
What is the noai meta tag and how does it protect your content from AI?
Learn about the noai meta tag, how it works to prevent AI training data collection, its limitations, and how to implement it on your website to protect your con...

An HTML meta tag that signals to AI training systems and web crawlers that website content should not be used for machine learning model training. Originally introduced by DeviantArt, it serves as a content protection mechanism and opt-out signal for creators concerned about unauthorized AI data collection.
An HTML meta tag that signals to AI training systems and web crawlers that website content should not be used for machine learning model training. Originally introduced by DeviantArt, it serves as a content protection mechanism and opt-out signal for creators concerned about unauthorized AI data collection.
The NoAI meta tag is a content protection mechanism implemented as an HTML meta tag that signals to AI training systems and web crawlers that a website’s content should not be used for machine learning model training. Originally introduced by DeviantArt in September 2022, the NoAI directive emerged as a grassroots response to concerns about artists’ work being scraped and used to train generative AI models without consent or compensation. The meta tag works by adding a simple HTML declaration to a webpage’s header, communicating a clear preference to AI systems that the content is off-limits for training purposes. While not legally binding in most jurisdictions, the NoAI tag represents an important opt-out mechanism for creators seeking to protect their intellectual property in an era of increasingly aggressive AI data collection.
Web crawlers (also called bots, spiders, or scrapers) are automated software programs that systematically browse the internet, following links and downloading content to index, analyze, or collect data for various purposes. These crawlers operate by reading the robots.txt file located in a website’s root directory, which contains instructions about which areas of the site should or should not be accessed by automated visitors. The robots.txt file uses specific directives like User-agent, Disallow, and Allow to communicate crawler permissions, though compliance is entirely voluntary and depends on whether the crawler’s developer chooses to respect these guidelines. Beyond robots.txt, websites can communicate preferences through HTTP headers and meta tags, which provide additional signals about content usage rights and restrictions. Different types of crawlers have varying levels of respect for these signals:
| Crawler Type | robots.txt Compliance | Meta Tag Respect | AI Training Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search Engines | High | High | Limited |
| AI Training Bots | Medium | Medium | Yes |
| Commercial Scrapers | Low | Low | Varies |
| Academic Bots | High | Medium | Research Only |
| Malicious Bots | None | None | Unrestricted |
The noai and noimageai directives serve related but distinct purposes in content protection, with the key difference lying in their scope and specificity. The noai directive is a broader signal indicating that all content on a page—including text, images, code, and other media—should not be used for AI training purposes, making it suitable for websites with mixed content types or those seeking comprehensive protection. The noimageai directive, by contrast, specifically targets only image content, allowing text and other non-image materials to potentially be used for training while protecting visual assets from AI model training. This distinction is particularly important for websites that may want to allow text-based AI indexing (for search engines or accessibility) while protecting their visual content from being used in generative image models. Here are the implementation differences:
<!-- Comprehensive protection for all content -->
<meta name="robots" content="noai">
<!-- Specific protection for images only -->
<meta name="robots" content="noimageai">
<!-- Combined approach for maximum clarity -->
<meta name="robots" content="noai, noimageai">
The NoAI meta tag can be implemented through multiple methods, each with different advantages depending on your technical infrastructure and specific needs. The most straightforward approach is adding the meta tag directly to your HTML <head> section, which applies the directive to individual pages and can be customized per-page if needed. For websites with many pages or those seeking a site-wide solution, implementing the directive through HTTP response headers provides a more scalable approach that applies uniformly across all content without requiring individual page modifications. Additionally, the robots.txt file can include directives targeting specific AI crawlers, though this method is less standardized than meta tags or headers. Here are the three primary implementation methods:
<!-- Method 1: HTML Meta Tag (most common) -->
<head>
<meta name="robots" content="noai">
</head>
# Method 2: robots.txt directive
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
X-Robots-Tag: noai
# Method 3: HTTP Header (via .htaccess or server configuration)
X-Robots-Tag: noai
For Apache servers, add to .htaccess:
<FilesMatch "\.(html|php)$">
Header set X-Robots-Tag "noai"
</FilesMatch>
For Nginx servers, add to your server block:
add_header X-Robots-Tag "noai" always;
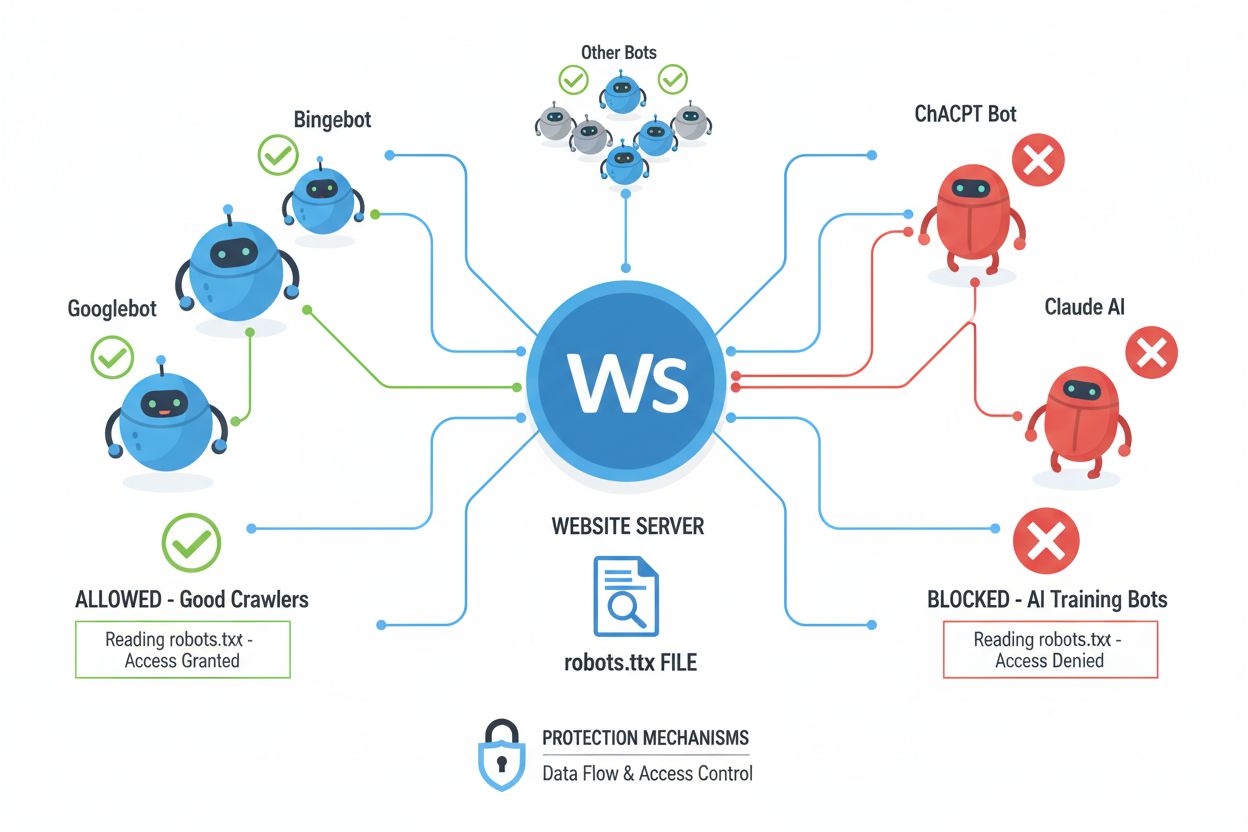
While the NoAI meta tag represents an important step toward content protection, it operates on an honor system that depends entirely on whether AI developers and data scrapers choose to respect the signal. Major AI companies like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic have begun respecting NoAI directives in their crawlers, but bad actors and rogue scrapers frequently ignore these signals, making the tag ineffective against determined data thieves. The effectiveness of NoAI is further limited by the fact that it only prevents future training on content; it cannot remove data already collected and used in existing models, nor does it provide legal recourse if violated. Compliance rates vary significantly across different AI systems, with some respecting the directive while others deliberately circumvent it, making NoAI a useful but incomplete solution. The tag also provides no protection against direct downloads, screenshots, or manual copying of content, and it cannot prevent use of your content by competitors who simply ignore the directive. For these reasons, NoAI should be considered one layer of a comprehensive content protection strategy rather than a complete solution.
The NoAI meta tag has achieved significant adoption among major AI companies and platforms, with OpenAI, Google, and Stability AI publicly committing to respect the directive in their training pipelines. DeviantArt’s implementation of NoAI has influenced broader industry conversations about ethical AI development and creator consent, leading to increased awareness among both AI developers and content creators. However, adoption remains inconsistent across the industry, with smaller AI companies, academic researchers, and commercial scrapers showing varying levels of compliance. The emergence of competing standards like C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) and discussions around machine-readable rights expressions suggest the industry is moving toward more sophisticated, legally-backed content protection mechanisms beyond voluntary meta tags. Industry organizations and standards bodies are actively working to formalize these protections, with the expectation that future AI regulation may require explicit compliance with content creator preferences, potentially transforming NoAI from a voluntary signal into a legally enforceable requirement.
Implementing NoAI protection should be part of a layered approach to content security rather than a standalone solution, combining technical, legal, and monitoring strategies for comprehensive protection. To maximize effectiveness, consider these best practices:
Additionally, maintain regular audits of your content protection implementation to ensure all pages include the appropriate directives, and consider using automated tools to scan for your content in public AI datasets and training repositories. Document your NoAI implementation as part of your content governance policy, and communicate these protections to your audience so they understand what steps you’re taking to protect their work if you’re a platform hosting user-generated content.
The noai directive protects all content types (text, images, code) from AI training, while noimageai specifically protects only image content. Use noai for comprehensive protection and noimageai when you want to allow text indexing but protect visual assets from generative image models.
No, the NoAI meta tag operates on an honor system and depends on whether AI developers choose to respect it. Major companies like OpenAI and Google respect it, but bad actors and rogue scrapers frequently ignore these signals, making it one layer of protection rather than a complete solution.
You can implement it three ways: add the HTML meta tag to your page header, set HTTP response headers on your server, or include directives in your robots.txt file. The HTML meta tag method is most common and straightforward for most website owners.
Major AI companies including OpenAI (ChatGPT), Google, Anthropic (Claude), and Stability AI have publicly committed to respecting NoAI directives in their training pipelines. However, compliance varies across smaller AI companies, academic researchers, and commercial scrapers.
Yes, you can use both simultaneously for maximum effectiveness. The NoAI meta tag and robots.txt directives work together to communicate your content protection preferences to different types of crawlers and systems.
Combine NoAI with other protection methods including HTTP headers, robots.txt rules, watermarking, access controls, and legal terms of service. Monitor your content in AI datasets and consider using tools to track unauthorized use.
While widely adopted by major AI companies, NoAI is not yet a formal W3C standard. However, industry organizations are working on more sophisticated standards like C2PA and machine-readable rights expressions that may eventually provide legal backing.
NoAI is most effective when combined with other methods like robots.txt, HTTP headers, watermarking, access controls, and legal protections. No single method provides complete protection, so a layered approach is recommended for comprehensive content security.
Track which AI systems are citing your brand and content with AmICited's AI monitoring platform. Know exactly how your work is being used by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems.

Learn about the noai meta tag, how it works to prevent AI training data collection, its limitations, and how to implement it on your website to protect your con...

Community discussion on the noai meta tag and whether it effectively protects content from AI training. Users share experiences and limitations of this approach...
Learn how to implement noai and noimageai meta tags to control AI crawler access to your website content. Complete guide to AI access control headers and implem...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.