
WAF Rules for AI Crawlers: Beyond Robots.txt
Learn how Web Application Firewalls provide advanced control over AI crawlers beyond robots.txt. Implement WAF rules to protect your content from unauthorized A...
The strategic practice of selectively allowing or blocking AI crawlers to control how content is used for training versus real-time retrieval. This involves using robots.txt files, server-level controls, and monitoring tools to manage which AI systems can access your content and for what purposes.
The strategic practice of selectively allowing or blocking AI crawlers to control how content is used for training versus real-time retrieval. This involves using robots.txt files, server-level controls, and monitoring tools to manage which AI systems can access your content and for what purposes.
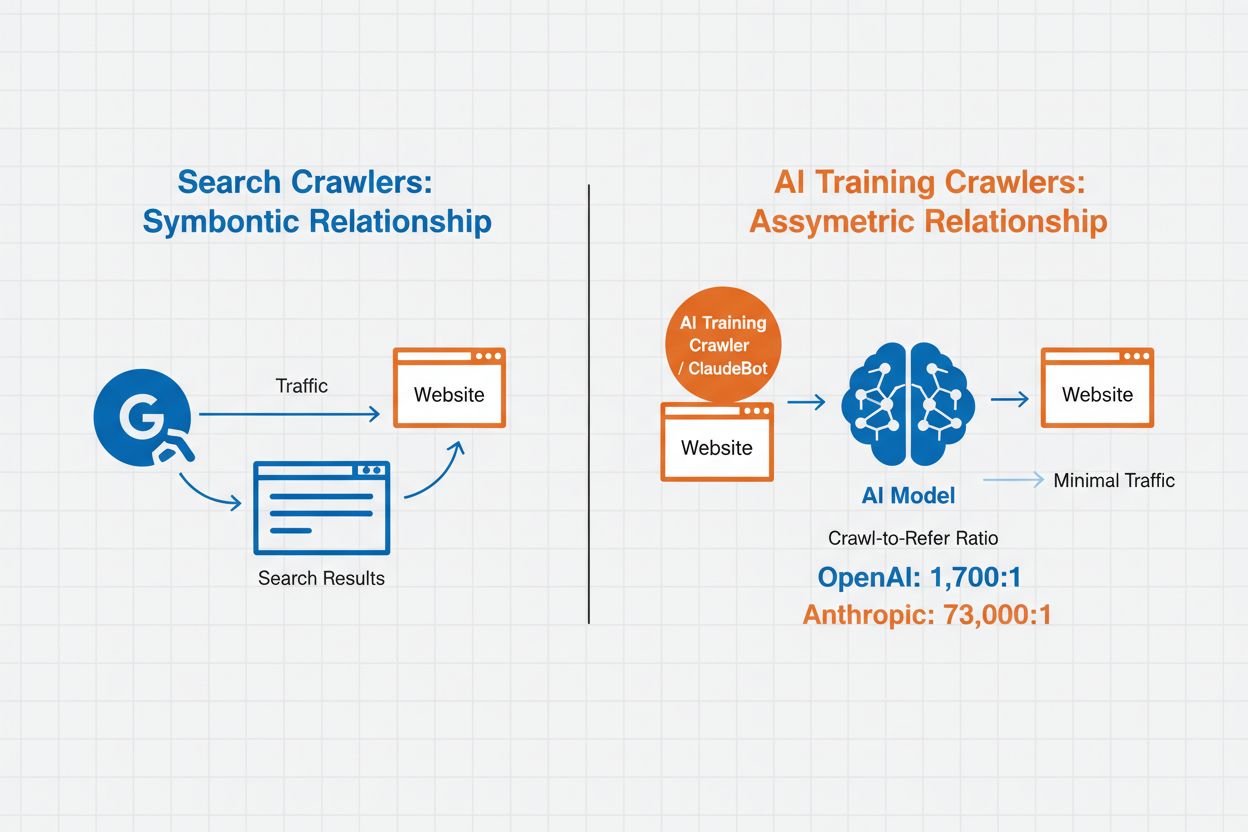
AI Crawler Management refers to the practice of controlling and monitoring how artificial intelligence systems access and use website content for training and search purposes. Unlike traditional search engine crawlers that index content for web search results, AI crawlers are specifically designed to gather data for training large language models or powering AI-powered search features. The scale of this activity varies dramatically between organizations—OpenAI’s crawlers operate at a 1,700:1 crawl-to-refer ratio, meaning they access content 1,700 times for every reference they provide, while Anthropic’s ratio reaches 73,000:1, highlighting the massive data consumption required to train modern AI systems. Effective crawler management allows website owners to decide whether their content contributes to AI training, appears in AI search results, or remains protected from automated access.
AI crawlers fall into three distinct categories based on their purpose and data usage patterns. Training crawlers are designed to gather data for machine learning model development, consuming vast amounts of content to improve AI capabilities. Search and citation crawlers index content to power AI-driven search features and provide attribution in AI-generated responses, enabling users to discover your content through AI interfaces. User-triggered crawlers operate on-demand when users interact with AI tools, such as when a ChatGPT user uploads a document or requests analysis of a specific webpage. Understanding these categories helps you make informed decisions about which crawlers to allow or block based on your content strategy and business goals.
| Crawler Type | Purpose | Examples | Training Data Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Model development and improvement | GPTBot, ClaudeBot | Yes |
| Search/Citation | AI search results and attribution | Google-Extended, OAI-SearchBot, PerplexityBot | Varies |
| User-Triggered | On-demand content analysis | ChatGPT-User, Meta-ExternalAgent, Amazonbot | Context-specific |
AI crawler management directly impacts your website’s traffic, revenue, and content value. When crawlers consume your content without compensation, you lose the opportunity to benefit from that traffic through referrals, ad impressions, or user engagement. Websites have reported significant traffic reductions as users find answers directly in AI-generated responses rather than clicking through to the original source, effectively cutting off referral traffic and associated ad revenue. Beyond financial implications, there are important legal and ethical considerations—your content represents intellectual property, and you have the right to control how it’s used and whether you receive attribution or compensation. Additionally, allowing unrestricted crawler access can increase server load and bandwidth costs, particularly from crawlers with aggressive crawl rates that don’t respect rate-limiting directives.
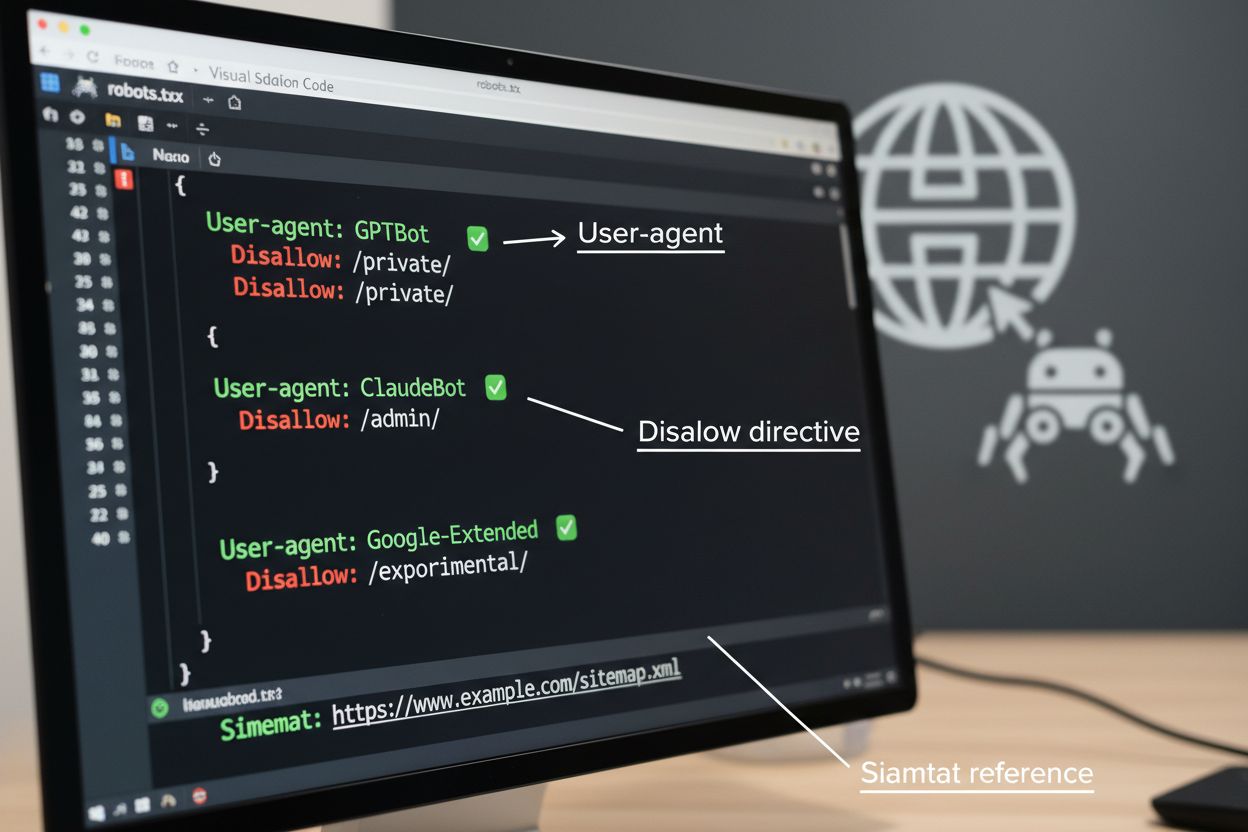
The robots.txt file is the foundational tool for managing crawler access, placed in your website’s root directory to communicate crawling preferences to automated agents. This file uses User-agent directives to target specific crawlers and Disallow or Allow rules to permit or restrict access to particular paths and resources. However, robots.txt has important limitations—it’s a voluntary standard that relies on crawler compliance, and malicious or poorly-designed bots may ignore it entirely. Additionally, robots.txt doesn’t prevent crawlers from accessing publicly available content; it merely requests that they respect your preferences. For these reasons, robots.txt should be part of a layered approach to crawler management rather than your only defense.
# Block AI training crawlers
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ClaudeBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Google-Extended
Disallow: /
User-agent: Meta-ExternalAgent
Disallow: /
# Allow search engines
User-agent: Googlebot
Allow: /
User-agent: Bingbot
Allow: /
# Default rule for other crawlers
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Beyond robots.txt, several advanced techniques provide stronger enforcement and more granular control over crawler access. These methods work at different layers of your infrastructure and can be combined for comprehensive protection:
The decision to block AI crawlers involves important trade-offs between content protection and discoverability. Blocking all AI crawlers eliminates the possibility of your content appearing in AI search results, AI-powered summaries, or being cited by AI tools—potentially reducing visibility to users who discover content through these emerging channels. Conversely, allowing unrestricted access means your content fuels AI training without compensation and may reduce referral traffic as users get answers directly from AI systems. A strategic approach involves selective blocking: allowing citation-based crawlers like OAI-SearchBot and PerplexityBot that drive referral traffic while blocking training crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot that consume data without attribution. You might also consider allowing Google-Extended to maintain visibility in Google AI Overviews, which can drive significant traffic, while blocking competitors’ training crawlers. The optimal strategy depends on your content type, business model, and audience—news sites and publishers may prioritize blocking, while educational content creators might benefit from broader AI visibility.
Implementing crawler controls is only effective if you verify that crawlers actually comply with your directives. Server log analysis is the primary method for monitoring crawler activity—examine your access logs for User-Agent strings and request patterns to identify which crawlers are accessing your site and whether they respect your robots.txt rules. Many crawlers claim compliance but continue accessing blocked paths, making ongoing monitoring essential. Tools like Cloudflare Radar provide real-time visibility into traffic patterns and can help identify suspicious or non-compliant crawler behavior. Set up automated alerts for attempts to access blocked resources, and periodically audit your logs to catch new crawlers or changing patterns that might indicate evasion attempts.
Implementing effective AI crawler management requires a systematic approach that balances protection with strategic visibility. Follow these eight steps to establish a comprehensive crawler management strategy:
AmICited.com provides a specialized platform for monitoring how AI systems reference and use your content across different models and applications. The service offers real-time tracking of your citations in AI-generated responses, helping you understand which crawlers are most actively using your content and how frequently your work appears in AI outputs. By analyzing crawler patterns and citation data, AmICited.com enables data-driven decisions about your crawler management strategy—you can see exactly which crawlers deliver value through citations and referrals versus those that consume content without attribution. This intelligence transforms crawler management from a defensive practice into a strategic tool for optimizing your content’s visibility and impact in the AI-powered web.
Training crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot collect content to build datasets for large language model development, consuming your content without providing referral traffic. Search crawlers like OAI-SearchBot and PerplexityBot index content for AI-powered search results and may send visitors back to your site through citations. Blocking training crawlers protects your content from being incorporated into AI models, while blocking search crawlers may reduce your visibility in AI-powered discovery platforms.
No. Blocking AI training crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and CCBot does not affect your Google or Bing search rankings. Traditional search engines use different crawlers (Googlebot, Bingbot) that operate independently from AI training bots. Only block traditional search crawlers if you want to disappear from search results entirely, which would harm your SEO.
Examine your server access logs to identify crawler User-Agent strings. Look for entries containing 'bot,' 'crawler,' or 'spider' in the User-Agent field. Tools like Cloudflare Radar provide real-time visibility into which AI crawlers are accessing your site and their traffic patterns. You can also use analytics platforms that differentiate bot traffic from human visitors.
Yes. robots.txt is an advisory standard that relies on crawler compliance—it's not enforceable. Well-behaved crawlers from major companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google generally respect robots.txt directives, but some crawlers ignore them entirely. For stronger protection, implement server-level blocking via .htaccess, firewall rules, or IP-based restrictions.
This depends on your business priorities. Blocking all training crawlers protects your content from being incorporated into AI models while potentially allowing search crawlers that may drive referral traffic. Many publishers use selective blocking that targets training crawlers while allowing search and citation crawlers. Consider your content type, traffic sources, and monetization model when deciding your strategy.
Review and update your crawler management policy quarterly at minimum. New AI crawlers emerge regularly, and existing crawlers update their user agents without notice. Track resources like the ai.robots.txt project on GitHub for community-maintained lists, and check your server logs monthly to identify new crawlers hitting your site.
AI crawlers can significantly impact your traffic and revenue. When users get answers directly from AI systems instead of visiting your site, you lose referral traffic and associated ad impressions. Research shows crawl-to-refer ratios as high as 73,000:1 for some AI platforms, meaning they access your content thousands of times for every visitor they send back. Blocking training crawlers can protect your traffic, while allowing search crawlers may provide some referral benefits.
Check your server logs to see if blocked crawlers still appear in your access logs. Use testing tools like Google Search Console's robots.txt tester or Merkle's Robots.txt Tester to validate your configuration. Access your robots.txt file directly at yoursite.com/robots.txt to verify the content is correct. Monitor your logs regularly to catch crawlers that should be blocked but still appear.
AmICited.com tracks real-time AI references to your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems. Make data-driven decisions about your crawler management strategy.

Learn how Web Application Firewalls provide advanced control over AI crawlers beyond robots.txt. Implement WAF rules to protect your content from unauthorized A...

Learn how to block or allow AI crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot using robots.txt, server-level blocking, and advanced protection methods. Complete technical g...

Learn how AI crawlers prioritize pages using crawl capacity and demand. Understand crawl budget optimization for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI, and Claude.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.