
How to Handle Duplicate Content for AI Search Engines
Learn how to manage and prevent duplicate content when using AI tools. Discover canonical tags, redirects, detection tools, and best practices for maintaining u...
AI Deduplication Logic refers to the automated processes and algorithms that AI systems use to identify, analyze, and eliminate redundant or duplicate information from multiple sources. These systems employ machine learning, natural language processing, and similarity matching techniques to recognize identical or highly similar content across diverse data repositories, ensuring data quality, reducing storage costs, and improving decision-making accuracy.
AI Deduplication Logic refers to the automated processes and algorithms that AI systems use to identify, analyze, and eliminate redundant or duplicate information from multiple sources. These systems employ machine learning, natural language processing, and similarity matching techniques to recognize identical or highly similar content across diverse data repositories, ensuring data quality, reducing storage costs, and improving decision-making accuracy.
AI deduplication logic is a sophisticated algorithmic process that identifies and eliminates duplicate or near-duplicate records from large datasets using artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques. This technology automatically detects when multiple entries represent the same entity—whether that’s a person, product, document, or piece of information—despite variations in formatting, spelling, or presentation. The core purpose of deduplication is to maintain data integrity and prevent redundancy that can skew analysis, inflate storage costs, and compromise decision-making accuracy. In today’s data-driven world, where organizations process millions of records daily, effective deduplication has become essential for operational efficiency and reliable insights.
AI deduplication employs multiple complementary techniques to identify and group similar records with remarkable precision. The process begins by analyzing data attributes—such as names, addresses, email addresses, and other identifiers—and comparing them against established similarity thresholds. Modern deduplication systems use a combination of phonetic matching, string similarity algorithms, and semantic analysis to catch duplicates that traditional rule-based systems might miss. The system assigns similarity scores to potential matches, clustering records that exceed the configured threshold into groups representing the same entity. Users maintain control over the inclusiveness level of deduplication, allowing them to adjust sensitivity based on their specific use case and tolerance for false positives.
| Method | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Phonetic Similarity | Groups strings that sound alike (e.g., “Smith” vs “Smyth”) | Name variations, phonetic confusion |
| Spelling Similarity | Groups strings similar in spelling | Typos, minor spelling variations |
| TFIDF Similarity | Applies term frequency-inverse document frequency algorithm | General text matching, document similarity |
The deduplication engine processes records through multiple passes, first identifying obvious matches before progressively examining more subtle variations. This layered approach ensures comprehensive coverage while maintaining computational efficiency, even when processing datasets containing millions of records.
Modern AI deduplication leverages vector embeddings and semantic analysis to understand the meaning behind data rather than just comparing surface-level characteristics. Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables systems to comprehend context and intent, allowing them to recognize that “Robert,” “Bob,” and “Rob” all refer to the same person despite their different forms. Fuzzy matching algorithms calculate the edit distance between strings, identifying records that differ by only a few characters—critical for catching typos and transcription errors. The system also analyzes metadata such as timestamps, creation dates, and modification history to provide additional confidence signals when determining whether records are duplicates. Advanced implementations incorporate machine learning models trained on labeled datasets, continuously improving accuracy as they process more data and receive feedback on deduplication decisions.
AI deduplication logic has become indispensable across virtually every sector that manages large-scale data operations. Organizations leverage this technology to maintain clean, reliable datasets that drive accurate analytics and informed decision-making. The practical applications span numerous critical business functions:

These applications demonstrate how deduplication directly impacts compliance, fraud prevention, and operational integrity across diverse industries.
The financial and operational benefits of AI deduplication are substantial and measurable. Organizations can significantly reduce storage costs by eliminating redundant data, with some implementations achieving 20-40% reductions in storage requirements. Improved data quality directly translates to better analytics and decision-making, as analysis based on clean data produces more reliable insights and forecasts. Research indicates that data scientists spend approximately 80% of their time on data preparation, with duplicate records being a major contributor to this burden—deduplication automation reclaims valuable analyst time for higher-value work. Studies show that 10-30% of records in typical databases contain duplicates, representing a significant source of inefficiency and error. Beyond cost reduction, deduplication strengthens compliance and regulatory adherence by ensuring accurate record-keeping and preventing duplicate submissions that could trigger audits or penalties. The operational efficiency gains extend to faster query performance, reduced computational overhead, and improved system reliability.
Despite its sophistication, AI deduplication is not without challenges and limitations that organizations must carefully manage. False positives—incorrectly identifying distinct records as duplicates—can lead to data loss or merged records that should remain separate, while false negatives allow actual duplicates to slip through undetected. Deduplication becomes exponentially more complex when dealing with multi-format data spanning different systems, languages, and data structures, each with unique formatting conventions and encoding standards. Privacy and security concerns arise when deduplication requires analyzing sensitive personal information, necessitating robust encryption and access controls to protect data during the matching process. The accuracy of deduplication systems remains fundamentally limited by the quality of input data; garbage in produces garbage out, and incomplete or corrupted records can confound even the most advanced algorithms.
AI deduplication has become a critical component of modern AI answer monitoring platforms and search systems that aggregate information from multiple sources. When AI systems synthesize responses from numerous documents and sources, deduplication ensures that the same information isn’t counted multiple times, which would artificially inflate confidence scores and skew relevance rankings. Source attribution becomes more meaningful when deduplication removes redundant sources, allowing users to see the true diversity of evidence supporting an answer. Platforms like AmICited.com leverage deduplication logic to provide transparent, accurate source tracking by identifying when multiple sources contain essentially identical information and consolidating them appropriately. This prevents AI responses from appearing to have broader support than they actually do, maintaining the integrity of source attribution and answer credibility. By filtering out duplicate sources, deduplication improves the quality of AI search results and ensures that users receive genuinely diverse perspectives rather than variations of the same information repeated across multiple sources. The technology ultimately strengthens trust in AI systems by providing cleaner, more honest representations of the evidence underlying AI-generated answers.
AI deduplication and data compression both reduce data volume, but they work differently. Deduplication identifies and removes exact or near-duplicate records, keeping only one instance and replacing others with references. Data compression, by contrast, encodes data more efficiently without removing duplicates. Deduplication works at the macro level (entire files or records), while compression works at the micro level (individual bits and bytes). For organizations with significant duplicate data, deduplication typically provides greater storage savings.
AI uses multiple sophisticated techniques to catch non-exact duplicates. Phonetic algorithms recognize names that sound alike (e.g., 'Smith' vs 'Smyth'). Fuzzy matching calculates edit distance to find records differing by only a few characters. Vector embeddings convert text into mathematical representations that capture semantic meaning, allowing the system to recognize paraphrased content. Machine learning models trained on labeled datasets learn patterns of what constitutes a duplicate in specific contexts. These techniques work together to identify duplicates despite variations in spelling, formatting, or presentation.
Deduplication can significantly reduce storage costs by eliminating redundant data. Organizations typically achieve 20-40% reductions in storage requirements after implementing effective deduplication. These savings compound over time as new data is continuously deduplicated. Beyond direct storage cost reduction, deduplication also reduces expenses associated with data management, backup operations, and system maintenance. For large enterprises processing millions of records, these savings can amount to hundreds of thousands of dollars annually, making deduplication a high-ROI investment.
Yes, modern AI deduplication systems can work across different file formats, though it requires more sophisticated processing. The system must first normalize data from various formats (PDFs, Word documents, spreadsheets, databases, etc.) into a comparable structure. Advanced implementations use optical character recognition (OCR) for scanned documents and format-specific parsers to extract meaningful content. However, deduplication accuracy may vary depending on format complexity and data quality. Organizations typically achieve best results when deduplication is applied to structured data within consistent formats, though cross-format deduplication is increasingly feasible with modern AI techniques.
Deduplication improves AI search results by ensuring that relevance rankings reflect genuine diversity of sources rather than variations of the same information. When multiple sources contain identical or near-identical content, deduplication consolidates them, preventing artificial inflation of confidence scores. This provides users with cleaner, more honest representations of evidence supporting AI-generated answers. Deduplication also improves search performance by reducing the volume of data the system must process, enabling faster query responses. By filtering out redundant sources, AI systems can focus on genuinely diverse perspectives and information, ultimately delivering higher-quality, more trustworthy results.
False positives occur when deduplication incorrectly identifies distinct records as duplicates and merges them. For example, merging records for 'John Smith' and 'Jane Smith' who are different people but share a surname. False positives are problematic because they result in permanent data loss—once records are merged, recovering the original distinct information becomes difficult or impossible. In critical applications like healthcare or financial services, false positives can have serious consequences, including incorrect medical histories or fraudulent transactions. Organizations must carefully calibrate deduplication sensitivity to minimize false positives, often accepting some false negatives (missed duplicates) as the safer trade-off.
Deduplication is essential for AI content monitoring platforms like AmICited that track how AI systems reference brands and sources. When monitoring AI responses across multiple platforms (GPTs, Perplexity, Google AI), deduplication prevents the same source from being counted multiple times if it appears in different AI systems or in different formats. This ensures accurate attribution and prevents inflated visibility metrics. Deduplication also helps identify when AI systems are drawing from a limited set of sources despite appearing to have diverse evidence. By consolidating duplicate sources, content monitoring platforms provide clearer insights into which unique sources are actually influencing AI responses.
Metadata—information about data such as creation dates, modification timestamps, author information, and file properties—plays a crucial role in duplicate detection. Metadata helps establish the lifecycle of records, revealing when documents were created, updated, or accessed. This temporal information helps distinguish between legitimate versions of evolving documents and true duplicates. Author information and department associations provide context about record origin and purpose. Access patterns indicate whether documents are actively used or obsolete. Advanced deduplication systems integrate metadata analysis with content analysis, using both signals to make more accurate duplicate determinations and to identify which version of a duplicate should be retained as the authoritative source.
AmICited tracks how AI systems like GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI reference your brand across multiple sources. Ensure accurate source attribution and prevent duplicate content from skewing your AI visibility.

Learn how to manage and prevent duplicate content when using AI tools. Discover canonical tags, redirects, detection tools, and best practices for maintaining u...
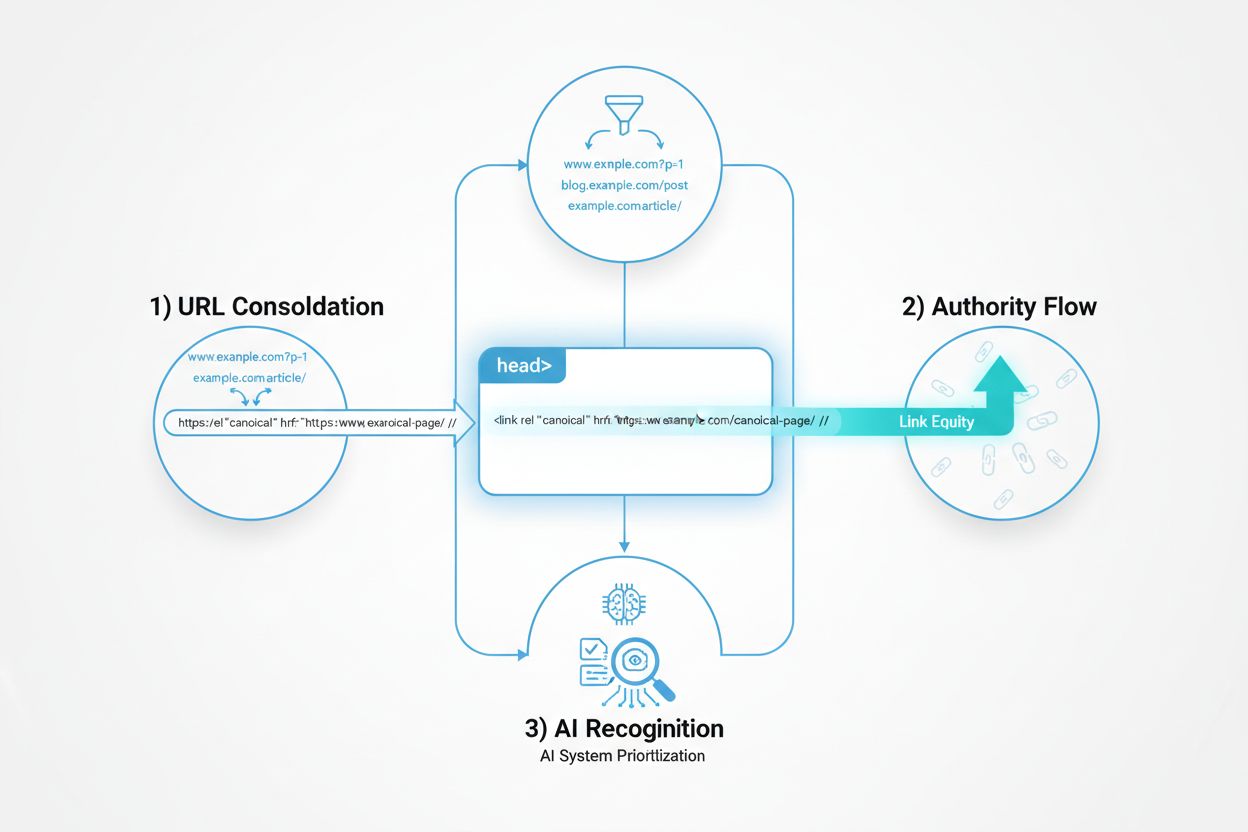
Learn how canonical URLs prevent duplicate content problems in AI search systems. Discover best practices for implementing canonicals to improve AI visibility a...
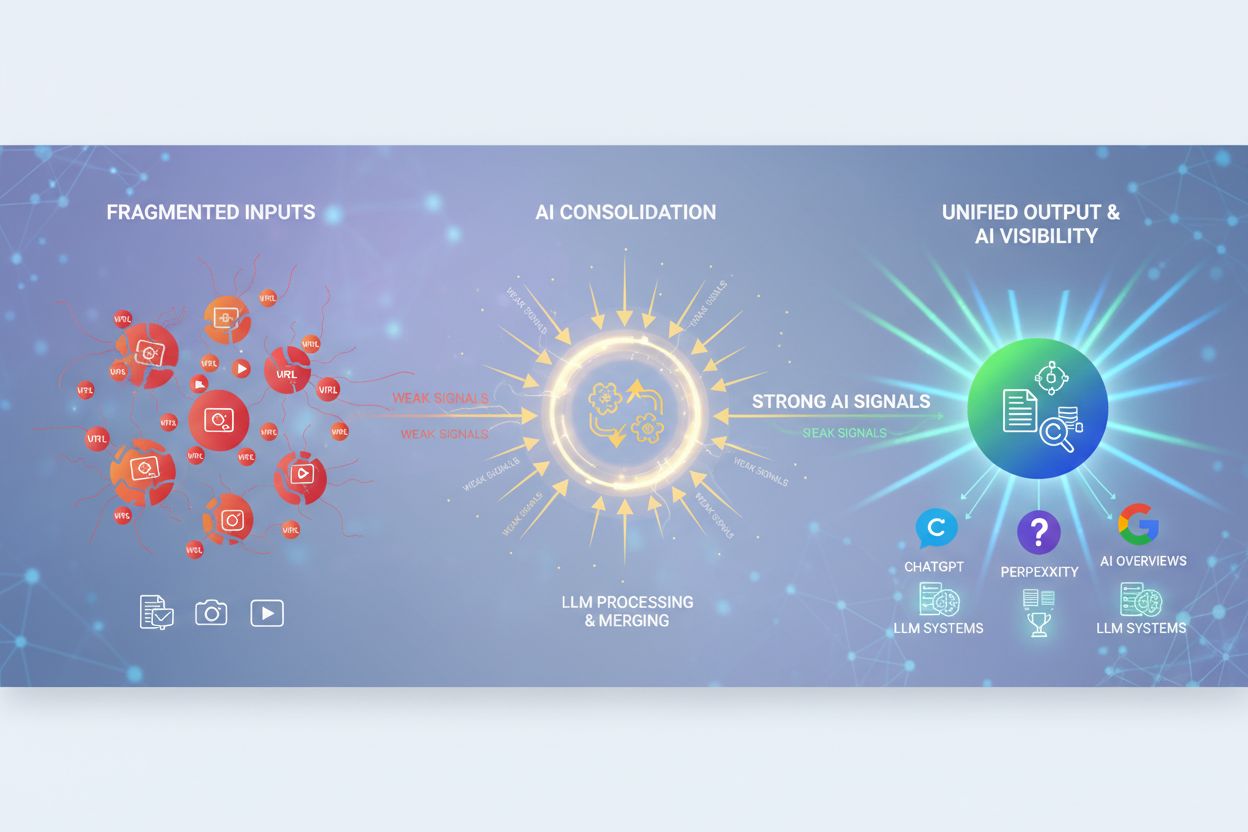
Learn what AI Content Consolidation is and how merging similar content strengthens visibility signals for ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.