operations, policies, and improvements builds trust that AI systems reflect in more positive sentiment.
AI hallucinations—where models invent features, misstate facts, or cite non-existent sources—occur when reliable information about your brand is scarce, forcing the model to fill gaps with speculation. Combat this by maintaining a single source of truth: consolidate all accurate information about your products, pricing, policies, and features into authoritative pages that are comprehensive, up-to-date, and easily crawlable by AI systems. Implement retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in your own chatbots and customer-facing tools, anchoring responses to verified documents rather than allowing speculation. When you discover hallucinations in AI responses, submit corrections through platform feedback channels (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google) with links to your authoritative documentation—maintaining a log of corrections helps you track improvement over time. Engage with high-influence domains cited in hallucinated responses; if a travel guide incorrectly describes your rental policies or a tech review omits your key features, contact the site owners with corrections and updated information. Provide proof points and certifications—publish independent audits, performance benchmarks, customer success metrics, and third-party certifications on your site, giving AI models authoritative evidence to cite instead of speculation. The more authoritative sources that accurately describe your brand, the less room LLMs have to hallucinate.
Protecting your brand from unintended negative associations requires proactive monitoring and governance. Implement negative keyword lists and brand safety filters when publishing ads or content—exclude terms associated with controversial topics, and regularly audit trending queries to ensure your brand doesn’t appear alongside off-brand content. Audit third-party affiliates and contributors before partnering with them; many high-influence domains cited by AI engines are third-party blogs and comparison sites, so review their broader content to avoid unintentional association with problematic material. Educate your social media and marketing teams on brand guidelines and acceptable language, creating clear escalation paths for removing unauthorized or misleading posts that could influence AI sentiment. Develop a crisis response plan for scenarios where your brand becomes linked to unsafe content—know how to quickly publish clarifications on your site, contact sources, and monitor whether corrections propagate into generative answers. Regular monitoring through tools like AmICited.com helps you detect unsafe associations early, before they become widespread in AI responses, allowing you to respond before sentiment damage becomes severe.
Effective AI reputation repair requires ongoing monitoring and measurement. Review how major AI engines describe your brand at least monthly, with weekly checks if your brand is fast-moving or highly visible. Track two critical metrics: time to detect (how quickly you spot negative sentiment changes) and time to repair (how quickly you address issues). Shorter detection times indicate strong monitoring practices, while shorter repair times show operational responsiveness. Use dedicated AI monitoring tools like AmICited.com (which tracks brand mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews), OtterlyAI (offering citation tracking and sentiment analysis), or Similarweb (providing detailed sentiment breakdowns by topic) to automate tracking and reduce manual work. These tools reveal not just whether your brand appears, but how it’s described, which sources influence sentiment, and how sentiment changes over time. Measure sentiment changes to determine whether your repair efforts are working—if you published new content addressing pricing confusion, monitor whether sentiment improves on price-related topics. Iterate based on results: if specific topics continue generating complaints despite your efforts, revisit your policies and messaging. Build accountability systems by assigning ownership of sentiment metrics to specific teams and reviewing progress regularly. Continuous improvement transforms reputation repair from a one-time project into an ongoing practice that keeps your brand perception positive as AI search evolves.
AI brand sentiment refers to how often and in what tone your brand is described across AI-generated responses from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. It matters because these AI systems now influence customer perception before they visit your website. Unlike traditional search engines that primarily return brand-owned content, AI engines synthesize information from reviews, forums, social media, and third-party sources, amplifying both positive and negative sentiment to millions of users.
Monitor your brand sentiment by regularly testing how major AI platforms describe your brand using relevant search prompts. Use dedicated AI monitoring tools like AmICited.com, OtterlyAI, or Similarweb that automatically track brand mentions, sentiment classification, and citation sources across multiple AI platforms. These tools provide dashboards showing sentiment mix (positive/neutral/negative percentages), topic-level breakdowns, and competitive benchmarking to identify where your brand perception needs improvement.
Negative sentiment typically stems from five sources: confusion or lack of information (unclear pricing, features), actual product or service problems (hidden fees, poor availability), inaccurate or hallucinated AI outputs (outdated information, false claims), brand safety risks (negative associations), and negative citations from unreliable sources. Identifying which cause drives your negative sentiment determines which repair strategy to implement.
Improve sentiment by addressing the root cause: create comprehensive FAQs and guides answering user questions, publish structured data markup to help AI systems cite your content, fix actual product problems, maintain authoritative source documentation, engage with high-influence domains that AI systems cite, and feature positive customer testimonials. Use AI monitoring tools to identify which specific topics and prompts trigger negative responses, then target your efforts where they'll have maximum impact.
High-influence domains are websites that AI engines cite most frequently when answering questions about your industry. Changes to content on these sites have outsized impact on how generative models describe your brand. If these authoritative sites omit your brand, present outdated information, or emphasize your weaknesses, AI systems will reflect that bias. Identifying and engaging with high-influence domains through outreach, guest posts, or collaboration is critical for improving brand sentiment.
Monitor your brand sentiment at least monthly, with weekly checks if your brand is fast-moving or highly visible. Regular monitoring helps you detect spikes caused by news events, product changes, or competitor campaigns before they significantly damage perception. Track two key metrics: time to detect (how quickly you spot sentiment changes) and time to repair (how quickly you address issues). Shorter detection and repair times indicate strong reputation management practices.
Yes, you can reduce hallucinations by maintaining authoritative source documentation on your website, submitting corrections through platform feedback channels (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google) with links to verified information, and engaging with high-influence domains to update their content. Implement retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in your own tools to anchor responses to verified documents. The more authoritative sources that accurately describe your brand, the less room LLMs have to hallucinate.
Dedicated AI monitoring tools are essential for effective reputation management. AmICited.com specializes in tracking brand mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews with sentiment analysis. OtterlyAI offers comprehensive citation tracking and competitive benchmarking. Similarweb provides detailed sentiment breakdowns by topic and competitor comparison. These tools automate monitoring, identify sentiment drivers, and measure whether your repair efforts are working, saving significant time compared to manual tracking.
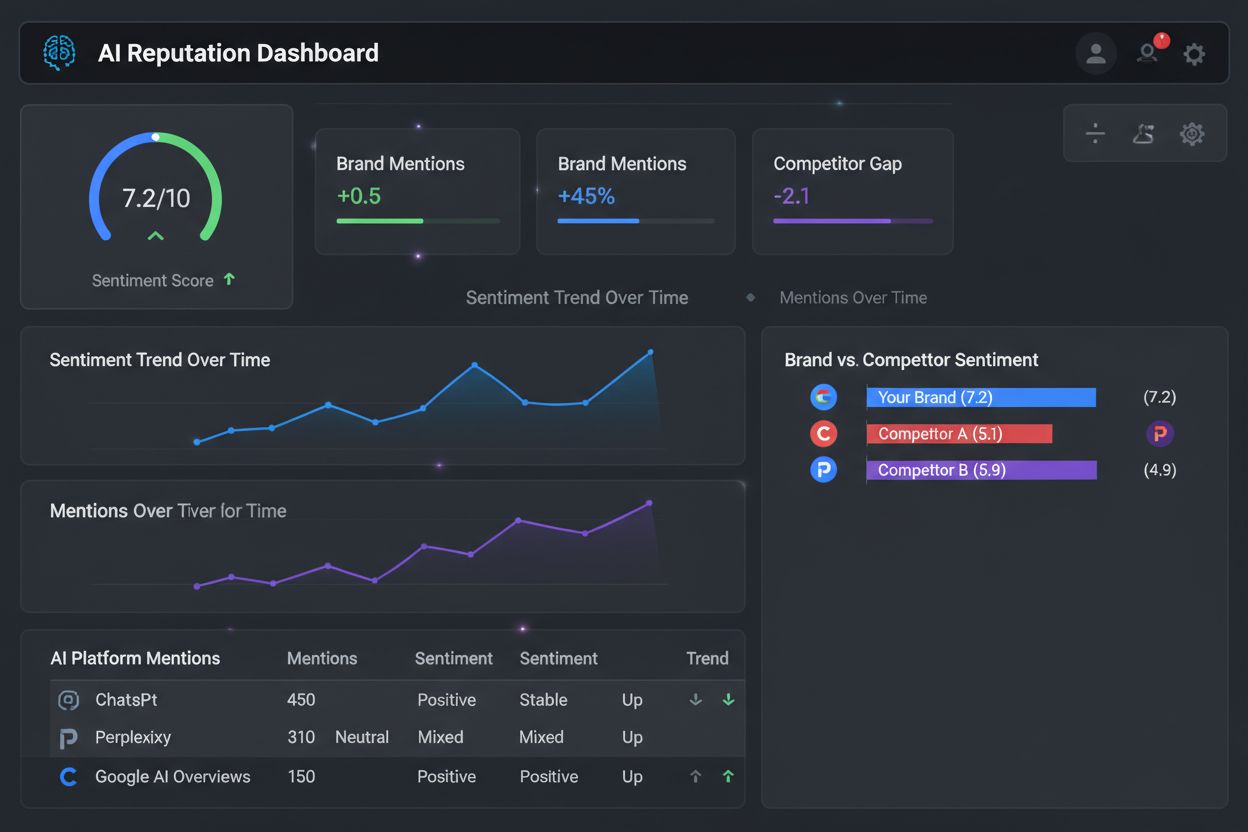
Track how your brand appears in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Get real-time alerts when sentiment changes and identify opportunities to improve your AI reputation.

Discover how LLMs perceive your brand and why AI sentiment monitoring is critical for your business. Learn to measure and improve your brand's AI perception.
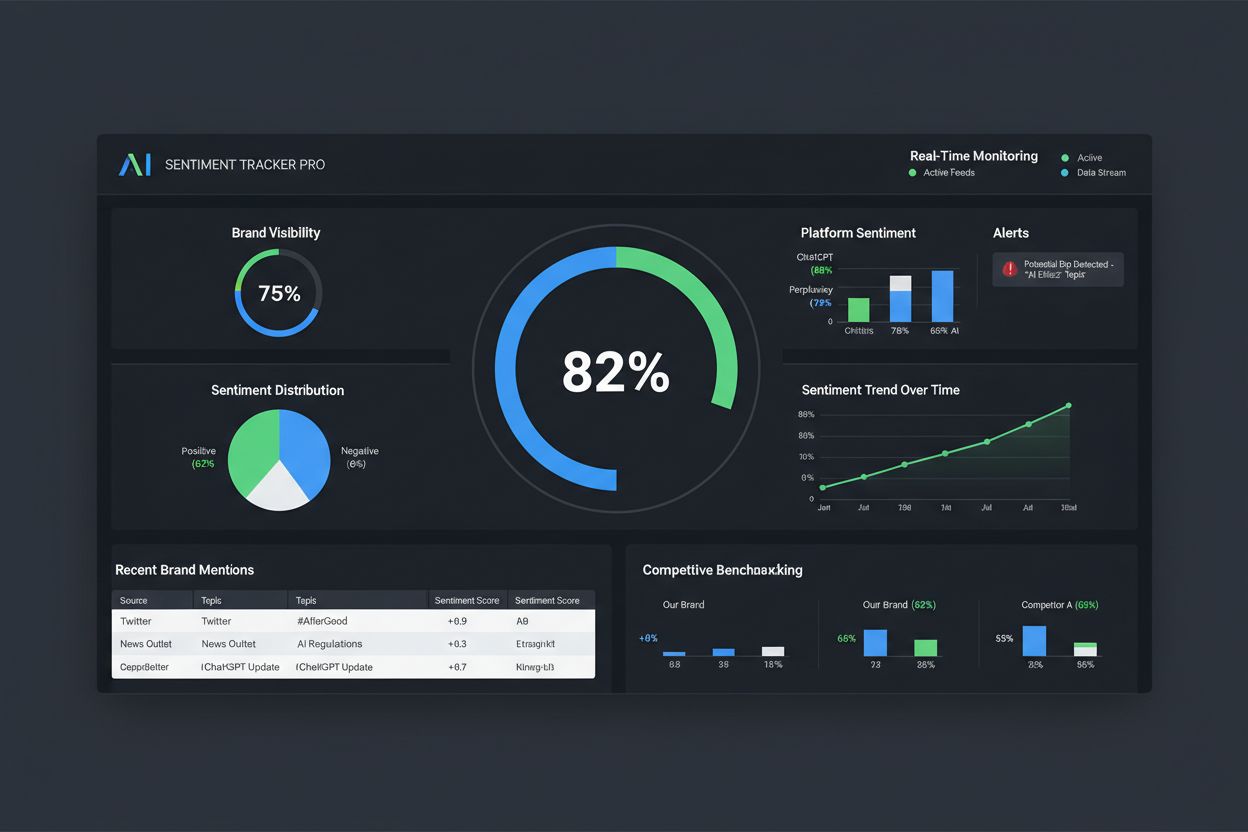
Learn how to track and improve brand sentiment in AI responses across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Discover why AI sentiment differs from traditional mon...

Learn how to set up AI brand monitoring to track your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Complete guide with tools, strategies, and best...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.